Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IP10G CeraWeb User Guide Version 6 7 March2011
Uploaded by
Анатолий ПетьковOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IP10G CeraWeb User Guide Version 6 7 March2011
Uploaded by
Анатолий ПетьковCopyright:
Available Formats
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
March 2011
Copyright 2011 by Ceragon Networks Ltd. All rights reserved.
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Notice
This document contains information that is proprietary to Ceragon Networks Ltd. No part of this publication may be reproduced, modified, or distributed without prior written authorization of Ceragon Networks Ltd. This document is provided as is, without warranty of any kind.
Registered TradeMarks
Ceragon Networks is a registered trademark of Ceragon Networks Ltd. FibeAir is a registered trademark of Ceragon Networks Ltd. CeraView is a registered trademark of Ceragon Networks Ltd. Other names mentioned in this publication are owned by their respective holders.
TradeMarks
CeraMap, PolyView, EncryptAir, ConfigAir, CeraMon, EtherAir, and MicroWave Fiber, are trademarks of Ceragon Networks Ltd. Other names mentioned in this publication are owned by their respective holders.
Statement of Conditions
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. Ceragon Networks Ltd. shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damage in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this document or equipment supplied with it.
Open Source Statement
The Product may use open source software, among them O/S software released under the GPL or GPL alike license ("GPL License"). Inasmuch that such software is being used, it is released under the GPL License, accordingly. Some software might have changed. The complete list of the software being used in this product including their respective license and the aforementioned public available changes is accessible on http://ne-open-source.licensesystem.com/.
Information to User
Any changes or modifications of equipment not expressly approved by the manufacturer could void the users authority to operate the equipment and the warranty for such equipment.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 2 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Table of Contents
1. General ................................................................................................................... 7
1.1 1.2 Getting Started ........................................................................................................... 7 Resetting after configuration changes ......................................................................... 7
2. Main View ............................................................................................................... 9 3. Faults ....................................................................................................................10
3.1 3.2 Current Alarms ......................................................................................................... 10 Event Log................................................................................................................. 11
4. PM & Counters .................................................................................................... 12
4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 4.9.1 4.9.2 4.9.3 4.9.4 4.9.5 4.9.6 4.9.7 PM graphs ............................................................................................................... 12 PM Commands ........................................................................................................ 13 RMON (Remote Monitoring) ..................................................................................... 13 TDM Trails ............................................................................................................... 14 Enhanced Traffic Manager ....................................................................................... 15 E1 ............................................................................................................................ 16 DS1 ......................................................................................................................... 17 STM-1/OC-3............................................................................................................. 18 Radio ....................................................................................................................... 19 Signal Level (RSL) ................................................................................................... 19 Aggregate ................................................................................................................ 20 MRMC ..................................................................................................................... 21 MSE ......................................................................................................................... 22 XPI Performance ...................................................................................................... 23 TDM Channels ......................................................................................................... 24 Ethernet ................................................................................................................... 25 4.9.7.1 Frame Error Rate ..................................................................................... 25 4.9.7.2 Throughput ............................................................................................... 26 4.9.7.3 Capacity ................................................................................................... 27 4.9.7.4 Utilization ................................................................................................. 29
5. Configuration....................................................................................................... 31
5.1 General .................................................................................................................... 31 5.1.1 Unit Parameters ....................................................................................................... 31 5.1.2 External Alarms ........................................................................................................ 33 5.1.2.1 Alarm input configuration (up to five independent inputs) .......................... 33 5.1.2.2 Alarm output configuration (single output) ................................................. 33 5.1.3 Management ............................................................................................................ 34 5.1.3.1 IP Configuration........................................................................................ 34 5.1.3.2 Management Ports ................................................................................... 34 5.1.4 Traps Configuration .................................................................................................. 35 5.1.5 Licensing.................................................................................................................. 36 5.1.5.1 Current License ........................................................................................ 36 5.1.5.2 Demo License .......................................................................................... 37
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 3 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.1.5.3 License Features ...................................................................................... 37 5.1.6 NTP ......................................................................................................................... 38 5.1.7 IP Table ................................................................................................................... 39 5.1.8 SNMP ...................................................................................................................... 40 5.1.8.1 SNMP Parameters ................................................................................... 40 5.1.8.2 SNMP V3 User Settings ........................................................................... 40 5.1.9 All ODU .................................................................................................................... 41 5.1.10 Versions ................................................................................................................... 42 5.1.10.1 IDU Versions ............................................................................................ 42 5.1.10.2 RFU Versions ........................................................................................... 42 5.2 5.2.1 5.2.2 5.2.3 5.2.4 Ethernet Switch ........................................................................................................ 43 Switch Configuration ................................................................................................ 43 STP Protocol ............................................................................................................ 46 RSTP and Ring RSTP .............................................................................................. 47 QoS & Rate Limiting ................................................................................................. 48 5.2.4.1 Ingress Classifier ...................................................................................... 49 5.2.4.2 VLAN Pbits Priority Remap ....................................................................... 51 5.2.4.3 Egress Scheduler ..................................................................................... 51 5.2.4.4 Ingress Rate Limiting ................................................................................ 52 5.2.4.5 Advanced Classifier - VLAN-ID to Queue .................................................. 53 5.2.4.6 Advanced Classifier - IP-Pbits to Queue ................................................... 54 5.2.4.7 Advanced Classifier - VLAN-Pbits to Queue ............................................. 54 5.2.4.8 Advanced Classifier Queue Weights ...................................................... 55 5.2.4.9 Advanced Classifier - Policer List .............................................................. 56 5.2.4.10 Advanced Classifier - Static MAC ............................................................. 56 5.2.4.11 Copy Ports Configuration .......................................................................... 57 5.2.5 Enhanced Traffic Manager ....................................................................................... 58 5.2.5.1 Preparing to use Enhanced Traffic Manager ............................................. 58 5.2.5.2 Configuration & Parameters...................................................................... 60 5.2.5.3 Classification Overview .......................................................................... 62 5.2.5.4 Classification Default settings ................................................................ 63 5.2.5.5 Classification First hierarchy .................................................................. 64 5.2.5.6 Classification - Second hierarchy .............................................................. 68 5.2.5.7 Classification - Third hierarchy .................................................................. 68 5.2.5.8 WRED ...................................................................................................... 72 5.2.5.9 Egress Shaper & Scheduler...................................................................... 73 5.3 Radio ....................................................................................................................... 75 5.3.1 Radio Parameters .................................................................................................... 75 5.3.1.1 Status Parameters .................................................................................... 77 5.3.1.2 Frequency Control .................................................................................... 78 5.3.1.3 Configuration Parameters ......................................................................... 78 5.3.1.4 XPIC Parameters ..................................................................................... 79 5.3.1.5 Green Mode ............................................................................................. 79 5.3.1.6 Multi Radio ............................................................................................... 80 5.3.2 Remote Radio .......................................................................................................... 82 5.3.3 Radio Thresholds ..................................................................................................... 83 5.3.4 MRMC Configuration ................................................................................................ 84 5.3.4.1 MRMC Configuration ................................................................................ 84 5.3.4.2 Current TX ............................................................................................... 84 5.3.4.3 Current RX ............................................................................................... 85 5.3.4.4 MRMC Table ............................................................................................ 85 5.3.4.5 MRMC Table ACM Scripts ..................................................................... 86 5.3.5 Traffic Priority ........................................................................................................... 88
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 4 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.3.6 ATPC ....................................................................................................................... 90 5.4 Interfaces ................................................................................................................. 91 5.4.1 Ethernet Ports .......................................................................................................... 91 5.4.1.1 Configuring a specific port ........................................................................ 92 5.4.1.2 Defining a LAG PORT .............................................................................. 94 5.4.1.3 Defining Fault Criteria ............................................................................... 96 5.4.2 E1 Ports ................................................................................................................... 97 5.4.2.1 Configuring the Line Coding ..................................................................... 97 5.4.3 Using an E1/T1 T-Card ............................................................................................ 98 5.4.4 DS1 Ports ................................................................................................................ 98 5.4.5 STM-1/OC-3 (T-Card) .............................................................................................. 98 5.4.6 Wayside Channel ................................................................................................... 101 5.4.7 User Channel ......................................................................................................... 102 5.4.8 EOW ...................................................................................................................... 103 5.4.9 AIS......................................................................................................................... 103 5.4.10 Sync Source........................................................................................................... 104 5.4.11 Clock Source.......................................................................................................... 105 5.5 Protection............................................................................................................... 106 5.5.1 Protection Parameters ............................................................................................ 106 5.5.1.1 Protection Configuration ......................................................................... 107 5.5.1.2 Mate Parameters .................................................................................... 107 5.5.1.3 Protection Switch Criteria ....................................................................... 107 5.5.1.4 Protection Commands ............................................................................ 107 5.5.2 Radio Diversity ....................................................................................................... 108 5.5.2.1 IF Combining Parameters ....................................................................... 108 5.5.2.2 Space Diversity 1+1 Baseband ............................................................... 109 5.6 Trails ...................................................................................................................... 111 5.6.1 Configuring TDM Trails .......................................................................................... 111 5.6.1.1 TDM Trails Configuration Notes .............................................................. 114 5.6.1.2 Connected Ports..................................................................................... 115 5.6.1.3 Cross Connection at the KLM Level ........................................................ 116
6. Service OAM ...................................................................................................... 118
6.1 6.1.1 6.1.2 6.1.3 6.1.4 6.1.5 6.1.6 MAID List ............................................................................................................... 118 MAID List Columns ................................................................................................ 118 MAID List Operations ............................................................................................. 119 MAID List MEPs ..................................................................................................... 119 Local MEP ............................................................................................................. 120 CCM Configuration ................................................................................................. 121 Remote MEP.......................................................................................................... 121 6.1.6.1 Remote MEP Columns ........................................................................... 121 6.1.6.2 Remote MEP ping window ...................................................................... 122 6.1.6.3 Adding a new remote MEP ..................................................................... 122 6.1.7 Linktrace ................................................................................................................ 123 6.2 MEP & MIP List ...................................................................................................... 124 6.2.1.1 Ethernet Port columns ............................................................................ 124 6.2.1.2 Port MEPs columns ................................................................................ 124 6.2.1.3 Port MIPs columns ................................................................................. 124 6.2.2 Add MEP to Port .................................................................................................... 125 6.2.3 Add MIP to Port ...................................................................................................... 125 6.3 Advanced ............................................................................................................... 126
Page 5 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.3.1 Manual Ping ........................................................................................................... 126 6.3.2 Manual Linktrace .................................................................................................... 127
7. Diagnostics & Maintenance .............................................................................128
7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.4.1 7.4.2 7.4.3 7.4.4 7.4.5 7.4.6 7.4.7 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7.9 Radio Loopback ..................................................................................................... 128 PDH Line Loopback ............................................................................................... 129 SDH Loopback ....................................................................................................... 129 Configuration Management .................................................................................... 130 Overview ................................................................................................................ 130 Uploading or downloading an archive ..................................................................... 131 Configuration Backup Management ........................................................................ 131 Archiving unit information ....................................................................................... 132 Configuring the FTP parameters............................................................................. 132 Resetting the configuration ..................................................................................... 133 Viewing the archive status ...................................................................................... 133 Software Management ........................................................................................... 134 RFU Download ....................................................................................................... 135 IDU-RFU Interface Monitoring ................................................................................ 136 Resets ................................................................................................................... 136 File List .................................................................................................................. 137
8. Security ..............................................................................................................138
8.1 8.2 Security Configuration ............................................................................................ 138 Users & Groups ..................................................................................................... 139
9. Appendix A FibeAir IP-10 Alarms Table ......................................................141
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 6 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
1.
General
This guide explains how to work with the FibeAir IP-10 Web Based Management. IP-10 management is used to perform configuration operations and obtain statistical and performance information related to the system. For full functionality and feature availability, upgrade the IDU to the latest released software version. You can obtain the latest software version and release notes at Ceragons FTP site. For access to the site, contact support@ceragon.com.
1.1
Getting Started
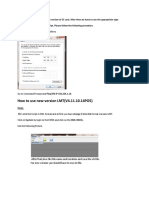
To start the web based management application: 1 Start your web browser. 2 In the URL address field at the top, type http://yourIP, and press Enter, whereby yourIP is the IP address of your FibeAir unit. The Login window is displayed.
3 Enter your user name and password, and click Apply. The Main View window appears:
Configuration and other operations are performed by clicking the menus on the left side of the page.
1.2
Resetting after configuration changes
Some changes that are made to the IP-10 configuration cannot be enabled until the IDUs are reset. The IDU reset process generally takes several minutes to complete. You can make all of the required changes to the IDU configuration
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 7 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
and then reset the IDU. This single reset executes all of the configurations that were changed. The following list contains some of the configuration changes that require resetting the IDU: Updating or changing the license. Configuring the MRMC table (modem script). Changing the Ethernet application type. (From Single pipe to Managed or Metro switch.)
After performing one of these configuration changes, the warning icon is displayed next to the field to indicate that the IDU must be reset. The following figure shows the Switch Configuration window after the Single pipe Ethernet application type has been selected.
For more information about resetting the IDU, see Resets on page 136.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 8 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
2.
Main View
The Main view window displays the IDUs that are in the shelf.
You can click on one of the IDUs to make that slot active. Click on a port. The configuration window for that port is displayed. Click Refresh to update the window.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 9 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
3.
3.1
Faults
Current Alarms
Select the Current Alarms item to view a list of alarms that are active in the system. For a full list of all of the IP-10 alarms, see Appendix A FibeAir IP-10 Alarms Table on page 141.
Each line on the page displays a different alarm. Click an alarm in the list to view Probable Cause and Corrective Action information for that alarm. The following list is an explanation of the columns in the Current Alarms section. Date & Time - The date and time the alarm was triggered appear in the column. Severity - The color of the icon indicates the severity of the alarm.
Module - The module that generated the alarm. Description - A description of the alarm.
Probable Cause The most likely cause of the alarm. Corrective Actions The recommended action(s) to take to resolve the cause of the alarm.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 10 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
To send the alarm list to the printer, from the Internet Browser menu bar select File > Print. To update the list, click Refresh.
3.2
Event Log
The event log is a list of historical events and alarm information.
The Event Log displays the last 200 events and alarms that occurred. If the number of events/alarms exceeds 200, the oldest events/alarms will be removed. The following list is an explanation of the columns in the Event Log window. # - Number of the event/alarm. Date & Time - The date and time the event/alarm was triggered. Severity - The color of the icon indicates the severity.
Module - The module that generated the event/alarm. State - The event/alarm status (Raised, Cleared). Description - A description of the event/alarm.
To clear the Event Log, click Clear. To update the Event Log, click Refresh. To print the Event Log, from the Internet Browser menu bar select File > Print.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 11 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.
4.1
PM & Counters
PM graphs
Many of the PM (Performance Monitoring) windows contain an option to display the PM data is a graph. To display the PM graph: From the top of the PM window, click . The PM graph is displayed.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 12 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.2
PM Commands
The Performance Monitoring commands window enables you to clear all performance monitoring measurements in the unit, except for RMON.
4.3
RMON (Remote Monitoring)
The RMON counters display values relating to the bridge performance. The counters are designed to support: RFC 2819, RMON MIB RFC 2665, Ethernet-like MIB RFC 2233, MIB II RFC 1493, Bridge MIB
The statistic counters are divided into ingress statistics and egress statistics.
To reset a counter, click Clear at the top of the column. To reset all counters, click Clear All.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 13 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
To update the list, click Refresh. To print the list, from the Internet Browser menu bar select File > Print.
4.4
TDM Trails
End-to-end PM measurements are taken for TDM trails. This PM is based on BER measurement, and not on code violation, which distinguishes it from line interface PMs. The measurements are the same as those for line interfaces (ES, SES, UAS, BBE), but are based on BER measurements. PM for trails is measured in the following cases, and is maintained in the relevant IDUs: End point interfaces: trail end line interfaces Radio interfaces that perform SNCP If TDM trail path protection is configured, the system performs measurement on both the primary and secondary paths. To display the TDM Trails PM: From the Trails List section, select the TDM trail. The Performance Monitoring data is displayed in a new pane to the right of the Trails List section.
To update the TDM Trails PM, from the bottom of the TDM Trails PM data list click Refresh. The following list explains the columns in the E1 PM Report. ES is the number of seconds during which errors occurred. SES is the number of severely errored seconds. UAS is the Unavailable Seconds value of the current interval. The value can be between 0 and 900 seconds (15 minutes). BBE is the number of background block errors. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
Page 14 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.5
Enhanced Traffic Manager
You can view a PM report for the Enhanced Traffic Manager of each queue. The report contains data from the most recent report interval.
Each PM is measured per queue in Max/Avg format. Green traffic refers to frames that comply with the configured CIR (Committed Information Rate). Yellow traffic refers to frames that exceed the configured CIR but are below the configured EIR (Excess Information Rate). At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. Avg. Green Displays the average green traffic in bps (bytes per seconds) during the report interval. Max Green - Displays the peak green traffic for one second during the report interval. Avg. Yellow Displays the average yellow traffic in bps (bytes per seconds) during the report interval. Max Yellow - Displays the peak yellow traffic for one second during the report interval. Integrity - indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 15 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.6
E1
The E1 page contains a separate PM window for each E1 link that is being used. You can configure if the displayed PM data covers the last 24 hours, in 15 min intervals, or covers a month, with daily intervals.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. The following list explains the columns in the E1 PM Report. ES is the number of seconds during which errors occurred. SES is the number of severely errored seconds. UAS is the Unavailable Seconds value of the current interval. The value can be between 0 and 900 seconds (15 minutes). BBE is the number of background block errors. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
To update the list, click Refresh. To print the list, from the Internet Browser menu bar select File > Print.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 16 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.7
DS1
The DS1 (T1) page contains a separate PM window for each DS1 link that is being used.
For Report Interval, you can select either every 15 minutes, or Daily for the list to include values for the entire day. The following list explains the columns in the DS1 PM Report. ES is the number of seconds during which errors occurred. SES is the number of severely errored seconds. UAS is the Unavailable Seconds value of the current interval. The value can be between 0 and 900 seconds (15 minutes). BBE is the number of background block errors. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
To update the list, click Refresh. To print the list, from the Internet Browser menu bar select File > Print.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 17 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.8
STM-1/OC-3
The STM-1 or OC-3 page contains a separate PM window for each STM-1/OC-3 link that is being used.
For Report Interval, you can select either every 15 minutes, or Daily for the list to include values for the entire day. The following list explains the columns in the E1 PM Report. ES is the number of seconds during which errors occurred. SES is the number of severely errored seconds. UAS is the Unavailable Seconds value of the current interval. The value can be between 0 and 900 seconds (15 minutes). BBE is the number of background block errors. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
To update the list, click Refresh. To print the list, from the Internet Browser menu bar select File > Print.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 18 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.9
4.9.1
Radio
Signal Level (RSL)
The RSL Performance Report page displays received signal level values measured over the past 24 hours, in 15 min intervals, or the past month, daily intervals.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. Min RSL values are the minimum received level measured during the interval. Max RSL values are the maximum received level measured during the interval. RSL Exceed #1 displays the number of seconds the RSL threshold #1value was exceeded during the current interval. RSL Exceed #2 displays the number of seconds the RSL threshold #2 value was exceeded during the current interval. Min TSL values are the minimum transmitted level measured during the interval. Max TSL values are the maximum transmitted level measured during the interval.
Page 19 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
TSL Exceed displays the number of seconds the TSL threshold value was exceeded during the current interval. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
To update the list, from the bottom of the Signal Level PM Report click Refresh. In the Thresholds Configuration area at the bottom of the value table, specify the value you want for the thresholds. The range of values appears at the end of the threshold line. To apply any change you made to the Thresholds Configuration, click Apply. To update the configured thresholds, from the Thresholds Configuration section click Refresh. To print the list, from the Internet Browser menu bar select File > Print.
4.9.2
Aggregate
The Aggregate Performance Report page displays tributary values measured over the last 24 hours, in 15 min intervals, or the past month, daily intervals.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. ES is the number of seconds during which errors occurred. SES is the number of severely errored seconds. UAS is the Unavailable Seconds value of the current interval. The value can be between 0 and 900 seconds (15 minutes). BBE is the number of background block errors. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
To update the Aggregate PM Report, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 20 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
To print the list, from the Internet Browser menu bar select File > Print.
4.9.3
MRMC
The MRMC Performance Report page displays 15-minute or daily values of Multi-Rate Multi-Constellation performance.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. Min Profile is the minimum radio profile during the last interval. Max Profile is the maximum radio profile during the last interval. Min BitRate (Mbps) is the minimum total radio throughput (Mbps), delivered during the last interval. Max BitRate (Mbps) is the maximum total radio throughput (Mbps), delivered during the last interval. Min Number of Allocated TDM VCs is the minimum number of TDM voice channels (E1/T1) delivered over the radio during the last interval. Max Number of Allocated TDM VCs is the maximum number of TDM channels (E1/T1) delivered over the radio during the last interval. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
To update the MRMC PM Report, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 21 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.9.4
MSE
The MSE Performance Report page displays the modems Minimum Square Error performance statistics. The values are for every 15 minutes or daily.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. Min MSE is the minimum MSE in dB, measured during the last interval. Max MSE is the maximum MSE in dB, measured during the last interval. MSE Exceed is the number of seconds the MSE exceeded the threshold (configured in the field below the table) during the last interval. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
To update the list, from the bottom of the MSE PM Report click Refresh. From the Threshold Configuration section:
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 22 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
MSE Threshold (dB) is the value that will be compared with the current MSE value, to calculate if the limit was exceeded.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the MSE Threshold Configuration, click Refresh.
4.9.5
XPI Performance
The XPI Performance page displays the Cross Polarization Interference value over 15 minutes or per day.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. Min XPI is the minimum XPI in dB, measured during the last interval. Max XPI is the maximum XPI in dB, measured during the last interval. XPI Exceed is the number of seconds the XPI exceeded the threshold (configured in the field below the table) during the last interval.
Page 23 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
To update the list, from the bottom of the XPI PM Report click Refresh. From the Threshold Configuration section: XPI Threshold (dB) is the value that will be compared with the current XPI value, to calculate if the limit was exceeded.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the XPI Threshold Configuration, click Refresh.
4.9.6
TDM Channels
The TDM Channels page displays the unavailable seconds (UAS) of the expected E1/T1 trails on the radio. When ACM decreases, the capacity of the radio is reduced, and several E1/T1 trails with not enough bandwidth in the radio link capacity may be dropped. When an E1/T1 trail is dropped, its Radio-TDM UAS counter PM will start counting the seconds for which the E1/T1 trail was not serviced.
To update the TDM Channel PM Report, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 24 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.9.7
4.9.7.1
Ethernet
Frame Error Rate The Frame Error Rate Performance Report page displays statistics of the Ethernet frame error rate (%) measured on the radio Ethernet port.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. Frame Error Rate (%) is the number of received error frames measured by the radio Ethernet port, relative to all frames received by the radio Ethernet port. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time. To update the Ethernet Frame Error Rate PM Report, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 25 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.9.7.2
Throughput The Throughput Performance Report page displays radio Ethernet throughput statistics (excluding TDM traffic), measured on the radio port.
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. Peak Throughput (bps) is the maximum throughput measured during the last interval. Average Throughput (bps) is the average throughput measured during the last interval. Throughput Exceed (Seconds) is the number of seconds the throughput exceeded the threshold (configured in the field below the table) during the last interval.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 26 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time.
To update the list, from the bottom of the Throughput PM Report, click Refresh. From the Threshold Configuration section: Throughput Threshold (Mbps) is the throughput value that will be compared with the current value, to calculate if the limit was exceeded. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the Throughput Threshold Configuration, click Refresh. 4.9.7.3 Capacity The Capacity Performance Report page displays statistics of the Ethernet capacity (including Ethernet data and overhead bytes) measured on the radio port.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 27 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval. Peak Capacity (bps) is the maximum capacity measured during the last interval. Average Capacity (bps) is the average capacity measured during the last interval. Capacity Exceed (Seconds) is the number of seconds the throughput exceeded the threshold (configured in the field below the table) during the last interval. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time. To update the list, from the bottom of the Capacity PM Report, click Refresh. From the Threshold Configuration section: Capacity Threshold (bps) is the capacity value that will be compared with the current value, to calculate if the limit was exceeded. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the Capacity Threshold Configuration, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 28 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
4.9.7.4
Utilization The Utilization Performance Report page displays statistics of Ethernet utilization (%) measured on the radio port. Ethernet utilization is a measurement of actual Ethernet throughput, relative to the potential Ethernet throughput of the radio (excluding TDM channels). Ethernet utilization during the last interval is displayed as one of five bins: 1 2 3 4 5 0-20% 20-40% 40-60% 60-80% 80-100%
At the top of the page, select the Report Interval.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 29 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Range of Peak Utilization (%) is the maximum utilization measured during the last interval. Range of Average Utilization (%) is the average utilization measured during the last interval.
Utilization Exceed (Seconds) is the number of seconds the value exceeded the threshold (configured in the field below the table) during the last interval. The Integrity column indicates whether or not the values received at that time and date are reliable. An x in the column indicates that the values are not reliable due to a possible power surge or power failure that occurred at that time. To update the list, from the bottom of the Utilization PM Report, click Refresh. From the Threshold Configuration section: Utilization threshold (%) is utilization threshold value, which must be configured in the bin resolution listed above. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the Utilization Threshold Configuration, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 30 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.
5.1
5.1.1
Configuration
General
Unit Parameters
This page allows you to view and define information for the IP-10 system.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 31 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
(Optional) In the System name field, enter a name for the node. By convention, this is the nodes fully qualified domain name. In the Slot label field, enter a name for the link. By convention, this is the name and slot label of the unit across the radio link. The read-only IP address field displays the IP address that is configured in the Management window. The read-only System Description field provides information about the FibeAir system. (Optional) In the Contact person field, enter the name of the person to be contacted when a problem with the system occurs. (Optional) In the System location field, enter the actual physical location of the node or agent. The System up time field is read-only and shows how long the system has been operating continuously. The read-only Voltage input field displays the current input voltage. In the Measurement system field, select the type of measurement you want the system to use: Metric or Imperial. The read-only IDU/RFU temperature fields display the current temperatures of the IDU and RFU. In the Date & Time Configuration section, click the calendar to set the date, and click the time area to set the time. Offset from GMT is the Hours and Minutes offset of the time of day from GMT (Greenwich Mean Time).
In the Daylight Saving Time section, you can configure the following options: Start Date - the date when daylight saving time will automatically be activated. End Date - the date when daylight saving time will automatically be terminated. Offset (in hours) - the required offset time, in hours, when daylight saving time is activated. In the IDU Serial/Part Numbers section, the following read-only information is displayed: IDU serial/part number fields display the serial and part numbers of the IDU. RFU serial/part number fields display the serial and part numbers of the RFU.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 32 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.1.2
External Alarms
The External Alarms page enables you to set up the external alarm system.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh. 5.1.2.1 Alarm input configuration (up to five independent inputs) Configure the following information for each external alarm: Admin sets the Alarm Input to Active (Enable) or Inactive (Disable). Text is free text for the alarm description. When an alarm input is raised, this text will appear as the alarm description text. Severity is used to configure the alarm's severity. When an alarm input is raised, the severity will be added to it. 5.1.2.2 Alarm output configuration (single output) Admin sets the alarm input to active (Enable), inactive (Disable) disregarding current raised alarms and Test. The Test option sends a test message to activate all the external alarms. Group is used to configure the group of alarms that will trigger an Alarm Output: Communication - Alarms related to traffic: radio, Ethernet line, TDM line Quality of Service Processing - Alarms related to software: configuration, resets, corrupted files Equipment - Alarms related to hardware, fan, RFU mute, power supply, and inventory. Environmental - Alarms relating to temperature. All groups - All of the groups above.
Page 33 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.1.3
Management
The Management page enables you to define local and remote IP addresses and parameters.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh. 5.1.3.1 IP Configuration In the Local IP Configuration area, enter the IP address of the local unit, its subnet mask, and the default gateway. Additionally, enter the Floating IP address. HW address displays the MAC address of the local unit. In the Remote IP Configuration area, enter the IP address of the remote unit and its subnet mask. Click Open Remote to open the remote unit's management page. 5.1.3.2 Management Ports In the Management Ports area, for Number of ports, specify the number of ports that will be used for management data. For Type, select the management mode of operation - Inband or Out of band.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 34 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
For In-band Management VLAN ID, specify the VLAN ID that will be used to manage the unit, when the In-band management type is used. In-band Management refers to a method in which the network management software sends management packets through the same network it is managing. This differs from out-of-band management in which the network management software uses a different network (overlay network) to communicate with the managed elements. For Capacity, select the bandwidth that will be allocated to the port(s). For Auto negotiation, select On to activate the feature, or Off to disable it. For Rate, select the bit rate you want for the port. For Duplex, select Half or Full.
5.1.4
Traps Configuration
This page is used to configure traps sent from a Network Element to the NMS system.
Each line in the Trap Managers list displays the setup for a manager defined in the system. To change the setup for a manager, click the plus box at the beginning of the line. In the Traps admin field, select Enable to activate trap administration. For Trap manager, specify the IP address to which traps will be sent. For Manager name, specify the manager's name. For Trap port, enter the number of the port through which traps will be sent. For SNMP trap Community, specify the community name for trap forwarding. For Heartbeat period (minutes) specify the period of the heartbeat trap. For Trap CLLI, you can enter free text that will be sent with the trap. For Trap status change filter, select On if you want a trap to be sent to the manager you defined only when the most-severe alarm of the unit changes. For example, if the most severe status in the system is warning, and a new warning alarm is raised, no trap will be sent (if you selected On for this
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 35 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
option). On the other hand, if the new alarm has the severity major, a trap will be sent to the manager you defined. For Send traps for alarms with severity, select the severity level(s) to determine which types of alarms will be forwarded. To select/clear all levels, click Select All. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
5.1.5
Licensing
This page allows you to view and set IP-10 licensing information.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh. 5.1.5.1 Current License In the Current License area, the following options are available: License type - Shows the current license type. License code - The code you enter to allow usage of specific system features.
Page 36 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.1.5.2
Demo License In the Demo License area, the following options are available: Demo admin - Use this option to activate the demo license. Demo timer - Displays the elapsed time of the demo license.
5.1.5.3
License Features In the License Features area, the following options are available: ACM license - Indicates whether or not the ACM feature is available. Switch application license - Displays the type of switch application (Pipe, Switch, or Metro). Capacity -Displays the maximum capacity available for the radio. Network resiliency license - Indicates whether or not the resiliency (RSTP/SNCP) feature is available. TDM capacity license - Indicates whether or not the TDM capacity license is available. It limits the amount of TDM trails that can be mapped to a radio. If this license is allowed, any radio script can be loaded but the number of trails is limited. TDM capacity value - Indicates the amount of TDM trail capacity corresponding to the TDM capacity license. Synchronization Unit License - Indicates whether or not the Synchronization Unit License (Synchronous Ethernet output) is allowed. Enhanced Traffic Manager License Indicates whether or not the Enhanced Traffic Manager is allowed. Per usage license - Allows unlimited usage of all features in the system, and generates a billing report of the current usage.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 37 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.1.6
NTP
This page allows you to view and set IP-10 Network Timing Protocol information.
For Admin, select Enable to activate the NTP client, or Disable to deactivate it. For Server IP, enter the IP address of the NTP server. Status shows the current condition of the NTP client, which can be Up or Down. Sync Server shows the IP address of the NTP server with which the system is currently synchronized. The values that can appear include: IP of the remote NTP server Local, if locked to the local elements real-time clock. NA, if not synchronized with any clock (valid only when Admin is set to Disable).
Poll Interval is the interval used by the NTP client to maintain synchronization with the current NTP server. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 38 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.1.7
IP Table
This page allows you to configure the characteristics of the peer port, which the local port of the element is connected to. Each IDU port has its own IP table, allowing the configuration of the characteristics of the peer port to which it is connected.
For Peer MAC address, enter the MAC address of the peer port. For Peer IP address, enter the IP address of the peer port. For Peer Slot ID, enter the slot ID of the element (IDU) the peer port is located in. The slot can be from 0 to 6, where 0 is used when the other side is a standalone unit, and 1-6 are used for the other sides XC slot IDs. For Peer port Number, enter the peer port number. For Peer Description, you can add a general description of the peer port. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 39 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.1.8
SNMP
This page allows you to configure SNMP parameters.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh. 5.1.8.1 SNMP Parameters Configure the following parameters: SNMP Version field - select V1 for SNMP V1, or V3 for SNMP V3. SNMP read community - Enter the password for the SNMP read community. SNMP write community - Enter the password for the SNMP write community.
5.1.8.2
SNMP V3 User Settings In the SNMP V3 User Settings area, you can configure the following: Security Mode - determines the SNMPv3 security mode, which can be: No security Authentication (default) Authentication Privacy Authentication Algorithm - valid only when security mode is not set to No security. The value can be MD5 or SHA. User name - the SNMPv3 user name. Password - if a security mode other than No security was selected, you will be prompted for a password, which has to be at least eight characters.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 40 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Click Change User Settings - to apply the SNMP V3 changes.
5.1.9
All ODU
This page allows you to activate support for the All ODU enclosure.
Select Enable for All ODU support, or Disable if your system is not configured as All ODU. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh. If you select Enable, the All ODU enclosure interface is activated, and the enclosure controller can then be powered to monitor fan failure alarms. When the enclosure is enabled, External Alarm Input #1 becomes an output, which together with 3.3V is used to drive the enclosures electronic board. External Alarm Input #2 is set with a specific text & severity, and is used to monitor any enclosure fan failure, and to raise an alarm for it (polarity change was required to adapt it to the enclosure behavior).
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 41 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.1.10
Versions
The Versions pages summarize all installed and running versions of the IDU and RFU.
5.1.10.1 IDU Versions
Target Device - Specific component that is contains the version. Running Version is the version that is currently running on the IDU. Installed Version is IDU software files that were successfully installed. Upgrade Package is IDU software files that were successfully downloaded to the IDU, and are ready to be installed when IDU upgrade is executed. Downgrade Package is IDU software files that were successfully downloaded to the IDU, and are ready to be installed when IDU downgrade is executed. To update the information, click Refresh. 5.1.10.2 RFU Versions
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 42 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
RFU Installed Versions - These are RFU software packages currently installed in the IDU, as part of the overall software package. RFU Running Versions - These are software versions that are currently running on the RFU. RFU Upgrade & Downgrade Versions - These are RFU software packages successfully downloaded to the IDU, and ready to be installed when RFU Software Download is executed. To update the information, click Refresh.
5.2
5.2.1
Ethernet Switch
Switch Configuration
FibeAir IP-10 supports Single Pipe and Managed Switch configurations. Single Pipe is the default option, and does not require a license configuring the IDU to Managed Switch requires a license. Single (Smart) Pipe is the default method, which allows only a single GBE interface for traffic (optical GBE-SFP or Electrical GBE, 10/100/1000 mbps). Traffic originating from any GBE interface will be sent directly to the radio and vice versa. This method allows QoS configuration. Other FE (10/100 mbps) interfaces are "functional" interfaces (WSC, Protection, Management).
Managed Switch is an 802.1Q VLAN-aware bridge, allowing L2 switching based on VLANs. Each traffic port can be configured as an "access" port or a "trunk" port, as follows:
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 43 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Type
VLANs
Allowed Ingress Frames
Only untagged frames (or frames tagged with VID=0 ("Priority Tagged") Only tagged frames
Allowed Egress Frames
Untagged frames
Access
Specific VLAN should be associated with the access port A range of VLANs or all VLANs should be associated with the trunk port Specific VLAN is used for the untagged frames A range of VLANs are associated with the tagged frames
Trunk
Tagged frames
Hybrid
Tagged and untagged frames
Tagged frames
The Managed Switch method allows QoS configuration, and all Ethernet ports are allowed for traffic. Metro Switch is an 802.1ad Provider Bridge, allowing Q-in-Q switching capabilities. Each traffic port can be assigned as a "Customer Network" port or a "Provider Network" port. The port attributes are listed in the following table: Type
Customer Network
VLANs
Specific S-VLAN should be associated with the customer network port A range of S-VLANs or all S-VLANs should be associated with the provider network port
Allowed Ingress Frames
Untagged frames or tagged (C-tag) frames Only S-tagged frames, (in accordance with the configured "provider ethertype", which is 0x88a8 by default)
Allowed Egress Frames
Untagged frames of tagged (C-tag) frames S-tagged frames, carrying the configured provider ether-type, (0x88a8 by default)
Provider Network
S-Tag Ether type can be configured to one of the following values: 0x88a8 (default), 0x8100, 0x9100, or 0x9200. In the Switch Configuration page, you can choose the Ethernet switching method.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 44 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Choose the method you want, as follows: Single pipe - Ethernet switching is disabled, whereby only a single Ethernet interface is used for traffic and the unit operates as a point-topoint microwave Ethernet radio. Managed switch - Ethernet switching is enabled and all the ports are used for traffic. Metro switch - This method is the same as Managed switch, but must be enabled to use Ethernet Q-in-Q provider switch. LAG Load Balancing can be configured as Simple XOR or HASH. Simple XOR performs XOR on the last three bits of the Packet Source MAC address (SA) and the Destination MAC address (DA), and according to the result, selects the link to be used in the LAG. The HASH mechanism distributes flows across multiple egress ports in a LAG. It uses a proprietary scrambling function, and uses the last three bits (LSBs) of the DA, SA. This means that two flows with the same three LSB bits, but different MSB bits, will still go to the same port. Thus, the HASH will simply distribute more evenly. In the Unit allowed VIDs area, you can define VLANs for the managed switch, as follows: 1 In the Operation field, select the operation you want to perform for the VLANs: Set - to add the VLANs to the database. Remove - to remove the VLANs from the database. Change name - to change the VLAN name you specified previously. Disable - to suspend usage of the VLAN you specified. Enable - to activate the VLAN you specified.
Page 45 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
2 In the Start VID and End VID fields, enter the VLAN start and end IDs. 3 In the Name field, specify a unique name for the VLAN. 4 Click Apply. The VLAN for the managed switch is defined. The defined VLANs are summarized at the bottom of the window. The following columns are in this section: VLAN ID Specific ID for this VLAN. Name Configured name for the VLAN. Status - Active or Passive Member Ports - Lists which IDU ports allow this VLAN.
To update the information, click Refresh.
5.2.2
STP Protocol
This page allows you to configure STP parameters. This option is available only when the system operates in the Managed or Metro Switch modes. STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) ensures a loop-free topology for any bridged LAN. Spanning Tree allows a network design to include spare (redundant) links for automatic backup paths, needed for cases in which an active link fails. The backup paths can be included with no danger of bridge loops, or the need for manual enabling/disabling of the backup links. Bridge loops must be avoided since they result in network flooding. You can choose between the Fast Ring RSTP and the standard RSTP protocols as defined in IEEE 802.1D.
Select the desired protocol, or Disable to deactivate the protocols. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 46 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.2.3
RSTP and Ring RSTP
These windows enable you to configure RSTP and Ring RSTP parameters and view status information. RSTP and Ring RSTP algorithms are designed to create loop-free topologies in any network design, which makes it sub-optimal to ring topologies. The configurations of RSTP and Ring RSTP parameters are identical.
In the (Ring) RSTP Status area, the following information is provided: Bridge ID - The ID of the bridge in the current monitored IDU. Root ID - The ID of the root bridge. Root Path Cost - The cost of the path from the current monitored IDU to the root bridge. Bridge Role - The role of the bridge, which can be Root or Designated. Priority - The priority of the bridge, which is part of the bridge ID.
In the (Ring) RSTP Configuration area, you can configure the following: In the Ethernet Ports that Support (Ring) RSTP table, each interface in the IDU can be configured with the following RSTP parameters.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 47 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Priority - Configure the specific priority for this interface. Path Cost - Configure the path cost for this port. The lower the value the more likely that port is used. Edge port - This port is not part of the ring itself, and is used as a service access port. Non-edge ports are those that construct the ring.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
5.2.4
QoS & Rate Limiting
The QoS feature allows you to configure classification and scheduling to ensure packets are forwarded and discarded according to their priority. QoS can be configured for all switch methods (Single Pipe, Managed Switch, and Metro Switch). The QoS flow is as follows:
Ingress Port #x 5 Policers (Ingress Rate Limiting)
Egress Port #y Shaper (Egress rate limiting)
Calssifier (4 Queues)
Marker
Queue Controller
Scheduler
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 48 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
The QoS & Rate Limiting window contains three sections: Interfaces - configure the QoS settings for each IDU interface port. Advanced - configure specific QoS parameters. Clicking on a link opens a separate window. Copy Ports Configuration - copies the QoS configuration of one interface port to a different interface port.
The Interface section window enables you to configure Quality of Service parameters for each Ethernet port. These parameters include: Traffic Priorities Egress Rate Limiting Ingress Rate Limiting
5.2.4.1
Ingress Classifier A frame ingressed to a port will be classified according to the following criteria: 1 First Criteria: MAC DA (Destination Address) based. A frame ingressed to a port, carrying a MAC DA that appears in the Static MAC table (see details below), will be classified, its VLAN Pbits will be overwritten (assuming the frame egress is tagged) according to the following options: Disable - No MAC DA classification or VLAN Pbits will be overwritten (no marking). Queue Decision - There will only be classification to queue. No marking. VLAN Pbits Overwrite - Only VLAN Pbits will be overwritten (marked). Classification according to a lower criteria. Queue Decision & VLAN Pbits Overwrite - Both classification and VLAN Pbits overwrite.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 49 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
2 Second Criteria: VLAN ID based. If the first criteria is not fulfilled (whether it is disabled, or the ingress frame does not carry a MAC DA that appears in the Static MAC table), classification and/or marking (VLAN Pbits overwrite, assuming the frame egress is tagged) will be decided according to the VLAN ID to Queue table (see below), in accordance with the following options: Disable - No VLAN ID classification or VLAN Pbits overwrite (marking). Queue Decision - Only classification to queue. No marking. VLAN Pbits Overwrite - Only VLAN Pbits overwrite (marking). Classification will be according to lower criteria. Queue Decision & VLAN Pbits Overwrite - Both classification and VLAN Pbits overwrite.
3 Third Criteria: If both the first and second criteria are not fulfilled (whether they are both disabled, or the ingress frame does not carry a MAC DA or VLAN ID that appears in the tables), it will be classified according to the following configuration: VLAN Pbits - Classification according to VLAN Pbits. Queue is assigned according to the VLAN Pbits Priority Remap table (see below). IP TOS - Classification according to IP TOS (IP precedence, or IP diffserv). Queue is assigned according to IP Pbits to Queue table (see below). VLAN Pbits over IP TOS - Classification according to VLAN Pbits, if the ingress frame carries a VLAN and has an IP header. IP TOS over VLAN Pbits - classification according to IP TOS, if the ingress frame carries a VLAN and has an IP header. Port (Default) - If any of the above criteria is not fulfilled, the default classification will be assigned to the ingress frame. Classifier Tables (in the Advanced field)
4 Default Classification - The default queue decision.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 50 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.2.4.2
VLAN Pbits Priority Remap
Single table per port. Allows you to remap VLAN-priority bit values 0-7, to any other preferable value in the range of 0-7. The number of table entries is eight (all CoS legal values). Remapping a table can be used to scale down some port priorities (for example, from 7:0 to 3:0), while at same time scaling up some port priorities (for example, from 7:0 to 7:4), or to ensure that specific priorities are reserved for specific purposes, by initially remapping all frames away from reserved priorities (for example, from 7:0 to 4:0, protecting priorities 7:5). 5.2.4.3 Egress Scheduler The Egress Scheduler section of the QoS & Rate Limiting window determines how frames are output from the queues.
The fourth queue is the Highest Priority Queue, and the first queue is the Lowest Priority Queue. The following scheduling schemes are supported: Strict for all queues. Strict for fourth queue, and HRR (Hierarchical Round Robin) for third, second, and first queues. Strict for fourth and third queues, and HRR for second and first queues. HRR for all queues.
Page 51 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
In the HRR scheduling scheme, a weight is assigned to each queue, so that frames egress from the queues according to their assigned weight, to avoid "starvation" of lower priority queues. In addition, frames will egress in a "mixed" manner, to avoid "bursts" of frames from the same queue. Each queue weight can be configured, and the weight will be used by the scheduler when the specific queue is part of the HRR scheduling scheme. The queue weight is a value between 1 and 32, and is configured via the Queue Weights table. The default queue weights are 8,4,2,1. Shaper - Determines the scheduler rate (egress rate limit). Select ON or OFF. The default is OFF. Shaper Rate - The following rate steps are available: For 64 Kbps <= Rate <= 960 Kbps, in steps of 64 Kbps. 5.2.4.4 For 1000 Kbps <= Rate <= 100,000 Kbps, in steps of 1000 Kbps. For 100,000 Kbps < Rate <= 1,000,000 Kbps, in steps of 10,000 Kbps.
Ingress Rate Limiting The Ingress Rate Limiting section of the QoS & Rate Limiting window determines the port ingress rate limit.
Attach Policer - Up to five policers per port can be configured, as follows: The system supports a color blind leaky bucket scheme. Each policer has the following parameters: CIR - Committed Information Rate. Rate limiting resolution: For 64 Kbps <= CIR <= 960 Kbps, in steps of 64 Kbps For 1000 Kbps <= CIR <= 100,000 Kbps, in steps of 1000 Kbps For 100,000 Kbps < CIR <= 1,000,000 Kbps, in steps of 10,000 Kbps CBS - Committed Burst Size. CBS is CIR-dependent, and should be configured in bytes: For 64 Kbps <= CIR <= 960 Kbps, 0 < CBS <= 273,404 bytes. For 1000 Kbps <= CIR <= 100,000 Kbps, 0 < CBS <= 132,585 bytes. For 100,000 Kbps < CIR <= 1,000,000 Kbps, 0 < CBS <= 4,192,668 bytes. Data Type - Rate can be limited based on the following data types: None (no limiting), Unknown unicast, Unknown multicast, Broadcast, Multicast, Unicast, Management, ARP, TCP-Data, TCPControl, UDP, Non- UDP, Non-TCP-UDP, Queue1, Queue2, Queue3, Queue4. Limit Exceed Action: Discard frame. To apply any change you made, click Apply.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 52 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
To update the information, click Refresh. 5.2.4.5 Advanced Classifier - VLAN-ID to Queue
Single table for all switches. Used to assign a queue to a frame, according to the frames VLAN-ID. The number of table entries depends on the number of VLANs that have a "Queue allocation" definition. By default, VLANs do not have a pre-determined "Queue allocation".
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 53 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.2.4.6
Advanced Classifier - IP-Pbits to Queue
Single table for all switches. Used to assign a queue to a frame, according to the frames IP priority bits (IP-Precedence or Diffserv), assuming the frame is an IP packet. The number of table entries is: IP Precedence configuration: 8 entries. DiffServ configuration: 64 entries. 5.2.4.7 Advanced Classifier - VLAN-Pbits to Queue
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 54 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Single table for all switches. Used to assign a queue to a frame, according to the frames Pbits (CoS), assuming the frame is tagged. The number of table entries is eight (all CoS legal values). 5.2.4.8 Advanced Classifier Queue Weights Each queue weight can be configured and is used by scheduler when the specific queue is part of HRR scheduling scheme. Queue weights can be configured in the range of 1-32, the higher the weight the higher the priority for that queue.
To configure the QoS queue weights: 1 From the Scheduler Queue drop-down menu, select one of the four QoS queues. 2 From the Weight drop-down menu, select the weight for that queue. 3 Click Apply. The queue weights are configured. 4 Click Refresh. The QoS current queue weights are displayed.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 55 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.2.4.9
Advanced Classifier - Policer List Click Policer List in the Advanced options area at the bottom of the QoS & Rate Limiting page. This page enables you to add policy rules to a policer.
Operation - add or delete the policer. Policer Name - assign a general purpose name for the policer. Note that the name cannot include spaces (you can use underscores instead). It is possible to configure up to five policy rules per policer. When a policer definition is completed, it can be associated with any port, by attaching its name to the port. This will enforce all policy rules of the policer on the port. If a policer is attached to a port, you can use the detach command to remove the policer (and all its policy rules) from the port. 5.2.4.10 Advanced Classifier - Static MAC Click Static MAC in the Advanced options area at the bottom of the QoS & Rate Limiting page. This table is used to load static MAC addresses to the forwarding table of the switch. The static MACs are never flushed.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 56 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
VLAN ID is the ID of the frame. Each frame is attached with a VLAN ID. Frames are learned and filed in the static MAC table under their VLAN ID. Static MAC is the 48-bit MAC address, in octet format (xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx). Forward to indicates which port the frame will be forwarded to. Priority sets the classification and/or VLAN Pbits overwrite (marking), according to the QoS configurations (see QoS & Rate Limiting page above). 5.2.4.11 Copy Ports Configuration The Copy Ports Configuration section is located at the bottom of the QoS & Rate Limiting for Slots page.
Since it is common to set QoS and rate limiting settings identically in several ports, this option can be used to copy the configurations from one port to another. This saves considerable time and prevents configuration errors. Copy Priorities Configuration - Copies all Traffic Priorities using the ingress classifier. Copy Rate Limiting Configuration - Copies the Policer configuration only.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 57 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.2.5
Enhanced Traffic Manager
The windows in this section enable you to configure the parameters for the Enhanced Traffic Manager (Enhanced QoS). The Enhanced Traffic Manager feature applies to the egress traffic on the Radio port (where the bottleneck is located). All the other ports function as usual. A specific license is required to use the Enhanced Traffic Manager feature.
5.2.5.1
Preparing to use Enhanced Traffic Manager This section describes how to prepare the system to enable the Enhanced Traffic Manager to minimize the impact on traffic. You must disable the egress shaper before you can use the Enhanced Traffic Manager. You should classify the in-band management traffic to ensure that the management signal is not affected. To prepare to use the Enhanced Traffic Manager: 1 Disable the QoS egress shaper. i From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > QoS & Rate Limiting. The QoS & Rate Limiting window is displayed. ii Expand the radio port (Ethernet #8). The Traffic Priorities section is displayed.
iii From the Egress shaper drop down menu, select Off. iv Click Apply. The egress shaper is disabled.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 58 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
2 Configure the classification of the in-band management signal. i From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. The CoS & Color Classification window is displayed.
ii From the 1st criterion, by in-band management VLAN Id drop-down menu, select Enable. iii In VLAN Id, enter the VLAN Id for the in-band management signal. This value is configured in the Management Ports section of the Management window. For more information about configuring the in-band management VLAN Id, see Management Ports on page 34. iv From the Color drop-down menu, select classification color for the inband management signal. v In CoS, enter the CoS value for the in-band management signal. Green - The in-band management signal complies with the CIR. Yellow - The in-band management signal complies with the EIR. vi Click Apply. The classification of the in-band management signal is configured. 3 If you are going to use the PTP (Precision Time Protocol) optimized transport feature, disable the Wayside channel. i From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Interfaces > Wayside Channel. The Wayside Channel window is displayed.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 59 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
ii From the Wayside admin drop-down menu, select Disable. iii Click Apply. The Wayside channel is disabled. 5.2.5.2 Configuration & Parameters You can enable the Enhanced Traffic Manager and Precision Time Protocol features from the Configuration & Parameters window. This window also enables you to configure the size of the eight Enhanced Traffic Manager queues. The maximum bandwidth of all the traffic queues is 4 Mbps. When you enable the Enhanced Traffic Manager, radio port egress traffic scheduling and shaping are performed in the Enhanced Traffic Manager module. Thus there are configuration changes that are performed on the egress shaper and scheduler: Egress shaper must be disabled in the switch. Instead egress shapers per priority queue can be configured in the Enhanced Traffic Manager windows. Egress scheduler in switch will be degenerated to All queues strict mode. Instead enhanced scheduler (based on WFQ algorithm) will be used in the enhanced QoS module. This configuration will be performed automatically upon activating the Enhanced Traffic Manager.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 60 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Enabling Enhanced QoS affects the traffic on the radio port. For more information about preparing the system to use the Enhanced Traffic Manager, see Preparing to use Enhanced Traffic Manager on page 58. Precision Time Protocol (PTP) optimized transport feature is a special channel with low Packet Delay Variation (PDV). This feature is essential for timing synchronization protocols e.g. IEEE 1588 and using the sync features. This protocol carries the signal for the sync clock and enabling PTP separates this signal (2 Mbps) from the Traffic Manager signal.
The Configuration section enables Enhanced Traffic Manager and Precision Time Protocol. To enable Enhanced Traffic Manager and Precision Time Protocol: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Configuration & Parameters. The Configuration & Parameters window is displayed. 2 From the Enhanced Traffic Manager drop-down menu, select Enable. 3 From the Precision Time Protocol drop-down menu, select Enable. 4 To apply any change you made, click Apply. 5 To update the information, click Refresh. PTP optimized transport mode and User Wayside channel are mutual exclusive features. You must disable the User Wayside channel before enabling the PTP optimized transport mode. For more information, see Wayside Channel on page 101. Enhanced Traffic Manager supports eight priority queues of configurable buffer size and you can configure the buffer size of each queue independently.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 61 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
The Queue Size section enables you to configure the buffer size of the priority queues. Changing queue size can impact traffic output. To configure a priority queue: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Configuration & Parameters. The Configuration & Parameters window is displayed. 2 From the Queue Size priority queue drop-down menu, select the buffer size. 3 Repeat the previous step for all necessary priority queues. 4 To apply any change you made, click Apply. 5 To update the information, click Refresh. 5.2.5.3 Classification Overview The classifier is a basic element of each Enhanced Traffic Manager mechanism. Each frame is given a Class of Service (CoS) and color (based on MEF 10.2 recommendations). Green frames refer to traffic that complies with the configured CIR. Yellow frames exceed the CIR, but are still less than the configured CBS. Users can define several criteria that classify Ethernet frames. All the classification criteria are divided into three hierarchies from the most specific to the general.
To enable Ethernet frames classification rules: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. 2 From the First Hierarchy section, select Enable for the classification criteria. More than one criterion can be selected.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 62 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
3 From the Second Hierarchy section, at the 1st criterion: by in-band management VLAN Id drop-down menu, select Enable. 4 From the Third Hierarchy section, select Enable for the classification criteria. More than one criterion can be selected. 5 Click Apply. The Ethernet frames classification rules are enabled. 5.2.5.4 Classification Default settings You can configure the default frame color and CoS for all unclassified frames. Additionally, you can change the queuing hierarchy of the CoS settings. The preconfigured setting for the CoS queuing hierarchy is that CoS 0 has the highest priority and CoS 7 has the lowest. To configure the default classification rule settings: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. The parameters for the default settings are located at the bottom of the window.
2 In the Default color drop-down menu, select Green or Yellow as the default frame color. 3 In Default CoS, enter the default Class of Service for frames. 4 Click CoS to Queue Classification. The CoS to Queue Classification window is displayed.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 63 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5 Expand a CoS. Enter the new Queue index for that CoS. 6 Click Apply. The new queue index is configured for that CoS. Each queue is a physical resource which can be assigned to accommodate frames of a specific (or several) CoS(s). 7 Repeat steps 5-6 for other CoSs that need to be changed. Click Close. The CoS to Queue Classification window is closed. 8 In the CoS & Color Classification window, click Apply. The default classification settings are configured. 5.2.5.5 Classification First hierarchy The first hierarchy contains the classification rules that apply to the most specific traffic parameters. The first hierarchy contains following classification criteria: Source MAC Address UDP Ports Known Destination Multicast MAC Addresses
Any or all of these criteria can be used to classify the CoS for the frames.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 64 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
To configure traffic classification rules according to the source MAC Address: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. The CoS & Color Classification window is displayed. 2 From the First Hierarchy section, click MAC Address Table. The MAC Address Table window is displayed.
3 From the Add New Entry section, configure the following parameters: Row number Number for this classification rule that is displayed in the # column. MAC address The source MAC address that is being classified. CoS (Class of Service) The traffic from this MAC address is designated with the configured CoS (0 7). Color The traffic from this MAC address is designated as Green (compliant) or Yellow (non-compliant).
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 65 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Up to 16 separate MAC addresses can be configured. 4 Click Apply. The source MAC address classification rules are configured. To configure traffic classification rules according to the UDP ports: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. The CoS & Color Classification window is displayed. 2 From the First Hierarchy section, click UDP Ports Table. The UDP Ports Table window is displayed.
3 From the Add New Entry section, configure the following parameters: Row number Number for this classification rule that is displayed in the # column. Source port The source UDP port that is being classified. Destination port - The destination UDP port that is being classified. CoS (Class of Service) The frames associated with this UDP port are designated with the configured CoS (0 7). Color The frames associated with this UDP port are designated as Green (compliant) or Yellow (non-compliant). Up to eight UDP port entries can be configured. 4 Click Apply. The UDP port classification rules are configured. The following list contains sample UDP port configurations: To specify classification by UDP source port only, you should configure the Destination port parameter to 0.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 66 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
To specify classification by UDP destination port only, you should configure the Source port parameter to 0. When you configure both the Source and Destination ports parameters contain non-zero values, the classification rule only applies to frames that match both the Source and Destination ports.
The Known Multicast MAC Addresses Table contains a list of 66 destination MAC addresses which are reserved for network protocols use. You can classify the CoS and color of traffic that is being sent to one of the predefined multicast MAC addresses. To configure traffic classification rules according to the known multicast MAC addresses: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. The CoS & Color Classification window is displayed. 2 From the First Hierarchy section, click Known Multicast MAC Addresses Table. The Known Multicast MAC Addresses Table window is displayed.
3 Expand the MAC address. 4 Configure the following parameters for that MAC address: CoS (Class of Service) The traffic to this MAC address is designated with the configured CoS (0 7). Color The traffic to this MAC address is designated as Green (compliant) or Yellow (non-compliant). Validity When Valid is selected, the classification rules are applied to frames that are sent to this destination MAC address. 5 Click Apply. The multicast MAC address classification rule is configured. 6 Repeat steps 3 - 5 for all the required destination MAC addresses.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 67 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.2.5.6
Classification - Second hierarchy The second hierarchy contains a classification rule according to in-band management VLAN ID. This classification rule is used to give high priority to the in-band management frames in order to prevent loss of the management signal on the remote sites. To configure the in-band management traffic classification rule: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. The CoS & Color Classification window is displayed.
2 From the Second Hierarchy section, configure the following parameters: VLAN Id The VLAN identifier number of the in-band management VLAN. Color The traffic from the in-band management VLAN ID is designated as Green (compliant) or Yellow (non-compliant). CoS (Class of Service) The traffic from the in-band management VLAN ID is designated with the configured CoS (0 7).
3 Click Apply. The in-band management VLAN ID classification rule is configured. 5.2.5.7 Classification - Third hierarchy The third hierarchy contains the classification rules that apply to the most general traffic parameters. The third hierarchy contains following classification criteria: VLAN P-Bits to CoS DSCP/TOS Bits to CoS MPLS exp Bits to CoS
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 68 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
The first classification rule in the third hierarchy manages the outgoing traffic according to the VLAN P-bits value that already exists on the frame. You can configure the CoS and frame color of the traffic according to the P-bits and CFI value of each frame. There are two CFI options for each P-bit and a total of 16 classification rules according to the VLAN P-bits. To configure VLAN P-bits traffic classification rules: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. The CoS & Color Classification window is displayed. 2 From the Third Hierarchy section, click VLAN P-Bits to CoS and Color Classification Table. The VLAN P-Bits to CoS and Color Classification Table is displayed.
3 Expand the combination of 802.1P Priority bits and CFI/DEI bit values. The following list explains the columns in this window: # - Number of the classification rule. 802.1 UP - The P-bits value for this classification rule. The range of options are 0 to 7. CFI/DEI - The CFI/DEI value for this classification rule. The options are 0 or 1. Class of Service - The configured CoS for this classification rule. Color - The configured color for this classification rule. CoS (Class of Service) The traffic with this P-bits and CFI/DEI value is designated with the configured CoS (0 7). Color The traffic with this P-bits and CFI/DEI value is designated as Green (compliant) or Yellow (non-compliant).
4 Configure the following parameters for P-bits value:
5 Click Apply. The multicast VLAN P-Bits classification rule is configured. 6 Repeat steps 3 - 5 for other VLAN P-Bits that need to be configured.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 69 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Differentiated Service Code Point (DSCP) or Type of Service (TOS) is a 6 bit length field inside the IP datagram header carrying priority information. The following figure describes the IPv4 datagram header format:
Classification by DSCP bits can be used for untagged frames as well as 802.1Q tagged and/or provider VLAN tagged frames. The classifier also supports classification by Traffic Class (TC) of the IPv6. Whatever IP protocol version is used, the classifier extracts the adjacent field automatically. To configure DSCP/TOC P-bits traffic classification rules: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. The CoS & Color Classification window is displayed. 2 From the Third Hierarchy section, click DSCP/TOS Bits to CoS and Color Classification Table. The DSCP/TOS Bits to CoS and Color Classification Table is displayed.
3 Expand the DSCP/TOS bits value. 4 Configure the following parameters for that DSCP/TOS value: CoS (Class of Service) The traffic with this DSCP/TOS bits value is designated with the configured CoS (0 7). Color The traffic with this DSCP/TOS bits value is designated as Green (compliant) or Yellow (non-compliant).
5 Click Apply. The DSCP/TOS classification rule is configured.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 70 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6 Repeat steps 3 - 5 for other DSCP/TOS bits values that need to be configured. MPLS experimental bits are used to provide QoS capabilities by utilizing the bits set in the MPLS labels. The following figure shows the MPLS label format:
Classification by MPLS experimental bits is supported in both untagged and/or 802.1Q/provider tagged frames. To configure MPLS experimental bits traffic classification rules: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Classification. The CoS & Color Classification window is displayed. 2 From the Second Hierarchy section, click MPLS exp Bits to CoS and Color Classification Table. The MPLS experimental Bits to CoS and Color Classification Table is displayed.
3 Expand the MPLS experimental bits value. 4 Configure the following parameters for that MPLS experimental bits value: CoS (Class of Service) The traffic with this MPLS experimental bits value is designated with the configured CoS (0 7). Color The traffic with this MPLS experimental bits value is designated as Green (compliant) or Yellow (non-compliant).
5 Click Apply. The MPLS experimental bits classification rule is configured.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 71 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6 Repeat steps 3 - 5 for other MPLS experimental bits values that need to be configured. 5.2.5.8 WRED Weighted Random Early Detect (WRED) mechanism can increase capacity utilization of TCP traffic by eliminating the phenomenon of global synchronization. Global synchronization occurs when TCP flows that share bottleneck conditions receive loss indications at the same time. This can result in periods during which link bandwidth utilization drops significantly as a consequence of simultaneous falling to slow start of all the TCP flows. For more information about using WRED with IP-10, see IP-10 Feature Description. To enable Enhanced Traffic Manager for WRED: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > WRED. The WRED window is displayed.
2 From the WRED admin section, click Enable. The Enhanced Traffic Manager for WRED is enabled. Each of the eight priority queues can be given a different WRED profile curve. This curve describes the probability of randomly dropping packets as the specific queue uses more bandwidth. You can configure a separate WRED profile curve for each priority queue. Additionally, you can configure different weights for yellow (non-compliant) and green (compliant) packets so that the system drops yellow packets first. To configure WRED traffic classification rules: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > WRED. The WRED window is displayed. 2 Expand the WRED queue. The WRED Thresholds queue configuration pane is displayed.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 72 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
3 Configure the following WRED parameters for the priority queue: Green packets low threshold Minimum throughput of green packets for this queue. When this value is reached, the system begins dropping green packets in this queue. Green packets high threshold Maximum throughput of green packets for this queue. After this value is reached, all green packets in this queue are dropped. Green packets maximal drop percentage Maximum percentage of dropped green packets for this queue. Yellow packets low threshold - Minimum throughput of yellow packets for this queue. When this value is reached, the system begins dropping yellow packets in this queue. Yellow packets high threshold - Maximum throughput of yellow packets for this queue. After this value is reached, all yellow packets in this queue are dropped. Yellow packets maximal drop percentage - Maximum percentage of dropped yellow packets for this queue.
4 Click Apply. The MPLS experimental bits classification rule is configured. 5 Repeat steps 2 - 4 for other MPLS experimental bits values that need to be configured. 5.2.5.9 Egress Shaper & Scheduler The Egress shaper feature is used to shape the traffic profile sent to the radio. The Enhanced Traffic Manager enables you to configure an Egress shaper for each priority queue. When using the Enhanced Traffic Manager feature, the egress scheduler uses the Weighted Fair Queue (WFQ) algorithm instead of Weighted Round Robin (WRR). Each priority queue is assigned a strict priority between 1 and 4 (4=High; 1=Low). WFQ weights are used to partition bandwidth between the queues of the same priority. For more information about using the Egress Shaper and Scheduler, see the IP-10 Feature Description Guide. To enable Egress Shaper and Scheduler: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Egress Shaper & Scheduler. The Egress Shaper & Scheduler window is displayed.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 73 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
2 From the Global Shaper admin section, click Enable. The Egress Shaper and Scheduler feature is enabled. To configure Egress shaper and scheduler for the priority queues: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Ethernet Switch > Enhanced Traffic Manager > Egress Shaper & Scheduler. The Egress Shaper & Scheduler window is displayed. 2 From the Queue Configuration section, expand a priority queue. The Egress Shaper & Scheduler queue configuration pane is displayed.
3 Configure the following Egress shaper and scheduler parameters for the priority queue: Priority Egress priority for this queue. The queue with a higher priority egresses before a lower one regardless of WFQ weights. WFQ weight Sets the ratio for allowed bandwidth to queues with the same priority. Sample configuration - queue 5 has a WFQ weight of 4, and queue 7 has a WFQ weight of 8. Under congestion conditions queue 7 would be allowed to transmit twice as much bandwidth as queue 5. Shaper admin When Enable is selected, the Egress shaper and scheduler configuration is used for this priority queue.
Page 74 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
CIR Committed Information Rate for this queue. CBS Committed Burst Size for this queue. Line compensation The number of bytes that is compensated in the shaper credits counting for the Inter-Frame Gap (IFG) and the preamble + SFD fields between the two consecutive Ethernet frames. The default value is 20 bytes which is the number of bytes used for IFG + preamble + SFD according to the Ethernet standard. You may want the Egress shaper to count in L2 by setting line compensation to 0. You can also punish short frame senders for the overhead they cause in the network by increasing the line compensation above 20 bytes.
5.3
Radio
The Radio menu includes the Radio Parameters and Radio Thresholds items.
5.3.1
Radio Parameters
The Radio Parameters window enables you to configure how the radio operates.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 75 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
The explanation of how to configure the IF Combining parameters is discussed in the Radio Diversity section. For more information, see IF Combining Parameters on page 108. This window also controls the MAC header compression feature. Radio transmission (compared with Fiber optics and other line base links) has limited bandwidth and compression is required to improve available capacity utilization. The benefit of using MAC header compression is that it can be used as a supplement to the other compression without affecting traffic performance. Ceragon proprietary MAC Header compression improves the effective throughput by up to 45%, and does not affect user traffic. MAC header compression is based on the following: Dropping the Preamble + SFD + IFG saves 20 bytes. Dropping the Ethernet type saves 2 bytes. Adding a GFP header adds 4 bytes.
In addition: Frequently repeating SA & DA are learned.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 76 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Learned DA & SA are not transmitted. A short pointer is used instead of the original 12 bytes. Effectiveness is reduced if a high number of L2 flows are used.
The capacity reached after header compression, in accordance with the Ethernet packet length, is as follows: Ethernet Capacity after Compression Packet Size
64 96 128 256 512 45% 29% 22% 11% 5%
5.3.1.1
Status Parameters The Status Parameters section of the Radio Parameters window displays the status of the RFU. To view the RFU status parameters: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Radio > Radio Parameters. The Radio Parameters window is displayed. 2 From the bottom of the Radio Parameters window, click Refresh. The current RFU status parameters are displayed in the Status Parameters section.
3 The RFU Installed Version section contains the following information: RFU type - The RFU used in the system (1500HP, RFU-C, other). Tx/Rx frequency separation - Read-only, Tx/Rx separation values. Tx/Rx level - Read-only, current Tx/Rx level values.
Page 77 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
MSE - Mean Square Error value, which quantifies the performance of the receiver. XPI level - Read only, displays the current cross polarization interference value. Defective blocks - Amount of blocks in which errors were detected. The larger the amount, the poorer the radio link quality.
4 To reset the counters in the Status Parameters section, from the bottom of the Radio Parameters window, click Clear Counters. 5.3.1.2 Frequency Control To configure the Tx and Rx frequencies: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Radio > Radio Parameters. The Radio Parameters window is displayed. 2 From the bottom of the Radio Parameters window, click Refresh. The current Tx and Rx frequencies are displayed in the Frequency Control section.
3 In Tx frequency, enter the transmission radio frequency. 4 In Rx frequency, enter the received radio frequency. 5 Select Set also remote unit, to configure the remote unit with the identical radio frequency configuration. 6 From the bottom of the Radio Parameters window, click Apply. The Tx and Rx frequencies are configured. 5.3.1.3 Configuration Parameters To configure the radio parameters: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Radio > Radio Parameters. The Radio Parameters window is displayed. 2 From the bottom of the Radio Parameters window, click Refresh. The current radio parameters are displayed in the Configuration Parameters section.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 78 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
3 From the Radio IF interface drop-down menu, select one of the following options: Enable Activates the radio interface. Disable Deactivates the radio interface. Allows the user to enable/disable the radio interface. Changing the Radio IF interface requires a system reset. 4 The Radio IF operational status field displays the current status of the radio interface. 5 From the Mute Tx drop-down menu select one of the following options: Enable Activates Tx muting. Disable Deactivates Tx muting. 6 In Max Tx level, enter the maximum operational Tx value. 7 In Link ID, enter the identification number of the link. When working with an IDU that has the Link ID feature on one end and an IDU that does not have this feature on the other end, set the Link ID to 1. 8 From the MAC header compression drop-down menu select one of the following options: Enable Activates MAC header compression. Disable Deactivates MAC header compression.
9 From the bottom of the Radio Parameters window, click Apply. The radio parameters are configured. 5.3.1.4 XPIC Parameters To view if XPIC is enabled: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Radio > Radio Parameters. The Radio Parameters window is displayed. 2 From the bottom of the Radio Parameters window, click Refresh. The current radio parameters are displayed in the XPIC Parameters section.
5.3.1.5
Green Mode You can enable Green Mode to reduce the amount of electricity that is used by the RFU. To view the Green Mode parameters: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Radio > Radio Parameters. The Radio Parameters window is displayed. 2 From the bottom of the Radio Parameters window, click Refresh. The current radio parameters are displayed in the Green Mode section.
Comment [YS1]: Need explanation for this section
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 79 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
The following parameters are displayed in this section: 5.3.1.6 Green mode admin - Displays whether green mode is active or not. Green mode ref rx level - Displays the current Ref Rx level.
Multi Radio Multi-radio enables two separate radio links to be shared by a single Ethernet port. This provides an Ethernet link over the radio with double capacity, which still behaves as a single layer-2 MAC. The two separate radio links may be implemented using XPIC or separate frequencies. This feature is available only for IDUs which are inserted in a shelf. Multi-radio cannot be used in tandem with the following features: 1+1 HSB Space Diversity Multi-radio feature is applicable for Ethernet data only. For TDM, each link remains separate, and users can decide to configure trails to either radio (or both, by using SNCP or ABR). You should ensure that the two radio links are using the same radio script in order for Multi-radio to perform at maximum efficiency. Since traffic is distributed between both carriers at layer 1 level, a failure in one of the radio links may cause all Ethernet frames to be affected. Therefore, Multi-radio performs actions to ensure graceful degradation in the case of a failure. You can configure a link to be blocked, so that the transmitter does not distribute data to this link and the receiver ignores it when combining. To configure the Multi Radio settings: 1 From the navigation tree, select Configuration > Radio > Radio Parameters. The Radio Parameters window is displayed. 2 From the bottom of the Radio Parameters window, click Refresh. The current radio parameters are displayed in the Multi Radio section.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 80 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
All of the configuration options are only displayed after Multi-Radio is enabled. 3 From the Multi-Radio admin drop-down menu, select one of the following options: Enable - Activates the Multi-radio feature. You must click Apply to display the other configuration options. Disable Deactivates the Multi-radio feature.
4 If necessary, click Apply. The Multi-radio is enabled and the Multi-radio configuration options are displayed. 5 When there is a problem with the IDU in slot #1, you should block traffic to that radio port. From the Block radio (slot #1) drop-down menu, select one of the following options: On - Blocking traffic to radio port in slot #1. All traffic is sent to radio part in slot #2. Off Default setting, no traffic is blocked.
6 When there is a problem with the IDU in slot #2 you should block traffic to that radio port. From the Block radio (slot #2) drop-down menu, select one of the following options: On - Blocking traffic to radio port in slot #2. All traffic is sent to radio part in slot #1. Off Default setting, no traffic is blocked.
7 From the Signal degrade admin drop-down menu, select one of the following options: Enable - If a signal degrades below the configured threshold, the link is shut down. Disable The system does not make any changes if there is a signal degrade problem. For more information on configuring the signal degrade threshold, see Radio Thresholds on page 83. 8 From the Excessive ber admin drop-down menu, select one of the following options: Enable - If the BER (Bit Error Rate) exceeds the configured threshold, the link is shut down. Disable The system does not make any changes if there is a BER problem. For more information on configuring the BER threshold, see Radio Thresholds on page 83. 9 Click Apply. The Multi-radio settings are configured.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 81 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.3.2
Remote Radio
In this page, you can configure how the remote radio operates.
Remote communication - The current communication status of the remote unit. Remote IP address - The IP address of the remote unit. To open the remote radio configuration, click Open Remote. Remote Rx level - The current Rx level of the remote unit. Remote force max Tx level - Used to force the remote unit maximum transmit level. Remote ATPC reference Rx Level - Used to configure the ATPC Rx level of the remote unit. Remote floating IP address - Used to configure the remote floating IP address.
To unmute the remote unit transmitter output, click Force Unmute. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 82 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.3.3
Radio Thresholds
In this page, you can configure radio threshold levels.
For Radio excessive BER threshold, click the drop-down list and select the level above which an excessive BER alarm is issued for errors detected over the radio link. For Radio signal degrade threshold, select the level above which a Signal Degrade alarm is issued for errors detected over the radio link. The Radio BER field is read-only and shows the value above which a BER alarm is issued for errors detected over the radio link. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 83 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.3.4
MRMC Configuration
In this page, you can configure MRMC script parameters.
5.3.4.1
MRMC Configuration MRMC Scripts displays the current selected radio script. Occupied bandwidth (MHz) displays the actual bandwidth occupied by the radio signal. This should not be confused with Channel Spacing, which indicates the allocated bandwidth for the RF channel. Operational mode can be ACM Adaptive, ACM Fixed, Regular (non ACM radio script). Min adaptive ACM profile is the minimum configured profile that will never be exceeded when ACM is active. Max adaptive ACM profile is the maximum configured profile that will never be exceeded when ACM is active. Adaptive Tx power admin displays is power admin is enabled. When enabled, the radio power is adjusted to the current profile that is being used.
5.3.4.2
Current TX ACM adaptive profile indicates the current ACM profile used for transmission. QAM indicates the current modulation used for transmission. Bitrate indicates the current transmitted bit rate, in Mbps.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 84 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.3.4.3
Current RX ACM adaptive profile indicates the current ACM profile used by the receiver. QAM indicates the current modulation used by the receiver. Bitrate indicates the current receiving bit rate, in Mbps.
5.3.4.4
MRMC Table This table contains all available radio scripts. Select the desired script and mode (regular or ACM). When you expand the line of the selected script (by clicking the +) all available options for the selected script will appear.
For regular scripts, select a radio script that does not have an ACM prefix. Expand the line (by clicking the +), and then click Apply.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 85 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.3.4.5
MRMC Table ACM Scripts ACM scripts can be distinguished from regular scripts by their ACM prefix. For ACM scripts, expand the line (by clicking the +).
Two options are available for ACM scripts: ACM Fixed Mode - In this mode, the ACM engine will be disabled. To select a desired profile, expand the line (click the +), and choose the profile. The radio will use only the profile you selected. ACM Adaptive Mode (shown in the page below) - In this mode, the radio will be adaptive, and the ACM engine will be enabled. To select a maximum profile, expand the line (click the +), and select the profile. The profile is the maximum that the ACM may reach, but never exceed.
When configuring ACM script with Adaptive Mode, you can determine whether or not the RFU power will be adaptive as well. In the Adaptive Power admin field, enable or disable the capability to adapt the power. In the Reference class field, configure the system reference class, which can be "Class-2/4/5B/6A" for ETSI, or FCC for FCC.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 86 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
ACM can operate in one of two scenarios: Increase capacity (increase throughput) Increase availability
The first scenario is for customers with links of several E1s in a low class, and now want to use ACM to add Ethernet traffic with lower availability. The second scenario is for customers who plan the link for a specific availability and capacity, but want lower capacity even in higher fades. In the first scenario, the user will plan the link according to low class channel, and when the condition allows, the link will increase the modulation. This increase of modulation may require lowering the output power to decrease the non-linearity of the transmitter for the higher constellations. Adaptive power options can be enabled or disabled. If disabled, the maximum Tx power in lower constellations is limited by the highest modulation. If enabled, the maximum Tx power in lower constellations is limited by the reference class configured, as listed in the following table. Reference Class Configuration
Class 2 Class 4 Class 5B Class 6A FCC
Reference QAM
4 16 64 256 4
If the adaptive feature is used, a few critical dBs can be gained in the lower constellations.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 87 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.3.5
Traffic Priority
When using ACM and the available radio bandwidth is changing, it can become necessary to drop some of the outgoing traffic. The Traffic Priority window enables you to configure whether TDM or Ethernet traffic should be dropped first. The system distinguishes between four different types of traffic: High-priority TDM trails Low-priority TDM trails High-priority Ethernet traffic Low-priority Ethernet traffic
TDM traffic is configured in the TDM Trails window (Configuration > Trails > TDM Trails). For more information on configuring TDM traffic priority, see Configuring TDM Trails on page 111. Ethernet traffic is prioritized according the priority of the QoS or Enhanced QoS queues. Ethernet traffic from queues with a lower priority are dropped when there is not enough bandwidth. For more information on configuring Ethernet traffic priority: QoS & Rate Limiting see Advanced Classifier Queue Weights on page 55. Enhanced Traffic Manager see Configuration & Parameters on page 60.
The following list details the priorities for the different Traffic Priority schemes: High TDM over Ethernet (default) iv TDM high priority v TDM low priority vi Ethernet High Ethernet over TDM i Ethernet high priority ii TDM high priority iii TDM low priority iv Ethernet low priority High TDM over high Ethernet i ii iii iv TDM high priority Ethernet high priority TDM low priority Ethernet low priority
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 88 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
To configure Traffic Priority: 1 From the Traffic priority scheme drop-down menu, select a Traffic Priority option. 2 In the High-priority Ethernet BW field, enter the available bandwidth for High-priority Ethernet traffic. 3 Click Apply. The Traffic Priority is configured. The following features should have identical configurations on both sides of the link: Each TDM trail should have the same priority. The High-priority Ethernet Bandwidth should be the same. The queue priority schemes should be the same.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 89 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.3.6
ATPC
ATPC admin - To enable/disable the ATPC (Automatic Transmit Power Control) mechanism. ATPC reference RSL - The RSL reference value for the ATPC mechanism.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 90 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.4
5.4.1
Interfaces
Ethernet Ports
In this page, you can configure Ethernet port parameters.
The following list explains the columns in the Ethernet Ports window. Operational Status is read-only and indicates whether or not the port is operating. Enabled A check mark indicates that this port is enabled. Interface Displays the port number. Connector Type Displays whether this port is using copper (RJ-45) cable or optical fiber. Speed & Duplex Displays some or all of the following parameters for this port: Auto negotiation Rate Actual Rate Actual Duplex Function Displays if this port is being used for Trunk, Access or Management. For Metro Switches, displays is the port is being used for C/N, P/N or Management. VLAN ID Lists all the allowed VIDs for this port. Learning A check mark indicates that Port Learning is enabled. Flow Control Displays whether Flow Control is On or Off.
Page 91 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Service Type Displays whether this port is a network or access point.
Automatic state propagation - This feature enables propagation of radio failures back to the line, to improve the recovery performance of resiliency protocols (such as xSTP). You can enable or disable this feature. 5.4.1.1 Configuring a specific port In the Managed Switch, Metro Switch, or Single Pipe Ethernet Ports area, you can configure the parameters for a specific port on the IDU. Single Pipe Ethernet Ports Configuration
In the Port admin field, select Enable if you want to activate the port. In the Connector type field, select RJ 45 or Optical connector type. In the Type field, the option depends on the Ethernet application, which may be from the following options: Single Pipe is not a valid field. Managed Switch - option can be Access, Trunk or Hybrid. Metro Switch - option can be Customer Network or Provider Network. Managed Switch Ethernet Ports Configuration
For Default VLAN ID (not used in the single pipe switch application), enter the VLAN ID number.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 92 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
For Auto Negotiation, select On if you want the system to control the flow of data. Flow Control (only used for the single pipe switch configuration), select On or Off to activate or deactivate the traffic control mechanism. Rate is read-only and displays the Ethernet rate. Port service type - Define whether this port is a network or access port. The Port service type is configured for the PolyView NMS. Ethernet services. Single Pipe Ethernet Ports Configuration - Optical SFP Connector
For Duplex, displays full or half duplex.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 93 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.4.1.2
Defining a LAG PORT Click Create Lag port to define a LAG port group.
Link aggregation allows the user to group several ports into a single logical channel bound to a single MAC address. Traffic sent to the ports in such a group is distributed through a load balancing function. The group is called a LAG. There can be up to three LAG groups per IDU. Only traffic ports (including a radio port) can belong to a LAG group. The following groups of ports can be in the same LAG (ports from different groups cannot be in the same LAG): Ports 1-2 and 8 (GBE ports and radio) Ports 3-7 (FE only ports)
To add or remove ports in the LAG group, select the desired port in the window. Ports selected for the LAG group are highlighted; and ports selected for deletion are cleared in the window. The system will not allow selection of ports with different configurations (such ports will not be highlighted). Ports removed from a LAG will remain with their existing parameters, but will be initially disabled to prevent loops. Deselecting all ports will clear the entire LAG port. A LAG port can be configured as LAG #1, #2, #3, since there can be up to three LAG ports in the system. When a LAG is created by adding a first port to it, the LAG will automatically inherit all characteristics of the ports, except for the xSTP role (edge, nonCeragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 94 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
edge), and the path cost. The LAG will initially receive default values for those parameters. In the Configuration page, the lag ports are listed in the Interface column.
In the Advanced line, you can click Allowed VIDs to assign VIDs to the LAG.
LAG Group Notes: For GBE LAG groups, both interfaces must be of the same type (electrical/optical). A radio port can be in a LAG with either electrical or optical line ports. All ports in a LAG group must be of the same data rate (10, 100, or 1000 Mbps). A GBE LAG group may include the radio port. The configurations must be identical in all ports before adding them to the LAG logical port.
Page 95 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.4.1.3
Defining Fault Criteria In the Fault Criteria area of the Ethernet Ports page, the following options allow you to determine which faults should be propagated back to the line.
Local LOF - When Automatic State Propagation is enabled, an LOF (Radio Loss of Frame) fault will always be propagated. Link ID Mismatch - When Automatic State Propagation is enabled, a Radio Link ID mismatch fault will always be propagated. MAC address ageing time - The aging time used by the MAC learning table can be a value between 15 and 3825 seconds. The default value is 300 seconds. Ethernet shutdown Rx profile threshold - When ACM adaptive mode is active, you can determine an Rx profile that will be considered a fault when the radio performance degrades below that profile. Local Excessive BER - When an Excessive BER alarm is raised locally, it will be propagated as a fault. Local LOC - When a Loss of Carrier alarm (only for optical GBE interface) is raised, it will be propagated as a fault. Remote Fault - If any of the events described above occurs at the remote (remote fault), it will be propagated locally as a fault.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 96 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.4.2
E1 Ports
In this page, you can configure E1 port parameters.
In the All Ports area at the top of the page, the parameters you can configure include the following: Excessive BER threshold - Click the drop-down list and select the level above which an excessive BER alarm is issued for errors detected over the radio link. Signal degrade threshold - Click the drop-down list and select the level above which a Signal Degrade alarm is issued for errors detected over the link.
5.4.2.1
Configuring the Line Coding Line code 1-8 and 9-16 Displays the T1 line coding, which can be B8ZS or AMI.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 97 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.4.3
Using an E1/T1 T-Card
The T-Card is not a stand-alone entity within the IP-10 IDU. When inserted in the system, the new interfaces become integral interfaces of the IP-10. As an example, if you insert a 16 x E1 T-Card in the IDU, no special menu will appear for it. Instead, E1s #17-32 will be added to the existing 1-16.
5.4.4
DS1 Ports
In this page, you can configure DS1 port parameters.
The parameters in this page are the same as those for the E1 Ports page above.
5.4.5
STM-1/OC-3 (T-Card)
The following diagram shows an IP-10 with an STM-1/OC-3 T-Card.
To configure the STM-1/OC-3 T-Card interface: 1 Click in the area of the STM-1/OC-3 interface, or, from the menus on the left side of the window, select Configuration, Interfaces, STM1 Ports (for an E1 board) or OC-3 Ports (for a T1 board). The following window appears:
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 98 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
2 Fill in the fields as follows: i Configure parameters in the STM-1 Configuration section. Port Admin - Select Enable to activate the interface, or Disable to deactivate it. Mute Tx - Used to force mute or unmute the T-Card interface. If muted, the radio will still receive signals, but will not transmit any. Outgoing signal clock source - the clock source used, which can be Internal clock, Loop, or STM-1 VC. The clock source and the clock source status may be different when the configuration does not match the current clock source in use, due to the signal failures listed below. If you choose Internal Clock (the default option), the quality will be SMC/SEC (ITU-T G.813). If you choose Loop (CDR mode), the signal clock source will be taken in accordance with the following table: Clock Source
Local clock Local clock
# LOF from Framer LOS from Optics Mode of Operation
1 2 LOF LOF LOS NO LOS Free run/holdover Free run/holdover
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 99 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
# LOF from Framer LOS from Optics Mode of Operation
3 4 NO LOF NO LOF LOS NO LOS N/A Lock mode (loop timing)
Clock Source
Local clock CDR
If you choose STM-1 VC, the signal will be synchronized to the signal clock derived from a TDM trail. The clock will be taken from the first VC-12 configured in the STM-1 port. There is no web support for this, but there is a way to change the VC source through the CLI using the following commands:
cd interfaces/sdh/stm1/ get sync-vc (shows the VC that the system will use as the clock
and sync)
Set sync-vc XX (XX = VC number) Clock source status The clock source that is currently set.
Synchronization VC - The VC channel that is used to synchronize the STM-1 interface. AIS VC Signaling Admin - when enabled, if a signal failure at the trail outgoing from the STM-1 interface occurs, the system will signal AIS at the VC level (AIS-V) in the V5 byte of the overhead. Line Tx Protection Mode - If you choose Normal, the system will behave regularly when configuring the system to 1+1 with the STM-1 card. The redundant STM-1 will not transmit signals unless the primary IDU performs a switch due to a failure. Choose Uni-direction MSP when the system is configured for 1+1 with STM-1 cards. Both cards will transmit, and the decision of which will actually function, will be decided by other equipment connected to it.
ii Configure parameters in the Trace Identifier (J0) section. Received Trace Identifier - Read-only field. The received trace identifier, used to verify ongoing connection to the transmitter. Transmit Trace Identifier - The trace identifier used to verify ongoing connection to the receiver. Expected Trace Identifier - The trace identifier that will be used to verify ongoing connection to the remote side of the link. Trace Identifier String Length - Can be between 1 and 15 characters. Excessive BER Threshold - The value can be 1e-3, 1e-4, or 1e-5. Signal Degrade Threshold - The value can be 1e-6, 1e-7, 1e-8, or 1e-9.
iii Configure parameters in the Thresholds section.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 100 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.4.6
Wayside Channel
In this page, you can configure wayside channel parameters.
The parameters you can configure include: Wayside admin - select Enable if you want to activate the channel. Capacity - select Narrow or Wide for the wayside channel capacity. Auto negotiation - select On if you want the system to control the data flow between the wayside channel and other ports activated in the system. Duplex - select Full or Half duplex. Rate - select the data rate for the port.
To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh. User Wayside channel and PTP optimized transport mode are mutual exclusive features. You should disable the PTP optimized transport mode before enabling the User Wayside channel. For more information, see Wayside Channel on page 101.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 101 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.4.7
User Channel
In this page, you can configure user channel parameters.
Admin - To enable or disable the user channel. Type - Two user channel types are available: Asynchronous RS-232 Asynchronous V.11/X.21
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 102 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.4.8
EOW
This page displays the EOW (Engineering Order Wire) channel status.
5.4.9
AIS
This page is used to enable/disable AIS (Alarm Indication Signal) Line Detection.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 103 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
If enabled, a signal failure is generated at the corresponding trail, which will cause the far end not to receive a signal (including trail ID indications). The trail status will show signal failure. In addition, an indication is sent to the relevant interface. This is not a system alarm, since the problem originates elsewhere in the network.
5.4.10
Sync Source
Synchronous Ethernet consists of the transport of a frequency timing reference through the Ethernet physical layer. It allows the receiving side of an Ethernet link to lock onto the physical layer clock of the received Ethernet signal, which was derived from a reference clock source. The receiver is therefore frequency-synchronized with the source. IP-10 allows synchronization of the frequency of the outgoing Ethernet carrier signal with any existing TDM trail.
To configure the sync source: 1 Select Primary. 2 From the IDU that is displayed, click the interface type (Line/STM-1/Radio) to select it as the synchronization source. 3 Select the interface number and click Apply. Repeat the procedure for the secondary sync source. If you choose an interface and then click Apply, the configuration will be cleared. The Sync Parameters section enables you to set the amount of time before the unit reverts back to the primary sync source. From the Sync source revertive timer field, enter the number of seconds that the unit waits before reverting to the primary sync source.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 104 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.4.11
Clock Source
The Clock Source window configures the ports that output the clock source.
The Current Configuration section displays the clock source output for each interface. You can configure each interface and select whether the clock source is based on a received sync source or the local internal IDU source. To configure the clock source: 1 From the Clock Source Selection section, click on an interface (Line/STM-1/Radio). A clock source drop-down menu is displayed. 2 From the clock source drop-down menu, select the clock source. E1 clock source - select the E1 port that outputs the clock source. Ethernet Clock source - select how the clock source is calculated: Local - internal Sync - received from sync source Radio - select the channel that outputs the clock source.
3 Click Apply. The clock source for that interface is configured.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 105 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5.5
5.5.1
Protection
Protection Parameters
In this page, you can configure IP-10 1+1 and 2+2 protection parameters.
In the Protection Admin field, Select 1+1 HSB, 2+2 HSB, or Disable, and click Apply. The following illustration shows the IDU configuration for a 2+2 HSB system. The shield icon to the left of the IDUs indicates that they are in a Protected configuration.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 106 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
The following sections appear when you select 1+1 HSB or 2+2 HSB.
5.5.1.1
Protection Configuration Protection admin - Used to enable or disable 1+1 or 2+2 protection. Protection mode - Shows if the unit is Active or Standby.
5.5.1.2
Mate Parameters Mate IP address - the IP address of the mate unit. Mate MAC address - the MAC address of the mate unit. Open Mate - a link for opening the remote mate unit.
5.5.1.3
Protection Switch Criteria External alarm #1 admin (enable/disable) - initiates a switchover when external alarm #1 is raised. Radio excessive BER admin (enable/disable) - initiates a switchover when a radio excessive BER alarm is raised. This option is only displayed when the MRMC script is regular or ACM running in Fixed mode.
5.5.1.4
Protection Commands Protection Lockout - freezes the current protection state. Protection force switch - forces a protection switchover and then freezes the protection state. Copy to mate status - Indicates the status of the Copy to mate command.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 107 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Manual Switch - issues a switchover, which will take affect when no other protection related alarms are raised. Copy to mate - copies all configurations to the mate unit (configuration synchronization between local and mate). To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
5.5.2
Radio Diversity
The Radio Diversity feature can be used with configurations that are using two antennas. There are two modes for using two antennas with a single system: 1+0 IF combining and 1+1 Space diversity. 1+1 Space diversity is a feature that enables the system to dynamically choose at every moment the best received signal between two radio carriers configured as 1+1 HSB. This allows data flow to be unaffected in the event of unwanted physical events affecting the radio channel, such as fading. It is implemented at the base-band level and thus requires no special RFU connections or upgrades. This feature is available only for IDUs which are inserted in a shelf. 1+0 (IFC - IF combining) is a feature for configurations that use two antennas with a single RFU-HP with two Rx ports and a single IDU. The selected signal line output is based upon the Rx signal at the RFU.
5.5.2.1
IF Combining Parameters IF Combining parameters are located at the bottom of the Radio Parameters window. (Configuration > Radio > Radio Parameters)
To perform delay calibration: Automatic - Click Calibrate. The system automatically calibrates the required delay between the signals from the main and diversity antennas. Manual - From Delay calibration, enter the signal delay in nanoseconds. Click Apply. RFU Mode - There are three options Main - Only the main antenna signal is selected. Diversity - Only the diversity antenna signal is selected.
Page 108 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Combined - The best signal from both antennas is selected. In order to use Combined mode, you must perform delay calibration.
RSL connector source - Select which antenna is the source for the external connector. Main - The main antenna is selected. Diversity - The diversity antenna is selected. Rx level diversity - The Rx level of the diversity antenna. Rx level combined - The Rx level of the combined signals. Delay calibration - (Only used for Combined mode) The delay between the main and diversity signals in order that they are calibrated correctly to be combined. Automatic delay calibration - Displays the system status of the automatic delay calibration feature. Success - the system has successfully calibrated the signal delay Failure - The system cannot automatically calibrate the signal delay. No action - The system has not performed an automatic delay calibration. Automatic delay calibration can only be performed when the system is error-free and there is no negative weather conditions. 5.5.2.2 Space Diversity 1+1 Baseband This section explains how to configure the Radio Diversity feature for a 1+1 Baseband configuration. The decision for the best signal line output is based upon performance of the modems.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 109 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Radio Diversity - Select Space diversity and click Apply, to enable the radio diversity feature. The Diversity Status section contains the following fields: Switch Counter - Displays the number of times that there was a switch between the main and standby IDUs Receive radio traffic - Which RFU is providing the signal to the active IDU. Operation mode - Displays whether Radio Diversity is enabled. The Revertive mode feature enables the system to automatically revert to the local RFU after it has switched to the mate RFU. The Revertive Parameters section contains the following fields: Revertive mode - Select Revertive to enable the system to revert back to the primary RFU. Primary RFU - Select whether the Local or Mate is the primary RFU. Revertive timer (seconds) - Configures the number of seconds that the system waits before reverting back to the primary RFU. The system only reverts to the primary RFU when the signal contains no errors. The Force Active section enables you to manually switch the active radio. Switch Request button - Clicking Switch Request, sends to message to the system to switch to the opposite radio. In a situation where the system does not allow you to switch radios using the Switch Request button, you can use the Force to radio option. Force to radio - This command forces the system to switch to the selected option from the drop-down menu. Select one of the following options:
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 110 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Local radio - When the Mate radio is active, select this option to force the system to switch radios. Mate radio - When the Mate radio is active, select this option to force the system to switch radios. Click Apply. The radios are switched.
5.6
5.6.1
Trails
Configuring TDM Trails
This page is used to configure the FibeAir IP-10 Cross Connect (XC) system for operation. FibeAir IP-10 Cross Connect system serves as a node in a microwave radio network. The system is designed to comply with requirements of a node in a network that aggregates several sites (downlinks) into a radio pipe (uplink). It can also be deployed in a mesh network configuration. The system consists of up to six IDUs placed together in a single chassis, for TDM traffic cross connect. The following figure displays a nodal enclosure that can contain up to six IP-10 IDUs:
Once the IDUs are linked through the common backplane (as shown in the photo above), the XC system is constructed by building trails. To configure the trails for Cross-Connect operation: 1 Start the IP-10 Web Management application. The following web page is an example of the IP-10 IDUs that appear in a nodal configuration.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 111 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Trail building is only done via the Main IDU (Slot 1 at the bottom). However, you can select any other IDU to set other configuration parameters for all the other IDUs in the shelf. 2 On the left side of the main window, select Configuration > Trails > TDM Trails. Initially, the page that appears is empty. 3 Click Add, to create a new trail. The Add New Trail window appears. 4 To select the E1/T1 ports for the trail, in the Add New Trail window: i Click the E1/T1 interface in any IDU ii Select the E1/T1, as shown in the example below.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 112 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
iii For STM-1/OC-3 trails, the window appears as follows:
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 113 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
5 To select the VC number you want to assign to the trail: Click the RF interface in any IDU, as shown in the example page above. 6 In the Add New Trail window, configure the new TDM trail. Configure the Protection options. If you want a secondary trail to cover the main trail if it fails, you must choose one of the following options: Protected 1+1 - used for an SNCP protected trail, with permanent use of bandwidth in both paths. Protected ABR - protected ABR (1:1), used for an SNCP protected trail with better use of the radio capacity in the unused path. If you chose Protected 1+1 or Protected ABR, a second interface will appear in the Add New Trail window, as follows: In the Trail ID field, enter the ID of the trail. This ID is used to ensure that the flow of data over the link matches the trail designations. In the Trail Description field, enter a textual description of the trail for further identification purposes. In the ACM Priority field, select High or Low. Adaptive Coding & Modulation employs the highest possible modulation during changing environmental conditions, which may be from QPSK to 256 QAM. If you select High for priority, the system will ensure that this trail is used to pass traffic when throughput for other trails is less efficient. In the Reserved/Operational field, set the trail to Operational to enable its operation. If you want to define the trail, but keep it inactive for the time being, select Reserved.
5.6.1.1
TDM Trails Configuration Notes For the trail to function properly, it must be configured accordingly on both sides of the link. If a unit (IDU) is disconnected from the nodal enclosure and ceases to function as part of the shelf configuration, the removal will be acknowledged as an alarm. The IDU can then function as a stand-alone unit, using a "default" E1/T1 configuration. You can configure E1/T1 ports in the E1/T1 Ports page:
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 114 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
However, note that you do not enable the ports in this page. The ports are enabled only in accordance with the trails that you configure, as described in this guide. 5.6.1.2 Connected Ports The following is an example of connected trail ports and their system status. Example of Trail List for the E1/T1 Interface
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 115 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Example of Trail List for the STM-1/OC-3 Interface
5.6.1.3
Cross Connection at the KLM Level Cross connection at the KLM level operates the same way as that for E1s. When a trail is defined, you can choose one of the interfaces to be an STM-1 VC-12. Note that in the CLI (Command Line Interface), this is done by setting the interface type to STM1 instead of Line. For example, for a trail between VC#1 in the radio and VC-12 #1 in the STM-1 interface of slot number one, you would use the following command:
add-trail id1 desc1 high operational unprotected 1 stm1 1 1 radio 1
As with other interface types, the number after the interface type represents the interface number. For STM-1, this means which VC-12 to use. The KLM slot to be used corresponds to the VC number chosen, as specified in the ITU-T G.707 clause 7.3 standard.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 116 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
The following table summarizes:
Thus, for example, interface number 35 corresponds to TS#35 in the above table, which is KLM address 252 (TU-3#2, TU-2#5, TU-12#2).
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 117 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.
6.1
Service OAM
MAID List
MAID (Maintenance Association Identifier) is an identifier for a Maintenance Association, unique over the domain that CFM is to protect against the accidental concatenation of service instances. The MAID has two parts: the Maintenance Domain Name and the Short MA Name.
6.1.1
MAID List Columns
# is the domain number (internal number of the displayed function). Status is the status of the current domain, which can be one of the following: No MEPs - only MAID configured, no MEPs. This state is used for empty domains, before defining MEPs, or for a domain that contains only MIPs. Monitoring - CFM (CCM) - proactive monitoring is running, no error found. Failure - connectivity error in at least one MEP. Domain name is the maintenance domain name. Level is the maintenance domain level. Association name is the maintenance domain association name. VLAN ID is the identification # of the VLAN Send CCM shows the CCM status: Disable - no continuity (CCM) frames are sent from the local MEP to remote MEPs. Enable - continuity (CCM) frames are sent from the local MEP to remote MEPs. CCM interval is the (periodic) time interval during which CCM messages are sent. Valid values include 1Sec, 10Sec, 1Min, and 10Min.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 118 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Click the + in each MAID entry for more options.
6.1.2
MAID List Operations
Click Add to add a new MAID.
In the Add Maid window, for Domain name specify the maintenance domain name. Level is the maintenance domain level. Association name is the maintenance domain association name. VLAN ID is the MAID VLAN ID.
To delete a MAID, from the MAID list section mark the checkbox at the end of its line, and click Delete selected. Click Apply to apply the changes. Click Refresh to refresh the page.
6.1.3
MAID List MEPs
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 119 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.1.4
Local MEP
Local MEP Columns: MEP ID - the local MEP ID. Direction - MEP direction (up or down). Ethernet port - the Ethernet port the MEP is located on. MAC address - Ethernet protection MAC address. Priority - the Pbit priority that the CCM message carries. LDI - Local Defect Indication. If the value Yes, a + in the right corner of the table describes the reasons for this bug. Connected - Local MEP connection status.
Add - add new local MEP. Delete selected - delete the selected local MEP.
The following parameters can be configured from the Add MEP to Port window: Ethernet port - Displays the selected port number on which the local MEP is located. Local MEP ID - The ID of the MAID local MEP. Level- Specify the MAID domain level. VLAN ID - Specify the MAID VLAN. Direction - The local MEP direction. Priority - The Pbit priority that the CCM message carries.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 120 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.1.5
CCM Configuration
The following options are available in the CCM Configuration section of the MAID List window: Send CCM - Select Disable if you don't want continuity messages (CCM) sent over the specific MAID. Select Enable if you want continuity messages (CCM) sent over the MAID. CCM Interval - Set the MAID time interval, which can be 1 second, 10 seconds, 1 Minute, or 10 Minutes.
6.1.6
Remote MEP
This section discusses the Remote MEP section of the MAID List window.
6.1.6.1
Remote MEP Columns The following list explains the columns in the Remote MEP section of the MAID List window. MEP ID - the remote MEP ID. Actual MAC address - The MAC address of the remote MEP, which the local MEP recognizes. Configured MAC address - Used when you decide to specify a selected MAC address for the remote MEP. Status - The local MEP connection status. Cross Check - Indicates if the current remote MEP was cross checked (preconfigured) or learned from incoming CCMs. RDI - Remote Defect Indication. Ping - Run ping (loopback) from the local MEP to a specific remote MEP ID by clicking the ping icon. Automatic Linktrace Displays whether Automatic Linktrace is enabled for this MEP. The checkbox column is used to delete the selection or issue a linktrace (ETH-LT) command from the local MEP to the current remote MEP.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 121 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.1.6.2
Remote MEP ping window Click the Ping to open the Remote MEP ping window.
The upper part of the window provides a short summary of the MAID and the remote MEP being pinged. The lower part shows the ping success rate percentage (LBM packet transmission over the received LBR packets).
6.1.6.3
Adding a new remote MEP From the Remote MEP section, click Add. The Add Remote MEP window is displayed.
Domain name - Maintenance domain name (appears automatically to prevent errors). VLAN ID - MAID VLAN (appears automatically to prevent errors). Remote MEP ID - the ID of the remote MEP. Configured MAC Address - (Optional) You can configure a specific MAC address.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 122 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.1.7
Linktrace
Mark a remote MEP checkbox (only one) and click Linktrace, to trace the link.
The upper part of the window provides a short summary of the MAID and the Remote MEP being traced. In the Linktrace Hops table: Reply TTL shows the hop number. Mac Address shows the hop (MEP/MIP) MAC address. Relay Action shows the hop LTM relay action. You can click Ping to ping a particular hop. Automatic Link-trace results appear at the bottom of the page. The table is refreshed automatically every fixed period of time (configurable, set to 15 min by default), displaying the last updated date and time.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 123 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.2
MEP & MIP List
This page shows in which Ethernet port the user defined an MEP or MIP.
6.2.1.1
Ethernet Port columns Ethernet Port - Shows the Ethernet port number. MAC Address - Shows the Ethernet port MAC address. Connector Type - Shows the Ethernet port connector type. Function - Shows the Ethernet port function. MEP or MIP Defined - When marked with a check indicates that you defined an MEP or MIP on this port.
6.2.1.2
Port MEPs columns MEP ID - the local MEP ID. Domain Name Level Association Name VLAN ID Direction - MEP direction (up or down). Send CCM CCM Interval Priority LDI
6.2.1.3
Port MIPs columns Domain Name Level -
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 124 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.2.2
Add MEP to Port
Click the Add button to add new local MEPs on the port.
Ethernet port - The port you will be adding (appears automatically to prevent errors). Local MEP ID - The ID of the local MEP (appears automatically to prevent errors). Level - Select the MAID level. VLAN ID - The MAID VLAN (appears automatically to prevent errors). Direction - select the MEP direction (up or down). Priority - Select the Pbit priority that the CCM message carries.
6.2.3
Add MIP to Port
Click the Add button to add MIPs from specific levels.
Ethernet port appears automatically to prevent errors. For Level, select the MIP level.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 125 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.3
Advanced
Under Service OAM in menu list on the left side of the window, click Advanced for additional MEP/MIP operations.
6.3.1
Manual Ping
Click the Manual Ping item to send a ping to the remote MEP/MIP.
MAC address is the target MEP/MIP MAC address. Level is the MAID level. VLAN ID is the ID of the VLAN. Priority is the Pbit priority bit for the outgoing ETH-LBM packets.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 126 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
6.3.2
Manual Linktrace
Click the Manual Linktrace item to send a linktrace command to the remote MEP/MIP.
MAC address is the target MEP/MIP MAC address. Level is the MAID level. VLAN ID is the ID of the VLAN. Priority is the Pbit priority bit for the outgoing ETH-LTM packets.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 127 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
7.
7.1
Diagnostics & Maintenance
Radio Loopback
In this page, you can set the parameters for a radio loopback test.
The parameters you can configure include: Timeout - the amount of time you want the test to run. IF loopback - select On if you want to perform an IF test. RFU RF loopback - select On if you want to perform an RFU RF test.
To apply any change you made and start the test, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 128 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
7.2
PDH Line Loopback
In this page, you can set the parameters for a PDH loopback test.
The parameters you can configure include: Timeout - the amount of time you want the test to run. # loopback - for each line interface, select On if you want to perform a loopback test, Off if you don't want to perform a test for that line, or Loopback towards radio to test the radio data flow.
To apply any change you made and start the test, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
7.3
SDH Loopback
In this page, you can set the parameters for an SDH loopback test.
Loopback timeout - the amount of time you want the test to run (in minutes).
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 129 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Line Loopback - select Enabled if you want to perform a loopback test, or Disabled if you don't want to perform a test for that line.
7.4
Configuration Management
In this page, you can perform system configuration operations.
7.4.1
Overview
Uploading a configuration involves the following steps: 1 Create archive - This command creates a default archive in the target (IDU). The IDU configuration will first be copied to this location. 2 Upload Archive - Uploading the IDU configuration to the host PC.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 130 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
7.4.2
Uploading or downloading an archive
Config download and upload status - Displays the current status of archive upload and download.
Click Upload Archive(s) to upload the system configuration archives to the server. Click Download Archive(s) to download configuration archives from the server to the local system.
7.4.3
Configuration Backup Management
This section describes how to backup a configuration to an archive or to restore all or part of the system to a previously archived configuration. There are four commands in this section that you can activate in this section. Click the command and a warning window is displayed to ensure that you want to continue with the selected action. Backup All Archives - Creates an archive of the current configuration of all units on the shelf. Backup Selected Unit - Creates an archive of the current configuration only for the selected slot. Restore All Units - Restores the configuration settings of all units on the shelf to the archived configuration in the file. Restore Selected Unit - Restores the configuration settings only for the selected slot to the archived configuration in the file.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 131 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
7.4.4
Archiving unit information
You can use the Create Archive command in the Unit Information section to create an archive of the IDU unit information. This information is displayed in Configuration > General > Unit Parameters. The archive includes unit information for all the IDUs.
Click Create Archive. A warning window is displayed. Click OK to continue and create an archive file or Cancel to return to the Configuration Management window. Unit info creation status - indicates whether or not the configuration file was created successfully. Unit info upload status - indicates whether or not the configuration file was uploaded successfully from target to host.
7.4.5
Configuring the FTP parameters
From the bottom of the Configuration Management window, select FTP Parameters. The FTP Parameters window is displayed.
Host IP - IP of the host where the archive is to be stored. Host path - path in the host (FTP directory) where the archive is to
be stored. For the default FTP path use set // for Windows, or set / for Linux.
User name - the user name for the FTP session. User password - password for the FTP session. If you use the default user name (anonymous), use the host login for the password.
To apply changes you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 132 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
7.4.6
Resetting the configuration
You can reset all of the IDUs to the default factory configuration. In the Set to Default Configuration area: Click Activate to set all the units to the default configuration.
A warning window is displayed. Click OK to reset the units or Cancel to return to the Configuration Management window.
7.4.7
Viewing the archive status
The Configuration Status window displays the most recent configuration management actions for each unit. Click Unit Configuration Backup Information to display the Configuration Status window.
The Configuration Status window contains the following columns: Slot Number Number of the IDU. Creation Time Date and time that the archive was created. Archive Size Size of the archive file in Kb. Last Operation Most recent configuration operation that was performed. Operation Time Date and time of the most recent configuration operation that was performed. Operation Status The unit status for configuration operations.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 133 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
7.5
Software Management
In this page, you can perform system software operations.
In the Software Management Status & Commands area: Status download - last software download status. Status install - last software installation status. Click Download to download newer packages from the remote server (without installation). Click Upgrade to upgrade all installed or requested packages. Click Rollback to undo the recent IDU application upgrade operation (one step back). Packages are still upgraded after a rollback is applied to the IDU! Rollback does not reverse a "downgrade" operation. To do so, use the "upgrade" command instead. Old Version: Click Download to download a package file for downgrade. Click Downgrade to install all downloaded files (for downgrade). The downgraded version will be activated only after a cold reset. New Version:
From the bottom of the Configuration Management window, select FTP Parameters. The Remote Server FTP Parameters window is displayed.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 134 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Server IP address and path - remote software update server URL, where the software updates reside. User name - login user name for the remote server. User password - password for the remote server.
To apply changes you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
7.6
RFU Download
In this page, you can perform RFU software download.
To perform the download, click Software Download. RFU software download status - shows the current state of RFU software download. RFU software download progress - shows the download progress.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 135 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
7.7
IDU-RFU Interface Monitoring
In this page, you can monitor the IDU-RFU traffic.
RFU receiver errors - monitors IDU-RFU interface errors detected by the RFU. IDU receiver errors - monitors IDU-RFU interface errors detected by the IDU
7.8
Resets
In this page, you can perform a reset operation on some or all of the IDUs in the shelf.
Shelf cold reset - Resets all the IDUs Extensions cold reset - Resets only the extension IDUs Reset a specific slot - Resets a specific IDU.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 136 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
7.9
File List
This page displays all application related files on the disk.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 137 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
8.
8.1
Security
Security Configuration
In this page, you can configure IP-10 security.
Upload public key status - The current status of the uploading process. Upload Public Key- Click Upload Public Key to upload the public key of the element. Download security status - The current status of the digital certificate download process. Download certificate (button) - Click to download the Target certificate (WEB server digital certificate) or Target ca certificate (WEB CA digital certificate) to the element. Download Certificate Parameters Security file name - Name of the digital certificate file. Security file type - The digital certificate type. The options include "Target certificate" for WEB server digital certificate, or "Target ca certificate" for WEB CA digital certificate.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential Page 138 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Security file format - The format of the downloaded digital certificate. Options include Pem or Der. WEB CA certificate - Select Enable if the downloaded file is WEB CA digital certificate or Disable if the file is "WEB server digital certificate". Security Parameters WEB Protocol - Determines whether the Web protocol is HTTP or HTTPS (Secured HTTP). Telnet protocol admin - Allows you to enable or disable the telnet protocol. Automatic logout period - The amount of minutes the system will wait for web activity before closing the management session. FTP Parameters Link - Use this link to configure FTP parameters. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To update the information, click Refresh.
8.2
Users & Groups
This page displays the users and groups defined in the system.
Click Add User to create a new user to the element. The Add User window is displayed.
In the Add a user window, enter the following information: User privilege - Can be one of the following: Viewer - This user cannot configure parameters, but only view them.
Page 139 of 167
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Operator - This user can configure all parameters in the system, except for security-related parameters (such as adding privilege groups). Admin - This user has all Operator privileges, as well as the ability to add new users. Tech (technician) - Has all Admin privileges, as well as access to the Linux OS shell.
User name - The name you want the user to have. Password - The password that will authenticate the user. Expiration date Click the calendar icon and select the expiration date for the users password. Password Aging Select the number of days for which a password is valid for this user. To apply any change you made, click Apply. To close the Add a user window, click Close.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 140 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
9.
Appendix A FibeAir IP-10 Alarms Table
The following table lists IP-10 alarms and provides information about their possible causes and corrective actions.
Name
ext-in-alarm
ID
101
Description
%1 Some bridge configuration may have been lost during last system reset.
Severity
Indeterminate
Origin
IDU
Probable Cause
User configured Input problem.
Corrective Action
Check source description, and correct accordingly.
Bridgeconfigurationloss
201
Warning
IDU
Power failure during configuration change.
Verify bridge configuration.
1 1 eeprom-accessfailure 2201 Error in TDM drawer type detection Major IDU 2 Inserted drawer not supported. Hardware error. 2 3 1 excessive-ber 301 E1/DS1 excessive BER on port #%1 Major IDU Line is not properly connected. External equipment is faulty. 1 2 3 4
Make sure drawer is properly inserted. Power cycle the system. Replace drawer Reconnect line. Check line cables. Check external equipment. Power cycle the system.
loopbacktowards-line
302
E1/DS1 loopback towards line on port #%1 E1/DS1 loopback towards radio on port #%1
Major
IDU
User configured system to loopback mode. User configured system to loopback mode.
Cancel loopback configuration.
loopbacktowards-radio
303
Major
IDU
Cancel loopback configuration. 1 2 3 4 Reconnect line. Check line cables. Check external equipment. Power cycle the system.
Page 141 of 167
1 loss-of-signal 304 E1/DS1 loss of signal on port #%1 Major IDU
Line is not properly connected. External equipment is faulty.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Line is not properly connected. External equipment is faulty.
Corrective Action
1 2 3 4 Reconnect line. Check line cables. Check external equipment. Power cycle the system.
Signal-degrade
305
E1/DS1 signal degrade on port #%1
Minor
IDU
std-trap-linkdown std-trap-link-up
308 307
E1/DS1 link down E1/DS1 link up E1/DS1 unexpected signal on port #%1
Indeterminate Indeterminate
IDU IDU 1 Port is disabled. Line is connected to a disabled port. 1 2 Enable relevant port. Disconnect cable from relevant port. Make sure all radio links are errorless along the path. Make sure source PDH signal is being received. Re-check synchronization path configuration. Check connection of FE cable. Replace FE cable.
unexpectedsignal
306
Warning
IDU
1 1 Eth-clocksource-signalfailure Sync Ethernet clock source signal failure Radio error along the sync path. Invalid clock signal at clock source. Configuration error. 3
4001
Major
IDU
Eth-loc-alarm
401
Ethernet loss of carrier on port #%1
1 Major IDU 2
FE cable disconnected. Defective FE cable.
Eth-tx-mutealarm
402
Ethernet Tx mute override on port #%1
Warning
IDU
Radio LOF/EXBER/Link ID on local or remote side (in pipe application). 1 Cable is not connected to the port. Cable is defective.
Check link.
gbe-loc-alarm
403
Gigabit Ethernet loss of carrier on port #%1
1 2
Major
IDU 2
Connect cable to the port. Replace cable.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 142 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Gigabit Ethernet SFP not inserted on port #%1 Gigabit Ethernet SFP Tx fault on port #%1 GBE Tx mute override on port #%1 Ethernet link down Ethernet link up Floating IP is enabled in a system configured to 1+0. An extra IP address is being unnecessarily used. Floating IP locked to fixed unit following excessive protection switches
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
1 Check SFP connector. Replace fiber.
gbe-sfp-alarm
404
Major
IDU
SFP is not inserted. 2
gbe-sfp-txalarm
405
Major
IDU
SFP malfunction. Radio LOF/EXBER/Link ID on local or remote side.
Replace SFP.
gbe-tx-mutealarm Std-trap-linkdown Std-trap-link-up
406
Warning
IDU
Check link.
408 407
Indeterminate Indeterminate
IDU IDU Protection admin is "disabled" but floating IP address is configured (value is different than 0.0.0.0). Set floating IP address to 0.0.0.0. Enable protection.
Fip-invalidprotection-conf
5002
Warning
IDU
Or
floating-ip-filterlock-alarm
5001
Major
IDU
Constant protection switches due to permanent errors in radio.
Perform protection lockout.
1 1 File-load-erroralarm 501 Firmware file load error (%1) Critical IDU 2 Firmware file is missing. System error on power up. 2 3 File-not-foundalarm 502 Firmware file not found (%1) Critical IDU Firmware file is missing. 1 2
Move Management to port 2. Download firmware file. Reset system. Download firmware file. Reset system.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 143 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Fade in the link. Defective IF cable. Fault in RFU. Fault in IDU.
Corrective Action
1 2 Check link performance. Check IF cable, and replace if required. Replace RFU. Replace IDU.
Radioexcessive-ber
601
Radio excessive BER
Major
IDU
2 3 4
3 4
radio-link-idmismatch
602
Link ID mismatch
Critical
IDU
Link ID is not the same at both sides of link. 1 2 Fade in the link. Defective IF cable. Fault in RFU. Fault in IDU. Different radio scripts at both ends of the link Fade in the link. Defective IF cable. Fault in RFU. Fault in IDU.
Configure same Link ID for both sides of link. 1 2 Check link performance. Check IF cable, and replace if required. Replace RFU. Replace IDU. Make sure same script is loaded at both ends of the link Check link performance. Check IF cable, and replace if required. Replace RFU. Replace IDU.
radio-lof
603
Radio loss of frame
Critical
IDU
3 4 5
3 4 5
1 radio-signaldegrade Radio signal degrade 2 3 4 std-trap-linkdown std-trap-link-up alarms-file 606 605 701 Radio link down Radio link up Alarm file not found. CLI configuration script download failed. Indeterminate Indeterminate Major IDU IDU IDU
1 2
604
Minor
IDU
3 4
The alarm file was deleted or is corrupted.
Download alarm file.
cli-scriptdownload-failed
721
Warning
IDU
Download failure.
Retry download procedure.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 144 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
cli-scriptdownloadsucceeded
ID
Description
CLI configuration script downloaded successfully. CLI configuration script activated.
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
722
Warning
IDU
cli-scriptexecuted
723
Warning
IDU 1 Correct CLI configuration script. Download corrected script. Execute script.
cli-scriptexecution-failed
725
CLI configuration script failed.
Warning
IDU
CLI configuration script execution failure.
2 3
cli-scriptexecutionsucceeded
724
CLI configuration script executed successfully. Cold reset event. Configuration backup failed. Configuration backup succeeded. Configuration file download failed. Configuration file download succeeded. Configuration restoring failed. Configuration restoring succeeded. Configuration file upload failed.
Warning
IDU
cold-reset-event Config-creationfailed Config-creationsucceeded configdownload-failed configdownloadsucceeded config-installfailed config-installsucceeded config-uploadfailed
702
Warning
IDU
Cold reset command was issued. Retry configuration creation.
703
Warning
IDU
704
Warning
IDU
705
Warning
IDU
Download failure.
Retry download procedure
706
Warning
IDU 1 Corrupt file. Internal SW error. 1 2 Re-install file. Download and install file.
707
Warning
IDU
708
Warning
IDU
709
Warning
IDU
Retry upload procedure.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 145 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
config-uploadsucceeded entity-init-failalarm entity-init-failevent
ID
710
Description
Configuration file upload succeeded. SW error: entity initialization failure. SW error: entity %1 initialization failure. IDU extreme temperature conditions. Fan failure. General HW failure %1. Backup kernel is running. Low input voltage. Errors in TDM backplane channel in connection with main.
Severity
Warning
Origin
IDU
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
711
Major
IDU
SW error during system initialization. SW error during system initialization. The external cooling/heating system is not operating. Defective fan unit. Defective HW. The kernel (/boot/uImage) is corrupted or missing. Low input to the system. 1 Extension or main unit equipment failure. Backplane failure. Extension or main unit equipment failure. Backplane failure. IDU HW failure. T-card HW failure.
Reset system.
712
Major
IDU
Reset system.
extremetemperature fan-failure generalhardware-failure
713
Warning
IDU
Turn on external cooling/heating systems. Replace fan unit. 1 2 Reset system. Replace IDU.
714 715
Minor Critical
IDU IDU
kernel-backup
716
Minor
IDU
Reinstall the SW.
low-inputvoltage
717
Warning
IDU
Check power supply voltage. 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 Reinsert unit. Power-cycle unit. Replace unit. Check backplane. Reinsert unit. Power-cycle unit. Replace unit. Check backplane. Reinsert unit. Power-cycle unit. Replace T-card. Replace IDU.
lvds-backplaneerror-extn
729
Major
IDU 2
1 lvds-backplaneerror-main 728 Errors in TDM backplane channel for slot # %1. Major IDU 2
lvds-db-error
730
Errors in TDM channel in connection with T-card.
1 Major IDU 2
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 146 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
1 Look in Alarm Log for matching Event. In the Event: Look for exact parameter that has failed. Set the parameter again via the CLI. The alarm is cleared after reset.
2 Param-set-failalarm 718 SW error: parameter set failed. Warning IDU SW error. 3
Param-set-failevent Public-keyupload-failed Public-keyuploadsucceeded warm-resetevent corruptdifferentialdelay-valuesfound-event
719
SW error: parameter %1 set failed. Public key upload failed. Public key upload succeeded. Warm reset event. Corrupt differential delay values found.
Major
IDU
SW error.
Reset system.
726
Warning
IDU
727
Warning
IDU SW reset in the system. Inventory file was found to be corrupt upon system power up. 1 Inventory file is missing. Inventory file was found to be corrupt upon system power up. 1 2 Download inventory file. Reset system. 1 2 Download inventory file. Reset system.
720
Warning
IDU
2502
Major
IDU
corrupted-filealarm
801
Inventory file (%1) is corrupted.
Critical
IDU
file-not-foundalarm
802
Inventory file (%1) was not found.
Critical
IDU
Inventory file is missing.
1 2
Download inventory file. Reset system.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 147 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 2 Configuration error. Defective Ethernet cables or cables disconnected. Fault in external equipment
Corrective Action
1 Check LAG physical configuration in both sides of link. Check cables and replace if required. Replace IDU.
Lagdegradationalarm
2701
Degraded functionality in LAG #%1.
Major
IDU 3
Configuration error. lag-loss-alarm 2702 LAG #%1 status down. Critical IDU Defective Ethernet cables or cables disconnected. Fault in external equipment demo-licenseabout-to-expirealarm Demo license is about to expire within 48 hours.
Check LAG physical configuration in both sides of link. Check cables and replace if required. Replace IDU. 1 Terminate demo license. Activate operational license. Terminate demo license. Activate operational license.
908
Major
IDU
Demo license activated by user.
1 demo-licensealarm 901 Demo license. Warning IDU Demo license activated by user. 2
license-demoexpired license-demostart-by-user license-demostop-by-user
902 903
Demo license expired. Demo license started by user. Demo license stopped by user.
Warning Warning
IDU IDU
Demo trial period has ended.
Obtain a valid license.
904
Warning
IDU
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 148 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
1 Compare unit's serial number with license serial number (3 left characters of license code with 3 right characters of Unit's serial). Check code license generation sequence. Contact Tech support.
license-load-fail
905
License load failure %1.
Warning
IDU 2
Invalid serial number license code does not match unit's serial number. License version mismatch. 2
3 license-loadsuccesfull License loading succeeded.
906
Warning
IDU 1 Check that the code was entered correctly. Call tech support for new license generation. Fix configuration to correspond to loaded licenses. Load proper license.
licenseviolation-alarm
907
License violation %1.
Warning
IDU
Unit does not match license feature set.
1 licenseviolationdetected bridge-xml-filealarm 909 License violation detected: %1. Warning IDU User configuration doesn't match licensed feature set
1015
Warning
IDU 1 Cable is not connected between protection ports. Cable is connected to wrong port. Cable is damaged.
cabledisconnectedalarm
1001
Mate IDU cable is not connected.
Major
IDU
Connect Ethernet cable to protection port of both IDUs. Replace cable.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 149 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
configurationmismatch-alarm copy-to-matecompletedevent copy-to-matefailure-event copy-to-matestarted-event
ID
1002
Description
Mate IDU configuration mismatch. Copy to mate completed. Copy to mate failed. Copy to mate started.
Severity
Major
Origin
IDU
Probable Cause
The configurations of the IDUs are not identical.
Corrective Action
Apply "Copy to Mate" from the desired IDU.
1003
Warning
IDU Initiate another Copy to Mate command.
1004
Warning
IDU
1005
Warning
IDU 1 Check the Tx level of Active unit. Check if Active unit was set to Mute. Check Active unit's RFU.
exc-berchange-remotetx-sent-event
1006
Request for change remote transmit on radio BER.
Major
IDU
Active Tx at local side is not transmitting.
3 User command Force Protection Switch. SW fault in synchronization of databases. User issued Protection Lockout
force-switchalarm
1007
Protection force switch.
Major
IDU
Clear Force Switch Command.
ipi-xml-filealarm lockout-alarm
1008
Protection SW activity fault. Protection lockout.
Warning
IDU
Reset Standby unit. Clear Lockout command 1 Check the Tx level of Active unit. Check if Active unit was set to Mute. Check Active unit's RFU. Check PM for fade in link path.
1009
Major
IDU
lof-changeremote-tx-sentevent
1010
Request for change remote transmit on radio loss of frame.
1 Warning IDU 2
Active Tx at local side is not transmitting. Fade in the link path.
3 4
manual-switchreq-event
1011
Protection manual switch request.
Warning
IDU
User request to perform local switch
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 150 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 IDU IP addresses are identical IDU IP subnets are not identical. In stand-alone configuration: protection cable is not properly connected. In stand-alone configuration: protection cable is damaged.
Corrective Action
Check IP address and subnet definition in both units. In stand-alone configuration: check Protection cable connectivity. In stand-alone configuration: replace Protection cable.
3 mate-commfailure-alarm 1012 Mate IDU communication error. Major IDU
protectionmode-changedevent
1013
Protection mode changed to %1 %2. Request for change remote transmit on radio signal degrade.
Warning
IDU 1 2 Link Fade. Defective IF cable. RFU fault. IDU fault. There are no valid packages for download at remote server. Communi cation with remote server is down. 3 Remote server access credentials are not valid. Remote server URL is not valid. 1 2 3 4 Check link performance. Check IF cable. Check RFU. Check IDU.
sd-changeremote-tx-sentevent
1014
Warning
IDU 3 4 1
2 Software download failed.
download-failed
1101
Warning
IDU
downloadsucceeded
1102
Software download succeeded.
Warning
IDU
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 151 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 There are no valid packages for installation at local update directory. One or more package has unresolved dependencies, i.e. requires another package(s) to be installed first.
Corrective Action
install-failed
1103
Software package installation failed.
2 Warning IDU
installsucceeded
1104
Software package installation succeeded. Modem firmware file not found. Modem was not loaded successfully. Modem WD reset. Radio script (LUT) is corrupt. Radio script (LUT) not found Incompatible script: %1 %2. Radio script is corrupt. Radio script not found. MRMC file is corrupt.
Warning
IDU
firmware-filemissing-alarm firmware-loaderror-alarm modem-wdreset-event fpga-filecurrupt-alarm fpga-file-notfound-alarm incompatiblescript-alarm modem-scriptfile-corruptalarm modem-scriptfile-not-foundalarm mrmc-filecorrupt-alarm
1201
Critical
IDU
Modem file is missing. 1 2 File is corrupt. System failure.
1 2 1 2
Download Modem file. Reset system. Download file. Reset system.
1202
Critical
IDU
1203 1301
Warning Critical
IDU IDU Faulty file. File was not downloaded to system. Incompatibility between RFU and loaded radio script. File is corrupt. Download radio script LUT. Download radio script. 1 2 Change RFU. Change Radio script.
1302
Critical
IDU
1303
Critical
IDU
1304
Critical
IDU
Download file.
1305
Critical
IDU
File not found.
Download file.
1306
Critical
IDU
File is corrupt.
Download file.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 152 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
mrmc-file-notfound-alarm radio-script-notsupported-byhw-alarm Rfu-file-corruptalarm Rfu-file-notfound-alarm incompatiblerfu-tx-calibration
ID
1307
Description
MRMC file not found. radio script not supported by hardware. RFU file is corrupt. RFU file not found. Incompatible RFU TX calibration. System reset required to apply configuration changes.
Severity
Critical
Origin
IDU
Probable Cause
File not found. Configuration from another system loaded into F-series hardware. File is corrupt. File not found. RFU calibration tables require IDC SW upgrade. 1 Radio was enabled and user disabled it. Radio was disabled and user enabled it Power cable disconnected. Power supply source failure. Hardware failure. Power cable disconnected. Power supply source failure. Hardware failure.
Corrective Action
Download file. 1 2 Change radio script. Make sure right hardware is installed.
1310
Critical
IDU
1308 1309
Critical Critical
IDU IDU
Download file. Download file.
1401
Major
RFU
Upgrade IDU SW.
1 2
system-resetrequired
Perform system reboot. Change relevant configuration to current value
2901
Warning
IDU 2
1 Under-voltagecondition-ps-1 2902 Under-voltage conditions in power supply #1. Major IDU 2 3 1 Under-voltagecondition-ps-2 2903 Under-voltage conditions in power supply #2. Major IDU 2 3
1 2 3 1 2 3
Connect power supply cable. Check power supply source. Replace IDU. Connect power supply cable. Check power supply source. Replace IDU.
radio-interfacechanged-byuser-event remotecommunicationfailure if-loopbackalarm
2801
Radio interface is currently %1 by user configuration. Remote communication failure. IF loopback.
Warning
IDU
User configuration
Enable the radio interface if use of the radio is desired Check link performance. Disable IF loopback.
1501
Major
IDU
Fade in the link. User enabled IF loopback.
1601
Warning
IDU
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 153 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
lock-detectalarm
ID
Description
IF lock detection.
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Extreme temperature condition. HW failure.
Corrective Action
1 2 1 2 Check installation. Reset IDU. Check IF cable and connectors. Verify that NType connector inner pin is not spliced. Replace IDU. Replace RFU. Check IF cable and connectors. Verify that NType connector inner pin is not spliced. Replace IDU. Replace RFU. Check IF cable and connectors. Verify that NType connector inner pin is not spliced. Replace IDU. Replace RFU.
1602
Critical
IDU 2
cable-open
1701
Cable open.
Major
IDU
Cable is not connected to IDU or RFU.
3 4 1 2 cable-short 1702 Cable short. Major IDU Physical short at the IF cable. 3 4 6 1 2 communicationfailure RFU communication failure. Defective IF cable. IF cable not connected properly. Defective IDU. Defective RFU. RFU software download in progress. 7
8 9
1703
Warning
IDU
3 4 5
For High Power RF Unit: 1 Check BMA connector on OCB. Check BMA connector on RFU. Reset the IDU/RFU. Replace RFU.
delaycalibrationfailure-1 delaycalibrationfailure-2
1704
RFU delay calibration failure 1. RFU delay calibration failure 2.
1 Warning RFU Defective RFU. 2 Warning RFU Calibration cannot be completed due to notch detection.
1705
Enter delay calibration value manually.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 154 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
1 Check installation conditions. Verify operation as per product's specs. Replace RFU. Check RFU connection to BP. Check that fans are connected to PS. Replace RFU BP cable. Replace specific fan or fan drawer. Replace RFU. Check if problem repeats and if errors/alarms reported. Replace ODU.
1 extreme-tempcond 1706 RFU extreme temperature. Warning RFU 2
Installation conditions. Defective RFU.
3 1 1 Defective / non-existent fan drawer. Defective RFU-to-fan drawer connection. Defective RFU.
2 fan-failure 1707 RFU fan failure. Warning RFU
3 4
5 1 freq-setautomatically 1708 Frequency was set automatically. Warning RFU Defective RFU. 2 hardwarefailure-1 hardwarefailure-2 1709 1710 RFU hardware failure 1. RFU hardware failure 2. Critical Critical RFU RFU Defective RFU. Defective RFU.
Replace RFU. Replace RFU. 1 Check IF cable connectors. Verify that NType connector inner pin is not spliced. Replace IDU. Replace RFU.
1 low-if-signal-torfu 1711 Low IF signal to RFU. Major RFU 2 3
IF cable connection. Defective RFU. Defective IDU.
3 4
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 155 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
1 2 Check IF cable and connectors. Verify that NType connector inner pin is not spliced. Replace IDU. Replace RFU.
No-signal-fromrfu
1712
Low signal from RFU.
Warning
IDU
No RX (140 MHz) signal from RFU.
3 4
For High Power RF Unit: Check BMA connector center pin is not spliced both on RFU and on OCB. Check installation conditions. Replace RFU Check installation conditions. Verify operation as per product's specs. Replace RFU. Replace IF cable/connector. Replace RFU. Replace IDU.
Pa-extremetemp-cond
1713
RFU PA extreme temperature.
1 Warning RFU 2
Installation conditions. Defective RFU.
2 1
powerdecreased-dueto-patemperature
1737
Power decreased due to high temperature.
1 Major ODU 2
Incorrect installation. Hardware failure.
3 1 Power-failure12v 1714 RFU power failure (12v). Major RFU Defective IF cable/connect or. Defective RFU. Defective IDU. Defective IF cable/connect or. Defective RFU. Defective IDU. 1 2 3 1 2 3
2 3 1
Power-failure1point5
1715
RFU power failure (1.5v).
Major
RFU
Replace IF cable/connector. Replace RFU. Replace IDU.
2 3
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 156 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Defective IF cable/connect or. Defective RFU. Defective IDU. Defective IF cable/connect or. Defective RFU. Defective IDU. Defective IF cable/connect or. Defective RFU. Defective IDU. Defective IF cable/connect or. Defective RFU. Defective IDU. Defective IF cable/connect or. Defective RFU. Defective IDU.
Corrective Action
1 2 3 Replace IF cable/connector. Replace RFU. Replace IDU.
Power-failure24v
1716
RFU power failure (24v).
Major
RFU
2 3 1
1 2 3
Power-failure6v
1717
RFU power failure (6v pro).
Critical
RFU
Replace IF cable/connector. Replace RFU. Replace IDU.
2 3 1
1 2 3
Power-failure6v-sw
1718
RFU power failure (6v SW).
Major
RFU
Replace IF cable/connector. Replace RFU. Replace IDU.
2 3 1
1 2 3
Power-failureminus-5v
1719
RFU power failure (-5v).
Major
RFU
Replace IF cable/connector. Replace RFU. Replace IDU.
2 3 1
1 2 3
Power-failurevd
1720
RFU power failure (Vd).
Critical
RFU
Replace IF cable/connector. Replace RFU. Replace IDU.
2 3
reset-occurred rfu-loopbackactive rfu-modechanged-tocombined rfu-modechanged-todiversity rfu-modechanged-tomain
1721 1722
RFU reset. RFU loopback. RFU mode changed to Combined. RFU mode changed to Diversity. RFU mode changed to Main.
Warning Major
RFU RFU User action. Disable RFU loopback.
1723
Warning
RFU
1724
Warning
RFU
1725
Warning
RFU
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 157 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
rfu-powersupply-failure
ID
1726
Description
RFU power supply failure.
Severity
Major
Origin
RFU
Probable Cause
At least one of the PSU voltages is too low. RSL is very low (typically below -80 dBm), link is down.
Corrective Action
Replace RFU. 1 Check antenna alignment & link planning. Check link settings (TX power, TX freq). Check antenna connections. Replace local/remote RFU. Check that the fault is not due to rain/multipath fading or lack of LOS. Check link settings (TX power, TX freq). Check antenna alignment. Check antenna connections. Replace local/remote RFU. Check that the fault is not due to rain/multi path fading or lack of LOS. Check link settings (TX power, TX freq). Check antenna alignment. Check antenna connections. Replace local/remote RFU.
rx-level-out-ofrange
1727
Rx level out of range.
For RFU-C: Warning RFU RSL is too low (typically below -83 dBm) or RSL is too high (typically above -26 dBm). 3 4
1 rx-level-path1out-of-range 1728 RFU Rx level path 1 out of range. Warning RFU 2 3
Improper installation. Fading event. Defective RFU.
3 4 5
1 rx-level-path2out-of-range 1729 RFU Rx level path 2 out of range. Warning RFU 2 3
Improper installation. Fading event. Defective RFU.
3 4 5
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 158 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Defective RFU. Defective XPIC cable connection. Defective RFU. Defective XPIC cable connection. Defective RFU. Defective XPIC cable connection.
Corrective Action
1 2 Replace XPIC cable. Replace RFU.
synthesizer-1unlocked
1730
Synthesizer 1 unlocked.
Major
RFU
1 synthesizer-2unlocked 1731 Synthesizer 2 unlocked. Major RFU 2
1 2
Replace XPIC cable. Replace RFU.
1 synthesizer-3unlocked 1732 Synthesizer 3 unlocked. Major RFU 2
1 2 1 2
Replace XPIC cable. Replace RFU. Replace RFU. In XPIC mode, replace mate RFU as well. Replace RFU. Intermediate solution reduce TX power.
synthesizerunlocked
1733
Synthesizer unlocked.
Major
RFU
One of the RFU synthesizers is unlocked. Defective RFU (the RFU cannot transmit the requested TX power). RFU Transmitter muted by user. IDC SW does not support the RFU.
1 2
tx-level-out-ofrange
1734
Tx level out of range.
Minor
RFU
tx-mute unknown-rfutype uploadfirmwarecanceled uploadfirmware-error uploadfirmware-failed uploadfirmwaresucceeded uploadsoftwarecanceled
1735
Tx mute IDU SW does not support this type of RFU. RFU FW upload cancelled. RFU FW upload error. RFU FW upload failed. RFU FW upload succeeded. RFU SW upload cancelled.
Warning
RFU
Unmute the RFU transmitter. Upgrade IDC SW.
1736
Major
RFU
1801
Warning
RFU
User action.
1802 1803
Major Major
RFU RFU
Retry upload. Retry upload.
1804
Warning
RFU
1901
Warning
RFU
Retry upload.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 159 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
uploadsoftware-error uploadsoftware-failed uploadsoftware-started uploadsoftwaresucceededevent
ID
1902 1903 1904
Description
RFU SW upload error. RFU SW upload failed. RFU SW upload started. RFU SW upload succeeded.
Severity
Warning Warning Warning
Origin
RFU RFU RFU
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
Retry upload. Retry upload.
1905
Warning
RFU
1 2 1 Local MEP error indication. Remote MEP error indication. Remote MEP loss of connectivity. 3 4
Check MAID definitions. Check remote MEP definitions. Check local MEP definitions. Run "CFM traceroute" to the remote MEP, then perform "CFM ping" to each MP (Maintenance Point) in order to find the broken point. Reinsert unit. Power-cycle unit. Check backplane. Re-insert unit. Power-cycle unit. Check backplane.
cfm-failure
2001
Ethernet services failure.
2 Warning IDU 3
1 bp-lof-alarm 2301 TDM backplane LOF for slot #%1. Critical IDU 2 1 communicationlost-with-idu 2302 Communication s lost with IDU #%1. Critical IDU 2
Extension or main unit equipment failure. Backplane failure. Extension or main unit equipment failure. Backplane failure.
1 2 3
1 2 3
extractiondetected
2303
IDU #%1 extraction detected.
Warning
IDU
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 160 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
idu-presencenot-detected
ID
Description
IDU #%1 presence not detected. IDU #%1 insertion detected.
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
IDU with TDM trails mapped to it was extracted from shelf.
Corrective Action
1 2 Insert IDU in shelf. Delete relevant TDM trails
2304
Minor
IDU
insertiondetected
2305
Warning
IDU 1 SW update performed in one unit only. Units with different SW version connected as protection mate Equipment error in extension IDU. Backplane communicatio ns error. Backplane communicatio ns failure. Equipment failure in extension units. SW update performed in main unit only. Units with different SW version connected as extensions. Perform SW update to mate unit
mate-versionmismatch
2306
SW running version mismatch with mate.
Major
IDU
1 protectionadminmismatch 2307 Protection mode mismatch for IDU #%1, %2. Minor IDU
1 2 3
Re-configure XC settings. Reset extension unit. Replace extension unit
1 protectionmode-mismatch Protection activity error for IDUs #%1, %2.
1 2
2308
Major
IDU
Replace units, one by one. Check backplane.
1 SW running version mismatch with extension unit in slot %1.
unit-versionmismatch
2309
Major
IDU
Perform SW update to relevant extension unit.
heartbeat a2ninitializationfailure
2101
Heartbeat Access to Network initialization failure.
Indeterminate
IDU 1 Equipment is faulty. SW/HW versions mismatch. 1 2 Power cycle the system. Check SW versions
2603
Critical
IDU
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 161 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Error in remote optical equipment configuration. Error in J0 expected string configuration. Error in J0 length configuration.
Corrective Action
j0-mismatch
2612
J0 Trace Identifier Mismatch.
2 Minor IDU
Check that remote equipment sent J0 string and length equals expected J0 configuration.
loopback-atstm1
2610
Loopback at STM-1 line interface. STM-1/OC-3 mute override.
Major
IDU
User configured loopback at STM1/OC-3 interface. User configured STM-1/OC-3 interface as silent. 1 Line is not properly connected. Cable is faulty. External equipment is faulty. Line is not properly connected. Cable is faulty. Equipment is faulty. STM-1/OC-3 SFP not attached. Line is not properly connected. Cable is faulty. Equipment is faulty. STM-1/OC-3 SFP not attached.
Cancel loopback configuration. Configure STM-1/OC3 interface to transmit. 1 2 3 4 Reconnect line. Check line cables. Check external equipment. Power cycle the system. Reconnect line. Check line cables. Check external equipment. Attach SFP. Power cycle the system. Reconnect line. Check line cables. Check external equipment. Attach SFP Power cycle the system.
mute-override
2608
Warning
IDU
stm1-excessiveber
2605
STM-1/OC-3 excessive BER.
Major
IDU
2 3
1 2 3 4 5
stm1-lof
2602
LOF in STM1/OC-3.
2 Critical IDU 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
stm1-los
2601
LOS in STM1/OC-3.
2 Critical IDU 3 4
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 162 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
1 Power cycle the system. Replace STM-1/OC-3 card
stm1-pllunlocked
2611
STM-1/OC-3 PLL unlocked.
Critical
IDU
Hardware failure in STM-1/OC-3 card.
1 stm1-sfp-notdetected 2604 STM-1/OC-3 SFP not detected. Major IDU
SFP not inserted properly. Incompatible SFP type. Damaged SFP SFP not inserted properly. Damaged SFP. Line is not properly connected. Cable is faulty. External equipment is faulty. Clock source configured from wrong VC. Radio LOF or equipment failure along the path of the synchronizatio n trail. LOS or AIS at the synchronizatio n source interface in the far end of the trail.
1 2
Reconnect SFP. Change SFP
2 3 1
stm1-sfp-tx-fault
2607
STM-1/OC-3 SFP Tx fault.
Major
IDU 2 1
1 2
Reconnect SFP. Change SFP.
1 2 3 4
Reconnect line. Check line cables. Check external equipment. Power cycle the system.
stm1-signaldegrade
2606
STM-1/OC-3 signal degrade.
Minor
IDU
2 3
stm1-syncclock-signalfailure
2613
STM-1 clock source signal failure.
Major
IDU 3
Make sure the configured VC is the end-point of the synchronization trail. Check status of synchronization trail. Check status of clock source interface.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 163 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
TDM backplane LOF in connection with main.
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Extension or main unit equipment failure. Backplane failure. Network TDM trail configuration error. Signal failure in TDM trail this may be due to equipment failure or AIS at the line input. Excessive BER in TDM trail. Signal degrade in TDM trail.
Corrective Action
1 2 3 Re-insert unit. Power-cycle unit. Check backplane
extension-bp-lof
2402
Critical
IDU 2 1
failure-in-oneor-more-tdmtrails
2403
Failure in one or more TDM trails.
Warning
IDU
Check TDM trails status.
illegal-trailconfiguration
2415
Conflicting trails are configured in protected IDUs %1 and %2.
Warning
IDU
Protection was enabled in pair of IDUs between which trails were previously configured. 1 Trail end-point failure detected for one or more trails. Trail end-point failure cleared for one or more trails.
1 2
Erase relevant trails. Disable protection in pair.
invalid-trailstatus-change
2406
Invalid trail status change %1 in trail %2.
Major
IDU 2
Perform reset in end-point IDU if exists. Replace endpoint IDU.
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 164 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Trail excessive BER detected for one or more trails. Trail excessive BER cleared for one or more trails. Trail ID spelling difference between trail ends. Network TDM trail configuration error. Errors in incoming signal. Trail ID mismatch detected for one or more trails. Trail ID mismatch cleared for one or more trails.
Corrective Action
trail-excessiveBER-change
2407
Trail excessive BER status change %1 in trail %2.
Major
IDU
Check links and equipment alarms along the TDM trail.
Check trail ID at both ends of the trail. Check network trail configuration. Check trail performance (BER) along the trail path and fix errored links if needed.
trail-idmismatch
2408
Trail ID mismatch in at least one trail.
Warning
IDU
trail-idmismatchchange
2409
Trail ID mismatch status change %1 in trail %2.
Warning
IDU
Check trail ID at both ends of the trail. Check network trail configuration.
trail-protectedforced-active
2410
Trail ID: %1, path: %2 forced active.
Warning
IDU
User command force active. 1 Signal failure along the active trail's path. User issued force active command to stand-by path.
Set force active to "none" for this trail.
trail-protectedswitch
2411
Trail protection switch performed in trail %1 due to %2.
Warning
IDU
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 165 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Trail signal degrade detected for one or more trails. Trail signal degrade cleared for one or more trails.
Corrective Action
trail-signaldegradechange
2412
Trail signal degrade status change %1 in trail %2.
Minor
IDU
Check links and equipment alarms along the TDM trail.
trail-signalfailure
Major (1) Fade in a link along the trail.
trail-signalfailure-change
2414
Trail signal failure status change %1 in trail %2.
Warning
IDU
(2) Equipment failure in a network element along the trail. (3) Trail not properly provisioned along the path. 1 One or more components were extracted from the system since trails were defined. Radio scripts have been replaced by narrower scripts since trails were defined.
Check links, equipment alarms and trail configuration along the TDM trail.
Replace missing components (IDUs, T-cards). Make sure radio scripts support required number of E1/DS1 trails through radio. Delete relevant trails.
trails-mappedto-inexistentinterfaces
2413
Trails mapped to inexistent interfaces in IDU #%1.
Warning
IDU
unsuccessfulconsecutivelogin-attempts
2501
Unsuccessful consecutive login attempts for user %1.
Warning
IDU
User mistake or security event.
Reset the user account (only "secure officer" or above user types allowed).
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 166 of 167
CeraWeb User Guide
Version 6.7
Name
ID
Description
Severity
Origin
Probable Cause
1 Modem script does not support XPIC. ODU does not support XPIC. The frequency of both radios is not equal. Different type of ODU. Protection is enabled. One of the IDUs HW does not support XPIC. Different scripts are loaded in the IDUs.
Corrective Action
2 3 Insufficient system configurations for XPIC support.
4 Major IDU 5 6
insufficientconfig-for-xpic
3001
Check which condition is lacking and resolve it.
insufficientconfig-for-xpicevent
3003
Condition for XPIC not met: 0x%1
Warning
IDU A change in the XPIC recovery mechanism took place.
xsm-event
3002
%1
Warning
IDU
Ceragon Proprietary and Confidential
Page 167 of 167
You might also like
- Ceragon-IP10E CLH ANSI Product Description PDFDocument108 pagesCeragon-IP10E CLH ANSI Product Description PDFJeandelaSagesseNo ratings yet
- Ceragon Training Program 2011 VER 2 Hand OutDocument15 pagesCeragon Training Program 2011 VER 2 Hand Outdrytool100% (1)
- XPIC and Allignment 2008Document127 pagesXPIC and Allignment 2008Anonymous SuO1HHNo ratings yet
- Ceragon - 1+1 Resilient Microwave Links - Technical BriefDocument8 pagesCeragon - 1+1 Resilient Microwave Links - Technical BriefzrzahzahNo ratings yet
- Ceragon Ceragon Licenses Secure Management Licens IP 20 SL SEC MAN SICE Distributore ItalianoDocument258 pagesCeragon Ceragon Licenses Secure Management Licens IP 20 SL SEC MAN SICE Distributore Italianoosvaldo franciscoNo ratings yet
- NetWorker 9.0 Performance Optimization Planning GuideDocument80 pagesNetWorker 9.0 Performance Optimization Planning GuideRaviNo ratings yet
- ALS Series: Microwave RadioDocument14 pagesALS Series: Microwave RadioFaiz MandeelNo ratings yet
- Ceragon 1500p GuideDocument70 pagesCeragon 1500p Guidechong.cheekin8686No ratings yet
- 241 - Ceragon - LAG CONFIG - Presentation v1.0Document17 pages241 - Ceragon - LAG CONFIG - Presentation v1.0mehdi_mehdi0% (1)
- Ceragon IP20N Commissioning Draft PDFDocument10 pagesCeragon IP20N Commissioning Draft PDFMazidRahmanNo ratings yet
- AGS20.l.d.us - Lealfet and DatasheetDocument6 pagesAGS20.l.d.us - Lealfet and Datasheetsimog1972No ratings yet
- Nokia: MCRNC Operation and MaintenanceDocument6 pagesNokia: MCRNC Operation and Maintenancekhallilus100% (1)
- RAMAN Amplifier Fiber SplicingDocument5 pagesRAMAN Amplifier Fiber SplicingGheePhotobotz100% (1)
- SOLiD gGENESIS DAS CommissioningGuide V1.0.0 20210430Document47 pagesSOLiD gGENESIS DAS CommissioningGuide V1.0.0 20210430Danny MunetsiNo ratings yet
- .1 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 9311, 9312, 9322, 9326, 9332 Node B - Software Upgrade Procedure Using OAM 8.1 - Inter Release UpgradeDocument65 pages.1 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 9311, 9312, 9322, 9326, 9332 Node B - Software Upgrade Procedure Using OAM 8.1 - Inter Release UpgradeAmrit Aulakh100% (1)
- 02376-00 ATCA-2210 SCM ReferenceDocument134 pages02376-00 ATCA-2210 SCM ReferencechandanimcasterNo ratings yet
- 3gpp Ts 36.331 Version 8.0.0 Release 8 (RRC - E-Utra)Document56 pages3gpp Ts 36.331 Version 8.0.0 Release 8 (RRC - E-Utra)urfriendlyjoeNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Over Multi E1 Converter PDFDocument84 pagesEthernet Over Multi E1 Converter PDFNguyễn Tuấn ViệtNo ratings yet
- Cygwin InstallDocument4 pagesCygwin InstallRevan Faredha Apparition100% (1)
- Ceragon - Book - IP10G - ADV - V1.5Document312 pagesCeragon - Book - IP10G - ADV - V1.5Loi Nguyen Tho100% (2)
- OptiX RTN 900 V100R009C10 Device Anti-Theft GuideDocument20 pagesOptiX RTN 900 V100R009C10 Device Anti-Theft Guideflavio kranNo ratings yet
- SJ 20100705104232 002 ZXMW PR10 S400 S500 V2 01 Digital Microwave System System Description PDFDocument56 pagesSJ 20100705104232 002 ZXMW PR10 S400 S500 V2 01 Digital Microwave System System Description PDFYann KouakouNo ratings yet
- CDMA RF Planning GuideDocument460 pagesCDMA RF Planning Guidemohitverma2411100% (1)
- 1500HP-PD-11-09 17 June 2010Document96 pages1500HP-PD-11-09 17 June 2010Vincent RitzerNo ratings yet
- BTS Login DocumentsDocument5 pagesBTS Login DocumentsNnaji MauriceNo ratings yet
- RNC Operation and MaintenanceDocument51 pagesRNC Operation and Maintenancemanuel100% (1)
- Integra X DS v1.06Document6 pagesIntegra X DS v1.06Stefan HartungNo ratings yet
- Ion B SeriesDocument4 pagesIon B SerieszqandahNo ratings yet
- RNC and NodeB Health CheckDocument300 pagesRNC and NodeB Health CheckKaramoko MamadouNo ratings yet
- Ip10 CliDocument24 pagesIp10 CliLauris JurisonsNo ratings yet
- BBU3900Document3 pagesBBU3900Ardhan BoyzzNo ratings yet
- SJ 20130319141920 002 ZXMW nr8120 v20301 System Descriptionpdf PDFDocument80 pagesSJ 20130319141920 002 ZXMW nr8120 v20301 System Descriptionpdf PDFjose damianNo ratings yet
- NN10300036UA08.1 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 9353 Wireless Management System - Workstation Client Application InstallationDocument64 pagesNN10300036UA08.1 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 9353 Wireless Management System - Workstation Client Application InstallationAmrit Aulakh0% (1)
- Split Mount MW - CommissioningDocument83 pagesSplit Mount MW - Commissioningmohaelex100% (1)
- 08-9696-308 Alcatel-Lucent 9370 RNC Physical Installation May09Document58 pages08-9696-308 Alcatel-Lucent 9370 RNC Physical Installation May09mansour14No ratings yet
- Airspan 4 GlteDocument52 pagesAirspan 4 Gltesunil1978No ratings yet
- 1678MCC R42 UK Training For CommissDocument64 pages1678MCC R42 UK Training For Commisstomsamcong100% (1)
- InterReach Unison DAS ManualDocument236 pagesInterReach Unison DAS ManualAlex CoronadoNo ratings yet
- CRT 8500Document151 pagesCRT 8500Sandra Milena ViracachaNo ratings yet
- Huawei WCDMA Radio Network Access Counter and KPIDocument57 pagesHuawei WCDMA Radio Network Access Counter and KPIClaudio Garretón Vénder100% (1)
- FPRB Installation Manual For SPD Rev AC PDFDocument45 pagesFPRB Installation Manual For SPD Rev AC PDFIvan Aguilar CornejoNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 23.216Document67 pages3GPP TS 23.216VeaceslavRomanNo ratings yet
- Mobileaccess1000 System With: Lte Siso SupportDocument43 pagesMobileaccess1000 System With: Lte Siso SupporttomNo ratings yet
- Eclipse Packet Node INU INUe ETSI Technical Specifications June 2012Document11 pagesEclipse Packet Node INU INUe ETSI Technical Specifications June 2012LitoNo ratings yet
- Pathloss 4.0 & MW Link Planning Part 2Document41 pagesPathloss 4.0 & MW Link Planning Part 2Dimas RioNo ratings yet
- Nokia Configuration Tool 6 0 UserguideDocument75 pagesNokia Configuration Tool 6 0 UserguidetestnationNo ratings yet
- Configure IPasolink400Document31 pagesConfigure IPasolink400ajus adyNo ratings yet
- DownloadTool - ReleaseNoteDocument10 pagesDownloadTool - ReleaseNoteRajaiah JagariNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Manet Routing Algorithm: Under The Guidance Of: P. Ramya SruthiDocument20 pagesSimulation of Manet Routing Algorithm: Under The Guidance Of: P. Ramya Sruthipandu_harshaNo ratings yet
- IP 10G BASIC Course Handbook v3.1Document262 pagesIP 10G BASIC Course Handbook v3.1Galih Yogi100% (1)
- Ceragon - IP-10 (1+1) Procedure PDFDocument7 pagesCeragon - IP-10 (1+1) Procedure PDFnazloenNo ratings yet
- WDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsFrom EverandWDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsAchyut K. DuttaNo ratings yet
- Making Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessFrom EverandMaking Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessNo ratings yet
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiNo ratings yet
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionFrom EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNo ratings yet
- RFU C Product DescriptionDocument44 pagesRFU C Product DescriptionSergio Ramirez LezamaNo ratings yet
- Waveguide EW63Document2 pagesWaveguide EW63Christiaan NijkampNo ratings yet
- Installation ManualDocument130 pagesInstallation ManualChristiaan NijkampNo ratings yet
- Manual Alvarion Breeze ConfigDocument118 pagesManual Alvarion Breeze ConfigChristiaan NijkampNo ratings yet