Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asthma
Uploaded by
Christina P. KalawCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asthma
Uploaded by
Christina P. KalawCopyright:
Available Formats
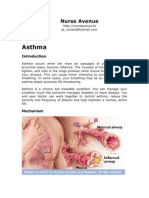
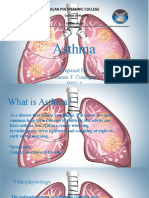
Bronchial asthma is a chronic disease which causes inflammation in bronchial tubes due to sensitivity to certain irritants and causes
irritation and difficulty in breathing. It is a chronic disease and those who are induced with the problem of bronchial asthma needs to be under medical treatment for almost life time. While children are the worst victim of bronchial asthma, adults are not spared. In fact this disease can affect any person irrespective of his/her age, location, and social status. Although bronchial asthma treatment cannot cure the disease completely but it can keep the spell of this problem under control and allows its victims leading a comparatively normal life. Consistent medicinal intervention and life style control are two prime issues for bronchial asthma treatment. Basically two types of medicines are administered for bronchial asthma treatment. One is Quick Relief Medicines, and second option is Long-term Control Medicines; the first one is called reliever as it relieves the acute complications and the second type is called preventers because intake of these medicines help to resist the recurrence of the disease in its intensified form. While the relievers provide instant relief, the preventers type of medicines attempt to improve the complete immunity system of the patients and help the bronchial asthma patients leading comparatively normal life style. Drugs, resembling two vital hormones in our body, are helpful for bronchial asthma treatment. These two hormones are hydrocortisone and adrenalin. Adrenaline is pumped into the bloodstream of the patient in the spell of emergency to have the reflex of body; adrenaline makes our pulse rate fast, creates a drive for hearts rapid action and prepares health system to encounter any sort of crisis. In bronchial asthma treatment the medicines which assist adrenaline for fighting crisis are called reliever. Hydrocortisone groups of medicines are administered for long-term relief from Bronchial asthma complications and long-term taking of these medicines help in reducing the intensity of the pain and sufferings of the asthma victim. Hydrocortisone group of medicines are steroid type and therefore works most efficiently against the spell of complications and suffocation of the patients. Another reliever medicine in bronchial asthma treatment is bronchodilator and it works as instant relief medicine of the patients in the midst of acute breathing crisis. These bronchodilator medicines are used at initial stage of treatment and for preliminary stage. In case of severe asthma attack, doctors prescribe steroid type of medicines for relief and well-being of the patient.
Bronchial Asthma Triggers
Bronchial asthma triggers may include: Smoking and secondhand smoke Infections such as colds, flu, or pneumonia Allergens such as food, pollen, mold, dust mites, and pet dander Exercise Air pollution and toxins Weather, especially extreme changes in temperature Drugs (such as aspirin, NSAID, and beta-blockers) Food additives (such as MSG) Emotional stress and anxiety Singing, laughing, or crying Perfumes and fragrances
Acid reflux
Signs and Symptoms of Bronchial Asthma
With bronchial asthma, you may have one or more of the following signs and symptoms: Shortness of breath Tightness of chest Wheezing Excessive coughing or a cough that keeps you awake at night
Diagnosing Bronchial Asthma
Because asthma symptoms don't always happen during your doctor's appointment, it's important for you to describe your, or your child's, asthma signs and symptoms to your health care provider. You might also notice when the symptoms occur such as during exercise, with a cold, or after smelling smoke. Asthma tests may include: Spirometry: A lung function test to measure breathing capacity and how well you breathe. You will breathe into a device called a spirometer. Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF): Using a device called a peak flow meter, you forcefully exhale into the tube to measure the force of air you can expend out of your lungs. Peak flow monitoring can allow you to monitor how well your asthma is doing at home. Chest X-ray: Your doctor may do a chest X-ray to rule out any other diseases that may be causing similar symptoms.
How to Fight Asthma Without Medication
Asthma is a condition that restricts airways and makes it difficult to breath. Allergies, stress, anxiety and exercise contribute to asthma attacks. Asthma medications can be expensive and have unwanted side effects. Fighting asthma naturally is a little more complicated, but the benefits are worth the time and effort. Instructions 1 Discover what allergies the person with asthma has. Avoid the allergens to prevent asthma attacks. 2 Eat foods that relieve asthma symptoms. Salmon, tuna and mackerel are rich with Omega 3 fatty acids, which reduce the production of inflammatory compounds, improve pulmonary function, and prevent constriction caused by exercise. The magnesium found in spinach, almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, beans and tofu helps reduce the occurrence of asthma attacks. Fruits and vegetables high in vitamin C and B reduce stress and inflammation. Prostaglandins found in onions relax bronchial muscles and open airways. Chick peas are a source of vitamin B6 which reduces wheezing. 3 Drink chlorine-free distilled or purified water. Studies have found that chlorine irritates
receptors in the throat and lungs. 4 Practice breathing exercises daily. Slowing breathe and inhale through the nose to slow and sometimes stop an asthma attack. Relax and breathe in through the nose and out through the mouth to strengthen the respiratory muscles. 5 Use essential oils. Marjoram, rose and frankincense help lungs expand and encourage deep breathing. Chamomile, germium, lavender, rose and marjoram reduce respiratory spasms and help relax bronchial muscles. Test the oils for allergens. The oils can be dropped in a warm bath, used in a humidifier or used on the soles of the feet. Lavender and eucalyptus are best used during an asthma attack because they relax and open airways.
You might also like
- Explaining Disease (Part 2)Document18 pagesExplaining Disease (Part 2)Eva Nia SeptikaNo ratings yet
- Reading 5 - AsthmaDocument3 pagesReading 5 - AsthmaLorena Lévano BastoNo ratings yet
- Module 5A: Dental Management of Patients With Asthma: Prepared By: Dr. Maria Luisa Ramos - ClementeDocument27 pagesModule 5A: Dental Management of Patients With Asthma: Prepared By: Dr. Maria Luisa Ramos - Clementeelaine100% (1)
- What Is Asthma?Document5 pagesWhat Is Asthma?RahmahNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument5 pagesChronic BronchitisJemalyn M. Saludar100% (2)
- What Is AsthmaDocument5 pagesWhat Is AsthmajayrizNo ratings yet
- What Is AsthmaDocument5 pagesWhat Is AsthmajayrizNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Nurse AvenueDocument13 pagesAsthma: Nurse AvenueWindi Lameck MarwaNo ratings yet
- ASTHMA IllnessDocument8 pagesASTHMA IllnessJM MARQUEZNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory DisordersDocument37 pagesUpper Respiratory DisordersClaire Maurice JuaneroNo ratings yet
- Asthma Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument7 pagesAsthma Diagnosis and Treatmentpragna novaNo ratings yet
- Asthma PDFDocument4 pagesAsthma PDFFa FaNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Prepared By: Genesis T. Consigna. BSN-3Document10 pagesAsthma: Prepared By: Genesis T. Consigna. BSN-3Digital ExpressNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument25 pagesASTHMAYUAN CAÑASNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument4 pagesASTHMAKhasim AgwilangNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument43 pagesAsthmaPriyanka PNo ratings yet
- Case Study Asthma Group 2Document17 pagesCase Study Asthma Group 2Kennedy PelicoNo ratings yet
- Acute ExaerbationDocument4 pagesAcute ExaerbationEden RamosNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument9 pagesAsthmaNiña Jemia CortezNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument18 pagesDiseases of The Respiratory and Circulatory SystemRaiah GuerraNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma: Presented byDocument34 pagesBronchial Asthma: Presented bysayyadsajidaliNo ratings yet
- ASTHMA333Document6 pagesASTHMA333June DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearDocument41 pagesRespiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearNancyNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of AsthmaDocument4 pagesSymptoms of AsthmaAthina Maricar CabaseNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisFrom EverandAsthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisNo ratings yet
- TCP PneumoniaDocument6 pagesTCP PneumoniaAnonymous FgT04krgymNo ratings yet
- Asthma in Children My PresentationDocument49 pagesAsthma in Children My PresentationPutra Skate100% (3)
- Nursing Theory: Asthma (Presentation)Document13 pagesNursing Theory: Asthma (Presentation)vinda astri permatasari100% (1)
- Medsurge - AsthmaDocument4 pagesMedsurge - AsthmaFrauline GagaracruzNo ratings yet
- Saira Hassan Dprf16e097 ClinicalDocument9 pagesSaira Hassan Dprf16e097 ClinicalAmrat AliNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Activity 8 Instrumentation 4 Phchem LabDocument3 pagesGroup 2 Activity 8 Instrumentation 4 Phchem LabJeyma DacumosNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Answers (Week 12)Document26 pagesRespiratory Answers (Week 12)CJ RelleveNo ratings yet
- Defenition of BronchitisDocument3 pagesDefenition of BronchitisulfhasNo ratings yet
- Aspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Asthma Overview: Infection Immune Indoor Allergens MoldDocument7 pagesAsthma Overview: Infection Immune Indoor Allergens Moldkhar_austriaNo ratings yet
- Medical Management: Pharmacologic TherapyDocument15 pagesMedical Management: Pharmacologic TherapyDiana Jalaynie S. SambolawanNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDocument9 pagesAsthma: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsAngel DamoNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument18 pagesBronchial AsthmaFarwaNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument9 pagesASTHMAHamza DibNo ratings yet
- Asthma Symptoms in ChildrenDocument7 pagesAsthma Symptoms in ChildrenXalmhen Salman C. HamidiNo ratings yet
- Shortness of Breath Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Care PlansDocument13 pagesShortness of Breath Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Care PlansRuffy AbdulazisNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Asthma and Lung DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Asthma and Lung DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pneumonia 3Document12 pagesPneumonia 3Dina M ElbakaryNo ratings yet
- AshmaDocument9 pagesAshmaAkarsh RamNo ratings yet
- Asthma ProjectDocument17 pagesAsthma ProjectNeha chandelNo ratings yet
- Life Long DisorderDocument7 pagesLife Long DisorderSwayne BrownNo ratings yet
- Tolleno (Pneumonia ER)Document4 pagesTolleno (Pneumonia ER)Hannah TollenoNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument21 pagesBronchial AsthmashaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Medication Management: Medications To Treat EmphysemaDocument10 pagesMedication Management: Medications To Treat EmphysemaNikki SalunaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 8Document12 pagesMapeh 8Maribeth Casuco Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument2 pagesASTHMAAnonymous KillerNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument22 pagesASTHMAKyle VargasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disease Report Group 2Document9 pagesRespiratory Disease Report Group 2Duc QuocNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Common Asthma Triggers Include: Signs and SymptomsDocument3 pagesAsthma: Common Asthma Triggers Include: Signs and SymptomsAlyanna CrisologoNo ratings yet
- SARS Respiratory System and FruitsDocument107 pagesSARS Respiratory System and FruitsGianniNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Asthma Management: Self-Care, Diet, and HomeopathyFrom EverandComprehensive Asthma Management: Self-Care, Diet, and HomeopathyNo ratings yet
- Asthma Definition:: CausesDocument10 pagesAsthma Definition:: CausesLoly IsrainiNo ratings yet