Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Terms chronic bronchitis Hemoptysis definitions
Uploaded by
Diane Kate Tobias MagnoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Terms chronic bronchitis Hemoptysis definitions
Uploaded by
Diane Kate Tobias MagnoCopyright:
Available Formats
Terms chronic brohchitis Hemoptysis cold, bronchitis, viral infections bacterial infection TB, pneumococcal Pna pulmonary edema
mycophasma pna early heart failure croup cold, bronchitis, pneumonia Orthopnea paroxysmal norcturnal dyspnea diaphoresis ventilation Internal respiration Normal adult chest
Definitions characterized by a history of productive cough for 3 month of the year for 2 years in a row Bloody sputum white or clear mucoid yellow or green rust colored pink frothy hacking cough dry cough barking cough congested cough the difficulty breathing when supine. state mumber of pilow needed to achieve comforts ex two pillow orthopnea awakening from sleep with SOB and needing to be upright to achieve comfort SOB episodes associated with night sweats is distribution of gas inot and out of the pulmoary airways (good air in bad air out) the exhange of gases at teh alvelolar level and the capillary level te thorax has an ellipitacl shape with an nateroposterior to transvers diameter 1:2 or 5:7 note equal anteroposterior to trasverse diameter and that ribs are horizontal instead of the normal downward slope. this is associated with normal aging and also with chronic emphysema and asthma as a rsult of hyperinflataion of lungs a markely sunken sternum and adjacent cartilages (also called funnel breast). depression begins at the second intercostal space to xiphoid with body of sterum. more noticeable on inspiration. Congential, not symptomatic.
barrel chest
pecus excavatum
Pecus Carinatum
a forward protrustion of the sternum, with ribs sloping back at either side and vertical depression along cosochondral junctions(pigeon breast) less common thatn pecus excavautm , but is a minor deformity and requires no treatment a later S-shaped curvaturs of the thoracic and lumabar spine. Note unequal shoulder and scapular height and unequal hip levels (adolescents) an exaggerated posterior eurvature of teh thoracic spine (humpback) that causes significant back pain and limited mobility (aging) occasional sighs puncutated the normal breathing pattern and are purposeful to expand alveoli. indicate emotional dysfunction or may lead to hyperventilation and dizziness rapid shallow breathing over 24 resp per min slow breathing. a drecreased by regular rated (less than 10) durg induced depression or respiratory center of medulla a cycle in which respiration gradulally wax and wane in a regular pattern , incrasing in rate and depth and then decreasing. period las 30-45 sec, with period of apnea lasting 20 sec. increased in both rate and depth . normally occurs with extreme exertion, fear or anxity. Blow off carbon dioxide and causing a decreased level in teh blood (alkalosis) an irregular showllow pattern caused by an overdose of narcotic or anethetics. similar to cheyn-stokes, expcet the at the pattern is irregular. A series of normal resp 3-4 is floowed by period of apnea. cycle lenght is variable lasting anywhere for 10 sec to 1 min. normal inspiration and prolonged expiration to overcome incrased airway resistance. In a person with CO lung disease and situation calling for incrased heart rat may lead to dyspneic episode be cause don't have enough time to fully expiraton air trapping discontinuous HIGH pithced shor crackling popping sounds heard durign inspiration that CAN NOT clear with cough Loud, LOW pitched bubbling and gurgling sound that start i early inspirtation and my contiue through expiration sounds like fin crackles byt do not last and arenot pathologic; disappear after
Scoliosis Kyphosis sigh frequent sigh tachypnea bradypnea
cheyn-stokes respiration
hyperventilation
hypoventilation
Biot's Respiration
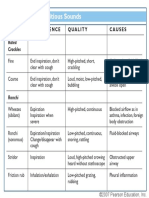
Chornic Obstructive Breathing dyspneic crakles (fine) crakles (coarse) Atelectatic crackles
the first few breaths; hear in axillae and bases (usually depent) of lungs A very superficial sound that is course and Low pitched; it has a grating quailty as if two pieces of leather are being rubbed together; sound just like crackles but close to ear; sound are louder if you push tehe stethoscope harder onto the chest . Heard on INSPIRATION and EXPIRATION High ptich musical squeaking sound that sound polyphonic. Predominate in expiratrion byt may occur on both inspiration and expiration Low pithced; monohonic single note, snoring , moaning sounds. Heard through out the cycle but predominate on expiration; may clear some with cough High pitched, inspirator crowing sound louder in the neck than over the chest Percusion sound heard over the lungs befor you make them cry for men with hairy chest what should you do the drease extraneous noise the sound of most breath sounds what part of the stethoscope is use for breath sounds assess heart or breath first when ausculttaon breath , listen to ______________ ventilatory cycle compare breath sound _______to________ A palpabe virbration on the chest have the patient say 99 and feel the vibration , sound generated for the larynx is trasmitted through the lungs where examiner can feel the vibration eaisly throught solid structures than air, the vibration produced sounds are percceptible when transmitted throught solid structures a course crackling caused by fine bead of air palpable under skin surface; casued by air leak into the SQ tissue. Campares to the sound of crumpling cellophane Report ASAP present in condisiton that cause consolidation of thissure or incrased density
:leural friction rub
Wheez (high-pitched) Sibilant Wheez (low ptiched) (sonorous rhonchi) Stridor Resonance when should you check kids lungs wet hair on chest high pithces diaphragm heart complete ventilatory cycle 1. side 2. side Tactile Fremitus how is tactile Fremitus assessed sound travels
creptius action if creptius is heard areas of INCREASED
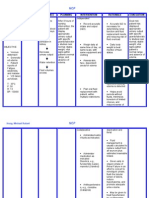
fremitus areas of DECRASED fremitus fine crackles coarse crackles atelectatic crackles normal voice sounds abnormal voice sounds when is voice sound used decreased vocal resonance increased vocal resonance drug with resp SE Epinephrine and beta blockers, NSAIDS and ASA Narcotic eupnea Hyperresonance dull Bronchial breath sounds Bronchovesicular breath sounds Vesicular breath sounds
of tissue ; tumor, pulmonary fibrosis, pnx presen when condition exist causing absence of air movement , obstructs transmission of vibrations; emphysema, copd, atelectasis, pneumothorax originate in alveoli, are often end-inspiration . Not cleared with cough. sounds like rolling hair between finger loud, bubbly noise , originate inteh larger airways , being mid inspiraton, may be slightly altered by cough ut will reappear shortly few crackles in teh bases disappears after first few breaths. not patologic heard only in the periphery dependent areas of the lungs vocal resonance is heard as muffled, non distinct pathology that incrase lung density enhances transmission of voice if any abnormalities have been detected during inspection, palpation or auscultation asthma, atelectasis, emphysema, pneumothorax pnx, plumonary fibrosis epinephrine, beta blockers, narcotic, NSAOD and ASA these drugs cause bronchospasm these drugs cause respitory depression normal breath breathing a lower pitched booming sound found when too much air is present as in emphysema or pneumothorax a not (soft , muffled thud) signals abnormal diensity in the lungs as with pnx, pleural effusion, atelectasis or tumor heard around trachea, loud, inspiration is shor and expiration is longer eard of the 2 main bronchi at 1st and 2nd ICSaath the sternal borader and posterior between scapulae, sound moderate, inspiration =expiration (coarse breath sounds) heard over the periphery the lungs, soft, breezy, inspiration is longer thatn
expiration Bronchophony Egophony listen to posterior chest as patient says "99", normal to hear muffuled non distinct abnormal to hear distinct and understandable listen to patient while saying (ee-ee-ee), sound like nondistinct "ee" if you hear "a-a-a" document E changed to A listen to person whispering :1-2-3", barely audible, abn with only small amount sof consolidation whipsered voice is clear and distincly, but still faint(soft) would sound like wishing directly into stethoscope sound not normally heard in the lungs or noral sounds auscultated in an abnormal place. Superimpose on normal breath sounds. breath sound may be absent or diminished feel this halow U-shaped depression just abofe the sternum in between th clavicles the breast bone the manubrium, the body and xiphoid preocess is the articulation of the manubrium and the body of he sternum and is continuous to the the second rib. The site of treacheal bifurcation into the right and left main bronchi. center of chest bsects the cner of each clavicle at a point halfway between the palpated sernoclavicular and acromioclavicular joint line do the joint of the shoulder line runs down from the apex ofhte axilla and lies between and parallel to the other two anterior and posterior continuse down for them posterior axillary fold where the latissius dorsi muscle inserts highest poin of lung tissue 3 or 4 cm above the inner third of the clavicles lower border rests on the diaphragm at about the sixth ribin the midclavicluar line.
whisper pectoriloquy
Adventitous sounds Asthma, emphysema, atelectasis suprasternal notch sternum sernal oagleor angle of louis midsternal line midclavicular line anterior axillary line midaxillary line posterior axillary line apex of lung base of lung
You might also like
- Thorax and LungsDocument11 pagesThorax and LungsJoel SantosNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- The Breath Sounds: Intensity (Or Loudness)Document6 pagesThe Breath Sounds: Intensity (Or Loudness)Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Breathe In, Breathe Out: Learning About Your LungsFrom EverandBreathe In, Breathe Out: Learning About Your LungsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Thorax and Lung - LectureDocument60 pagesThorax and Lung - LectureТаншолпан ШохбутоваNo ratings yet
- Respiratory gymnastics (Translated): Purification - Health - Strength - EnergyFrom EverandRespiratory gymnastics (Translated): Purification - Health - Strength - EnergyNo ratings yet
- Thorax and Lungs ReferenceDocument8 pagesThorax and Lungs Referencegwynth ripaldaNo ratings yet
- Lung Sounds On Percussion and AuscultationDocument3 pagesLung Sounds On Percussion and AuscultationKanika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cardio AssessementDocument9 pagesCardio AssessementPoonam soniNo ratings yet
- Skills Lab-Thorax ExaminationDocument141 pagesSkills Lab-Thorax ExaminationfajrinnnNo ratings yet
- Final Death Note - Compre NotesDocument1,550 pagesFinal Death Note - Compre NotesSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- Lung SoundsDocument35 pagesLung SoundsRaluca AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Lung Examination: AbnormalDocument56 pagesLung Examination: AbnormalBECAREFUL89ANo ratings yet
- Respi SystemDocument6 pagesRespi SystemKalichandren ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation 1Document155 pagesOxygenation 1Khatlen BagaresNo ratings yet
- MVS Pulmonary AuscultationDocument8 pagesMVS Pulmonary Auscultationvashini9151No ratings yet
- 8 Lung Auscultation Points and SoundsDocument11 pages8 Lung Auscultation Points and SoundsCHARIEMAE CA�AZARES100% (1)
- The Thorax and Lungs - BATESDocument4 pagesThe Thorax and Lungs - BATESsitalcoolk100% (2)
- Respiratory System-Review PathoDocument100 pagesRespiratory System-Review PathoSadiePartington-RiopelleNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Signs and SymptomsDocument11 pagesRespiratory Signs and SymptomsChristiany Racho SalduaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Lung and ChestDocument50 pagesAssessment of Lung and ChestAbdurehman Ayele100% (1)
- Abnormal Breath SoundsDocument3 pagesAbnormal Breath SoundsIndra PermanaNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANDocument60 pagesLungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANRabia IsrafilNo ratings yet
- Breath Sounds Incredibly EasyDocument4 pagesBreath Sounds Incredibly EasyMatthew Ryan100% (3)
- Lung Sounds Guide: Vesicular, Bronchial, Crackles & MoreDocument24 pagesLung Sounds Guide: Vesicular, Bronchial, Crackles & MoreAswinNo ratings yet
- Breath SoundDocument4 pagesBreath SoundkamaluNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDocument27 pagesPemeriksaan ThoraxYaasinta ArlaesNo ratings yet
- Suara ParuDocument31 pagesSuara ParuSuyanto nduduNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Assessment: Other SystemsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System Assessment: Other SystemsChetan KumarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Maysa Fall2015 PDFDocument126 pagesRespiratory Maysa Fall2015 PDFbaasheNo ratings yet
- Bates Thorax Lungs With TermsDocument4 pagesBates Thorax Lungs With Termscrystalshe100% (1)
- IPPADocument4 pagesIPPAIsaac KipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDocument27 pagesPemeriksaan ThoraxSubchanPrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fisik ThoraxDocument16 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik ThoraxYudiWatanabeNo ratings yet
- Rev Widya Physical Examination of Respiratory SystemDocument72 pagesRev Widya Physical Examination of Respiratory SystemYuliaNo ratings yet
- Thorax and LungsDocument3 pagesThorax and LungsRailyn MacalaladNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument34 pagesRespiratoryanasokour100% (1)
- Breath Sounds: ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesBreath Sounds: ConsiderationsKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Chest and Lungs HandoutDocument2 pagesAssessment of The Chest and Lungs Handoutkaren solibaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExaminarionDocument40 pagesRespiratory ExaminarionAbdelrahman AldemerdashNo ratings yet
- Auscultation Sites and Normal Breath SoundsDocument22 pagesAuscultation Sites and Normal Breath SoundsFatima Ivan CenizaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Examination - Knowledge at AMBOSSDocument1 pagePulmonary Examination - Knowledge at AMBOSSKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Lung SoundDocument2 pagesLung SoundRJay AlavazoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Assessment & DiagnosticsDocument9 pagesRespiratory Assessment & DiagnosticsAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PEDocument42 pagesRespiratory System PEyeabsira2116No ratings yet
- Risk Factors and Signs of Pulmonary DiseaseDocument3 pagesRisk Factors and Signs of Pulmonary DiseaseAnonymous b4P7PDNo ratings yet
- Chest Pulmophysiothera PY: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPDocument35 pagesChest Pulmophysiothera PY: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPFloriza de LeonNo ratings yet
- Breathing SoundsDocument3 pagesBreathing Soundsalthea jade villadonga100% (1)
- Examination of Respiratory SystemDocument78 pagesExamination of Respiratory Systemwidya sri hastutiNo ratings yet
- Jarvis Chapter 18 Study GuideDocument5 pagesJarvis Chapter 18 Study GuideEmily Cheng100% (2)
- Lung ExaminationDocument14 pagesLung Examinationსალომე მუმლაძე “Slay” TMANo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDocument36 pagesPemeriksaan ThoraxVaiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Adventitious Breath SoundsDocument1 pageAdventitious Breath SoundsEdwin Delos Reyes AbuNo ratings yet
- Physical Diagnoses: Respiratory SystemDocument72 pagesPhysical Diagnoses: Respiratory SystemAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Normal and Abnormal Findings of Thorax and LungsDocument3 pagesNormal and Abnormal Findings of Thorax and LungsOtherin Ojibwa TejanoNo ratings yet
- Lung Auscultation Sounds GuideDocument3 pagesLung Auscultation Sounds GuideCristina TofanNo ratings yet
- Sailor Hospitalized with HemoptysisDocument18 pagesSailor Hospitalized with HemoptysisMarissaevisNo ratings yet
- Assessmentpulmonary 151014090912 Lva1 App6892Document63 pagesAssessmentpulmonary 151014090912 Lva1 App6892sasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- Multiple Myeloma2Document9 pagesMultiple Myeloma2Diane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Diane EeeDocument3 pagesDiane EeeDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- LactuloseDocument2 pagesLactuloseDiane Kate Tobias Magno100% (1)
- Nasogastric Tube InsertionDocument11 pagesNasogastric Tube InsertionDiane Kate Tobias Magno100% (1)
- CKD NCPDocument3 pagesCKD NCPjosanne938No ratings yet
- CVA Case StudyDocument20 pagesCVA Case Studybetchai18100% (5)
- Chronic Kidney Disease 2Document83 pagesChronic Kidney Disease 2Diane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Multiple MyelomaDocument5 pagesMultiple MyelomaDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Diane Kate E. Tobias: Use of Over-the-Counter Cough and Cold Medications in Children Younger Than 2 YearsDocument3 pagesDiane Kate E. Tobias: Use of Over-the-Counter Cough and Cold Medications in Children Younger Than 2 YearsDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Multiple Myeloma2Document9 pagesMultiple Myeloma2Diane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Multiple MyelomaDocument46 pagesMultiple MyelomaDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- ICU-Acquired Pneumonia Outcomes With or Without DiagnosisDocument4 pagesICU-Acquired Pneumonia Outcomes With or Without DiagnosisDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Related To Multiple Myelom1Document15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Related To Multiple Myelom1Diane Kate Tobias Magno100% (1)
- NCP For CVADocument18 pagesNCP For CVAmolukas101100% (6)
- Multiple MyelomaDocument5 pagesMultiple MyelomaDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Managing Fluid Volume for Renal FailureDocument2 pagesManaging Fluid Volume for Renal FailureMark Angelo Chan100% (13)
- Newstart 2Document5 pagesNewstart 2Diane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Related To Multiple Myelom1Document15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Related To Multiple Myelom1Diane Kate Tobias Magno100% (1)
- Thesis Research 1Document27 pagesThesis Research 1Diane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- What Is Constipation?: Diarrhea Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument51 pagesWhat Is Constipation?: Diarrhea Irritable Bowel SyndromeDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Glenda S. Bermudez: Carreer ObjectivesDocument2 pagesGlenda S. Bermudez: Carreer ObjectivesDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Benevoence 2Document7 pagesBenevoence 2Diane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Salivary DiseasesDocument43 pagesSalivary DiseasesDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Non-Pharmaceutical Therapy For Hypertension: LifestyleDocument1 pageNon-Pharmaceutical Therapy For Hypertension: LifestyleDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument3 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionDiane Kate Tobias Magno100% (1)
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument3 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionDiane Kate Tobias Magno100% (1)
- Activityintolerancerelated Tomuscle OrcellularhypersensitivityDocument3 pagesActivityintolerancerelated Tomuscle OrcellularhypersensitivityDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNo ratings yet
- Glycerol Uptake Preserves Cut Juvenile Foliage of Eucalyptus CinereaDocument11 pagesGlycerol Uptake Preserves Cut Juvenile Foliage of Eucalyptus CinereaAndreaNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology in An Aquatic EnvironmentDocument47 pagesHuman Physiology in An Aquatic EnvironmentMARIA CAMILA RENGIFO CAICEDONo ratings yet
- COPD Case PresentationDocument50 pagesCOPD Case PresentationSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- ABLSDocument86 pagesABLSRenée Alejandra100% (2)
- Neonatal Chest X-RayDocument19 pagesNeonatal Chest X-RaydeborapkphnNo ratings yet
- 4 Handling Common Problems Pitfalls Pravit Edited DemoDocument5 pages4 Handling Common Problems Pitfalls Pravit Edited DemoBambang DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Espiratory System AutopsyDocument80 pagesEspiratory System AutopsyAbu ArshadNo ratings yet
- ST - Hypoxia & Cellular InjuryDocument59 pagesST - Hypoxia & Cellular InjurylalitrajindoliaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science MCQs-Respiration in OrganismsDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science MCQs-Respiration in Organismssiba padhy100% (3)
- Descaling Liquid - WilhelmsenDocument13 pagesDescaling Liquid - WilhelmsenfernandaNo ratings yet
- Yoga and Breathing: Muscles Work TogetherDocument2 pagesYoga and Breathing: Muscles Work Togethervksk1951No ratings yet
- Ba Duan JinDocument5 pagesBa Duan JinpenfoNo ratings yet
- The Laryngeal Mask Airway: Technical Guidelines and Use in Special SituationsDocument10 pagesThe Laryngeal Mask Airway: Technical Guidelines and Use in Special Situationsjangkrik21No ratings yet
- Biophysical Aspects of Human Thermoregulation During Heat StressDocument25 pagesBiophysical Aspects of Human Thermoregulation During Heat StressNataly CRNo ratings yet
- Pathology Lecture 1 MSADocument6 pagesPathology Lecture 1 MSAcejix87209No ratings yet
- Nursing Process Focus Drug Study TemplateDocument2 pagesNursing Process Focus Drug Study TemplateArgie Mae VallegaNo ratings yet
- Practice On Pulmonary Hygiene and Associated Factors Among Health Professionals Working in Two Government Hospitals at Amhara, EthiopiaDocument4 pagesPractice On Pulmonary Hygiene and Associated Factors Among Health Professionals Working in Two Government Hospitals at Amhara, EthiopiaayuNo ratings yet
- MTV 1000 VENTILADOR DE TRANSPORTE EMERGENCIADocument2 pagesMTV 1000 VENTILADOR DE TRANSPORTE EMERGENCIAFernando Trujillo100% (1)
- Bio4 5Document11 pagesBio4 5ミーチェルNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation Troubleshooting Skill Respiratory Therapy COVID 19 Toolkit - 070420Document8 pagesMechanical Ventilation Troubleshooting Skill Respiratory Therapy COVID 19 Toolkit - 070420Sirgut TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument13 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesTanmayee MuppaneniNo ratings yet
- Initial Assessment of the Mechanically Ventilated PatientDocument21 pagesInitial Assessment of the Mechanically Ventilated Patientmochkurniawan100% (3)
- Bronchial Asthma (Case Study)Document12 pagesBronchial Asthma (Case Study)Adriane Coma100% (1)
- Curriculum OF: Higher Education Commission Islamabad - PakistanDocument196 pagesCurriculum OF: Higher Education Commission Islamabad - PakistanShahid Ahmed HeeraNo ratings yet
- Dispnea Pada Pasien Multipel Fraktur Ekstremitas: Post Open Reduction Internal FixationDocument5 pagesDispnea Pada Pasien Multipel Fraktur Ekstremitas: Post Open Reduction Internal Fixationwinda oderaNo ratings yet
- Airway Obstruction Post COVID CaseDocument48 pagesAirway Obstruction Post COVID CaseCindy GoNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Active Cycle of Breathing TechniquesDocument2 pagesLeaflet Active Cycle of Breathing TechniquesDearbhla ShannonNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia On The MoveDocument256 pagesAnaesthesia On The MoveSanna Huhtamaki100% (2)
- Home Based CareDocument34 pagesHome Based CaremewselectionsNo ratings yet
- IJSO Biology Module - 3Document207 pagesIJSO Biology Module - 3Ikhbaat Atiqur RehmanNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Secure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeFrom EverandSecure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (16)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)