Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care Deficit
Uploaded by
Frances Anne PasiliaoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care Deficit
Uploaded by
Frances Anne PasiliaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Saint Louis University School of Nursing Baguio City
Nursing Care Plan: Proper
Submitted to: Mrs. Ma. Theresa Macaraeg, RN
Submitted by: SAYSON, John Mark C. BSN III E3
June 2012
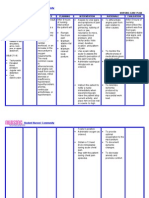
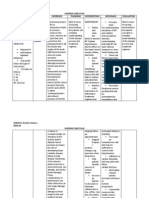
NCP # 1: Hypertension, CAD ASSESSMENT S> Nu sag paminsan ket agsakit met daytoy ko (nape) ken maul-ulaw ak pay. O>with vital signs of: Elevated BP 130/100mmHg Decreased PR 58bpm weak and irregular RR 18cpm To 36oC >appears weak >alert and oriented >with capillary refill of 2 seconds >skin is cool to touch >negative edema noted >patient was ordered for CBR without BRPs A>Ineffective Tissue Perfusion [Peripheral and Cardiopulmonary] related to altered hemodynamics
EXPLANATION OF THE PROBLEM It is a decrease in oxygen resulting in the failure to nourish the tissues at the capillary level. The tissues perfusion problems can exist without decreased cardiac output and tissue perfusion. It happens when the arteries that supply blood to heart muscle and to other parts of the body that become hardened and narrowed. This is due to the buildup of cholesterol and other material, called plaque, on their inner walls. This buildup is called atherosclerosis. As it grows, less blood can flow through the arteries. As a result, the heart muscle can't get the blood or oxygen it needs. This can lead to chest pain or a heart attack and in the case of the patient elevated blood pressure.
GOAL AND OBJECTIVES Goal: The patient will manifest stable vital signs specially the BP. LTO>After 3 days of collaborative care the patient will demonstrate an increase in perfusion as evidenced by: 1. Strong peripheral pulses 2. Vital signs within normal range 3. Maintained the absence of edema 4. Maintained mental status STO>After 8 hour shift of collaborative management the patients BP will decrease from 130/100mmHG to 120/80mmHG
INTERVENTION Monitor Blood Pressure
RATIONALE To gather baseline data and identify possible occurrence of complications. To gather baseline data and to compare existing assessment which can be used as tool in assessing clients status or response to therapy To continuously monitor for changes throughout the contact with the patient. To determine complications such as pulmonary emboli and hypoxia, and to provide early interventions. To determine adequacy of oxygen in the peripheries by mainly assessing the time at which blood refills the capillaries A high cardiac workload can eventually lead to the veins, lungs and tissues becoming full of backed up fluid causing congestion To conserve energy and lower tissues oxygen demands Drug response and toxic levels may be altered by
EVALUATION
Palpate for the quality of pulses
Assess level of consciousness
Observe for signs of chest pains, cyanosis and respiratory distress
Measure capillary refill
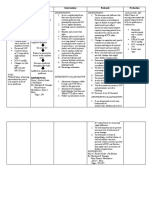
STO>After 10-15minutes of health teaching, the client and the SO will verbalize understanding of: a. Hypertension Reference: Medical Surgical including its causes, th Nursing by Ignatavicius 6 prevention, and Edition management b. Therapeutic regimen including pharmacological and non-pharmacological management
Caution the client to avoid activities that increases cardiac workload
Provide quiet environment conducive for rest Administer medications with caution
decreased tissue perfusion Assist in ambulation and positioning To limit energy consumption and respiratory effort. To avoid gasping of air causing tachypnea, this provides inadequate oxygen to the body. For the client to understand benefits of adhering to the therapeutic regimen and to include the client in the management. To alert the health care team and provide early intervention. To prevent complications. To provide knowledge about hypertension.
Reinforce importance of strict adherence to therapeutic regimen
Instruct to verbalize unusual discomfort such as dizziness, pain and respiratory discomfort Educate about Hypertension including its causes, prevention and management. Ascertain nonpharmacological management of hypertension such as rest and HWB on the nape area
For the patient not to rely on medications but also to nonpharmacological management which has less side effects.
References: Medical Surgical Nursing by Ignatavicius 6th Edition Medical and Surgical Nursing by Brunner and Suddarth 10th Edition
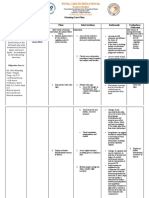
NCP # 2: Immobility caused by stroke ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE PROBLEM S>Hindi pa siya naliligo at nag This is a state in which a toothbrush simula nung na person experiences a confine siya dito sa hospital. difficulty in performing tasks of daily living, such as O> dressing, feeding, bathing, FEEDING: and toileting. The patient had inability to handle utensils a history of stroke last 2010 with both hands which resulted to paralysis of inability to prepare food and right upper extremities. open containers Motor deficits are the inability to chew foods that obvious effect of stroke. are difficult to masticate Symptoms are caused by DRESSING: destruction of neurons in the Inability to put on and pyramidal pathways, this are remove clothes by himself nerve fiber in the brain and BATHING: passing to the spinal cord to Patient was ordered for CBR the motor tract. without BRP thus patient is Paralysis is the complete loss restricted to get out of the of muscle function for one or bed to bathe with assistance more muscle groups. of the relatives. Paralysis can cause loss of TOILETING: feeling or loss of mobility in Patient was ordered for CBR the affected area. As a result, without BRP thus patient is patient is now assisted by his using adult diapers. family. A>Self Care Deficit [Feeding, Bathing, Dressing and Toileting] related to musculoskeletal impairment secondary to stroke Medical Surgical Nursing by Ignatavicius 6th Edition
OBJECTIVES LTO> After 3 days of nursing intervention, patient will demonstrate techniques or lifestyle changes to meet selfcare needs. STO> After 10-15 minutes of nursing interventions, patient will identify personal resources that can provide assistance and be able to verbalize knowledge of health care practices. STO> After 5-10 minutes of health teaching on ROM exercises, the client and SO will verbalize understanding regarding its importance, benefits, and how it is done.
INTERVENTION Establish rapport
RATIONALE To gain trust and cooperation not only to the client but also to the family. Provides data regarding mobility and ability to perform activities within limitations without injury and frustrations. To identify hindrances that can affect the adherence to therapeutic regimen. To identify developmental level to which client can understand. Promotes muscle tone, circulation, joint flexibility, prevents contractures and weakness. Provides safe support for immobility and other self-care activities to promote independence if tolerated.
EVALUATION
Assess for type and severity of immobility, impairment, muscle flaccidity, spasticity and coordination
Assess barriers to participation
Assess memory / intellectual functioning
Provide passive ROM to the affected site and active ROM on other limbs as tolerated
Use assistive devices appropriate for personal hygiene such as articles for brushing teeth and clothing that is easily managed to dress and undress Educate on ROM exercises and health practices
To share knowledge on ROM exercises and health practices that can help to patient giving self-care.
References: Medical and Surgical Nursing by Brunner and Suddarth 10th Edition Fundamentals of Nursing by Potter and Perry 3rd Edition
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plans for Neurological PatientDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plans for Neurological PatientJam AbantaoNo ratings yet
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionjamiemapanaoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument6 pagesDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarNo ratings yet
- Monitoring cerebral perfusion in stroke patientDocument9 pagesMonitoring cerebral perfusion in stroke patientKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Risk For InjuryDocument2 pagesRisk For InjuryRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyNo ratings yet
- NCP Cva Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesNCP Cva Impaired Physical MobilityMaricar Azolae MascualNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionRosalie Delfin90% (10)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- CVA Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- NCP AnginaDocument3 pagesNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- NCP For StokeDocument5 pagesNCP For StokeMemedNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationsweethoney220% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthAna Ramos LopezNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance Care PlanDocument4 pagesActivity Intolerance Care Planapi-315890029No ratings yet
- Ncp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Document2 pagesNcp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce67% (3)
- Burns - Tissue Perfusion, IneffectiveDocument3 pagesBurns - Tissue Perfusion, Ineffectivemakyofrancis20100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: by The Wife During InterviewDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: by The Wife During InterviewJayson SamonteNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionStephanie Louisse Gallega Hisole100% (2)
- Chorioamnionitis NCPDocument8 pagesChorioamnionitis NCPjunard258067% (3)
- GENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANDocument4 pagesGENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANFran LanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- Monitor for signs of fluid overload: increasing dyspnea, rales, edema, weight gain. Notify physician if presentDocument3 pagesMonitor for signs of fluid overload: increasing dyspnea, rales, edema, weight gain. Notify physician if presentmakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- Patient's Anxiety Managed Through Coping StrategiesDocument4 pagesPatient's Anxiety Managed Through Coping StrategiesAaLona Robinson86% (7)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputTiffany Mathis100% (1)
- NCP CHFDocument2 pagesNCP CHFaldrin1920No ratings yet
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 pagesAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNo ratings yet
- CRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocument3 pagesCRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPchubbielitaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with LymphedemaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Patient with Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- NCP - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion R/T Space Occupying Lesion (Neuroblastoma On Frontal Lobe)Document4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion R/T Space Occupying Lesion (Neuroblastoma On Frontal Lobe)Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (4)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortRis NapolisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Assessment and Interventions for HypovolemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Assessment and Interventions for HypovolemiaKat Brija100% (1)
- Altered Nutrition Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesAltered Nutrition Nursing DiagnosisAndrea BroccoliNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusionsyderman999No ratings yet
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sDocument4 pages"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesNursing Care for Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusionalliahjoyce ignacioNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care Planjudssalangsang86% (7)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionDocument16 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionFreisanChenMandumotan100% (1)
- NCP CvaDocument4 pagesNCP CvamannyV1990100% (1)
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Document3 pagesNCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce100% (3)
- NCP for Acute Coronary Syndrome AssessmentDocument3 pagesNCP for Acute Coronary Syndrome Assessmentsarahtot67% (3)
- Risk For Impaired SwallowingDocument3 pagesRisk For Impaired SwallowingCalimlim Kim100% (1)
- NCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)Document2 pagesNCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)moodlayers50% (6)
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- Acute pain and hypertension risksDocument2 pagesAcute pain and hypertension risksKat TaasinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument2 pagesFluid Volume ExcessRodel Yacas100% (5)
- NCP CVADocument2 pagesNCP CVANicholas KingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionIshaBrijeshSharmaNo ratings yet
- Managing Acute Renal PainDocument22 pagesManaging Acute Renal PainMaricris S. Sampang100% (1)
- DIABETES Nursing ManagementDocument11 pagesDIABETES Nursing ManagementKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPSarah Younes AtawnehNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Imbalance Care PlanDocument7 pagesNutrition Imbalance Care PlanMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPannamargie07No ratings yet
- Reducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresDocument10 pagesReducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresKier Jucar de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- WALADocument19 pagesWALAFrances Anne PasiliaoNo ratings yet
- Lupus, SLEDocument2 pagesLupus, SLEFrances Anne Pasiliao100% (2)
- ReadmeDocument3 pagesReadmeFrances Anne PasiliaoNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument3 pagesReadmeFrances Anne PasiliaoNo ratings yet
- Final BG FinalDocument19 pagesFinal BG FinalFrances Anne PasiliaoNo ratings yet
- ANDAYA, Kristine Alexis L. BSN218 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesANDAYA, Kristine Alexis L. BSN218 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAlexis TineNo ratings yet
- Snakes in India - Tradition and The Truth PDFDocument5 pagesSnakes in India - Tradition and The Truth PDFhoticeforuNo ratings yet
- Dagger's EdgeDocument34 pagesDagger's EdgeShanikea RamsayNo ratings yet
- Pedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Document73 pagesPedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Medisina101No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AmoebiasisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Amoebiasisderic97% (35)
- BIO01 CO1 PPT - An Overview of The CellDocument60 pagesBIO01 CO1 PPT - An Overview of The CellCHRISTIAN MATTHEW DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- BioPsych - Reviewer (MIdterm Exam) - Chapter 1Document6 pagesBioPsych - Reviewer (MIdterm Exam) - Chapter 1Francis Xavier AlcazarNo ratings yet
- Heat StressDocument39 pagesHeat StressDelando CoriahNo ratings yet
- แนวข้อสอบ National license - Hematology PDFDocument7 pagesแนวข้อสอบ National license - Hematology PDFTanawat SingboonNo ratings yet
- ANS & CVS Response To Exercise v2Document18 pagesANS & CVS Response To Exercise v2chow wing yin amandaNo ratings yet
- Benign Diseases of ThyroidDocument70 pagesBenign Diseases of ThyroidMounica MekalaNo ratings yet
- FCA (SA) - Part - II - Past - Papers 10Document30 pagesFCA (SA) - Part - II - Past - Papers 10matentenNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease and Memory Drugs PDFDocument97 pagesAlzheimer's Disease and Memory Drugs PDFbradbaderNo ratings yet
- 3B Arm Model - M11Document28 pages3B Arm Model - M11rswongym449No ratings yet
- Principle of The Method Quality Control: Alkaline PicrateDocument1 pagePrinciple of The Method Quality Control: Alkaline PicrateRisqon Anjahiranda Adiputra100% (1)
- Prokaryotic Cells: Eukaryotes Vs Prokaryotes: What's The Difference?Document8 pagesProkaryotic Cells: Eukaryotes Vs Prokaryotes: What's The Difference?Anggun Teh PamegetNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory Systemrosario marcelaNo ratings yet
- % Chapter 3: Regulation of Gas Content in BloodDocument33 pages% Chapter 3: Regulation of Gas Content in BloodK CNo ratings yet
- Cerebral EdemaDocument5 pagesCerebral EdemaAdilah AdeebNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fitness TrainingDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Fitness TrainingShailendra Singh ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument19 pagesCase StudyChristine MccombsNo ratings yet
- Globin Synthesis PDFDocument6 pagesGlobin Synthesis PDFmanoj_rkl_07100% (1)
- Medial Longitudinal FasciculusDocument5 pagesMedial Longitudinal FasciculussakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Sarns Modular Perfusion System 8000: A Flexible, Dependable, and Cost-Efficient Modular Blood Pumping SystemDocument4 pagesSarns Modular Perfusion System 8000: A Flexible, Dependable, and Cost-Efficient Modular Blood Pumping SystemAdvancemicronics MedicalsystemsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyTin BernardezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Foundations of BiochemistryDocument5 pagesChapter 1 The Foundations of BiochemistryghurapNo ratings yet
- The Gut Microbiota-Brain AxisDocument15 pagesThe Gut Microbiota-Brain AxisMateo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 13 EyeDocument46 pagesCh. 13 Eyefatucha87No ratings yet
- Maxillomandibular Advancement As The Initial Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: Is The Mandibular Occlusal Plane The Key?Document9 pagesMaxillomandibular Advancement As The Initial Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: Is The Mandibular Occlusal Plane The Key?Jorge Antonio Espinoza YañezNo ratings yet
- Inductions To LearnDocument7 pagesInductions To LearnMichael HobbsNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesisFuturephd3000No ratings yet