Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antioxidant and Lifespan Extension Activities of Cordyceps Sinensis in Oxidative Stress
Uploaded by
Luigi TinioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antioxidant and Lifespan Extension Activities of Cordyceps Sinensis in Oxidative Stress
Uploaded by
Luigi TinioCopyright:
Available Formats
ANTIOXIDANT AND LIFESPAN EXTENSION ACTIVITIES OF CORDYCEPS SINENSIS CS IN OXIDATIVE STRESS AND AGING MODELS
Jia-Shi Zhu, Yan Zhang, Jieying Yang, Ningzhi Tan, Angela Mastaloudis, and Chunsheng Zhao 1 2 2 Pharmanex Research Institute, Provo, UT 84601; Pharmanex Beijing Clinical Pharmacology Center: Xinkang Road, Beijing 100088, China; 3 School of Pharmacy, Shihezi University, Shihezi City, Xinjiang 832000, China
1,2,3 2 2 2 1 2
ABSTRACT Cordyceps sinensis has traditionally been used in China as a strategy to combat aging. We have reported the e ects of Cordyceps sinensis Cs-4 (Cs-4) a mycelia fermentation product of C. sinensis, in glucose-lipid-energy metabolisms, anti-fatigue, and endurance enhancement. In this study, we examined the e ect of Cs-4 on lifespan extension and antioxidant status in mice. For the lifespanextension study, 250 mice 12 months of age (both sexes) received either vehicle or Cs-4 (0.5, 1.0 or 1.5g/kg diet). Caloric intake was adjusted to match the levels for controls twice per week. Compared to controls, the Cs-4 dosage groups 75% survival time was extended 94-108 days, 50% survival time extended 10-66 days, 25% survival time extended 2944 days, and 12.5% survival time extended 750 days (86 weeks so far; treatment continues). The Kaplan-Meier Survivor analysis revealed the extended lifespan and the reduced risks of death by Cs-4. The antioxidant activity was tested in mice (6 months old) that received 60 days of vehicle or Cs-4 (0.5, 1.0 or 1.5 g/kg diet) and a single dose of 11Gy 60Co gamma-radiation on day 60. Compared to controls, Cs-4 prevented the depletion of plasma total thiol-groups, GSH and GSH-peroxidase, liver CAT, SOD, and GSH-reductase (p<0.05) caused by radiation exposure. Cs-4 also prevented the radiation-induced increases in liver protein carbonyls and 8-OHdG (p<0.05) observed in the control group. In conclusion, Cs-4 supplementation signicantly improves the bodys antioxidant capacity and extends the lifespan in mice, supporting the traditional anti-aging uses of Cs-4 in humans. INTRODUCTION 1. Cordyceps sinensis is traditionally believed to have anti-aging activities and to promote longevity. 2. C. sinensis and its mycelia fermentation product C. sinensis Cs-4 have a broad spectrum of health benets, including the therapeutic activities of improving cardiovascular, liver, lung, and kidney functions. (Zhu et al. J Altern Compl Med. 4:289303, 429457,1998) 3. We reported the endurance enhancement and anti-fatigue properties of Cs-4 and the improvement of energy, glucose, and lipid metabolisms by Cs-4 in animals and humans. (Dai et al. J Altern Compl Med. 7:231, 2001; Zhao et al. J Altern Compl Med. 8:309, 2002; Xiao et al. Chin J Integrat Med. 10:187, 2004; Li et al. Chin J Clin Pharmacy 16:274, 2007; Li et al. Shanghai J Prevent Med. 20:367, 2008; Wang et al. 2008 Symposium Chin Assoc Med Mycol. pp157164) 4. The aim of this study was to test the lifespan-extension e ect and antioxidant activity of Cs-4 in mice.
LIFESPAN EXTENSION STUDY METHODS 8-month-old mice fed normal chow until 12 months of age. At 12 months, mice were randomized into one of four groups matched for gender and weight.
GROUPS:
ANTIOXIDANT METHODS
BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES STUDY
DIET AND ENDPOINTS:
200 100 0
Non radiation control
Caloric intake of treatment groups was adjusted bi-weekly to match the intake of the control group Deaths recorded daily Lifespan study is ongoing LIFESPAN STUDY IN MICE
radiation control
-22%; p<0.05
500
60
Control: Normal mouse chow Treatment 1: Chow containing Cs-4: 500 mg/kg BW Treatment 2: Chow containing Cs-4: 1000 mg/kg BW Treatment 3: Chow containing Cs-4: 1500 mg/kg BW
GSH-Px (U/mg pro.)
Mice were randomized into ve groups and treated for 64 consecutive days by gavage. Mice received 11Gy 60Co gamma-radiation on day 60 to induce oxidative stress and damage (except non-radiation control group). The study was completed on the fourth day and the liver and blood samples of all mice were collected and analyzed for antioxidant enzymes and biochemical markers of oxidative stress. ANTIOXIDANT ENZYMES: 1. Superoxide dismutase (SOD)* 2. Catalase (CAT) 3. Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) 4. Glutathione reductase (GSH-Rd)* 5. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)* *Data not shown Mice randomized into ve groups:
Non-radiation control (n=15)
Cs-4 Prevented Depletion of Liver GSH Peroxidase
700 600 500 400 300
MARKERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS: 1. Total thiol groups and glutathione 2. Total protein carbonyl groups 3. 8-OHdG in liver
1000 Cs- (mg/kg)
1500
Co- Gy
8-month-old
Treatment starts at age of 12 months
~3+ years all mice dead
Cs-4 Prevented Depletion of Plasma GSH
Glutathiones (mg/L)
8 6 4 2 0
Cs-4 Attenuated Increases in Liver Protein Carbonyls and 8-OHdG
8 30 7 6 25
Radiation control WEEKS OF CS 2 Live 8 Live 4 Live 4 Live 0 (days) Cs-4 500 mg/kg
(n=15) (n=15)
-25.3%; p<0.05
Vehicle control Cs-4 500 mg/kg Cs-4 1000 mg/kg Cs-4 1500 mg/kg CS
46 Dead 40 Dead 44 Dead 44 Dead
Cs-4 1500 mg/kg (n=15) 60
60
5 4
8-OHdG (ng/g liver tissue)
GSH-Px (U/mg pro.)
DEATHS AND SURVIVORS AFTER
Cs-4 1000 mg/kg (n=15)
20
15
-15.5%; p=0.05
+26%; p<0.05
+22%; p<0.05
+22%; p<0.05
-33%; p<0.05
1000
63
10
2 1
DELAYS NORMAL DEATH OF MICE
Cordyceps sinensis (Berk.) Sacc.
Isolation & Purication
(Collected from Qinghai-Tibetan plateau of China)
Kaplan-Meier Cumulative Survival Plot for Time 1 Censor Variable: Censor 1 Grouping Variable: Group 1
1.0
Co Collect (11Gy) blood & liver Cs-4 Prevented Depletion of Plasma Thiols
0.7
Non radiation control
radiation control
500
60
1000 Cs- (mg/kg)
1500
0
Non radiation control
0
Non radiation control radiation control
Co- Gy
radiation control
500
60
1000 Cs- (mg/kg)
1500
500
60
Co- Gy
Co- Gy
Cs- (mg/kg)
Cs-4 Prevented Depletion Liver Catalase
40
SUMMARY
CONCLUSION
Cs-4
0.6 0.5 -21%; p<0.05 0.4 0.3
CAT (U/mg pro.)
(A fungal strain of Paecilomyces hepiali Chen et Dai) Industrial Fermentation
Cum. survival
0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0
Thiol groups (mmol/L)
(Cs-4 500 mg/kg)
1. Supplementation with Cordyceps sinensis Cs-4 prolongs lifespan in an aging mouse model. 2. Cordyceps sinensis Cs-4 supplementation increased antioxidant protection and reduced oxidative stress in mice exposed to radiation. 3. Cordyceps sinensis Cs-4 supplementation signicantly improves the bodys antioxidant capacity, protects against oxidative damage, and extends the lifespan in mice, supporting the traditional use of Cs-4 as an anti-aging strategy in humans.
30 20 10 0 -23.5%; p<0.05
Cordyceps sinensis
POSTER WAS PRESENTED AT THE OXYGEN CLUB OF CALIFORNIA 2010 WORLD CONGRESS IN SANTA BARBARA, CALIFORNIA; MARCH 2010 WHERE IT RECEIVED THE DSM NUTRACEUTICAL RESEARCH AWARD.
(control)
Cordyceps sinensis Cs-4
100
200
300 400 Time
500
600
700
Non radiation control
radiation control
500
60
1000 Cs- (mg/kg)
1500
Co- Gy
Non radiation control
radiation control
500
60
1000 Cs- (mg/kg)
1500
Co- Gy
-21%; p=0.05
1500
-12.5%; p<0.05
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Byssinosis PDFDocument8 pagesByssinosis PDFFaza AlhinduwanNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Diffusion Active - Transport+studentDocument35 pagesOsmosis Diffusion Active - Transport+studentMetaknight360 LiveNo ratings yet
- Teachers' Health Examination Card (CS Form 86)Document4 pagesTeachers' Health Examination Card (CS Form 86)Maria Angellie S. Bellido - EramisNo ratings yet
- RECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2Document62 pagesRECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2RadianNasution100% (1)
- Qualitative Tests for Bile ComponentsDocument8 pagesQualitative Tests for Bile ComponentsSoh Rodriguez100% (1)
- DR Anu Arasu How Trauma Affects Your HormonesDocument14 pagesDR Anu Arasu How Trauma Affects Your HormonesShalu SaharanNo ratings yet
- Hyperlipedemia PPDocument51 pagesHyperlipedemia PPrabarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular DisordersDocument7 pagesChapter 31 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular DisordersMichael Boado100% (1)
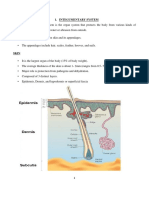
- The Integumentary System: Layers and Functions of SkinDocument8 pagesThe Integumentary System: Layers and Functions of SkinAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Limbic SystemDocument17 pagesLimbic SystemYhemmy Lhawal JummyNo ratings yet
- ANS & CVS Response To Exercise v2Document18 pagesANS & CVS Response To Exercise v2chow wing yin amandaNo ratings yet
- Manifest From The HeartDocument25 pagesManifest From The HeartTuta Velesije Bg100% (2)
- Analysis - Bio - NEET 2023Document5 pagesAnalysis - Bio - NEET 2023oniichanNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Preoperative Pulmonary RiskDocument19 pagesEvaluation of Preoperative Pulmonary RiskCharlieBrown_QBNo ratings yet
- % Chapter 3: Regulation of Gas Content in BloodDocument33 pages% Chapter 3: Regulation of Gas Content in BloodK CNo ratings yet
- 1 - OB 1 (Maternal Anatomy)Document13 pages1 - OB 1 (Maternal Anatomy)Gen XNo ratings yet
- Functional Hypertrophy: The Secret To Increasing Muscle Without Losing Speed and StrengthDocument2 pagesFunctional Hypertrophy: The Secret To Increasing Muscle Without Losing Speed and Strengthtodd455No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On RhinitisDocument15 pagesLesson Plan On Rhinitiskiran mahal100% (4)
- Principles & Practice of First AidDocument298 pagesPrinciples & Practice of First AidJoshua100% (2)
- Pharmacology Question BankDocument24 pagesPharmacology Question BankSiri SriNo ratings yet
- How Sleep Deprivation Affects Students' Academic PerformanceDocument50 pagesHow Sleep Deprivation Affects Students' Academic PerformanceAstrophile0% (2)
- LP UapDocument18 pagesLP UapHat MutisalNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Running and JoggingDocument2 pagesHealth Benefits of Running and JoggingOsamaNo ratings yet
- Pregnant woman with painful swollen legDocument12 pagesPregnant woman with painful swollen legjimmojonesNo ratings yet
- The Ionization of Amino Acids at Physiological pHDocument4 pagesThe Ionization of Amino Acids at Physiological pHNatasha MahatantilaNo ratings yet
- Aqa Byb1 W QP Jun07Document12 pagesAqa Byb1 W QP Jun07李超然No ratings yet
- Assessment of Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument15 pagesAssessment of Fluid and ElectrolyteDip Ayan MNo ratings yet
- Pedia2 Sepsis (Dr. Seng)Document3 pagesPedia2 Sepsis (Dr. Seng)Tony DawaNo ratings yet
- Standard and Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing HandoutDocument17 pagesStandard and Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing HandoutDarcyNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Energy Metabolism and Intermittent Fasting: The Ramadan PerspectiveDocument16 pagesNutrients: Energy Metabolism and Intermittent Fasting: The Ramadan PerspectiveAlejandro Estrada RiosNo ratings yet