Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fuels
Uploaded by
The_MBCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fuels
Uploaded by
The_MBCopyright:
Available Formats
Fuels
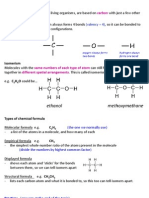
Fuels can be ranked on their ability to auto-ignite This is known as the octane rating.
A higher number leads to less knocking in the engine, meaning it is better for the car. Heptane is 0, and 2,2,4 trimethylpentane is 100. This increases efficiency, the life of the car and decreases the cost of maintenance.
Reforming
Cracking Catalytic lower temperatures, but uses zeolite catalysts to reduce carbon chain length. Thermal uses high temperatures and pressure to reduce carbon chain lengths.
Isomerisation
Fuels can be changed to increase their octane rating Fuels with branched, cyclic or short hydrocarbons have lower octane numbers, and therefore the chance of knocking will be decreased.
Reforming involves converting alkanes into arenes (cycloalkanes), by using platinum as a catalyst and temperatures of roughly 500 degrees C. The arenes can be further reformed into aromatic compounds.
Isomerisation adds functional alkyl groups onto a straight-chain hydrocarbon. It involves using zeolite as a molecular sieve to separate the isomers out. Platinum is used as a catalyst.
The Products of Burning Fuels
This is the best case scenario Water and Carbon Dioxide
Also, you may get unburnt hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide (CO is toxic to haemoglobin) when the fuel is burnt in less oxygen
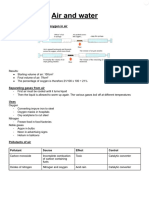
Fuels, when burnt, release numerous chemicals into the atmosphere. Some are polluting, whereas others are relatively harmful.
Oxides of sulfur are formed when fossil fuels containing sulfur are burnt. The sulfur is released and reacts with the oxygen in the air.
Acid Rain
Nitrogen dioxide forms Nitric Acid, and sulfur dioxide forms Sulfuric Acid. These can fall as acid rain (leads to corrosion and killing fish in lakes)
Oxides of nitrogen are formed when nitrogen and oxygen from the air react in the extreme pressures and temperatures of the engine. They may lead to acid rain or the formation of groundlevel ozone (which is toxic)
Photochemical Smog
When Unburnt Hydrocarbons and oxides of nitrogen escape from the car, they react in sunlight to form ground-level ozone. This is a component of photochemical smog, which irritates eyes and causes breathing problems.
You might also like
- IGCSE Chemistry - Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Organic ChemistryChemistryKlipz98% (40)
- Ic Engine FUELSDocument44 pagesIc Engine FUELSkalaisselvaneNo ratings yet
- Emissions in Si & Ci EngineDocument16 pagesEmissions in Si & Ci EngineDeepanshu Jain100% (1)
- Petroleum Refinery Lab. Report No.1Document8 pagesPetroleum Refinery Lab. Report No.1Siyar SaleemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Technology of PetroleumDocument83 pagesChemistry and Technology of PetroleumManish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Kerosene Distillate HydrotreatingDocument3 pagesKerosene Distillate HydrotreatingRio Rinaldi100% (2)
- Petrochemical Industry - Production ProcessDocument40 pagesPetrochemical Industry - Production ProcessAyie Arie AyitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AmmoniaDocument15 pagesIntroduction To AmmoniaHameed Akhtar100% (1)
- Fuel AnalysisDocument34 pagesFuel AnalysisYedla Santosh kumar100% (2)
- Hydrogen ProductionDocument14 pagesHydrogen ProductionAbid YusufNo ratings yet
- Fuel CombustionDocument30 pagesFuel CombustionfauziotNo ratings yet
- Air and Water ChemistryDocument24 pagesAir and Water ChemistryShaman Samuel GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument14 pagesChemistry NotesMina TadrosNo ratings yet
- 8 Fuels and Earth SciencesDocument6 pages8 Fuels and Earth SciencessophiederryNo ratings yet
- Lab Session # 10: 10.0 Emission Control Technique Principle Vehicle EmissionsDocument6 pagesLab Session # 10: 10.0 Emission Control Technique Principle Vehicle Emissionsmsaqibraza93No ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Part - A: I. HydrocarbonsDocument20 pagesUnit - 4 Part - A: I. HydrocarbonsJVCNo ratings yet
- Air and WaterDocument2 pagesAir and WaterPraveenaNo ratings yet
- Crude OilDocument21 pagesCrude OilAlex LochaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sulphur and Catalyst (AutoRecovered)Document3 pagesChemistry Sulphur and Catalyst (AutoRecovered)Nelsen GabrielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15, 16 - Air and Water & Sulfur & Inorganic Carbon PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 15, 16 - Air and Water & Sulfur & Inorganic Carbon PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Motors in Chemical Eng.Document6 pagesMotors in Chemical Eng.Guillermo CúmezNo ratings yet
- 4.C Alkanes ASDocument13 pages4.C Alkanes ASytshortsfromopus65No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry '13Document33 pagesOrganic Chemistry '13Princess KimNo ratings yet
- Diesel Exhaust Gas AftertreatmentDocument16 pagesDiesel Exhaust Gas AftertreatmentlukhmanNo ratings yet
- REPORT HDS - EditedDocument28 pagesREPORT HDS - EditedARSAL HASHMINo ratings yet
- 1 Lesson 2 - Alkanes As FuelsDocument17 pages1 Lesson 2 - Alkanes As FuelsShiv PatelNo ratings yet
- GO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic AcidDocument18 pagesGO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic AcidcikaifaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen IndustriesDocument53 pagesNitrogen Industriesmulugeta damisuNo ratings yet
- Paper in Fuel Additives IraqDocument9 pagesPaper in Fuel Additives IraqMohamad El NaggarNo ratings yet
- Air NotesDocument11 pagesAir NotesFatima AliNo ratings yet
- Crude OilDocument3 pagesCrude OilNickstar592No ratings yet
- Chem Unit 1 PDFDocument32 pagesChem Unit 1 PDFomjee7408No ratings yet
- Module 5 - CombustionDocument25 pagesModule 5 - CombustionKaren Joy BabidaNo ratings yet
- Combustion Basic InformationDocument11 pagesCombustion Basic InformationbekkuNo ratings yet
- Air and WaterDocument9 pagesAir and WaterFrancis EssilfieNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Year 11 ChemistryDocument12 pagesAlkanes: Year 11 ChemistryGanta BooomNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refining Fourth Year DR - Aysar T. JarullahDocument5 pagesPetroleum Refining Fourth Year DR - Aysar T. JarullahSaad NadeemNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engines: Vehicle Emission RegulationsDocument11 pagesDiesel Engines: Vehicle Emission Regulationssheetal62No ratings yet
- Fuel Technology: Prepared byDocument22 pagesFuel Technology: Prepared bysubham kunduNo ratings yet
- Crude Petroleum1Document12 pagesCrude Petroleum1AdiNo ratings yet
- Catalytic ConverterDocument2 pagesCatalytic ConverterYoNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesOrganic ChemistrybethanyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahDocument9 pagesChemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahOuail BalahNo ratings yet
- Principle of CombustionDocument9 pagesPrinciple of CombustionTin Aung KyiNo ratings yet
- Unit V Fuels and Combustion 9Document19 pagesUnit V Fuels and Combustion 9Er S Karthick AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- 4.1.4,5,6 Properties of Gaseous FuelsDocument5 pages4.1.4,5,6 Properties of Gaseous FuelsOkky Kusumo Indradi100% (1)
- Emission Control: Exhaust Emissions Are Produced by Cars, Buses, andDocument10 pagesEmission Control: Exhaust Emissions Are Produced by Cars, Buses, andsonabrar10100% (1)
- Lecture - 6 Exhaust Gas RecirculationDocument47 pagesLecture - 6 Exhaust Gas RecirculationUmar ChNo ratings yet
- Combustion Note 1Document2 pagesCombustion Note 1Haradip MahilaryNo ratings yet
- Industry and The Environment - Crude OilDocument2 pagesIndustry and The Environment - Crude OilTekani TrimNo ratings yet
- Steam Reforming or Steam Methane Reforming Is A Method For ProducingDocument4 pagesSteam Reforming or Steam Methane Reforming Is A Method For Producingtriatmi lusitaNo ratings yet
- Pollutants Produced by A Car Engine: GasolineDocument16 pagesPollutants Produced by A Car Engine: GasolineHarpreet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil. The Process of Refining Involves The Following StepsDocument4 pagesCrude Oil. The Process of Refining Involves The Following StepsSai Ram MotupalliNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONS Module3Document22 pagesHYDROCARBONS Module3Mugara Waitega PeterNo ratings yet
- Some Common Pollutants: Air Pollution: Harmful Substances in The AirDocument3 pagesSome Common Pollutants: Air Pollution: Harmful Substances in The AirFehmeed AlchemyNo ratings yet
- Combustion: 4 2 2 2 2 2 4 6 (Discuss)Document5 pagesCombustion: 4 2 2 2 2 2 4 6 (Discuss)Ren H. RoxasNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Properties of Non-MetalsDocument14 pagesPatterns and Properties of Non-MetalsiluvreadingbooksNo ratings yet
- AIR NotesDocument5 pagesAIR NotesjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Engine Controls & SensorsDocument9 pagesEngine Controls & Sensorsrudey18No ratings yet
- Acetylene, the Principles of Its Generation and Use: A Practical Handbook on the Production, Purification, and Subsequent Treatment of Acetylene for the Development of Light, Heat, and PowerFrom EverandAcetylene, the Principles of Its Generation and Use: A Practical Handbook on the Production, Purification, and Subsequent Treatment of Acetylene for the Development of Light, Heat, and PowerNo ratings yet