Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Physiology
Uploaded by
Siva ShanmugamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Physiology
Uploaded by
Siva ShanmugamCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Physiology
M. Marks: 200 Theory: 100 Practical: 100
1. Introduction on Physiology. 2. Cell and tissue, its structure. 3. Body Fluid: Blood: Composition and general function of plasma, Blood cells structure and function- Red Blood cells, white blood cells including numbers and approximate length of life position, structure and function of cell of reticulo endothelial system Blood clotting including bleeding time and clotting time, factors accelerating and slowing the process Blood group and their significance, Rh- Factor, Haemoglobin and ESR Formation of Blood, tissue fluid and Lymph 4. Cardio Vascular System - Structure and properties of Heart muscles and nerve supply of Heart. Structure and functions of arteries, capillaries and veins, Cardiac cycle and Heart sound, Factors affecting Heart Rate and its regulation, Cardio-vascular reflexes, Blood pressure and its regulation, physiological variation, peripheral resistance, Factors controlling Blood Pressure, Haemorrhage 5. Respiratory System Mechanism of Respiration, changes in diameters of thorax, Intrapleural and Intrapulmonary pressure, Quantities of Lung Volume, Tidal and Residual Volume, Vital Capacity, Gaseous interchanges in lung and tissues Control of Respiration Nervous and Chemical significance of change in rate and depth, transportation of oxygen and carbon-di-oxide, Respiratory statesHypoxia, Asphysxia, Cyanosis, Acclimatization 6. Digestive System
General arrangement of alimentary canal, liver and pancreas position, structure. 7. Reproductive System
Development of Puberty, Male Sex Hormones, Spermatogenesis, Female Sex Hormones, Menstrual cycle, Ovulation, Pregnancy and Lactation, Function of Placenta 8. Excretory System Gross and minute structures of kidney, renal circulation, mechanism of formation of urine. Glomerular filtration rate and tubular function, renal function. 9. Endocrine System Structure and function of pituitary (anterior and posterior) gland, Thyroid, ParaThyroid, Adrenal Cortex, Adrenal Medulla, Thymus and Pancreas, Blood Sugar regulation
10. Skin Structure and Function 11. Neuromuscular Physiology:
a. Cell Membrane: Ionic and potential gradient and transport b. Muscle: Types of Muscular tissue, gross and microscopic structure, function,
Basis of muscle contraction, changes in muscle contraction. Electrical Biphasic and Monophasic action potentials, chemical, thermal and physical changes, Isometric and Isotonic contraction, Motor units and its properties clonus, tetanus, all or none law, fatigue Nerve: Gross and microscopic structure of nervous tissue, One Neuronegeneration of action potential- nerve impulse-condition Neuromuscular Junction Degeneration, regeneration of peripheral nerves, Wallerian Degeneration, Electro tonus and Pflagers law. Types and properties of receptors, types of sensations, synaptic reflex arc and its properties occlusion, summation , subminimal fatigue etc Tracts Ascending and Descending tracts of the spinal cord, Pyramidal Tracts Functions of Cerebral Cortex Functions of Cerebrum Functions of Cerebellum Functions of Basal Ganglia Thalamus: Connection and function Reticular Formation: Tone, Posture and Equillibrium Autonomic Nervous System Special Senses: Eye errors of refraction, lesions of visual pathways Speech and its Disorders Ear and vestibular apparatus, taste, olfactory and somatic sesations
c.
d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. p. q.
9. Physiology of Exercise and Work a. Neuromuscular activity, Human Movement, Physiological mechanism in movement behaviour, skill, strength, endurance, analysis of movement b. Circulatory and respiratory response to exercise and work, the heart, blood circulation, body fluid changes, pulmonary ventilation, gas exchange and transport c. Effects of exercise and work on other body functions
Physiology Practical
To study the following Physiological Phenomena: 1. Identification of blood cells and different counts. 2. White Blood Cell Count. 3. Red Blood Cell Count. Clotting Time and Bleeding Time 4. Haemoglobin percentage 5. E.S.R. and Blood groups.
6. Bleeding time and clotting time 7. Pulse rate, Heart rate and measurement of Blood Pressure. 10. Respiratory rate and Auscultation. 11. Reflexes Superficial and Deep Sensations 12. Tests for functions of Cerebrum. 13. Tests for functions of Cerebellum.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- RUKUS March 2010Document32 pagesRUKUS March 2010RUKUS Magazine29% (14)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Upper Limb Fractures & Dislocations GuideDocument57 pagesUpper Limb Fractures & Dislocations Guideمعتز فرعون100% (2)
- Upper Limb Fractures & Dislocations GuideDocument57 pagesUpper Limb Fractures & Dislocations Guideمعتز فرعون100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Abdomen: Anatomy and RegionsDocument10 pagesThe Abdomen: Anatomy and RegionsSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Skull Bone Surface Markings and LandmarksDocument12 pagesSkull Bone Surface Markings and LandmarksSiva Shanmugam100% (1)
- NFPA 72 Fire Alarm TrainingDocument376 pagesNFPA 72 Fire Alarm TrainingFavori gcbNo ratings yet
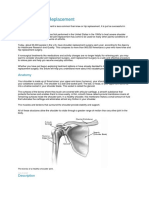
- Shoulder Joint ReplacementDocument10 pagesShoulder Joint ReplacementSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Use Acupressure to Conceive FasterDocument15 pagesUse Acupressure to Conceive Fastersale18100% (1)
- Knee Joint Structure and FunctionDocument16 pagesKnee Joint Structure and FunctionSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Post-op cardiac surgery physiotherapyDocument25 pagesPost-op cardiac surgery physiotherapySiva Shanmugam100% (5)
- Stress and FilipinosDocument28 pagesStress and FilipinosDaniel John Arboleda100% (2)
- ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: A GUIDE TO DIAGNOSIS AND PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENTDocument24 pagesANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: A GUIDE TO DIAGNOSIS AND PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENTSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- PT Management of Restrictive Lung DiseaseDocument16 pagesPT Management of Restrictive Lung DiseaseSiva Shanmugam25% (4)
- MAQUET CARDIOHELP Disposables HLS - Module - Advanced PDFDocument2 pagesMAQUET CARDIOHELP Disposables HLS - Module - Advanced PDFXavi AnpiNo ratings yet
- Activity No 1 - Hydrocyanic AcidDocument4 pagesActivity No 1 - Hydrocyanic Acidpharmaebooks100% (2)
- Femoral Neck Fracture Diagnosis and Treatment GuideDocument40 pagesFemoral Neck Fracture Diagnosis and Treatment GuideSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Superiorandinferiorradioulnarjointbmj 131209070529 Phpapp01Document24 pagesSuperiorandinferiorradioulnarjointbmj 131209070529 Phpapp01Siva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Lung Anatomy Explained: Structure, Lobes, Root & SupplyDocument21 pagesLung Anatomy Explained: Structure, Lobes, Root & SupplySiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- IFT Article UsefulDocument6 pagesIFT Article UsefulSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Cage Components and JointsDocument30 pagesThoracic Cage Components and JointsSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Peripheralnerveinjury 170820154807Document50 pagesPeripheralnerveinjury 170820154807Siva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- HVPSGDocument4 pagesHVPSGSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- UltravioletradiationDocument49 pagesUltravioletradiationSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- HVPSGDocument4 pagesHVPSGSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- The Hip JointDocument6 pagesThe Hip JointSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Indications For Knee ArthroplastyDocument16 pagesIndications For Knee ArthroplastySiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- SampleEvals 0Document252 pagesSampleEvals 0Siva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Emg p2Document32 pagesEmg p2Siva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- ONE2 10 ElbowDocument33 pagesONE2 10 ElbowSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- JOINT PATTERN AND CARDIO-RESPIRATORY ASSESSMENT GUIDEDocument17 pagesJOINT PATTERN AND CARDIO-RESPIRATORY ASSESSMENT GUIDESiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument26 pagesCopdSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument11 pagesCystic FibrosisSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument6 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument6 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Special Test For Elbow JointDocument3 pagesSpecial Test For Elbow JointSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument36 pagesEndocrine SystemMario AndreiNo ratings yet
- Myth and Realism in The Play A Long Day's Journey Into Night of Eugene O'neillDocument4 pagesMyth and Realism in The Play A Long Day's Journey Into Night of Eugene O'neillFaisal JahangeerNo ratings yet
- FINALS REVIEWER ENVI ENGG Topic 1Document8 pagesFINALS REVIEWER ENVI ENGG Topic 1As ReNo ratings yet
- Live Performance Award Ma000081 Pay GuideDocument48 pagesLive Performance Award Ma000081 Pay GuideDan LijndersNo ratings yet
- OC - PlumberDocument6 pagesOC - Plumbertakuva03No ratings yet
- Base para Detectores de Humo y Temperatura KIDDE KI-SBDocument2 pagesBase para Detectores de Humo y Temperatura KIDDE KI-SBAnderson CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogeological Characterization of Karst Areas in NW VietnamDocument152 pagesHydrogeological Characterization of Karst Areas in NW VietnamCae Martins100% (1)
- Solids Level Measurement Application Guide en 78224 PDFDocument144 pagesSolids Level Measurement Application Guide en 78224 PDFwalcalNo ratings yet
- Válvulas Flomatic USADocument40 pagesVálvulas Flomatic USAEfrain DuarteNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, Experimental and Theoretical Characterizations of A NewDocument7 pagesSynthesis, Experimental and Theoretical Characterizations of A NewWail MadridNo ratings yet
- Neurons and Nerve Impulses: Nandika Arora and Risa Gaikwad (11 G2)Document17 pagesNeurons and Nerve Impulses: Nandika Arora and Risa Gaikwad (11 G2)RisaNo ratings yet
- Aphasia PDFDocument4 pagesAphasia PDFRehab Wahsh100% (1)
- Model Fs CatalogDocument4 pagesModel Fs CatalogThomas StempienNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Worksheet AssessmentsDocument3 pagesPhysical Education Worksheet AssessmentsMichaela Janne VegigaNo ratings yet
- Esaote MyLabX7Document12 pagesEsaote MyLabX7Neo BiosNo ratings yet
- Puskesmas Dua Puluh Tiga Ilir Publishes Vaccination Ticket ListDocument98 pagesPuskesmas Dua Puluh Tiga Ilir Publishes Vaccination Ticket ListLaboratorium PKM 23 IlirNo ratings yet
- XDocument266 pagesXTrần Thanh PhongNo ratings yet
- WSO 2022 IB Working Conditions SurveyDocument42 pagesWSO 2022 IB Working Conditions SurveyPhạm Hồng HuếNo ratings yet
- Steam System Design RequirementsDocument29 pagesSteam System Design RequirementsAthirahNo ratings yet
- MEDICO-LEGAL ASPECTS OF ASPHYXIADocument76 pagesMEDICO-LEGAL ASPECTS OF ASPHYXIAAl Giorgio SyNo ratings yet
- Request Baha Alert PPMPDocument3 pagesRequest Baha Alert PPMPLö Räine AñascoNo ratings yet
- Grab Go Porter S 5 ForcesDocument2 pagesGrab Go Porter S 5 ForcesUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- FB77 Fish HatcheriesDocument6 pagesFB77 Fish HatcheriesFlorida Fish and Wildlife Conservation CommissionNo ratings yet
- 2020-11 HBG Digital EditionDocument116 pages2020-11 HBG Digital EditionHawaii Beverage GuideNo ratings yet
- Simple Syrup I.PDocument38 pagesSimple Syrup I.PHimanshi SharmaNo ratings yet