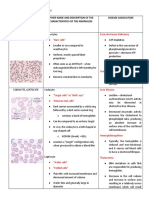
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Catha
Uploaded by
Jobz Dela CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Catha
Uploaded by
Jobz Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
BREAD
JEEP
Catharina r. gamueda
BED
HEN
DEFINITION:
vitamin A n. A fat-soluble vitamin or a mixture of vitamins, especially vitamin A1 or a mixture of vitamins A1 and A2, occurring principally in fish-liver oils, milk, and some yellow and dark green vegetables, and functioning in normal cell growth and development. Its deficiency causes hardening and roughening of the skin, night blindness, and degeneration of mucous membranes. Also called retinol. vitamin B complex n. A group of water-soluble vitamins including thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, pyridoxine, folic acid, inositol, and vitamin B12 and occurring chiefly in yeast, liver, eggs, and some vegetables. Also called B complex. Vitamin C: An essential nutrient found mainly in fruits and vegetables. The body requires vitamin C to form and maintain bones, blood vessels, and skin.
Definition: Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. It's not found in many foods unless they have been fortified with supplemental vitamin D. Normally, your body makes vitamin D when your skin is exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D is required by your body to absorb and utilize calcium, which keeps your bones and teeth strong. A vitamin D deficiency leads to weakened bones and rickets in children and osteomalaciain adults.
Definition: Vitamin E is a member of the fat-soluble family of vitamins that also includes vitamin D, vitamin K and vitamin A. Vitamin E is important as an antioxidant that protects the cells of your body from free radical damage. Vitamin E is also an important component of the immune system and is necessary to repair DNA.
Definition: A member of the fat-soluble family of vitamins that also includes vitamin D, vitamin E and vitamin A. Vitamin K is important for normal blood clotting and may help to keep your bones strong as you age. Vitamin K deficiency is rare, but may occur after long-term use of antibiotics. It is important to note that people who are taking blood thinners should consult with their doctors or pharmacists about vitamin K supplementation because taking extra vitamin K can reduce the effectiveness of blood thinners.
Iron: An essential mineral. Iron is necessary for the transport of oxygen (via hemoglobin in red blood cells) and for oxidation by cells (via cytochrome). Deficiency of iron is a common cause of anemia. Food sources of iron include meat, poultry, eggs, vegetables and cereals (especially those fortified with iron). According to the National Academy of Sciences, the Recommended Dietary Allowances of iron are 15 milligrams per day for women and 10 milligrams per day for men. Iron overload can damage the heart, liver, gonads and other organs. Iron overload is a particular risk in people who may have certain genetic conditions (hemochromatosis) sometimes without knowing it and also in people receiving recurrent blood transfusions. Iron supplements meant for adults (such as pregnant women) are a major cause of poisoning in children.
Definition: Calcium is a major mineral and is the most abundant mineral in the human body. Most of it is stored in the bones and teeth (about 99 percent), and the rest is in your blood, muscles and extracellular fluid. Calcium is necessary for strong bones and teeth, plus it plays an important role in blood clotting, muscle contraction, hormonal secretion and normal nervous system function.
Definition: Zinc is a trace mineral you need for normal growth and healthy immune system function. It's involved in protein production, DNA synthesis and cell division. Zinc is also necessary for hundreds ofenzymes that function in different chemical reactions, and is also crucial for a normal sense of smell and taste. Definition: Potassium is a major mineral that is necessary for normal growth and for making proteins from amino acids that come from your diet. It's also needed for metabolizing carbohydrates. Potassium is an electrolyte, which means it carries an electrical current. Electrolytes regulate the pH and fluid balance of your body. Most of the potassium in your body is found in the cells of your body. Definition: Iodine is a trace mineral that your body needs to synthesize thyroid hormones that are necessary for regulating your body's growth, development, metabolism and body temperature. Most iodine in your body is found in the thyroid gland, but some is also found in the blood and muscles.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- RBC AnomaliesDocument10 pagesRBC AnomaliesSHUPATUSSAINo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Wechsler Intelligence Scale For ChildrenDocument4 pagesWechsler Intelligence Scale For ChildrenCyndi Whitmore67% (3)
- MCQ of HematologyDocument22 pagesMCQ of Hematologydrafq200063% (8)
- ABO, RH, Minor Blood Grps AHG Test Pretransfusion Test Automation in BBDocument32 pagesABO, RH, Minor Blood Grps AHG Test Pretransfusion Test Automation in BBJill Arciaga0% (1)
- Thyroid UltrasoundDocument62 pagesThyroid UltrasoundYoungFanjiens100% (1)
- 3rd Quarter Exam Science 10Document3 pages3rd Quarter Exam Science 10Rizel Shaira Hope TanamanNo ratings yet
- Virus TableDocument3 pagesVirus TableFrozenManNo ratings yet
- Survival in Long CaseDocument7 pagesSurvival in Long CaseRapid MedicineNo ratings yet
- ManagementDocument63 pagesManagementJobz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- An Uhf Wireless Power Harvesting System-Analysis and DesignDocument10 pagesAn Uhf Wireless Power Harvesting System-Analysis and DesignJobz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Referral Letter - MFIDocument1 pageReferral Letter - MFIJobz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nod 32 PassDocument2 pagesNod 32 PassJobz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Biology of Stem Cells: An Overview: Pedro C. Chagastelles and Nance B. NardiDocument5 pagesBiology of Stem Cells: An Overview: Pedro C. Chagastelles and Nance B. NardiMayuri DuttaNo ratings yet
- tmpB0FF TMPDocument184 pagestmpB0FF TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Javt 15 I 1 P 54Document5 pagesJavt 15 I 1 P 54Aryanto AntoNo ratings yet
- Development of An Immuno-Based Colorimetric Assay For White Spot Syndrome VirusDocument6 pagesDevelopment of An Immuno-Based Colorimetric Assay For White Spot Syndrome VirusendorengasNo ratings yet
- G8 B-Thall Chromatogram Interpretation Guide1Document58 pagesG8 B-Thall Chromatogram Interpretation Guide1Kwok Hoi ShanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyTyrNo ratings yet
- Five Day Diet AnalysisDocument4 pagesFive Day Diet AnalysisphyreflyNo ratings yet
- 3.2 The Kidneys and HomeostasisDocument2 pages3.2 The Kidneys and HomeostasisNirmala Josephine0% (3)
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Streptococcus PyogenesDocument16 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of Streptococcus PyogenesRima Carolina Bahsas ZakyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Bioinformatics - A New Emerging ScienceDocument3 pagesClinical Bioinformatics - A New Emerging ScienceSUMAN CHAUDHURINo ratings yet
- Module For Students 1 - 2 - 3-1 EditDocument15 pagesModule For Students 1 - 2 - 3-1 EditJanuardi IndraNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review of Global Efforts on COVID-19 Vaccine DevelopmentDocument22 pagesA Comprehensive Review of Global Efforts on COVID-19 Vaccine DevelopmentBeverly EstoqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Physiology of HaemoglobinDocument26 pagesLecture On Physiology of HaemoglobinMubasharAbrarNo ratings yet
- M.03 Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument5 pagesM.03 Non-Mendelian Geneticsno veNo ratings yet
- Bayer Pharma RD Event 2023Document135 pagesBayer Pharma RD Event 2023ranvijay.rajput515No ratings yet
- 2402 CH 17 Endocrine System (Part 1) PDFDocument23 pages2402 CH 17 Endocrine System (Part 1) PDFHarry RussellNo ratings yet
- Current Challenges and Opportunities in Treating GlioblastomaDocument34 pagesCurrent Challenges and Opportunities in Treating GlioblastomaJubairNo ratings yet
- Propofol Anesthesia EffectsDocument4 pagesPropofol Anesthesia EffectsdidyahfNo ratings yet
- Week1 LR-2Document4 pagesWeek1 LR-2AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Yasser Al Kadri and Zaid Al AzemDocument14 pagesYasser Al Kadri and Zaid Al Azemalsakar26No ratings yet
- AutismDocument30 pagesAutismLIWANGA LIWANGANo ratings yet
- Gene TherapyDocument3 pagesGene TherapyGleeson Jay NiedoNo ratings yet