Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Antipsychotic
Uploaded by
Louela de AsasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Antipsychotic
Uploaded by
Louela de AsasCopyright:
Available Formats
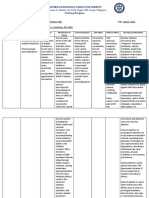
Trade Name Thorazine
Generic Name Chlorpromazine
Frequency / Route
Classification Antiemetic, Antipsychotic, Tranquilizer
Action Depresses brain areas that control activity and aggression, including the cerebral cortex, Hypothalamus, and limbic system, by an unknown mechanism.
Indication - To manage symptoms of psychotic disorders or control manic manifestations of manic-depression in outpatients - To control acutely disturbed or manic hospitalized patients - To treat nausea and vomiting
Contraindication Comatose states; hypersensitivity to chlorpromazine, phenothiazines, or their components; use of large amounts of CNS depressants
Nursing Responsibility Dont open or crush E.R. capsules. Chlorpromazine shouldnt be used to treat dementia-related psychosis in the elderly because of an increased risk of death. Protect concentrate from light. Use cautiously in patients with cardiovascular, hepatic, or renal disease because of increased risk of developing hypotension, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Trilafon
Perphenazine
Antiemetic, Antipyschotic
Depresses areas of the brain that control activity and aggression, including cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, and limbic system, by an unknown mechanism. Also prevents nausea and vomiting by inhibiting or blocking dopamine receptors in medullary chemoreceptor trigger zone and peripherally by blocking vagus nerve in the GI tract.
- To treat psychotic disorders - To treat severe nausea and vomiting
Blood dyscrasias; bone marrow depression; cerebral arteriosclerosis; coma; concurrent use of CNS depressants (large doses); coronary artery disease; hepatic impairment; hypersensitivity to perphenazine, other phenothiazines, or their components; myeloproliferative disorders; severe CNS depression; severe hypertension or hypotension; subcortical brain damage
Shouldnt be used to treat
dementia-related psychosis in the elderly. Use cautiously in patients with depression or hepatic, pulmonary, or renal dysfunction and in elderly patients Monitor temperature frequently, and notify prescriber if it rises Monitor blood pressure of patient who takes large doses especially if surgery is indicated, because of the increased risk of hypotension.
Prolixin
Fluphenazine
Antipsychotic
May block postsynaptic dopamine receptor sites in the CNS. This action may depress areas of the brain that control activity and aggression, including the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, and limbic system.
To control psychotic disorders
Blood dyscrasias, bone marrow depression, cerebral arteriosclerosis, coma, concomitant use of large amounts of another CNS depressant, coronary artery disease, hepatic dysfunction, hypersensitivity to phenothiazines, myeloproliferative disorders, severe CNS depression, severe hypertension or hypotension, subcortical brain damage
Use cautiously in patients with a history of glaucoma or renal impairment. Monitor temperature; a significant, unexplained rise can indicate intolerance and a need to discontinue drug. Notify prescriber immediately if this occurs. Watch for signs of hepatic failure, such as jaundice. Notify prescriber about worsening psychotic Symptoms Advise patient not to mix oral solution with beverages that contain caffeine (coffee, cola), tannins (tea), or pectins (apple juice). Caution patient about possible dizziness or lightheadedness. Be aware that high doses and large dosage changes in patient with a seizure disorder may lower seizure threshold. Frequently monitor blood pressure and assess for chest pain in patients with heart disease. Administer drug with food, milk, or a full glass of water to minimize GI distress. Instruct patient to notify prescriber immediately if she develops unusual symptoms.
Mellaril
Thioridazine
Antipsychotic
Depresses areas of the brain that control activity and aggression, including the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, and limbic system by blocking postsynaptic dopamine2 (D2) receptors. Drug may relieve anxiety by indirectly reducing arousal and increasing filtration of internal stimuli to the brain stem reticular activating system.
To treat schizophrenia in patients unresponsive to other antipsychotic drugs
Coma; concurrent use of drugs that inhibit the metabolism of thioridazine ,concurrent use of drugs that prolong the QT interval; concurrent use of high doses of a CNS depressant; history of arrhythmias; hypersensitivity to the drug. Severe CNS depression; severe hypertensive.
Serentil
Mesoridazine
Antipsychotic
It has a piperidine side-chain and is a metabolite of thioridazine. It acts by blocking postsynaptic CNS dopamine receptors.
To treat schizophrenia in patients who failed to respond to other antipsychotic drugs, either because they were ineffective or because intolerable adverse effects prevented attainment of effective dose
Severe CNS depression and coma; prolonged QT interval (>450 msec), including congenital prolongation; history of arrhythmias. Lactation.
Monitor serum potassium level before and during therapy, and administer potassium supplements as prescribed. Monitor patient for neuroleptic malignant syndrome Assess patient for signs of blood dyscrasias, including cellulitis, fever, and pharyngitis. Advise patient to change position slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
Navane
Thiothixene
Antipsychotic
Increases dopamine turnover by blocking postsynaptic dopamine receptors in the mesolimbic system. Eventually, dopamine neurotransmission decreases, resulting in antipsychotic effects.
To treat psychotic disorders, such as acute psychosis, psychotic depression, and schizophrenia
Blood dyscrasias, coma, hypersensitivity to thiothixene or its components, Parkinsons disease, severe CNS depression, shock, use of quinidine
Administer thiothixene capsules with food or milk if needed to minimize GI distress. Dont give drug within 1 hr of an antacid. Urge patient to avoid smoking or to begin a smoking cessation program while taking thiothixene. Encourage patient to avoid extreme temperature changes during drug therapy Use haloperidol cautiously in patients with a history of prolonged QT interval, patients with uncorrected electrolyte disturbances, Avoid stopping haloperidol abruptly unless severe adverse reactions occur. Monitor for signs of
Haldol
Haloperidol
Antidyskinetic , Antipsychotic
May block postsynaptic dopamine receptors in the limbic system and increase brain turnover of dopamine, producing an antipsychotic effect.
- To treat psychotic disorders - To treat nonpsychotic behavior disorders and Tourettes syndrome - To treat acute psychotic episodes
Comatose conditions, severe CNS depression, Parkinson's disease, lesion of the basal ganglia.
- To provide longterm antipsychotic therapy for patients who require parenteral therapy Loxitane Loxapine Antipsychotic May treat psychotic disorders - To treat psychotic by blocking dopamine at disorders and postsynaptic receptors in the schizophrenia brain.With prolonged use, - To treat acute loxapine enhances exacerbations of antipsychotic effects by causing psychotic depolarization blockade of disorders dopamine tracts, resulting in decreased dopamine neurotransmission. Blood dyscrasias, bone marrow depression, cerebrovascular disease, coma, coronary artery disease, hypersensitivity to loxapine or its components, impaired hepatic function, myeloproliferative disorders, severe druginduced CNS depression, severe hypertension or hypotension. Hypersensitivity to molindone, its components, or other antipsychotic drugs, including haloperidol, loxapine, phenothiazines, and thioxanthenes
neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Advise patient to take tablets with food or a full glass of milk or water to reduce GI distress.
Tell patient not to take antacids and antidiarrheals within 2 hours of loxapine. Caution patient to avoid alcohol while taking loxapine. Assess for signs of tardive dyskinesia, including involuntary protrusion of tongue and chewing movements.
Moban
Molindone
Antipsychotic
Stelazine
Trifluoperazine
Antianxiety, Antipsychotic
Occupies dopamine receptor sites in the reticular activating and limbic systems in the CNS. By blocking dopamine activity in these areas, molindone reduces the symptoms of psychosis, helping the patient to think and behave more coherently. Inhibits dopamine D2 receptors in the brain. It has weak anticholinergic and sedative effects but strong extrapyramidal and antiemetic effects. It controls severely disturbed, agitated or violent behaviour but may also be used for nonpsychotic anxiety.
To manage symptoms of psychotic disorders
-To treat psychotic disorders -To relieve anxiety
Preexisting CNS depression and coma; bone marrow depression, blood dyscrasias, liver disease, hypersensitivity to phenothiazines, prolactin dependent tumours. Pregnancy (1st trimester), lactation.
Assess patient for signs and symptoms of neuroleptic malignant syndrome Instruct patient to follow treatment regimen and to notify prescriber before discontinuing drug because gradual dosage reduction may be needed. Use trifluoperazine cautiously in patients with glaucoma because of drugs anticholinergic effect. Advise patient to take drug with food Instruct patient to notify prescriber immediately if she experiences difficulty swallowing or speaking
Clozaril
Clozapine
Antipsychotic
May produce antipsychotic effects by interfering with dopamine binding to dopamineespecially D4 receptors in the limbic region of the brain and by antagonizing adrenergic, cholinergic, histaminic, and serotoninergic receptors.
To treat severe schizophrenia unresponsive to standard drugs; to reduce risk of recurrent suicidal behavior in schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorders
Angle-closure glaucoma, coma, history of clozapineinduced agranulocytosis or severe granulocytopenia, hypersensitivity to clozapine or its components, myeloproliferative disorders, severe CNS depression, uncontrolled epilepsy, WBC count below 3,500/mm3
Use cautiously in patients with hepatic, renal, or cardiovascular disease and in elderly patients with dementia related psychosis Monitor temperature. Inform patient that hell need weekly blood tests. Instruct patient to avoid hazardous activitiesuntil drugs CNS effects are known. Monitor for orthostatic hypotension Monitor patients blood glucose and lipid levels as ordered Urge patient to avoid alcohol because of its additive CNS effects. Caution diabetic patient to monitor blood glucose level closely Monitor patients blood pressure routinely during therapy Notify prescriber if patient develops tardive dyskinesia or urinary incontinence. Advise patient to avoid alcohol and smoking during olanzapine therapy. Monitor patients blood glucose level routinely because olanzapine may increase risk of hyperglycemia.
Risperdal
Risperidone
Antipsychotic
Selectively blocks serotonin and dopamine receptors in the mesocortical tract of the CNS to suppress psychotic symptoms.
To manage psychotic disorders
Hypersensitivity to risperidone or its components
Zyprexa
Olanzapine
Antipsychotic
May achieve antipsychotic effects by antagonizing dopamine and serotonin receptors. Anticholinergic effects may result from competitive binding to and antago-nism of the muscarinic receptors M1 through M5.
-To treat psychosis -To treat manic phase of acute bipolar disorder -As adjunct to treat acute bipolar disorder -To treat agitation associated with schizophrenia and bipolar I mania
Angle-closure glaucoma; lactation. IM: History of CVS disease, heart surgery.
Seroquel
Quetiapine
Antipsychotic
May produce antipsychotic effects by interfering with dopamine binding to dopamine type 2 (D2)-receptor sites in the brain and by antagonizing serotonin 5-HT2, dopamine type 1 (D1), histamine H1, and adrenergic alpha1 and alpha2 receptors.
-To treat schizophrenia -To manage psychotic disorders other than schizophrenia -To treat depressive episodes in bipolar disorder -To treat acute manic episodes in bipolar I disorder
Hypersensitivity to quetiapine or its components
Geodon
Ziprasidone
Antipsychotic
Selectively blocks serotonin and dopamine receptors in the mesocortical tract of the CNS, thereby suppressing psychotic symptoms.
-To treat schizophrenia -To treat acute manic or mixed episodes of bipolar disorder -As adjunct to lithium or valproate for maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder
Concurrent use of other drugs that prolong QT interval, history of arrhythmia, hypersensitivity to ziprasidone or its components, history of prolonged QT interval, recent acute MI, uncompensated heart failure AV block, cardiac arrhythmias, congenital heart disease, history of congenital long-QT syndrome; hypersensitivity to paliperidone, risperidone, or its components
Invega
Paliperidone
Antipsychotic (Atypical)
The main active metabolite of risperidone, paliperidone selectively blocks serotonin and dopamine receptors in mesocortical tract of CNS to suppress psychotic symptoms.
To treat schizophrenia
Monitor patients (particularly young adults) closely for suicidal tendencies Monitor patient for orthostatic hypotension Instruct patient to take quetiapine with food to reduce stomach upset. Instruct patient to rise slowly from a seated or lying position to reduce the risk of dizziness or fainting. Monitor patient, especially elderly woman, for involuntary movements Monitor patients blood glucose and lipid levels routinely, as ordered Instruct patient to take ziprasidone with food to increase absorption. Advise patient to avoid hazardous activities until CNS effects are known. Drug shouldnt be given if patient has a condition that severely narrows GI tract Instruct patient to take tablet whole with liquid. Urge patient to rise slowly from sitting or lying to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
Abilify
Aripiprazole
Atypical antipsychotic
May produce antipsychotic effects through partial agonist and antagonist actions. Aripiprazole acts as a partial agonist at dopamine (especially D2) receptors and serotonin (especially 5-HT1A) receptors.
-To treat acute schizophrenia; to maintain stability in patients with schizophrenia -To treat acute manic and mixed episodes in bipolar I disorder -To treat agitation in schizophrenia or bipolar mania - To treat irritability associated with autistic disorder
Breast-feeding, hypersensitivity to aripiprazole or its components
Use cautiously in patients with CV disease, cerebrovascular disease, or conditions that would predispose them to hypotension. Also use cautiously in elderly patients because of increased risk of serious adverse cerebrovascular effects, such as stroke and transient ischemic attack. Monitor patient for difficulty swallowing or excessive somnolence Advise patient to get up slowly from a lying or sitting position during aripiprazole therapy to minimize orthostatic hypotension. Urge patient to avoid alcohol during aripiprazole therapy.
You might also like
- DRUG STUDY PsycheDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Psychejulesubayubay5428100% (1)
- Psychia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPsychia Drug StudyJustin 葉志明 Yap Delapaz100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyHennah Reblando100% (3)
- GENERIC/BRAND MECHANISM OF CLASSIFICATION ACTIONDocument3 pagesGENERIC/BRAND MECHANISM OF CLASSIFICATION ACTIONEmJay Balansag100% (5)
- Psych Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- Drug Study ZiprasidoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study ZiprasidoneArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- DS HaloperidolDocument3 pagesDS HaloperidolbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Drugs Psych WardDocument4 pagesDrugs Psych WardIris CaberteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyYasminGianneDeOcampoBarizoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyTarquin Tomada100% (2)
- Drug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)Document5 pagesDrug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)kuro hanabusa100% (2)
- Name of Drug Generic Name: Chlorpromazine BrandDocument1 pageName of Drug Generic Name: Chlorpromazine BrandkarenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- Dosage and Nursing Responsibilities for OlanzapineDocument1 pageDosage and Nursing Responsibilities for OlanzapineJeyser T. Gamutia50% (2)
- Zopiclone clinical worksheetDocument2 pagesZopiclone clinical worksheetMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- FluphenazineDocument4 pagesFluphenazineimthebossNo ratings yet
- Olanzapine Drug StudyDocument1 pageOlanzapine Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- Buspirone Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBuspirone Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Flupentixol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFlupentixol Drug StudyEmJay Balansag0% (1)
- Drug Study ClonazepamDocument3 pagesDrug Study ClonazepamJohn Rey AbadNo ratings yet
- Librium ChlordiazepoxideDocument2 pagesLibrium ChlordiazepoxideENo ratings yet
- Drug Study AntipsychoticDocument7 pagesDrug Study AntipsychoticDiana VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Clorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Imipramine Tofranil Melipamine Phenelzine Nardil Drug StudyDocument5 pagesImipramine Tofranil Melipamine Phenelzine Nardil Drug StudyHamimah Bint Ali100% (1)
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyjennachristy03100% (3)
- Chlorpromazine drug infoDocument2 pagesChlorpromazine drug infoevalyn dane50% (2)
- Anti-Depressants: Sertraline, Flouxetine, MitrazapineDocument20 pagesAnti-Depressants: Sertraline, Flouxetine, MitrazapineBobbie Sison67% (3)
- Drug Study For Thiothixene and OlanzapineDocument3 pagesDrug Study For Thiothixene and OlanzapineHARVEY SELIMNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJezzy Ann F. SarrozaNo ratings yet
- Librium Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLibrium Drug StudyCherry BangsilanNo ratings yet
- Lithium CarbonateDocument2 pagesLithium CarbonateArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine, Ferrous SulfateDocument6 pagesChlorpromazine, Ferrous SulfateFlora Angeli PastoresNo ratings yet
- Nursing Considerations for BenzodiazepinesDocument4 pagesNursing Considerations for BenzodiazepinesKuro Hanabusa100% (2)
- DRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Document5 pagesDRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Pearl Princess Guerrero100% (2)
- HaloperidolDocument2 pagesHaloperidolMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorDocument4 pagesEffectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Clozapine (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClozapine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (3)
- Alprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsDocument2 pagesAlprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- TRIAZOLAMDocument4 pagesTRIAZOLAMEzequiel RosalesNo ratings yet
- Divalproex Sodium (Depakote ER)Document1 pageDivalproex Sodium (Depakote ER)karenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- RisperidoneDocument2 pagesRisperidoneDayan Cabriga100% (1)
- Drug Study FluvoxamineDocument2 pagesDrug Study FluvoxamineAngeline de Gala0% (1)
- ClonazepamDocument2 pagesClonazepamjhezelle05100% (2)
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 pagesCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Drug Study-ChlorpromazineDocument1 pageDrug Study-ChlorpromazineMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayDocument4 pagesQuetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)Document5 pagesDrug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Olanzapine)Document1 pageDrug Study (Olanzapine)Eden Marie Francisco100% (1)
- School of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeDocument3 pagesSchool of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeMiggsNo ratings yet
- QuetiapineDocument1 pageQuetiapineHanna Se100% (1)
- Bupropion Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBupropion Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- DisulfiramDocument1 pageDisulfiramIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- ChlorpromazineDocument3 pagesChlorpromazineMarinel AgultoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyJaessa Feliciano50% (2)
- Lithium DrugstudyDocument2 pagesLithium DrugstudyJezzy Ann F. SarrozaNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic DrugsDocument81 pagesPsychotropic DrugsJoan100% (2)
- Metoclopromide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoclopromide Drug Studymarklesterdeguzman087No ratings yet
- Drug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsDocument57 pagesDrug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs ExplainedDocument78 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs ExplainedPrincess VanquirayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Mother TDocument14 pagesDrug Study Mother TEuzelle Jeena ArandaNo ratings yet
- Drug Stud1Document5 pagesDrug Stud1Louela de AsasNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument7 pagesAtrial FibrillationLouela de AsasNo ratings yet
- Violence and AbuseDocument2 pagesViolence and AbuseLouela de AsasNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric TubeDocument41 pagesNasogastric TubeLouela de Asas100% (1)
- FNCP DraftDocument14 pagesFNCP DraftLouela de AsasNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis-Med ForbesDocument8 pagesDrug Analysis-Med ForbesJustine Mark SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Health History and PhysicalDocument9 pagesHealth History and PhysicalLouela de AsasNo ratings yet
- Activated Charcoal Fights Heart Disease in Kidney PatientsDocument1 pageActivated Charcoal Fights Heart Disease in Kidney PatientsLouela de AsasNo ratings yet
- La LaDocument2 pagesLa LaLouela de AsasNo ratings yet
- Treatment For DiarrheaDocument6 pagesTreatment For DiarrheaLouela de AsasNo ratings yet
- La LaDocument2 pagesLa LaLouela de AsasNo ratings yet
- Treatment For DiarrheaDocument6 pagesTreatment For DiarrheaLouela de AsasNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psychopharmacology of Eating Disorders: A Research UpdateDocument11 pagesClinical Psychopharmacology of Eating Disorders: A Research UpdategloriaNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic DrugsDocument54 pagesAntipsychotic DrugsJackNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesQuick Reference Guide April 2019 PDFAaron ShokarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PsychopharmacologyDocument99 pagesLecture 3 PsychopharmacologyPavan chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Fresh Mock For Dec 2016 (Test 7) NEWDocument37 pagesFresh Mock For Dec 2016 (Test 7) NEWKanaga6432No ratings yet
- Schizophrenia NCP and DrugstudyDocument11 pagesSchizophrenia NCP and DrugstudyElle Monge100% (2)
- MCQsDocument10 pagesMCQsrawalian100% (2)
- PsychosisDocument11 pagesPsychosisChan's RoomNo ratings yet
- 4 5891148413604464740Document26 pages4 5891148413604464740kelid IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Dextromethorphan in Cough Syrup - The Poor Man's PsychosisDocument4 pagesDextromethorphan in Cough Syrup - The Poor Man's PsychosisMursalinNo ratings yet
- Zyprexa 020592 S 063,021086 S 041 LBLDocument5 pagesZyprexa 020592 S 063,021086 S 041 LBLbonjovicamoiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Psychosis and Its DiagnosisDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Psychosis and Its DiagnosisYazan Mahafza100% (1)
- Delirium and Acute Confusional States - Prevention, Treatment, and Prognosis - UpToDateDocument18 pagesDelirium and Acute Confusional States - Prevention, Treatment, and Prognosis - UpToDateKarina CabayNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics, Hypnotics, Sedatives and AntidepressantsDocument16 pagesAnxiolytics, Hypnotics, Sedatives and AntidepressantsChengDNo ratings yet
- NCM105 13th PsychopharmacologyDocument17 pagesNCM105 13th PsychopharmacologyKamx MohammedNo ratings yet
- Psych Meds Review MaterialDocument2 pagesPsych Meds Review MaterialMary Romaine Dela Pasion100% (7)
- Psychiatry History & Suicide Risk Assessment TemplatesDocument32 pagesPsychiatry History & Suicide Risk Assessment TemplatesDuncan Jackson100% (1)
- 229 & 229-1 EXH 1 Connecting P To VA To W SummaryDocument33 pages229 & 229-1 EXH 1 Connecting P To VA To W SummaryCarolynNo ratings yet
- Early Onset Psychotic DisordersDocument51 pagesEarly Onset Psychotic Disordersdrkadiyala2100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S2667382722000096 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S2667382722000096 MainAndrea SalazarNo ratings yet
- Stuttering Treatment and Its PharmacologyDocument8 pagesStuttering Treatment and Its Pharmacologybaba ababNo ratings yet
- Effects of Antipsychotic Drugs On Memory and AttentionDocument12 pagesEffects of Antipsychotic Drugs On Memory and AttentiondesbestNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Drugs: Presentation By-Sumaiya SadafDocument19 pagesAntipsychotic Drugs: Presentation By-Sumaiya SadafSweta ShahNo ratings yet
- AntipsychoticsDocument51 pagesAntipsychoticsShailja SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Case Study 1Document12 pagesMental Health Case Study 1api-507291324No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Anger, Hostility, and AggressionDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Anger, Hostility, and AggressionCatia Fernandes100% (1)
- Antipsychotics: There Is No Cure For Schizophrenia Just Symptomatic Control Is DoneDocument48 pagesAntipsychotics: There Is No Cure For Schizophrenia Just Symptomatic Control Is Donevarsham2No ratings yet
- Augmentation Strategies in Obsessive Compulsive DisorderDocument18 pagesAugmentation Strategies in Obsessive Compulsive DisorderLucijano Andreas SoftićNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology of Atypical Antipsychotics: An Update: EXCLI Journal October 2014Document30 pagesClinical Pharmacology of Atypical Antipsychotics: An Update: EXCLI Journal October 2014RencyNo ratings yet
- Mental Health PharmacologicalDocument6 pagesMental Health PharmacologicalKyla Mae De GraciaNo ratings yet