Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theme of 2. Bases of Orthopedic Stomatology and (Ortodontii)
Uploaded by
Ojo IgbagbolereOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Theme of 2. Bases of Orthopedic Stomatology and (Ortodontii)
Uploaded by
Ojo IgbagbolereCopyright:
Available Formats
Theme of 2. Bases of orthopedic stomatology and [ortodontii].
Functional anatomy of maxillofacial system. Influence of the loss of teeth, maxillodental deformations on the general state of the human organism. Dental, maxillofacial prosthetics. Special preparation of the cavity of the mouth before prosthetics. Clinic and prosthetics of the defects of the crown of tooth. Clinic and prosthetics with the partial and total loss of teeth. Maxillofacial prosthetics. Forms of the defects of maxillofacial region, orthopedic apparatuses. [Ortodontiya] as science. Classification of orthodontic apparatuses, the periods of the treatment of orthodontic pathologies.
Functional anatomy of maxillofacial system. Maxillofacial system is represented: 1. 2. 3. By skeleton, which consists of the maxillary, nose and zygomatic bones. By teeth - organs, fitted out to the breaking up of food. By organs, intended for capturing of food and closing of oral opening (lip, mimic musculature).
4. By organs, which participate in the formation of food lump and which ensure its advance into the throat (language, cheeks, solid and the soft palate, uvula). 5. By masticatory and mimic musculature.
6. With three pairs of the salivary glands, whose secret facilitates the chewing of food, the formation of food lump, it provides the chemical phase of digestion in the mouth. 7. by Temporal- mandibular joints.
The deformation of maxillodental of system in adult person is developed after the removal of teeth gradually, and in children and adolescents - considerably more rapid. It does not disturb patient, but it is diagnosed by doctor with the inspection of dental rad in the state of central occlusion. In the later stages of this form of deformation the teeth deprived of antagonists can displace to the mucous membrane of opposite jaw. As a result chronic micro-injury is developed compression reconstruction of mucous membrane, which is clinically manifested by the topographically changed configuration of the relief of the toothless section of alveolar branch. Chronic injury can lead to the malignancy of mucous membrane in the zone of injury. Maxillodental system as a result of the loss of teeth undergoes the inevitable changes, as a result which appears this illness, as it periorodontitis. Furthermore, food enters the gastrointestinal tract of that of badly crushed, which leads to the disturbance of the function of internal organs.
What is prosthetics.
Prosthetics - this is the treatment of patients with different diseases of maxillofacial system by different orthopedic means (prostheses, tire, crown, supplementary sheet). Prosthetics is conducted both with the therapeutic purpose - restoration of mastication, speech, ingestion, function of masticatory muscles, disrupted aesthetics and with the preventive for retaining of the remained teeth, prevention of further destruction of dental arcs and joints. Prosthetics is employed also was when carried out the operation of the partial removal of the bones of jaw (tumor, inflammatory diseases). In this case they try to use maximally small and maximally convenient constructions of prostheses. In what cases prosthetics of teeth is conducted. Prostheses use for the following purposes:
- the substitution of the defects of the solid cloths of tooth; - the substitution of the defects of dental numbers; - the substitution of toothless jaws; - the substitution of the alveolar branch (branch of the bone of upper jaw, on which they are located are teeth) and jaws. During the consultation in stomatologist- orthopedist. First of all, orthopedist establishes, is whether the defeat of masticatory apparatus his degree. After complete inspection and formulation of diagnosis is compiled the plan of orthopedic treatment, in which it is included:
- the special preparation of the cavity of mouth for prosthetics; - the complex of therapeutic orthopedic measures; - the development of the construction of prosthesis and form of prosthetics; - the installation of prosthesis.
Preparation of the cavity of mouth for the orthopedic treatment. Before the orthopedic treatment complex therapeutic and surgical treatment for the purpose of the preparation of soft and solid tissues of maxillofacial region for prosthetics is conducted. This connected with the fact that in patient there can be different diseases of the cavity of mouth, which can prevent prosthetics. For example, caries, stomatitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cavity of mouth), scar changes in the mucous membrane after the previous inflammatory diseases and injuries, different anomalies of the development of maxillodental system.
Stomatologist- therapeutist conducts to patients the sanitation of the cavity of mouth, moves away the dental deposits (dental attack, dental stone), treats the diseases of the mucous membrane of the cavity of mouth and periodontium. Stomatologist- surgeon moves away teeth and tooth roots, which do not be subject to conservative (nonsurgical) treatment. Complex of therapeutic orthopedic measures before prosthetics. Orthopedic treatment includes the series of the clinical and laboratory stages, number and sequence of which it is dictated by the construction of prosthesis and by the tactics of treatment itself. Orthopedic treatment can warn a number of complications from the side of the organs of the cavity of mouth, if it is carried out in proper time. The special training of the patient by orthopedist- stomatologist includes the concrete plan of orthopedic treatment depending on the form of prosthesis. It is conducted for the purpose of lightening the procedure of prosthetics, creation of conditions for the fixation of prosthesis, warning of the injury of orthopaedic bed. According to the recommendation of orthopedist in the surgical office is conducted the complex of the plastic operations, which are directed toward the creation of conditions for the best fixation of prostheses (elimination of belts, scars, plastic of the cavity of mouth, the correction of the form of alveolar branch, plastic of the bridles of lips, language and others). Development of the construction of prosthesis and form of prosthetics. Prosthesis in the transfer from the Latin designates the artificial part of the body. For the orthopedic treatment detachable and nondetachable prostheses adapt. By the construction the prostheses are divided into:
- single crowns; - supplementary sheet; - pin teeth; - bridge-shaped and cantilever prostheses; - plate (partial and complete) prostheses; - arched prostheses. All enumerated constructions are the basis of the orthopedic treatment of maxillodental system.
Arched prostheses.
Bridge-shaped prostheses. Installation of prosthesis. Selection and the installation of prosthesis is determined by the stage of the destruction of a dental number, but not technical capabilities or desire of patient. In accordance with this rule at the initial stages of the disturbance of the dental numbers, when defects have small value, but the periodontium of teeth is not struck, use bridge-shaped prostheses. With the first signs of the manifestation of the diseases of periodontium arises a question about the application of arched prostheses. When loss is significant and the remained teeth it is insufficient for the installation of arched prosthesis, plate prostheses use. Orthopedic treatment is considered final, if it includes all forms of the prostheses, necessary for this patient in accordance with the plan of orthopedic treatment and if orthopedist, using different procedures, comes to the conclusion that the prosthesis fulfills its functions, and orthopaedic bed is in healthy state.
Maxillofacial orthopedics. It is the division of general orthopedics and is occupied by correction and substitution of defects with any kind the damage of solid and soft tissues in the region of jaws and face.
These disturbances can be innate or acquired. The inherent defects include the clefts of the solid and soft palate and upper lip. The acquired disturbances appear as a result: 1) the previous diseases (syphillis, lupus), 2) the injury of production or everyday). 3) operational interference apropos of different inflammatory processes, tumors and T. p. With respect to each of the enumerated cases the forms of prostheses and the methods of their production will be different. The aid of specialists (stomatologist- orthopedist and dental technician) gives the possibility to restore in patient the disrupted functions and to improve his exterior view.
Maxillofacial prosthetics has its special features and it is connected with some difficulties, which distinguish it from usual dental prosthetics; therefore they call it sometimes complex. Damages to maxillofacial region can be accompanied by the severe consequences in the form of functional disorders and rough disfiguration of face. The defects of face cause not only local functional disturbances, but also disorders digestive, nervous and other systems. The greatest interest the patients with the defects of the average and lower zone of face introduce for the stomatologists. The defects of the lower part of face can be isolated, i.e., in the form the defect only of bone of lower jaw, and combined - in the form the defect of lower jaw and soft tissues of face (lower lip and chin). The defects of the middle part also can be in the form isolated damage to the bone of upper jaw and sky or defects of upper jaw and soft tissues of face (upper lip, cheek, nose, the angles of mouth). The orthopedic apparatuses, used with the defects of maxillary bones, according to the function are divided into: Replacing; Fixing; Forming; Mixed.
The replacing apparatuses, or prostheses use for the substitution of defect, which was being formed after the healing of injury or pathologic process of maxillary bone. Purpose of apparatus - to restore the function of organ, and to sometimes and hold broken ends of jaw from the displacement or soft tissues of face from the retraction. The replacing apparatuses include also the prostheses after the resection of jaw. The fixing apparatuses are auxiliary. They adapt for the fastening of the broken ends of lower jaw with the bone plastic, with the isolated defects of lower jaw. The forming apparatuses also relate to the auxiliary. They adapt for the formation of plastic material with the dermal-plastic operations with the defects of bone and soft tissues of face. The mixed apparatuses use when apparatus it must fulfill different functions. For example, the replacing apparatus can simultaneously fulfill the functions of that forming and fixing the broken ends of jaw.
Orthodontics, orthodontia, or orthodonture (Greek. orthos - straight line, Lat. dens, dentis
- tooth) - the division of stomatology, which is occupied by the study of etiology, diagnostics, the methods of preventive maintenance and treating the maxillodental anomalies. The preferred object of the interferences in orthodontia is the masticatory- vocal apparatus of children and adolescents. However, it should be noted that in children the sphere of action of orthodontia exceeds the limits of facial skeleton and directly the cavity of mouth. The object of the examination of orthodontia are the disturbances, which appear in the process of the formation of masticatory- vocal apparatus. Orthodontia is not occupied by deformations, i.e., by the damages, which arose as a result injuries or diseases, correcting only anomalies of development the, for example, genetically caused defects. Orthopedic stomatology is occupied by the correction of deformations. The tasks of orthodontia are the normalization of form and sizes of dental numbers, the correction of increase and development of the apical bases of jaws, maxillary bones, the normalization of occlusion and the creation of the optimum dynamic relationship of the bringing and abducting muscles. The final goal of orthodontia is an improvement in the aesthetics of face and the guarantee of ideal occlusion. Methods of treatment. At present the majority of orthodontia entertain idea themselves about the need for the beginning of the correction of anomalies still from the moment of the beginning of an increase in the milk teeth. This connected with the fact that the most early beginning of correction at the childhood possesses the prolonged effect, and due to an exuberance in the bone structures and larger elasticity of cloths it can be carried out within the more short times. The effectiveness of orthodontia is limited by the age of patient and by the nature of anomaly. Thus, orthodontia it can effectively change the reciprocal location of teeth and dental numbers, but it is not capable of effectively influencing the anomaly of the development of jaws and facial skeleton. In orthodontia adapt the following methods of treatment: Equipment By apparatus- surgical Surgical
Functional (therapeutic gymnastics T. p.)
treatment consists of the 2nd stages: active and retention. The direct elimination of anomaly is produced with the active. With retention is achieved the fastening of the obtained result for the purpose of the guarantee of steadfast remission after the removal of apparatuses. It should be noted that apparatuses often can lead to the damage to the dental enamel also of periodontium and subsequently cause different diseases of teeth. For the preventive maintenance of data of complications it is important to in proper time produce the replacement of apparatuses and to accurately calculate the necessary acting force. Orthodontic apparatuses.
Apparatuses in orthodontia are divided on the fulcrums and using the methods of action. The following groups of apparatuses are separated. Apparatuses for mechanical action (active) Nondetachable apparatuses for mechanical action. Detachable apparatuses for mechanical action. Apparatuses for functional action (passive) Nondetachable apparatuses for the functional action Detachable apparatuses for functional action. Apparatuses for the combined action.
You might also like
- Adult OrthodonticsDocument192 pagesAdult Orthodonticsnikita100% (4)
- Psychological Disorders Chapter OutlineDocument13 pagesPsychological Disorders Chapter OutlineCameron PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology IntroductionDocument10 pagesNursing Pharmacology IntroductionMarianne Joyce ManzoNo ratings yet
- Immediate Complete DenturesDocument74 pagesImmediate Complete DenturesPuneet Pandher100% (1)
- CPG Management of Heart Failure (4th Ed) 2019Document161 pagesCPG Management of Heart Failure (4th Ed) 2019Muaz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Prostho-Perio-Restorative Interrelationship ADocument6 pagesProstho-Perio-Restorative Interrelationship AAlipio GarcíaNo ratings yet
- WHO Global Report Traditional & Complementary Medicine 2019Document228 pagesWHO Global Report Traditional & Complementary Medicine 2019Ellyana PerwitasariNo ratings yet
- Review of Dental ImplantDocument10 pagesReview of Dental Implantmar100% (1)
- Presentasi Maxillofacial ProsthesisDocument35 pagesPresentasi Maxillofacial ProsthesisImeLdaMargaRethaNo ratings yet
- Selective Androgen Receptor ModulatorsDocument7 pagesSelective Androgen Receptor ModulatorsRafael HelenoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ProsthodonticsDocument98 pagesIntroduction To ProsthodonticsmarwaNo ratings yet
- Completedenture Theory and PracticeDocument1,233 pagesCompletedenture Theory and PracticeMostafa Fayad100% (7)
- Treatment Planning Single Maxillary Anterior Implants for DentistsFrom EverandTreatment Planning Single Maxillary Anterior Implants for DentistsNo ratings yet
- Preventive ProsthodonticsDocument13 pagesPreventive Prosthodonticsbhuvanesh4668100% (1)
- THE ORTHODONTICS EFFECTIVE ROLE IN PROSTHODONTIC FIELDDocument31 pagesTHE ORTHODONTICS EFFECTIVE ROLE IN PROSTHODONTIC FIELDHamza BelhajNo ratings yet
- Interceptive Orthodontics ReviewDocument4 pagesInterceptive Orthodontics ReviewAyu Nur A'IniNo ratings yet
- Perio-Ortho Symbiosis: A Review Article: Dr. Apeksha Ghai and Dr. Mayur KaushikDocument3 pagesPerio-Ortho Symbiosis: A Review Article: Dr. Apeksha Ghai and Dr. Mayur Kaushikmohammad naufalNo ratings yet
- Human Factors Classification CertificationDocument12 pagesHuman Factors Classification CertificationVinod DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Liver Disease and CirrhosisDocument5 pagesChronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosisaqil ithninNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Orthodontic Treatment On PeriDocument10 pagesImpacts of Orthodontic Treatment On PeriCatia Sofia A PNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Orthodontics: A ReviewDocument7 pagesInterdisciplinary Orthodontics: A ReviewGauri KhadeNo ratings yet
- Romana Protetica ArticolDocument12 pagesRomana Protetica ArticolAnca HaiducuNo ratings yet
- By: Mohammad Al-Tamimi: To ProsthodonticsDocument8 pagesBy: Mohammad Al-Tamimi: To ProsthodonticsPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dental SpecialtiesDocument6 pagesDental Specialties6f7ns7fb2wNo ratings yet
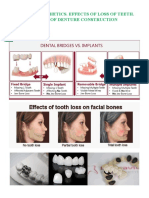
- Unit Iv. Prosthetics. Effects of Loss of Teeth. Stages of Denture ConstructionDocument7 pagesUnit Iv. Prosthetics. Effects of Loss of Teeth. Stages of Denture ConstructionTolea SirghiNo ratings yet
- Dental Specialities and Their RolesDocument5 pagesDental Specialities and Their RolesRadu DraghiceanuNo ratings yet
- Mouth Preperation RPDDocument14 pagesMouth Preperation RPDSadishNo ratings yet
- Dental specialties guideDocument21 pagesDental specialties guideRadu DraghiceanuNo ratings yet
- The Orthodontist's Role in 21st Century Periodontic-Prosthodontic TherapyDocument19 pagesThe Orthodontist's Role in 21st Century Periodontic-Prosthodontic TherapyAna Maria Montoya GomezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Prosthodontics طسابلادبع د دمحأDocument4 pagesLecture 1 Prosthodontics طسابلادبع د دمحأڊرآڪۅڵا ڃأنۅڛNo ratings yet
- MD II S5 - Specialties in Dentistry-2Document4 pagesMD II S5 - Specialties in Dentistry-2DANIEL-NICOLAE MARINNo ratings yet
- Open QuestionsDocument32 pagesOpen QuestionsMostafa FayadNo ratings yet
- Articol RJMEDocument4 pagesArticol RJMELaura IosifNo ratings yet
- Lectura 2 MorfoDocument2 pagesLectura 2 MorfoSebastián SerranoNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Orthodontics: A ReviewDocument5 pagesInterdisciplinary Orthodontics: A ReviewGauri KhadeNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Surgery Oral SurgeryDocument24 pagesOrthognathic Surgery Oral SurgeryFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Asds 02 0215Document3 pagesAsds 02 02156mf9jf6h99No ratings yet
- Extreme Root Resorption Associated With Induced Tooth Movement - A Protocol For Clinical ManagementDocument8 pagesExtreme Root Resorption Associated With Induced Tooth Movement - A Protocol For Clinical Managementcarmen espinozaNo ratings yet
- Dental Specialties RecognizedDocument1 pageDental Specialties RecognizedAsma NawazNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Prosthodontics ReconstructionDocument5 pagesMaxillofacial Prosthodontics ReconstructionThe Lost GuyNo ratings yet
- Multistage Implantology-Orthodontic-Prosthetic Treatment: A Case ReportDocument10 pagesMultistage Implantology-Orthodontic-Prosthetic Treatment: A Case ReportDragos CiongaruNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv. Prosthetics. Effects of Loss of Teeth. Stages of Denture ConstructionDocument8 pagesUnit Iv. Prosthetics. Effects of Loss of Teeth. Stages of Denture ConstructionStanislavNemtanuNo ratings yet
- Caso Clínico de Implante Imediato Com o MarguteDocument8 pagesCaso Clínico de Implante Imediato Com o Margutealessandra camposNo ratings yet
- 35 2 281 Kraljevic enDocument5 pages35 2 281 Kraljevic ensss2013No ratings yet
- Total Edentation Clinical Notions Constantiniuc MarianaDocument101 pagesTotal Edentation Clinical Notions Constantiniuc MarianaIulia IleNo ratings yet
- Interceptive Orthodontics-A Short Review: April 2011Document5 pagesInterceptive Orthodontics-A Short Review: April 2011Vijay ChinthaNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Surgery For Patients With Maxillofacial DeformitiesDocument25 pagesOrthognathic Surgery For Patients With Maxillofacial DeformitiesahmedatefNo ratings yet
- Under Supervision: Prof .DR: Maher FoudaDocument35 pagesUnder Supervision: Prof .DR: Maher FoudaAnushriya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic: The Art and Science of Supplying ArtificialDocument4 pagesProsthetic: The Art and Science of Supplying Artificialsaleh alawdiNo ratings yet
- Artigo 5Document9 pagesArtigo 5joao pauloNo ratings yet
- First Lecture Studying Notes - MFPDocument12 pagesFirst Lecture Studying Notes - MFPالعمري العمريNo ratings yet
- Extraoral and Mid-Facial Prostheses CareDocument5 pagesExtraoral and Mid-Facial Prostheses CareahmedfikryNo ratings yet
- Mouth Preparation for Removable Partial Denture TreatmentDocument76 pagesMouth Preparation for Removable Partial Denture TreatmentShemi SirajNo ratings yet
- GRUPO I ORTO. ContemporaryDentalOcclusioninOrthodonticsDocument5 pagesGRUPO I ORTO. ContemporaryDentalOcclusioninOrthodonticsJessica BastoNo ratings yet
- Medical University of Varna Faculty of Dental Medicine Prosthetic Dentistry QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesMedical University of Varna Faculty of Dental Medicine Prosthetic Dentistry Questionnairesnehal jaiswalNo ratings yet
- DentistryDocument22 pagesDentistryDrShweta SainiNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontics Dentistry: Assignment 1Document3 pagesProsthodontics Dentistry: Assignment 1ameer mousaNo ratings yet
- Interferences, Centric Occlusion, ImplantsDocument35 pagesInterferences, Centric Occlusion, ImplantsDuncan MakNo ratings yet
- PerioDocument1 pagePerioSarah LewisNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Non Surgical Treatment 3.1.1 Maxillary Anterior Protrusion Nursing English 2 by IlhamDocument12 pages3.1 Non Surgical Treatment 3.1.1 Maxillary Anterior Protrusion Nursing English 2 by IlhamWiratama SuryaNo ratings yet
- Corticotomy-Assisted OrthodonticsDocument6 pagesCorticotomy-Assisted Orthodonticsyui cherryNo ratings yet
- 34 3 329 Vojvodic enDocument2 pages34 3 329 Vojvodic enDiana BărbulescuNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction OrthodonticsDocument25 pages1.1 Introduction OrthodonticsShany Schwarzwald100% (1)
- Mouth Prep VikasDocument35 pagesMouth Prep VikasVikas AggarwalNo ratings yet
- BifosfonatosyortodonciaDocument8 pagesBifosfonatosyortodonciavivigaitanNo ratings yet
- 3 Badr2016Document22 pages3 Badr2016Daniel Espinoza EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Sindrome de TurnerDocument13 pagesSindrome de TurnerVALENTINA CORNELLNo ratings yet
- GERD-PPI MisconceptionsDocument2 pagesGERD-PPI MisconceptionsLie LhianzaNo ratings yet
- Makna MsiaDocument19 pagesMakna Msiadivaglrboy9023No ratings yet
- FP Rescue Plan TemplateDocument7 pagesFP Rescue Plan TemplateEmrahNo ratings yet
- Sensors: Low-Cost Air Quality Monitoring Tools: From Research To Practice (A Workshop Summary)Document20 pagesSensors: Low-Cost Air Quality Monitoring Tools: From Research To Practice (A Workshop Summary)SATRIONo ratings yet
- Major Case Presentation On Acute Pulmonary Embolism WithDocument13 pagesMajor Case Presentation On Acute Pulmonary Embolism WithPratibha NatarajNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sanjida Sultana's CVDocument4 pagesDr. Sanjida Sultana's CVHasibul Hassan ShantoNo ratings yet
- Snigdha Dasgupta Sexual DisorderDocument13 pagesSnigdha Dasgupta Sexual DisorderSNIGDHA DASGUPTANo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlanRenato Torio100% (1)
- The So Called Oedematous Skin DiseaseDocument22 pagesThe So Called Oedematous Skin Diseaseمحمد على أحمد أحمدNo ratings yet
- DVT Case StudyDocument3 pagesDVT Case StudyCrystal B Costa78No ratings yet
- Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin As A Treatment of COVID-19Document6 pagesHydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin As A Treatment of COVID-19Larissa ChaveirinhoNo ratings yet
- Sample Employee Stress QuestionnaireDocument1 pageSample Employee Stress Questionnairesanthosh222250% (2)
- Jejunostomy Feeding Tube Placement in GastrectomyDocument14 pagesJejunostomy Feeding Tube Placement in GastrectomyHarshit UdaiNo ratings yet
- Agriculture, biotech, bioethics challenges of globalized food systemsDocument28 pagesAgriculture, biotech, bioethics challenges of globalized food systemsperoooNo ratings yet
- FMTDocument29 pagesFMTCynfully SweetNo ratings yet
- Laws of Malaysia: Act A1648Document42 pagesLaws of Malaysia: Act A1648ana rizanNo ratings yet
- Strategi Koping Ibu Dengan Anak Penderita Kanker (Studi Deskriptif Di Komunitas Peduli Anak Kanker Dan Penyakit Kronis Lainnya)Document15 pagesStrategi Koping Ibu Dengan Anak Penderita Kanker (Studi Deskriptif Di Komunitas Peduli Anak Kanker Dan Penyakit Kronis Lainnya)Yan ParirakNo ratings yet
- CptchildDocument2 pagesCptchildapi-3709645No ratings yet
- PED011 Final Req 15Document3 pagesPED011 Final Req 15macabalang.yd501No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Physical AssessmentDocument6 pagesCardiovascular System Physical Assessmentpulsating humNo ratings yet
- Bone Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and StagingDocument22 pagesBone Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Stagingjinal BhadreshNo ratings yet
- Welcome Plan Welcome CorpsDocument10 pagesWelcome Plan Welcome Corpscs310201No ratings yet