Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PTB
Uploaded by
Eunice BautistaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PTB
Uploaded by
Eunice BautistaCopyright:
Available Formats
PTB
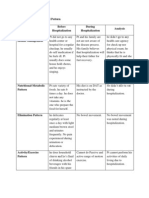
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS S/sx: Wt loss night sweats low fever, non productive to productive cough anorexia, Pleural effusion and hypoxemia cervical lymphadenopathy The worlds deadliest disease and remains as a major public health problem. Badly nourished, neglected and fatigued individuals are more prone Susceptibility is highest in children under 3 years AKA: Kochs disease: Galloping consumption
PPD ID macrophages in skin take up Ag and deliver it to T cells T cells move to skin site, release lymphokines activate macrophages and in 48-72 hrs, skin becomes indurated > 10 mm is (+) Chest xray - cavitary lesion Sputum exam sputum culture
Dx:
The National Tuberculosis Control Program Targets: 1. 2. Mgmt: short course 6-9 months long course 9-12 months Follow-up 2 wks after medications non communicable o 3 successive (-) sputum - non communicable o rifampicin - prophylactic To cure at least 85% of the sputum smear positive TB patient discovered. Detect at least 70% of the estimated new sputum smear positive TB cases. Vision: A country where TB is no longer a public health problem. Mission: Ensure that TB DOTS services are available to the communities. Goal: To reduce the prevalence and mortality from TB by half by the year 2015
MDT side effects r-orange urine i-neuritis and hepatitis p-hyperuricemia e-impairment of vision s-8th cranial nerve damage Methods of Control Prompt treatment and diagnosis BCG vaccination Educate the public in mode of transmission and importance of early diagnosid Improve social condition
TUBERCULOSIS
a highly communicable disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a slender, rod-shaped aerobic bacteria, acid-fast that does not produce sporm. - Mycobacterium tuberculosis primarily affects the pulmonary system, especially the upper lobes, where the oxygen content is greatest, but can also affect other areas of the body, such as the brain, intestines, peritoneum, kidney, joints, and liver, - Tuberculosis (TB) has an insidious onset, and many client are not aware of the symptoms until the disease is well advanced - A multidrug-resistant strain (MDR-TB) of TB can exist as a result of improper or noncompliant use of treatment programs and the development of mutations in the tubercle bacilli - The goal of the treatment is to prevent transmission, control symptoms, and prevent progression of the disease TRANSMISSION Via airborne route by droplet infection After the infected individual has received TB medication for 2 to 3 weeks, the risk of transmission is greatly reduced PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
droplets enter the lungs
2-12 weeks
Ghons focus: tubercle bacilli, macrophages,
Caseous necrosis 2-3 weeks PPD (+) Lypmph node (+)
Reactivation TB
Scar tissue
Ghons complex: Primary lung lesion Lymph node granuloma
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS may be asymptomatic in primary infection fatigue, lethargy, anorexia, weight loss low-grade fever chills night sweats persistent cough and the production of mucoid and mucopurulent sputum, which is occasionally streaked with blood
CHEST ASSESSMENT chest x-ray is not definitive, but the presence of multinodular infiltrates with calcification in the upper lobes suggests TB if the disease is active, caseation and inflammation may be seen on the chest x-ray SPUTUM CULTURES sputum specimens are obtained for an acid-fast smear a sputum culture identifying Mycobacterium Tuberculosis confirms the diagnosis after medications are started, sputum samples are obtained again to determine the effectiveness of therapy most clients have negative cultures after 3 months of compliance with medication therapy
MANTOUX TEST the most reliable determinant of infection with TB a positive reaction does not mean that active disease is present but indicates exposure to TB or the presence of inactive (dormant) disease once the test result is positive, it will be positive in ant future tests a small amount (0.1mL) of intermediate-strength purified protein derivative (PPD) containing 5 tuberculin units is administered intradermally in the forearm an area of induration measuring 10mm or more in diameter, 48 to 72 hours after injection, indicates that the individual has been exposed to TB for individuals with HIV infection or who are immuno-suppressed, a reaction of 5mm or greater is considered positive once an individuals skin test is positive, a chest x-ray is necessary to rule out active TB or to detect old, healed lesions
You might also like
- MultivitaminDocument1 pageMultivitaminKatie McPeek88% (8)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studystayawake18No ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect NSG - ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesDrug Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect NSG - ResponsibilitiesEunice BautistaNo ratings yet
- GordonsDocument3 pagesGordonsEunice BautistaNo ratings yet
- Case Study CholelithiasisDocument21 pagesCase Study Cholelithiasisfayeiruguin83% (6)
- Case Study CholelithiasisDocument21 pagesCase Study Cholelithiasisfayeiruguin83% (6)
- Tables of Normal ValuesDocument6 pagesTables of Normal ValuesEunice BautistaNo ratings yet
- YunisDocument5 pagesYunisEunice BautistaNo ratings yet
- Daryl CombiventDocument1 pageDaryl Combiventberks4eyesNo ratings yet
- PTBDocument4 pagesPTBEunice BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyEunice BautistaNo ratings yet
- NCP For AnemiaDocument1 pageNCP For AnemiaEunice BautistaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elizabeth Stevens ResumeDocument3 pagesElizabeth Stevens Resumeapi-296217953No ratings yet
- Gacal v. PALDocument2 pagesGacal v. PALLynne SanchezNo ratings yet
- (U) Daily Activity Report: Marshall DistrictDocument5 pages(U) Daily Activity Report: Marshall DistrictFauquier NowNo ratings yet
- Poli TipsDocument83 pagesPoli TipsJoyae ChavezNo ratings yet
- Bba - Fa Ii - Notes - Ii Sem PDFDocument40 pagesBba - Fa Ii - Notes - Ii Sem PDFPRABHUDEVANo ratings yet
- English File Intermediate. Workbook With Key (Christina Latham-Koenig, Clive Oxenden Etc.) (Z-Library)Document2 pagesEnglish File Intermediate. Workbook With Key (Christina Latham-Koenig, Clive Oxenden Etc.) (Z-Library)dzinedvisionNo ratings yet
- CCOB 021 and CCOC 021 Module Outline For 2022Document5 pagesCCOB 021 and CCOC 021 Module Outline For 2022Matodzi ArehoneNo ratings yet
- 121 Diamond Hill Funds Annual Report - 2009Document72 pages121 Diamond Hill Funds Annual Report - 2009DougNo ratings yet
- How To Survive Economic CollapseDocument4 pagesHow To Survive Economic CollapseZub AleandruNo ratings yet
- College Hazing Essay 113bDocument6 pagesCollege Hazing Essay 113bapi-283630039No ratings yet
- Transformation of Green Areas in Urban Landscape of Lucknow: Need For Holistic Intervention With Respect To River GomtiDocument10 pagesTransformation of Green Areas in Urban Landscape of Lucknow: Need For Holistic Intervention With Respect To River GomtiASHUTOSH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Standard Oil Co. of New York vs. Lopez CasteloDocument1 pageStandard Oil Co. of New York vs. Lopez CasteloRic Sayson100% (1)
- APLN - Audit Report 2018Document133 pagesAPLN - Audit Report 2018Dini DesvarhozaNo ratings yet
- Part II. Market Power: Chapter 4. Dynamic Aspects of Imperfect CompetitionDocument9 pagesPart II. Market Power: Chapter 4. Dynamic Aspects of Imperfect Competitionmoha dahmaniNo ratings yet
- Amazon Go ReportDocument3 pagesAmazon Go ReportkatyaNo ratings yet
- Ligutan V CA (Full Text)Document15 pagesLigutan V CA (Full Text)Yaz CarlomanNo ratings yet
- P 141Document1 pageP 141Ma RlNo ratings yet
- "Land Enough in The World" - Locke's Golden Age and The Infinite Extension of "Use"Document21 pages"Land Enough in The World" - Locke's Golden Age and The Infinite Extension of "Use"resperadoNo ratings yet
- Purging CostSavingsDocument2 pagesPurging CostSavingscanakyuzNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping BasicsDocument19 pagesBookkeeping BasicsAbeer ShennawyNo ratings yet
- What Is GlobalizationDocument19 pagesWhat Is GlobalizationGiovanni Pierro C Malitao JrNo ratings yet
- Proposing A New InitiativeDocument8 pagesProposing A New InitiativeMike WonderNo ratings yet
- Organzational Climate On InnoationDocument23 pagesOrganzational Climate On Innoationlucky prajapatiNo ratings yet
- FOB Price (Free On Board) - What Is FOB PriceDocument3 pagesFOB Price (Free On Board) - What Is FOB PriceFarooq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Soal SemesterDocument5 pagesSoal SemesterWayan HamalNo ratings yet
- Quotes For Essay and Ethics CompilationDocument5 pagesQuotes For Essay and Ethics CompilationAnkit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- The Six Day War: Astoneshing Warfear?Document3 pagesThe Six Day War: Astoneshing Warfear?Ruben MunteanuNo ratings yet
- All JD 2019 For StudentsDocument110 pagesAll JD 2019 For StudentsShivam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chelsea FC HistoryDocument16 pagesChelsea FC Historybasir annas sidiqNo ratings yet
- Auditing Unit - 5 by Anitha RDocument16 pagesAuditing Unit - 5 by Anitha RAnitha RNo ratings yet