Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manual VSC
Uploaded by
Kaushik ChakrabortyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manual VSC
Uploaded by
Kaushik ChakrabortyCopyright:
Available Formats
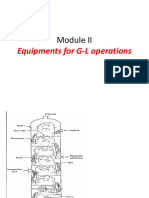
MANUAL FOR VSC PUMP
Instructions on Installations, Operation and Maintenance of Horizontal Two Stage Split Casing Centrifugal Pump
Manufactured By :
Varat Pump & Machinery Pvt. Ltd.
20, Netaji Subhas Road, Kolkata 700001 West Bengal, INDIA Ph. No.: 033-2230 1903, 2243 4500 FAX No.: 033-2230 1535/6274 E-Mail : Varat@cal2.vsnl.net.in
DOC. NO. : VP-MM-010A/0
Page 1 of 14
1.0 1.1
GENERAL This book let covers instructions for following Models of VARAT Horizontal Centrifugal Axial Split Casing Pump Model: 80VSC-76 100VSC-76 100VSC 16
1.2 1.3 2.0 2.1
When the pumps are received sometime before the use of the pump it should be located in dry place. The coupling should be rotated once in a month to prevent pilling of bearing surfaces. When the pumps kept idle for a period after one use, it should be cleaned properly and overhauling should be made before long storage. INSTALLATION LOCATION The pump should be located as near the liquid source as possible. This will minimize the suction lift and pump will give better performance. Ample space should be provided on all the sides so that the pump can be inspected while in operation and can be serviced conveniently whenever required.
2.2
FOUNDATION The foundation should be sufficiently substantial to absorb any vibration and to form a permanent rigid support for the base plate. This is important in maintaining the alignment of a direct connected unit. A concrete foundation on a solid base is advisable. Foundation bolts of the proper size should be embedded in the concrete located by a drawing or template. A pipe sleeve about two and one-half diameter larger than the bolt should be used to allow movement for the final position of the foundation bolts.
2.3
ALIGNMENT Pumps and drivers that are supplied by the manufacturers, mounted on a common base frame are accurately aligned before despatch. All base frames are flexible to some extent and alignments are likely to be disturbed during transit to some extent and therefore must not be relied upon to maintain the factory alignment. Re-alignment is necessary after the complete unit has been leveled on the foundation and again after the grout has set and foundation bolts have been tightened. The alignment must be checked after the unit is piped up and re-checked periodically.
2.4
LEVELLING When the unit is received with the pump and driver mounted on the base plate, it should be placed on the foundation and the coupling halves disconnected. The coupling should not be reconnected until all alignment operations have been completed. The base plate must be supported evenly and placed closed to the foundation bolt. In each case, the supports should directly under the part base plate carrying the greatest weight and spaced closely enough to give uniform support. A gap of about 25 to 50 mm should be allowed between the base plate and foundation of grouting. Supporting will be such that it will not be distorted or sprung by the uneven distribution of the weight. Adjust the wedges until the shafts of the pump and driver are in level. Check the coupling faces, suction and discharge flanges for the horizontal or vertical position by means of spirit level.
Page 2 of 14
2.5
FLEXIBLE COUPLING A flexible coupling will not compensate for misalignment of the pump and driver shafts. The purpose of the flexible coupling is to compensate for temperature changes and to permit the movement of the shafts without interference with each other while transmitting power from the driver to the pump.
2.6
MISALIGNMENT There are two types of misalignment between the Pump shaft and the driver shaft: (a) Angular misalignment: Shafts with axis concentric but not parallel. (b) Parallel misalignment: Shafts with axis Parallel but not concentric.
The unit can then be grouted by soft concrete under the edges. DIAL GAUGE ALIGNMENT An approved method for putting the coupling halves in final accurate alignment is by the use of a dial indicator. Check the alignment by straight edge and fillers as accurately as possible as described below. Fasten the indicator to the pump half of the coupling with the indicator button resting on the other half of the coupling periphery (FIG 3). Set the dial to the 0 and chalk mark the coupling half beside where the bottom rests. For any check, top or bottom or sides, rotate both shafts by the same amount i.e. all readings on the dial must be made with bottom beside the chalk mark. The dials reading will indicate whether the driver has to be raised or lowered or moved to either side. Accurate alignment of shaft center can be obtained with this method.
Page 3 of 14
2.7
GROUTING When the alignment is correct, the foundation bolts should be tightened evenly but not too firmly. Working soft concrete under the edges can then grout the unit. Foundation bolts should not be fully tightened until the grout is hardened, usually 48 hours after pouring.
2.8
PIPING Both suction and delivery pipes and accessories should be independently supported near the pump so that when the flange bolts are tightened no strain will be transmitted to the pump casing. It is usually advisable to increase the size of both suction and delivery pipes at the pump nozzles in order to decrease the loss of head from friction and for the same reason piping should be arranged with as minimum bends as possible, as these should be made with a long radius wherever possible. The pipe lines should be free from scales, welding residuals etc., and have to be mounted in such way that they can be connected to suction and delivery flanges without any stress on the pump. Adequate supports should be given to pipe lines so that the weight of the pipelines does not fall on the pump. The use of minimum number of the bends and other fittings will minimize the friction losses.
2.9
SUCTION PIPE The suction pipe should be as short as possible. This can be achieved by placing the pump close to the liquid to be pumped. The suction pipe must be kept free from air leaks. This is particularly important when the suction lift is high. A horizontal suction line must have a gradual rise towards. To the pump. Any high point in the pipe will be filled with air and thus prevent proper operative of the pump. A concentric taper piece should not be used in a horizontal suction line as it forms an air pocket in the top of the reducer and the pipe. Use an eccentric per piece (FIG. NO.- 4). The end of the suction pipe must be well submerged to avoid whirlpools and ingress of air but must be kept clear of any deposits of mud, silt grit etc. The pipe must be clear from any side of wall by at least 450mm. The end of the suction pipe should be provided with a strainer of sufficient open area.
Page 4 of 14
2.10
DELIVERY PIPE A check (non-return) valve and a gate or sluice valve-regulating valve) should be installed in the discharge line. The check valve placed between the pump and the gate valve is to protect the pump from excessive pressure and to prevent water running back through the pump in case of failure of the driving machine i.e.-excessive backpressure. Discharge piping should be provided with a sluice valve to control the discharge, if required. The valve is used in primary, starting and when shutting down the pumps. If increases are used on the discharge side to increase the size of discharge piping they should be placed between the check valve and pump.
2.11
VACCUM EQUALIZING LINE (AND LIQUID LINE) If the pump draws from system under vacuum a equalizing pipe must be carried from the highest point of the suction line, however, as close to the suction flange of the pump as Possible, to the top of the feed tank to keep gas bubbles that might have been entrapped in the flow from entering the pump. The line should be fitted with an isolating valve, which should be closed only for maintenance work on the pump set. Apply sealing liquid (external sealing) to the shaft seal cage to prevent entry of air in the case of pumps with packed stuffing box. It is convenient to tap the sealing liquid from the delivery line above the non-return valve. Arrangement explained in FIG. NO.-5.
2.12
FOOT VALVE It is advisable to install a foot valve to facilitate priming of pump. Foot valve should have sufficient clear passage for water. Care must be taken to prevent foreign matter from being drawn into the pump or choking the foot valve and for this purpose an efficient strainer should be provided.
2.13
STUFFING BOXES AND PACKING Stuffing boxes should be carefully cleaned and the packing placed in them. Be sure that sufficient packing is placed at the back of the water seal cage. If the water to be pumped is dirty or gritty, sealing water should be piped to the stuffing boxes from clean outside source of supply in order to
Page 5 of 14
prevent damage to the packing and shaft. In placing the packing, each packing ring should be cut to the proper length so that ends come together but do not overlap. The succeeding rings of packing should be placed in the Stuffing Box so that the joints of the several rings of packing are staggered and cutting the shaft. If the stuffing box is not properly packed, friction in stuffing box prevents turning the rotor by hand. On starting the pump, Stuffing Box Packing should be left slightly loose without causing an air leak, and if it seems to leak instead of putting too much pressure on the gland, put some heavy oil in the stuffing box until the pump works properly and then gradually tighten up the gland. The packing should be occasionally changed. MECHANICAL SEAL (APPLICABLE FOR BALANCE SEAL) Since mechanical seals are made in a wide variety of designs, the instruction for the specific seal must be carefully studied and followed exactly. A Mechanical Seal is a precision device and must be treated accordingly. If any leakage is found, observe carefully whether it is found :1) Between shaft & sleeve or 2) Between stuffing box flange and sleeve or 3) Between stuffing box and seal cover For clause no.1 O ring between shaft and sleeve are to be replaced. For clause no.2 if adequate leakage from the sleeve surface is found then after inspection of the seal face damage, compression of the seal is to be increased. Unscrewing 4 nos. align screws for holding rotary part on the sleeve, you have to slide the seal rotary part towards the stationary part and tightening the 4 nos. align screw can do this. You have to keep the compression of the seal about 3 to 4 mm. If the leakage is little then it is normally through the `O Ring provided inside the rotary seal. The ring may be required to be replaced. For clause no.3 tighten the 4 nos. gland nut (No. 29), if any further leakage found then seal cover O ring/gasket (No.21) is to be replaced. 2.14 LUBRICATION Pump is usually provided with grease cap. Initially fill up grease at grease cap provided at bearing bracket. 2.15 BALL BEARING Correct maintenance of ball bearings is essential. The bearing manufacturers give the following as guide to relubrication periods under normal conditions. Quarterly when on continuous duty. Half yearly when on eight-hour per day duty. The bearings and housings should be completely cleaned and recharged with fresh oil after 2500 hours or the nearest pump overhaul time. 2.16 PRIMING No pumping action occurs unless the pump casing is filled with liquid. Pump casing and suction pipe must therefore be completely filled with the liquid and thus all air removed before the pump is started. Several different priming methods can be used depending on the kind of installation and service involved. (1) Liquid level above pump level. Pump is set below liquid level of source of supply so that liquid always flows to pump under positive head. Priming with Foot Valve.
(2)
Page 6 of 14
When pump is installed on suction lift with foot valve at the end of suction line, fill pump with water from some outside source till all air is expelled and water flows through air vent. (b) When there is liquid under some pressure in the discharge pipe, priming can be effected by bypassing the pressure liquid around the check and gate valve. Of course, the initial priming must be effected from some outside source. NOTE: In this case, the foot valve must be capable of withstanding pump pressure and possible surge. (3) Priming by ejector: An ejector operated by steam, compressed air or water under pressure and connected to air vent on top of casing can be used to remove air from and prime the pump on suction lift installations. Priming by dry vacuum pump: A hand or power pump sucks in all the air from the casing and the suction pipe, and thus primes the system
(a)
(4)
3.0
PREPARATION OF PUMP STARTING:
After the pump and the drive are mounted, the plant should be prepared for starting. The following rules should be observed before starting the pump:
3.1
The pins are pad should be inserted into the coupling not before making sure of the correct rotation of drive motor. In case of the drive rotating in the wrong direction, the connection of two cable conductors supplying the current to the motor should be interchange in case of DOL starting. Check presence of oil in bearings and correct location of water deflector on shafts that ensure flashing, quenching, lubrication in case of mechanical seal as well as if required as per design. Gland packing should be tightly stuffed, but not over tightened. The sealing packing should be tightened to such an amount as to allow the pumping liquid to seek to the outside. Over tightening of sealing packing causes quick wear out of shaft sleeves, increases its friction and lowers the efficiency factor of the whole plant. Check the free rotation of pump rotor, turning it by hand to verify any major obstruction or friction with wearing parts. Check the proper order of suction and pressure pipelines, tightening of flanges, fittings of inlet valve and presence of drain plug, air cock for vent etc. Check the correct direction of rotation of pump and drive. The pump rotor should rotate according to direction of rotation marked on pump. Getting reasonably sure of the proper order of the whole plan and its readiness for operation, the suction pipe should be primed with water / liquid. Arrangement for priming funnel and three ways connection of pressure gauge with air-cock after delivery flange but before delivery sluice valve is required. The pump is being filled up (Primed) until the air-cock produces water jet without air bubbles. Then the primary funnel, air-cock and sluice valve is required to be closed. After all these operation and checking, the pump is ready for starting.
3.2
3.3
3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7
3.8
Page 7 of 14
4.0
4.1
STARTING AND STOPPING OF THE PUMP:
The pump should be loaded gradually, when the drive is engaged. When the prime movers attain full speed, the regulating sluice valve should be smoothly opened. This will avoid overloading of the drive. On the other hand it should be kept in mind that a lengthy operation with completely close sliding valve is likewise to be avoided, since this causes unnecessary heating of the liquid in the pump. By controlling the sliding valve the required flow and head may be obtained. After setting of pressure gauge at required point, check ampere consumption. If found value exceeds required value, pump should be stopped
4.2
4.3
5.0
BEARINGS:
The pump is supplied with anti-friction ball bearings at DE and angular contact ball back to back at NDE (2 nos. Bearing to be provided as per drawing, keeping open side of two bearings outward) and Lock by bearing nut with lock washer as applicable. One thrust collar ring inserted between bearing and shaft edge. Generally SKF/NBC/RHP equivalent bearings are used.
6.0
LUBRICANT:
Bearings are normally grease lubricated. Bearing temperature is permissible to rise 40 degree Centigrade above ambient temperature. Lithium based wheel bearing grease must be used of reputed brand.
7.0
STUFFING BOX:
Stuffing Boxes are extra deep and suitable for balance mechanical seal. Mechanical seal must be over oiled before starting the pump after long time storage.
8.0
GASKET
Compressed asbestos packing gasket for joining of volute casing is used. However, packing gasket suitable to handle corrosive liquid and high temperature fluid is supplied against specific requirements.
9.0
COUPLING
Normally pin bush type flexible coupling is used. Other type of coupling may be supplied against specific requirements.
10.0
GUIDE RING / WEARING RING
Replaceable throat bush as guide ring and ring to protect the both side of impeller provided at casing in VSC type pumps.
Page 8 of 14
11.0
SHAFT SLEEVES
Replaceable sleeve for protecting the shaft for gland packed pump and for balance seal, step down sleeve is being provided.
12.0
SPARE PARTS
One set Anti-friction bearing, Wearing Ring, Shaft Sleeve, Gland Packing, Casing Gasket must always be kept with the actual users of the pump to ensure uninterrupted service from the pump.
Page 9 of 14
13.0
SL. NO. 1. DEFECTS Pump does not deliver liquid.
TROUBLE SHOOTING
CAUSES (1)Insufficient quantity of water/water not filled in pump casing (2) Incorrect direction of rotation. (3) Pump is clogged. REMEDY (1) Fill up pump casing with clear water or liquid to be pumped. (2) Change the direction of rotation of prime mover. (3) Check up Impeller may clog. Clean Suction pipe and Strainer. (4) Check up speed of prime mover and adjust. (5) Reduce Suc. Lift. (6) Prevent leakage in suc. Pipe. (7) Correctly install the Suc. Line. (8) Check up the opening of line valve. (9) Replace Shaft-Sleeve & Gland Packings. (10) Liquid viscosity to be checked & corrected. (11) Replace the pump with a suitable designed capacity. (1) Check up speed of prime mover and adjust. (2) Prevent leakage in suction pipe and fittings. (3) Check up vertical head and frictional losses. (4) Fill up the pump casing. (5) Check up rubber Flap assembly & leakage from pump casing. (6) Replace the shaft Sleeve/Gland Packing. (7) Measure the clearance between Impeller and Wearing Plate and adjust by using proper Packing. (8) Avoid High Suction lift and Suction piping.
(4) Pump speed too low. (5) Suc. Lift too high. (6) Leakage in Suc. Pipe. (7) Incorrect layout of Suc. Line. (8)Valve in Suc. Line not open properly. (9) Shaft Sleeve & Gland packing worn and air leaks. (10) Delivery liquid too viscous. (11) Incorrect selection of pump for operating condition. (1) Speed too low. (2) Leakage in Suction side fitting and piping (3) Discharge Head too high. (4) Pump Casing empty. (5) Rubber Flap Valve clogged. (6) Shaft Sleeve/Gland packing worn and air leaks. (7) More clearance between Impeller and Wearing Plate.
2.
Flow not adequate.
(8) Suction lift too high or suction pipe too long.
Page 10 of 14
SL. NO. 3.
DEFECTS Pump takes more Power.
CAUSES 1) Speed too high. (2) Head less than rating. (3) Shaft Bent (4) Miss-alignment of the set. (1) Prime mover not running at rated speed. (2) Leakage through Gland Packing. (3) Too much clearance between Impeller and Wearing plate.
REMEDY (1) Check and correct the speed. (2) Provide minimum head. (3) Check and replace the Shaft. (4) Correct the alignment. (1) Check the speed of Prime mover and correct it. (2) Replace Gland Packing. (3) Measure the clearance between Impeller and Wearing plate and adjust by using proper packings. (1) Fill up the pump casing.
4.
Rated pressure not developed.
5.
Pump vibrates and makes more noise.
(1) Pump casing not filled with Water/Liquid (it is only possible only during priming time). (2) Suction lift too high. (3) Miss- alignment (4) Foundation not rigid (5) Shaft bent (6) Bearing Worn out (7) Lack of Lubrication (8) Pump operating at very low capacity. (1) Miss- alignment (2) Shaft bent (3) Excessive Grease or lack of grease. (4) Dirty water getting into Bearings.
(2) Reduce the suction lift or install the Foot valve. (3) Correct the alignment. (4) Check up the foundation bolt. (5) Replace the shaft (6) Check & replace Bearing. (7) Lubricate the Bearings. (8) Reduce total head. (1) Correct the alignment. (2) Check the shaft condition. (3) Check up lubrication. (4) Protect bearing neatly.
6.
Bearings have short life.
Page 11 of 14
14.0 MAINTENANCE
Preventative maintenance schedule are the periodical checks and precautions by which possibilities of failures and breakdowns are made very remote. 14.1 Daily Checks 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 14.2 Pressure gauge reading Bearing temperature Leakage through stuffing box Noise and vibration Voltage and current Constant flow of cooling water.
Periodical Maintenance 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Replace the grease for bearing lubrication Change the stuffing box packing. Check the alignment of the pump set Calibrate the measuring instruments Check the sealing and cooling connections etc.
15.0 OVERHAULING
Normally the pump will be due for overhauling after about 3000 working hours. Pump dismantling and assembling should be done by skilled personal. Special attention should be given to continuous running pumps & advice is to keep stand by pump for emergency services. 15.1 1. 2. DISMANTLING OF PUMP: Remove pressure gauge, grease pot, seal flash/gland cooling pipe, and other fittings. The Design advantage of this VSC pumps is dismantling the pump for over oiling without removing the suction & delivery flange connection can be done. If pin bush type coupling is provided than remove pin-bush bolt by unscrewing it and remove pr. Gauge ,auxiliary fittings if fitted with the pump Remove bolt (no 27) and dowel pin provided to fixed up of bearing bracket of both side and pull out the gland flange(no 28) after unscrewing the gland nut from both side so that it released from the gland stud (no 29). now remove dowel pin and bolts used to fixed up upper and lower casing. After removal of the bolt use forcing thread bolt provided on upper casing. Start to tightening 4 nos. forcing bolt gradually when upper half casing will be retouched from the lower half casing. Lift the upper half straight vertically with the help of chain pulley. After removal of upper half the total dynamic assembly is visible to you. Remove all the gland packing and split lantern ring. Now lift out the shaft assembly fitted with impellers, wearing rings, gland flange (if not split) and bearing housing . In case of mechanical seal pump special are should be taken to protect face of seal during handling.
3.
4.
5.
Page 12 of 14
Page 13 of 14
6.
Now to dismantle the dynamic components, you have to pull out the bearing housing along with bearing from driving end, remove the cod screw provided at coupling and take out pump coupling half. Detach both sides bearing cover of the housing by unscrewing bolt. Take out bearing from housing by hammering gently with a socket on the centre rotary ring of the bearing. Take out water deflector, gland flange, lantern ring, mechanical seal (if applicable unscrew 4 nos. cod screw provided to hold in directly on shaft. In case of balance seal will be provided on a sleeve which you find screwed up with the shaft) and wearing ring. To remove component from the non driving end you have to follow the same method but after removal of bearing end cover you will find a bearing lock nut and washer. Unlock the clip of the lock washer and than unscrew the lock nut. After removal of components rest of parts are 2 nos impeller with sleeve and sleeve double (for balance seal impeller lock nut and washer). For gland packing (for balance seal unfold the tongue of both side lock washer) remove impeller / sleeve lock nuts by unscrewing it from both side. Pull out the pump impeller from either side and take out impeller distance piece. Remove bearing lock nut before removal of the bearing from the shaft. Pull out bearings from the shaft from both ends. If self align Bearing at NDE is After removal of all above pump parts it is necessary to check up properly for any wear and tear and if any parts are found to be worn out, the same should be replaced or rectified. Wearing rings (Item no. 05) & guide bush (Item no.20) if required to be replaced. REASSEMBLING OF PUMP : Before reassembling all parts are to be cleared and it is advised to paint all the parts which are without machined faces. Paints should be dry before reassembling. Bearings are to be cleaned with petrol. All machined faces should be rubbed with Mobil-oil.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
15.2
1.
Assembly of pump starts with Fitting of dynamic assembly which includes fitment of impeller, sleeve, bearing and bearing housing with shaft. First fixed up the impeller key and insert impeller from both side of shaft keeping impeller distance piece in the center between the two impellers. Dont forget to take care about direction of rotation of impeller. After fixed of impeller Insert sleeve from both side and than sleeve nuts. Some of pumps are designs with threaded sleeve. (for balance Mech. Seal, insert impeller lock nut with washer ) than tighten the nuts from both side (not full tight ,final adjustment may be done latter on after fixed up bearing housing. Next provide throat bush for stuffing box, lantern ring, (mechanical seal with sleeve for balance seal), gland flange (dont forget to place gasket of gland flange for mech. Seal) , and water thrower one by one. Like wise same items are also to be inserted from driving end. For mechanical seal pump, seal cover is to be fitted with stationary part of the seal by hand press fit providing O ring for it.
2.
Now press fit 2 nos. angular contacts bearing back to back with the NDE bearing housing fixed up inside bearing cover (2 nos. Bearing to be provided as per drawing, keeping open side of two bearings outward) .similarly insert one no. ball bearing inside D.E. bearing housing and provide inside bearing cover.
Page 14 of 14
3.
Now insert NDE bearing housing fitted with bearing through shaft after providing thrust collar ring and tighten by bearing nut with lock washer and lock it. Other DE bearing housing as fitted with bearing to with a approximation of its position, keeping it little bit away from its position on the shaft. Now after lifting the total assembly, you have to put it on the lower half of pump casing, keeping bushes and wearing ring right in position, care should be taken about right position of lock pin /lock collar of wearing ring and guide bushes. First tighten the NDE bearing housing after providing both side bearing housing align with dowel pin between housing and lower casing. After full tightening of NDE bearing housing, provide the bearing end cover with 3 nos. bolt provided for it. Next tighten the DE bearing housing and fixed up front bearing cover with bolt. If pump is with mechanical seal, keep gland flange fitted with stationary face pressed by hand with casing face and bring the rotary seal face with sleeve so that it touches with the stationary face, remove gland flange and allow rotary seal assembly (fitted with sleeve for balance seal) to move towards flange 3 to 4 mm (or as recommended by seal manufacturer) and tighten the screw provided at rotary part of seal ( for balance seal screw of the sleeve fitted with rotary part). Now your lower part assembly is ready to fixed up with your upper casing. Check the clean surface of the both half casing before placement of upper half on lower half casing. Replace casing gasket and care should be taken regarding edges of gasket especially for mechanical seal where gland flange face touched with casing. Now check up the about dynamic assembly by rotate with hand weather it touches with casing or not. If your centerline of impeller does not coincides with casing centre line than you can axially move both of impeller together by fighting and loosing both side impeller lock nut or double sleeve lock nut as applicable. After aligning of rotor assembly lift the upper half of casing and fixed up on lower casing keeping line with dowel pin and tighten 4 nos. pillar bolt and than all the casing bolt cross wise one by one. Put coupling key at shaft, fit pump half coupling and tighten the coupling grub screw.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Provide two nos. packing than place lantern ring and again three nos. packing for gland pack pump. Now provide split gland flange. For mechanical seal pump, before fixed up of seal cover along with the stationary seal, place gasket /O ring carefully. Tighten gland nut cross wise but not too hard. Similarly fixed up other side stuffing box component. Now the assembly is ready to fit with volute casing providing one recommended ring gasket. Fit all grease pot, seal / gland flash pipe, pressure gauge and other fittings. This completes the reassembling.
8.
You might also like
- Bosch Rexroth VPV and SV Variable Volume Vane Pumps: Installation ManualDocument2 pagesBosch Rexroth VPV and SV Variable Volume Vane Pumps: Installation ManualEng-Mohammed SalemNo ratings yet
- O&M Manual For Vms PumpDocument11 pagesO&M Manual For Vms PumpKaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Iom Manual 250 Series Centrifugal Pump: M15794, Rev 0Document17 pagesIom Manual 250 Series Centrifugal Pump: M15794, Rev 0hebert perez50% (2)
- Plunger Pump ManualDocument23 pagesPlunger Pump Manualgovindharajalu75% (4)
- Hankison MD25 Thru MD75 IM 7-6-09Document16 pagesHankison MD25 Thru MD75 IM 7-6-09aNo ratings yet
- Lube Oil System and JOP SOP - Docx-1Document38 pagesLube Oil System and JOP SOP - Docx-1SonratNo ratings yet
- TF500 22a - PV3 300 16Document6 pagesTF500 22a - PV3 300 16Jimmy HaddadNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual VCP Upto 80mmDocument16 pagesMaintenance Manual VCP Upto 80mmKaushik Chakraborty0% (1)
- VWS Pump Manual (Varat Pump & Machinery Pvt. LTD.)Document20 pagesVWS Pump Manual (Varat Pump & Machinery Pvt. LTD.)Kaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Kirloskar Pump InstallationDocument34 pagesKirloskar Pump Installationmksingh_22No ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump Halco 2500 ManualDocument16 pagesCentrifugal Pump Halco 2500 ManualMohammad Mehdi50% (2)
- Magnum 1 2500Document16 pagesMagnum 1 2500adrianram1100% (1)
- Industrial and General Purpose: Owners ManualDocument22 pagesIndustrial and General Purpose: Owners ManualoscarpabaNo ratings yet
- 600ws Plunger OmegaDocument37 pages600ws Plunger Omegaariel feNo ratings yet
- Omega 600S ManualDocument36 pagesOmega 600S ManualLeandroNo ratings yet
- Omega 600S Manual PDFDocument36 pagesOmega 600S Manual PDFjosebernal_mzaNo ratings yet
- Manual: STD: Is-5120: Series: VCPDocument21 pagesManual: STD: Is-5120: Series: VCPKaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Instruction For Installation Guidelines Vertical Turbine PumpDocument27 pagesInstruction For Installation Guidelines Vertical Turbine PumpReagan FlemingNo ratings yet
- Pump Installation and Operations: Should Include Valves On Both Suction and Discharge Lines. They Should BeDocument5 pagesPump Installation and Operations: Should Include Valves On Both Suction and Discharge Lines. They Should BeBurhoneySonNo ratings yet
- Dragon 178 Series Pumps: Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions For 1-800-231-8198Document16 pagesDragon 178 Series Pumps: Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions For 1-800-231-8198jesus alfonso fragozo calderonNo ratings yet
- 42 80 - 4280 Motor Mounted Pump - IOI PDFDocument4 pages42 80 - 4280 Motor Mounted Pump - IOI PDFLokesh ModemzNo ratings yet
- Vertical Turbine Firefighting Pump InstallationDocument4 pagesVertical Turbine Firefighting Pump InstallationWahid HusainNo ratings yet
- Installation and Service Instructions: Excellence at Work. Excellence in LifeDocument15 pagesInstallation and Service Instructions: Excellence at Work. Excellence in LifeHerman JonesNo ratings yet
- Installation AND Operation Manual: PremierDocument23 pagesInstallation AND Operation Manual: Premieralejandro jimenezNo ratings yet
- VO Model O & M ManualDocument17 pagesVO Model O & M ManualJigyesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- PIPING GUIDE How To Do Pump Piping With Layout Ex - 1579767576697 PDFDocument17 pagesPIPING GUIDE How To Do Pump Piping With Layout Ex - 1579767576697 PDFGiridhar Parab100% (1)
- Elgin Centrifugal Pump Manual - 052018Document37 pagesElgin Centrifugal Pump Manual - 052018Andrew GoadNo ratings yet
- Pump Installation, Operation and MaintenanceDocument25 pagesPump Installation, Operation and Maintenancebayu kusumaNo ratings yet
- Dosing PumpDocument10 pagesDosing PumpniceseshaNo ratings yet
- Manual Bomba LT HyosungDocument25 pagesManual Bomba LT HyosungEliecerNo ratings yet
- Commercial Pumps: Installation and Operating InstructionsDocument8 pagesCommercial Pumps: Installation and Operating InstructionsrakeshamechNo ratings yet
- E, F & G Series Centrifugals: Installation InstructionsDocument8 pagesE, F & G Series Centrifugals: Installation InstructionsjhonNo ratings yet
- How To Do Pump Piping With Layout ExplainedDocument13 pagesHow To Do Pump Piping With Layout Explainedvenkat100% (1)
- CVP Model ManualDocument28 pagesCVP Model ManualpolsiemprealdoNo ratings yet
- Tuthill - C Series Service ManualDocument22 pagesTuthill - C Series Service ManualbenkaouhaNo ratings yet
- Manual 1008-1010Document12 pagesManual 1008-1010Edgar Eduardo Tellez RuizNo ratings yet
- Multistage Centrifugal Pumps: Vertical Inline ModelsDocument16 pagesMultistage Centrifugal Pumps: Vertical Inline ModelsBang MatNo ratings yet
- Major Factors Affecting The Pump PerformanceDocument6 pagesMajor Factors Affecting The Pump PerformancesandystaysNo ratings yet
- PDF 44201222333PMKPDSDocument63 pagesPDF 44201222333PMKPDSAnbarasan NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Ar ManualDocument43 pagesAr ManualParamasivan. SNo ratings yet
- Install and Operation Manual B&S Pump BSM PumpDocument7 pagesInstall and Operation Manual B&S Pump BSM Pumppr_oilNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Vertical Pump Installation and MaintenanceDocument6 pagesStainless Steel Vertical Pump Installation and Maintenancejoshua gomezNo ratings yet
- 卧式离心泵说明书英文(大连双龙)Document16 pages卧式离心泵说明书英文(大连双龙)kamal arabNo ratings yet
- Piping Connection ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesPiping Connection ConsiderationsGrundfosEgyptNo ratings yet
- Berkeley Ownwes ManualDocument28 pagesBerkeley Ownwes ManualMoses Alvarado100% (1)
- Multiflo W: Horizontal Multistage PumpsDocument14 pagesMultiflo W: Horizontal Multistage Pumpsbayu enasoraNo ratings yet
- Single Line Installation and System Startup/trouble Shooting Bulletin SL-300Document4 pagesSingle Line Installation and System Startup/trouble Shooting Bulletin SL-300Torres Toledo JttNo ratings yet
- Condensate Extraction Pump: GeneralDocument5 pagesCondensate Extraction Pump: GeneralAnonymous DKv8vpNo ratings yet
- Low Pressure Pumps: Installation and Start-Up InstructionDocument12 pagesLow Pressure Pumps: Installation and Start-Up InstructionsmithworkNo ratings yet
- Instructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenanace For Sam Turbo Pump TypeDocument38 pagesInstructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenanace For Sam Turbo Pump Typevikash kumarNo ratings yet
- Pipe StrainDocument5 pagesPipe StrainJack WeaverNo ratings yet
- Liquid Ring Vacuum Pumps Intial Start Up ProceduresDocument3 pagesLiquid Ring Vacuum Pumps Intial Start Up ProceduresFA Ay100% (1)
- Le 26SDocument4 pagesLe 26Skrisu92No ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument14 pagesOperation and Maintenance ManualmehtahemalNo ratings yet
- Polder Pumps ManualDocument7 pagesPolder Pumps ManualHiren PatelNo ratings yet
- Type Mha & Mla: Instructions On Installation Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar PumpDocument30 pagesType Mha & Mla: Instructions On Installation Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar Pumparunpsts100% (1)
- D SeriesDocument20 pagesD SeriesJorge A VilalNo ratings yet
- Installation and OperationDocument9 pagesInstallation and Operationabdullatif_asNo ratings yet
- Series 4030: Base Mounted Pump Installation and Operating InstructionsDocument8 pagesSeries 4030: Base Mounted Pump Installation and Operating InstructionsrakeshamechNo ratings yet
- Correct Pump InstallationDocument6 pagesCorrect Pump InstallationEry GatotNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax: Group 3Document16 pagesGoods and Services Tax: Group 3Kaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Volkswagen Firing Without HiringDocument32 pagesVolkswagen Firing Without HiringKaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Asian Paints Case PresentationDocument3 pagesAsian Paints Case PresentationKaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Wallet Usage in IndiaDocument20 pagesMobile Wallet Usage in IndiaKaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis of Thomas GreenDocument6 pagesCase Analysis of Thomas GreenKaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- 11Document9 pages11Kaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump AssemblyDocument1 pageCentrifugal Pump AssemblyKaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Varat Pump and Machinery Pvt. Ltd.Document59 pagesVarat Pump and Machinery Pvt. Ltd.Kaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Manual: STD: Is-5120: Series: VCPDocument21 pagesManual: STD: Is-5120: Series: VCPKaushik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Calculating Pump HeadDocument6 pagesCalculating Pump HeadAshok Kumar PillaiNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Door Open-Close SystemDocument6 pagesPneumatic Door Open-Close Systemalex58% (12)
- Performance Improvement of Venturi Wet Scrubber: April 2015Document10 pagesPerformance Improvement of Venturi Wet Scrubber: April 2015Ahmad Anas Nagoor GunnyNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer EquipmentsDocument46 pagesMass Transfer EquipmentsVish VishwasNo ratings yet
- Booklet Ninnelt EnglishDocument16 pagesBooklet Ninnelt EnglishharoonshaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:components of Pneumatic Component Unit 1:the Air Service Unit ComponentDocument5 pagesChapter 2:components of Pneumatic Component Unit 1:the Air Service Unit ComponentEdrian Rey Tablante BrizoNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Cheat Sheet:: Pumps, Useful Work Turbines, Effective WorkDocument2 pagesExam 2 Cheat Sheet:: Pumps, Useful Work Turbines, Effective WorkShyam PolacondaNo ratings yet
- Boiler FixtureDocument10 pagesBoiler FixtureMohd ZafreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Fluids Kinematics: Velocity and Description MethodsDocument21 pagesChapter 4: Fluids Kinematics: Velocity and Description MethodsADIL BAHNo ratings yet
- Molar Volume of Gas: Section 4.3 Pg. 169-171Document9 pagesMolar Volume of Gas: Section 4.3 Pg. 169-171SSudhakarNo ratings yet
- 04 DST ConceptsDocument29 pages04 DST ConceptsH-sam A-somethingNo ratings yet
- Gastite Sizing ChartsDocument28 pagesGastite Sizing ChartsSlwRdrNo ratings yet
- 42NH Ductable in Room Fan Coil With Multi Speed Motor: Performance Summary For Soba Za IgruDocument2 pages42NH Ductable in Room Fan Coil With Multi Speed Motor: Performance Summary For Soba Za Igruvelikimag87No ratings yet
- Basic Anesthesia Machine ChecklistDocument1 pageBasic Anesthesia Machine ChecklistMark Colos CruzNo ratings yet
- Mersen Process Technologies ProviderDocument6 pagesMersen Process Technologies ProviderIbhar Santos MumentheyNo ratings yet
- PE and PD-section 1-4 RobertoDocument26 pagesPE and PD-section 1-4 RobertoJayvee FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Vessel Geometry Considerations For Bottom-Mount Magnetically Driven Agitators in The Biopharmaceutical IndustryDocument4 pagesVessel Geometry Considerations For Bottom-Mount Magnetically Driven Agitators in The Biopharmaceutical Industrysushaantb400No ratings yet
- MPFM Data SheetDocument2 pagesMPFM Data SheetPedro NuñezNo ratings yet
- Scheme Assg1 Fluids Mechanics 1 Bmm2533 Sem 1 2011 2012Document7 pagesScheme Assg1 Fluids Mechanics 1 Bmm2533 Sem 1 2011 2012AsadullahSafiNo ratings yet
- Rev 01 MPD Choke Panel DatasheetDocument2 pagesRev 01 MPD Choke Panel DatasheetCricri CriNo ratings yet
- Peristaltic Pump: Seminar ReportDocument29 pagesPeristaltic Pump: Seminar ReportAmruth SNo ratings yet
- Iso 11114-1 1997Document50 pagesIso 11114-1 1997shah harshitNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids: Ahmad Shoja-Sani, Ehsan Roohi, Mohsen Kahrom, Stefan StefanovDocument16 pagesEuropean Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids: Ahmad Shoja-Sani, Ehsan Roohi, Mohsen Kahrom, Stefan StefanovasdasddasNo ratings yet
- L1 - FPSO IntroductionDocument32 pagesL1 - FPSO IntroductionZulkamal RoseleyNo ratings yet
- Additional TermsDocument3 pagesAdditional TermsJamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Performance Standard Competencies/Skill SDocument5 pagesGas Laws: Performance Standard Competencies/Skill SDENOMINATORNo ratings yet
- API Product SpecificationsDocument2 pagesAPI Product SpecificationsOswaldo Zamorano Manzano100% (1)
- PICV-Fig1932 IOM-Hatts PDFDocument4 pagesPICV-Fig1932 IOM-Hatts PDFSujit RajanNo ratings yet