Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan 6 Impaired Gas Exchange
Uploaded by
dbryant0101Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan 6 Impaired Gas Exchange
Uploaded by
dbryant0101Copyright:
Available Formats
Case Scenario # 3
Adult ICU
INSTRUCTIONS: For this case study, you will develop a Nursing Care Plan using SNL, the Standardized
Nursing Languages of NANDA, NOC and NIC (NNN). You will be completing the blank nursing care plan
that accompanies this scenario.
• Patient is a 58-year-old man admitted to a medicine unit one week ago with a diagnosis of
atypical pneumonia. He was doing fine yesterday on O2 6L by NC.
Time Vital Signs/Data Intervention/Tx Response
7am-12noon Urine Output = 0 ml
Requires increasing FiO2
12noon Lasix 40 mg IVP at 12noon O = 800 ml
1500 PO2 – 85% (on 100% rebreather mask) Tx to CCMU
• minimally moving air
• using accessary muscles for breathing
Arrival in CCMU • Unresponsive, Etomidate for the intubation
1515 • Breathing at 45 breaths/min, • Intubated w/ #8 Shiley
• Cyanotic, • Vent Settings: 100% FiO2, AC 14,
• Cold, mottled skin, and VT 650.
• Pedal pulses heard only by Doppler,
• Generalized edema.
• Rhythm = ST with a rate of 120.
• BP = 96/58.
• Temp = 96.6 axillary
1525 SPO2 drops to 70%. He is immediately suctioned for thick
Post Intubation tan secretions, copious amounts.
1530 SPO2 increases to 90%. First ABG = 90-
Post-suctioning 65-45-7.42-26.
Resp. rate = 14. His suction requirements
become minimal
1535 • BP drops to 57/36. Immediately
• Given 2.5 liters of 0.9% saline IV
• Started on Dopamine at 20
mcg/kg/min.
1545 His BP responded to 120/75.
Next 2 hours Dopamine is titrated down to 10
1545-1745 mcg/kg/min
IV fluid is decreased to 150 cc/hr.
Bilateral soft wrist restraints were
applied
As he became more responsive, he began
reaching for his ETT
1745-1845 • BP increased
Next hour • Became alert & oriented x 3
• Understood explanations given to him.
1850 The restraints were removed.
Adult ICU Medicine 1
Functional Health Patterns*
Ø The Functional Health Patterns that are relevant for this gentleman are:
Activity-Exercise
Cognitive-Perceptual
Health Perception-Health Management
Ø Activity-Exercise is the most affected functional health pattern for this gentleman.
* Nursing assessment data is organized in Functional Health Patterns. Functional Health Patterns can help direct
the choice of Nursing Diagnoses. The eleven functional health patterns are Health Perception-Health Management;
Cognitive-Perceptual; Nutritional-Metabolic; Elimination; Activity-Exercise; Sleep/Rest; Self-Perception/Self-
Concept; Role/Relationship; Sexuality/Reproductive; Coping/Stress/Tolerance; and Value/Belief.
Choosing the Nursing Diagnosis (es)
These nursing diagnoses are appropriate for this patient. In practice, you may select
additional nursing diagnoses.
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas Exchange
Defining Characteristics: dyspnea, decreased O2 saturation despite high
FIO2, unresponsiveness, and cyanosis
Related Factors: atypical pneumonia and possible pulmonary embolus.
Nursing Diagnosis: Decreased Cardiac Output
Defining Characteristics: low BP, cyanosis, rapid heart rate, and
unresponsiveness
Related Factors Etiology: hypovolemia (he had received Lasix. Decreased BP is
common with the initiation of positive pressure
ventilation causing decreased venous return to the
heart especially in the face of hypovolemia) or
Entomidate side effect (minimal risk).
Ø While both nursing diagnoses are appropriate, for purposes of this exercise
let’s use
Impaired Gas Exchange.
Ø On the nursing care plan form write in the nursing diagnosis, identifying the
defining characteristics and related factors.
Adult ICU Medicine 2
Choosing the Nursing Outcomes (NOCs)
• The next step is to select nursing outcomes that can best affect this nursing diagnosis.
• Listed below are two appropriate nursing outcomes for this gentleman.
Nursing Outcome(s)
Respiratory Status: Gas Exchange
Indicators: Ease of breathing
Dyspnea at rest not present
Cyanosis not present
Neurological Status IER
Restlessness not present
Fatigue not present
Pao2 WNL
Paco2 WNL
O2 saturation WNL
Respiratory Status: Ventilation
Indicators: Respiratory rate IER*
Respiratory rhythm IER
Ease of breathing
Dyspnea at rest not present
Tidal volume IER
Vital capacity IER
*IER = In expected range
Select one of the above listed nursing outcomes for this care plan exercise, go to the
nursing care plan and check the indicators that you think will best measure your
patient’s progress towards the outcome that you’ve chosen. You will need to rate you
patient’s current status for each indicator.
Now that you have chosen your outcome for this gentleman, you will select the
interventions that will best meet this outcome.
Adult ICU Medicine 3
Choosing the Nursing Interventions - NIC
• If you have chosen the NOC, Respiratory Status: Gas Exchange continue
below.
• If you have chosen the NOC, Respiratory Status: Ventilation go to that
section and select your interventions and activities.
NOC - Respiratory Status: Gas Exchange
The following two Nursing Interventions, Acid – Base Management and Energy
Management are appropriate for this gentleman. Review the activities listed
below each NIC and select 5 activities that apply. Write these five on the
nursing care plan in the activity column respectively for Acid-Base
Management and Energy Management.
NIC: Acid-Base Management3(pg.118)
• Maintain patent IV access • Maintain patent airway • Monitor ABG & electrolyte
levels
• Monitor hemodynamic status • Position to facilitate adequate • Monitor for symptoms of
ventilation respiratory failure
• Monitor for respiratory • Monitor determinants of • Provide oxygen therapy
pattern tissue oxygen delivery
• Provide mechanical ventilatory • Monitor determination of • Obtain ordered specimen for
support oxygen consumption lab analysis of acid-base
balance
• Monitor for worsening • Reduce oxygen consumption • Monitor neurological status
electrolyte imbalance
• Provide frequent oral hygiene • Promote orientation • Monitor for loss of acid( e.g.
vomiting)
• Monitor for loss of • Administer prescribed alkaline • Instruct pt &/or family on
bicarbonate(e.g. fistula medications based on ABG actions instituted to treat the
drainage & diarrhea) results acid-base imbalance
Adult ICU Medicine 4
Again, review the activities listed below the NIC and select 5. Write these
five on the nursing care plan in the activity column for Energy Management.
NOC: Respiratory Status: Gas Exchange
NIC: Energy Management3 (pg.302) Activities
• Determine pt’s physical • Limit environmental stimuli to • Encourage verbalization of
limitations facilitate relaxation feelings about limitation
• Determine causes of • Monitor nutritional intake to • Determine pt’s/significant other’s
fatigue(e.g. treatments, pain & ensure adequate energy perception of causes of fatigue
medications) resources
• Monitor/record pt’s sleep • Monitor pt for evidence of • Monitor cardiorespiratory
pattern & number of sleep excess physical & emotional response to activity
hours fatigue
• Consult with dietitian about • Arrange physical activities to • Reduce physical discomforts that
ways to increase intake of reduce competition for oxygen could interfere with cognitive
high-energy foods supply to vital body functions function & self-
(e.g. avoid activity immediately monitoring/regulation of activity
after meals)
• Set limits with hyperactivity • Determine what & how much • Monitor location & nature of
when it interferes with others activity is required to build discomfort or pain during
or with the pt endurance movement/activity
• Promote bedrest/activity • Encourage alternate rest & • Limit number of & interruptions
limitation activity periods by visitors
• Use passive &/or active range • Provide calming diversional • Encourage an afternoon nap
of motion exercises to relieve activities to promote
muscle tension relaxa6tion
• Assist pt to schedule rest • Avoid care activities during • Plan activities for periods when
periods scheduled rest periods the pat has the most energy
• Assist patient to sit on side of • Assist with regular physical • Monitor administration & effect
bed, if unable to transfer or activities of stimulant & depressants
walk
• Encourage physical activity • Monitor pt’s oxygen response • Assist pt to understand energy
to self-care or nursing conservation principles
activities
• Instruct pt/SO to recognize • Instruct pt/so to notify • Teach pt & significant other
signs & symptoms of fatigue health care provider if signs 7 techniques of self-care that will
that require reduction in symptoms of fatigue persist minimize oxygen consumption
activity
• Assist pt to identify task that • Assist pt to self-monitor by • Assist pt to limit daytime sleep to
family & friends can perform developing & using a written providing activity that promotes
in the home to prevent/relieve record of calorie intake & wakefulness
fatigue energy expenditure
• Encourage pt to choose • Assist pt to identify • Evaluate programmed increases in
activities that gradually build preferences for activity levels of activities
endurance
Assist pt/so to establish realistic activity goals
Adult ICU Medicine 5
NOC: Respiratory Status: Ventilation
• Select 5 nursing activities that are appropriate for this patient and write them on
the care plan in the activity column for Airway Management.
NIC: Airway Management: Activities3(pg.132)
• Open the airway, using chin lift or jaw • Position pt to maximize • Identify pt requiring
thrust technique ventilation potential actual/potential airway
insertion
• Insert oral or nasopharyngeal airway • Perform chest physical • Administer bronchodilators
therapy
• Encourage slow, deep breathing; • Instruct how to cough • Assist with incentive
turning; & coughing effectively spirometer
• Auscultate breath sounds, noting areas • Perform endotracheal or • Remove secretions by
of decreased or absent ventilation & nasotracheal suctioning encouraging coughing or
presence of adventitious sounds suctioning
• Teach pt how to use prescribed inhalers • Administer humidified air • Regulate fluid intake to
or oxygen optimize fluid balance
• Administer ultrasonic nebulizer • Monitor respiratory & • Administer aerosol
treatments oxygenation status treatments
• Position to alleviate dyspnea
NIC: Mechanical Ventilation: Activities3 (pg. 431)
• Monitor for respiratory muscle • Monitor for impending • Instruct pt & family about rationale
fatigue respiratory failure & expected sensations associated
with use of mechanical ventilators
• Monitor for decrease in exhale • Provide oral care • Monitor effectiveness of mechanical
volume & increase in ventilator on pt’s physiological &
inspiratory pressure psychological status
• Initiate calming techniques • Monitor ventilator pressure • Position to facilitate
readings & breath sounds ventilation/perfusion matching
• Monitor pt’s progress on • Monitor for adverse • Stop NG feedings during suctioning
current ventilator settings & effects of mechanical & 30-60 minutes before chest
make appropriate changes ventilation: infections, etc. physiotherapy
• Collaborate with physician to • Perform chest physical • Perform suctioning, based on
use CPAP or PEEP to minimize therapy adventitious sounds &/or ventilatory
alveolar hypoventilation pressures
• Monitor degree of shunt, vital • Monitor effects of • Administer muscle-paralyzing agents,
capacity, MVV, Vd/Vt, ventilator changes on sedatives, & narcotic analgesics
inspiratory force, & FEV1 for oxygenation: ABG, SaO2,
readiness to wean from SvO2, end-tidal CO2, Qsp/Qt
mechanical ventilation, based & A-aDO2 levels & pt’s
on agency protocol subjective response
• Promote adequate fluid & nutritional intake
Adult ICU Medicine 6
Congratulations!
You have successfully completed your first nursing care plan using
the standardized nursing language vocabularies of NANDA, NOC and
NIC.
1. If you wish to received CE for this educational activity, please
complete the evaluation form and return along with $10 to:
Carol Williams, MS, RN, C
Educational Services for Nursing
University of Michigan Health System
300 North Ingalls, 6B12
Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-0436
2. If you are working with a coordinator please give your quiz, evaluation
and completed nursing care plan to your coordinator.
Adult ICU Medicine 7
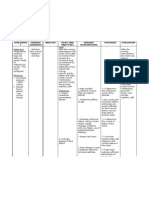
Adult ICU
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Patient Name
Defining Characteristics (Signs & Symptoms)
❏ ❏ ❏
❏ ❏ ❏
❏ ❏ ❏
Related Factors (Etiology)
❏ ❏
❏ ❏
❏ ❏
NOCs (Outcomes)
Measurement Scale Score:
1 = Severe
2 = Substantial
3 = Moderate
Respiratory
4 = Slight
Status 5 = None
Ventilation ❏ respiratory rate IER*
❏ respiratory rhythm IER
❏ ease of breathing
❏ dyspnea at rest not present
❏ tidal volume IER
❏ vital capacity IER
DATE/TIME
INITIALS
Measurement Scale Score:
1 = Severe
2 = Substantial
3 = Moderate
Respiratory 4 = Slight
Status: 5 = None
❑ ease of breathing
Gas ❑ dyspnea at rest not present
Exchange ❏ cyanosis not present
❑ neurological status IER
❏ restlessness not present
❏ fatigue not present
❏ Pao2 WNL**
❏ Paco2 WNL
❏ O2 saturation WNL
DATE/TIME
INITIALS
*IER = in expected range **WNL = within normal limits
Adult ICU Medicine 8
NIC (interventions) ACTIVITIES: MODIFICATIONS:
❑
❑
Energy
Management ❑
DATE/TIME
ACTIVITIES: MODIFICATIONS:
❑:
❏
Mechanical ❏
Ventilation ❑
DATE/TIME
ACTIVITIES: MODIFICATIONS:
❏
Acid-Base ❏
Management ❏
DATE/TIME
ACTIVITIES: MODIFICATIONS:
❏
❏
Airway
❏
Management
❏
DATE/TIME
OTHER INTERVENTIONS: SIGNATURE BOXES:
• •
• •
Adult ICU Medicine 9
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Impaired Gas ExchangeYum C86% (65)
- 2021 ACLS Study GuideDocument20 pages2021 ACLS Study GuideShane Brown83% (12)
- Moses Barber 1652-1733 of South Kinston Rhode IslandDocument149 pagesMoses Barber 1652-1733 of South Kinston Rhode Islanddbryant0101100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceYum C88% (26)
- Nellis Family HistoryDocument247 pagesNellis Family Historydbryant0101No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway Clearancearlee marquez96% (118)
- Bouck of Schoharie & OntarioDocument231 pagesBouck of Schoharie & Ontariodbryant010175% (4)
- An Authentic History of Lancaster County Part 2Document305 pagesAn Authentic History of Lancaster County Part 2dbryant0101100% (6)
- Hypertrophy Max - Primer PhaseDocument21 pagesHypertrophy Max - Primer PhaseRV810100% (6)
- Respiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesFrom EverandRespiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeBenedicto RosalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Tissue Perfusionbrenhood78% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas Exchangecuicuita100% (3)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- Case Study Exam 1Document7 pagesCase Study Exam 1Tro Wact100% (1)
- Vasopressors and InotropesDocument31 pagesVasopressors and InotropesReza Prakosa SedyatamaNo ratings yet
- NCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityDocument4 pagesNCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Evanghelia Dupa Iuda CompletaDocument7 pagesEvanghelia Dupa Iuda CompletaciclopulNo ratings yet
- Baptisms Marriages Methodist Episcopal Church Newburgh NYDocument28 pagesBaptisms Marriages Methodist Episcopal Church Newburgh NYdbryant010180% (5)
- Eapp SHS QuizDocument17 pagesEapp SHS QuizacademicsandpapersNo ratings yet
- CHCECE002 Theory Tasks v8Document46 pagesCHCECE002 Theory Tasks v8Palvi Sharma100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 4 Gas Exchange, ImpairedDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan 4 Gas Exchange, Impaireddbryant0101100% (6)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument22 pagesNursing Care PlanjamNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For "DYSRHYTHMIAS"Document12 pagesNursing Care Plan For "DYSRHYTHMIAS"jhonroks79% (14)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument22 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangecheenapberberNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentNinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Acute PainDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Acute Paindbryant010199% (69)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPMark Benedict Ocampo VelardeNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument1 pageNCP Impaired Skin Integritysinister17No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Infection)Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan Infection)Kez Domine100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputCarmela Balderas Romantco80% (5)
- NCP CR Impaired Spontaneous VentilationDocument8 pagesNCP CR Impaired Spontaneous VentilationJosett Romano75% (4)
- NCP Nursing Care Plan For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDSDocument6 pagesNCP Nursing Care Plan For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDSTina Larsen100% (4)
- NCP PneumoniaDocument28 pagesNCP PneumoniaW'ton Borbe83% (6)
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocument1 pageImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNo ratings yet
- NCP-Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument1 pageNCP-Deficient Fluid Volumejanmichael8No ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeGabriel Tolentino70% (10)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageImpaired Gas ExchangeAdelaine LorestoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJoy Arizala CarasiNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin Integrityapi-371817493% (30)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputTiffany Mathis100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 7 Knowledge DeficitDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 7 Knowledge Deficitdbryant0101100% (8)
- Self Care DeficitDocument4 pagesSelf Care DeficitEllaine RamirezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis & Careplan SamplesDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis & Careplan SamplesE94% (18)
- Impaired Tissue IntegrityDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue IntegrityJacoJone11100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- Mpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesMpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanTheSweetpea5010% (2)
- Ncp-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNcp-Ineffective Airway Clearancelouanne0550% (2)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument26 pagesNursing Care PlanPrincessLienMondejarNo ratings yet
- Weaning IndicesDocument28 pagesWeaning IndicesSri HarshaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Exam 1Document7 pagesCase Study Exam 1Tro WactNo ratings yet
- Increased ICPDocument22 pagesIncreased ICPCHARLOTTE DU PREEZNo ratings yet
- BLS & First Aids Presentation Prime Traning CenterDocument75 pagesBLS & First Aids Presentation Prime Traning Centermarawanosama50No ratings yet
- Case Study Exam 1Document7 pagesCase Study Exam 1Tro Wact100% (1)
- 01 - Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pages01 - Bronchial AsthmaFrank VaronaNo ratings yet
- Doctors OrderDocument9 pagesDoctors OrderReal TetisoraNo ratings yet
- Acls Study Guide 2016 For Pulse 2016Document8 pagesAcls Study Guide 2016 For Pulse 2016eng78ineNo ratings yet
- Scenario Title: Community Acquired Pneumonia Learning Outcomes: 1. Assessment and Recognition of The Signs and Symptoms of PneumoniaDocument6 pagesScenario Title: Community Acquired Pneumonia Learning Outcomes: 1. Assessment and Recognition of The Signs and Symptoms of PneumoniaDud AccNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)Document12 pagesPaediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)zacklim_2000100% (1)
- Role of Physiotherapy in ICUDocument68 pagesRole of Physiotherapy in ICUprasanna3k100% (2)
- DR - Rajalakshmi.C: Emergency Physician MMHRC Institute of Emergency MedicineDocument22 pagesDR - Rajalakshmi.C: Emergency Physician MMHRC Institute of Emergency MedicineP Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- PALS Practice 1 Hypovolemic ShockDocument64 pagesPALS Practice 1 Hypovolemic ShockGlen LazarusNo ratings yet
- Should Be Available at All Sites If Feasible, Include at Sites (Not Required)Document5 pagesShould Be Available at All Sites If Feasible, Include at Sites (Not Required)Ahmed QlhamdNo ratings yet
- Intubations Outside ICUDocument79 pagesIntubations Outside ICUzulham effendyNo ratings yet
- 4Document4 pages4Abdul Hamid NoorNo ratings yet
- A Hudson Valley Simmons Family Part 1Document124 pagesA Hudson Valley Simmons Family Part 1dbryant010150% (2)
- From The Ashes of Angels 1Document13 pagesFrom The Ashes of Angels 1dbryant0101No ratings yet
- A Hudson Valley Simmons Family Part 4Document123 pagesA Hudson Valley Simmons Family Part 4dbryant0101No ratings yet
- Game of Life-eBookDocument101 pagesGame of Life-eBookWarrior SoulNo ratings yet
- The Narragansett Historical Register Vol 1-2 Part 2Document238 pagesThe Narragansett Historical Register Vol 1-2 Part 2dbryant0101100% (1)
- Gov Henry Bull & DescendantsDocument8 pagesGov Henry Bull & Descendantsdbryant0101No ratings yet
- Record of The Rust Family Part 3Document187 pagesRecord of The Rust Family Part 3dbryant0101100% (2)
- A Hudson Valley Simmons Family Part 3Document124 pagesA Hudson Valley Simmons Family Part 3dbryant0101100% (2)
- The Narragansett Historical Register Vol 3-4 Part 1Document453 pagesThe Narragansett Historical Register Vol 3-4 Part 1dbryant0101No ratings yet
- Gardner-Gardiner Rhode IslandDocument42 pagesGardner-Gardiner Rhode Islanddbryant0101100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Acute PainDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Acute Paindbryant010199% (69)
- Record of The Rust Family Part 1Document189 pagesRecord of The Rust Family Part 1dbryant0101No ratings yet
- Record of The Rust Family Part 2Document189 pagesRecord of The Rust Family Part 2dbryant0101100% (1)
- Ness Family History Part 4Document75 pagesNess Family History Part 4dbryant0101100% (1)
- Ness Family History Part 2Document78 pagesNess Family History Part 2dbryant0101100% (1)
- Ness Family History Part 3Document78 pagesNess Family History Part 3dbryant0101No ratings yet
- Chronicles of The Family BakerDocument414 pagesChronicles of The Family Bakerdbryant0101100% (2)
- Relating Nursing Diagnoses To Drug TherapyDocument7 pagesRelating Nursing Diagnoses To Drug Therapydbryant0101No ratings yet
- 4th Book of Records Town of South Amp Ton Long Island NYDocument370 pages4th Book of Records Town of South Amp Ton Long Island NYdbryant0101No ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Keystone of Your Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis Keystone of Your Care Plandbryant010167% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis Made SimpleDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Made Simpledbryant0101100% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan Sheet SampleDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Sheet Sampledbryant0101100% (5)
- 2nd Book of Records Town of South Amp Ton Long Island NYDocument408 pages2nd Book of Records Town of South Amp Ton Long Island NYdbryant0101No ratings yet
- Baptisms-Marriage Register of Old Dutch Church of Kingston Ulster Co NYDocument824 pagesBaptisms-Marriage Register of Old Dutch Church of Kingston Ulster Co NYdbryant0101No ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Perdarahan ObstetriDocument10 pagesTatalaksana Perdarahan ObstetriAfiani JannahNo ratings yet
- Bfhi Implementation 2018 AppendixDocument7 pagesBfhi Implementation 2018 AppendixssNo ratings yet
- Disaster Desa 3Document22 pagesDisaster Desa 3Nicole TaylorNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Craig Haney in Support of Plaintiff's Emergency MotionDocument8 pagesDeclaration of Craig Haney in Support of Plaintiff's Emergency MotionKate ChatfieldNo ratings yet
- Smith L (2017) Nursing Times 113: 12, 20-23Document59 pagesSmith L (2017) Nursing Times 113: 12, 20-23Derick RanaNo ratings yet
- AMC Training ModuleDocument7 pagesAMC Training ModuleChristine EffendyNo ratings yet
- Political SelfDocument53 pagesPolitical SelfMelizza Fajardo BañanoNo ratings yet
- MOS For T&C For CO2 System-1Document6 pagesMOS For T&C For CO2 System-1Tarek Mahmoud GhazyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 SspeDocument12 pagesLesson 6 SspeMa. Leonor Nikka CuevasNo ratings yet
- Blue BookDocument414 pagesBlue Bookshamsa mwambaNo ratings yet
- 02 - IRAOvulation Induction For TheDocument11 pages02 - IRAOvulation Induction For TheHartanto LieNo ratings yet
- Bazooka Monthly Current Affairs August 2023 CompressedDocument134 pagesBazooka Monthly Current Affairs August 2023 CompressedarjunNo ratings yet
- Control of Nonconforming Work019 Af.r4Document6 pagesControl of Nonconforming Work019 Af.r4Massimiliano PorcelliNo ratings yet
- OrthoDocument22 pagesOrthosivaleela gNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4Document2 pagesCase Study 4Dwaine TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Standardized Data Set (SDS) - Client Questions: Revision Date: June 1, 2009Document8 pagesStandardized Data Set (SDS) - Client Questions: Revision Date: June 1, 2009Ilyas LuNo ratings yet
- SB 154Document14 pagesSB 154Phillip StuckyNo ratings yet
- Drug Development Process: Preclinical StageDocument4 pagesDrug Development Process: Preclinical Stagepeter mwangiNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Bhawna Joshi Msc. Nursing 1 YearDocument52 pagesPresented By: Bhawna Joshi Msc. Nursing 1 YearBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- OOS Investigation and Where You Are Going Wrong: Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesOOS Investigation and Where You Are Going Wrong: Page 1 of 3Sangram KendreNo ratings yet
- Basal Level of Anti-Müllerian Hormone Is Associated With Oocyte Quality in Stimulated CyclesDocument5 pagesBasal Level of Anti-Müllerian Hormone Is Associated With Oocyte Quality in Stimulated CyclesCherysaNo ratings yet
- 27 - LEAN Weekly Guide - October 19Document2 pages27 - LEAN Weekly Guide - October 19ЕленаNo ratings yet
- Psychological ChangesDocument36 pagesPsychological ChangesAndrei La MadridNo ratings yet
- Vytalyze CBD Oil Where To Buy, Read Price, Reviews & Scam!Document3 pagesVytalyze CBD Oil Where To Buy, Read Price, Reviews & Scam!muriellearrNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Section 1 - Product & Company IdentificationDocument8 pagesSafety Data Sheet Section 1 - Product & Company IdentificationBoyet BaldeNo ratings yet
- Perdarahan ObstetryDocument43 pagesPerdarahan ObstetryPutri EffendyNo ratings yet
- Essay On Technology 3 Selected Essays On TechnologyDocument1 pageEssay On Technology 3 Selected Essays On TechnologyMuradNo ratings yet