Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mefenamic Acid
Uploaded by
XtinegoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mefenamic Acid
Uploaded by
XtinegoCopyright:
Available Formats
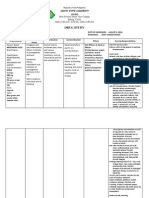
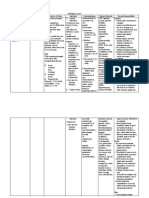
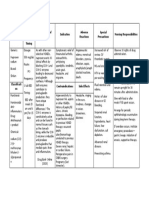
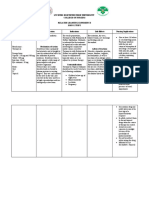
DRUG DATA
CLASSIFICATION
MECHANISM OF ACTION > aspirin-like drug that has analgesic, antipyretic and antiinflammatory activities. These activities appear to be due to its ability to inhibit cyclooxygenase & also antagonize certain effects of prostalgadins Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: well absorbed Distribution: wide Metabolism: liver Excretion: kidneys (50%) liver (20%) Half-life: 2-4 hours Onset: unknown Peak: 2-4 hours Duration: unknown
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: mefenamic acid Trade Name: Acidan, Analcid, Aprostal, Biostan, Calibral, Dolfenal, Dolmetine, Escandar, Fenexan, Gardan, Gisfen, harpinac, Istan, Mecid-A, Mefenax, Ponstan, Proxyl, Revalon, Selmac, Spegic, Totagesic. Tyhostan, Zapan Minimum Dose: 250 mg 1 tab TID PO Maximum Dose: 500 mg 1 tab TID PO Contents: mefenamic acid Availability and Color: Capsule/Tablet: 250 mg, 500 mg Route: PO Source: Brener, T., Rita, M.D., Nursing 2007 Drug Handbook. th Philadelphia (27 ed.) Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, p. 22-23
Pharmacologic: CNS drugs Therapeutic: NSAIDs Pregnancy Category: rd C ; D in 3 trimester
> relief of pain including muscular, rheumatic, traumatic, dental, postoperative and postpartum pain, headache migraine, fever and dysmenorrhea
> contraindicated in pts hypersensitivity to drug or other NSAIDs > contraindicated in those who have experienced asthma, urticaria or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin > contraindicated in pts with acute active ulceration or chronic inflammation of either upper or lower GI tract Precaution: > use cautiously in pts with history of ulcers or GI bleeding, asthma, epilepsy, kidney or liver disease Drug Interaction: > Drug-drug. ACE inhibitors: May decrease antihypertensive effects. Monitor BP. Aspirin: May increase risk of ulcers. Diuretics: May reduce the natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazides in some pts. Methotrexate: May inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. > Drug-herb. Dong quia, fever few, garlic, ginger, horse chest nut, red clover: May increase risk in bleeding. > Drug-lifestyle. Long term alcohol use, smoking: May cause gastric irritation or bleeding.
CNS dizziness, headache, nervousness, tremors CV congestive heart failure, hypertension, tachycardia, sycope GI gas pain, diarrhea/ constipation, vomiting, dyspepsia, peptic ulceration, nausea Metabolic weight changes Respiratory asthma, dyspnea Skin rash, alopecia, photosensitivity, pruritus Urogenital Cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, oliguria/polyuria, renal failure
Before > Assess pts pain before therapy: location, duration, frequency, precipitating and aggravating factors > Tell pt to report history of allergic reactions to NSAIDs before starting therapy > Prepare food to intake with drug > Assess if the pt has taken drug that may decrease the medications effectiveness > Inform patient need and importance of the drug to him/her During > Administer with food or milk to decrease gastric symptoms > Do not increase dose without physicians order > Administer drug with full glass of water to enhance absorption > Do not crush, dissolve or chew capsules/tablets > Caution in pts with history of peptic ulcer or GI bleeding, epilepsy or liver disease > Observe 15 Rs of drug administration After > Instruct pt not to take drug for more than 7 days >Advise pt to immediately report persistence or failure to relieve pain > Tell pt to report occurrence of drug induced adverse reactions > Teach pt that all NSAIDs, including mefenamic acid, may harm the liver > Discuss in detail all aspects of the drug therapy: reason for taking the drug & expected results
You might also like
- Cavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidDocument3 pagesCavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Mefenamic Acid)Document4 pagesDRUG STUDY (Mefenamic Acid)Paolo Digo67% (6)
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument1 pageMefenamic Acid Drug StudyBer AnneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Mefenamic Acid and CephalexinDocument5 pagesDrug Study Mefenamic Acid and CephalexinRoselle Soriano100% (3)
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyJude LabajoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument1 pageKetorolacAngela Tenorio100% (1)
- Mefenamic AcidDocument1 pageMefenamic AcidChiara Tenorio Ü100% (2)
- Mefenamic Acid Drug Study FormDocument2 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug Study FormKuro Mufu100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY OXYTOCIN, METHERGINE EtcDocument9 pagesDRUG STUDY OXYTOCIN, METHERGINE EtcPatricia Reese YutiamcoNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument1 pageMefenamic Acid Drug Studymilkv70% (10)
- Drug Mechanism Of Action Indications Adverse NursingDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism Of Action Indications Adverse NursingKristine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Gentamycin DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesGentamycin DRUG STUDYMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesParacetamol Drug StudyEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 04-21-09Document2 pagesDrug Study 04-21-09obietobiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineDocument5 pagesDrug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineLLan Kristine Lazarito100% (1)
- Cephalosporin Drug StudyDocument1 pageCephalosporin Drug StudyJehadadNo ratings yet
- CefiximeDocument2 pagesCefiximenarucute01224No ratings yet
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDocument6 pagesDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉No ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument1 pageMefenamic AcidKristine Artes AguilarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- VACCINES Hepatitis B and Tetanus Vaccine StudyDocument2 pagesVACCINES Hepatitis B and Tetanus Vaccine StudyCarlo AniagNo ratings yet
- PLASILDocument2 pagesPLASILmilesmin100% (1)
- Drug Study DisudrinDocument1 pageDrug Study DisudrinGrant Kenneth Dumo AmigableNo ratings yet
- UnasynDocument1 pageUnasynrachieeeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NurseryDocument6 pagesDrug Study NurseryPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Naproxen Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageNaproxen Sodium Drug StudyKarl Lourenz Deysolong100% (1)
- Evening PrimroseDocument1 pageEvening PrimroseMeranie Tiglao AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- IsoxsuprineDocument1 pageIsoxsuprineAndrean EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CephalexinDocument2 pagesDrug Study CephalexinMarc Jayson TobiasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug Studycruz_johnraymond100% (1)
- Terramycin - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTerramycin - Drug StudyBolasoc, HazelNo ratings yet
- DS HydralazineDocument3 pagesDS HydralazineGe LoNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Senokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)Document2 pagesSenokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)E100% (1)
- Ferrous Sulfate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFerrous Sulfate Drug Studyjanice paralejas100% (1)
- PiroxicamDocument2 pagesPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDan Dan Soi T50% (2)
- Final Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFinal Drug StudyCherry Lou Correos Tejada100% (2)
- DRUG AmikacinDocument2 pagesDRUG Amikacinrholiboi100% (1)
- Drugs StudyDocument6 pagesDrugs StudyAllan MacacapagalNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHydralazine Drug StudyErika Robella100% (1)
- Buscopan relieves GI spasmsDocument2 pagesBuscopan relieves GI spasmsChin Chan100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY CefuroximeLyana Stark92% (39)
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Celecoxib NubainDocument4 pagesDrug Study Celecoxib NubainMaiko TyNo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesFerrous SulfateRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesRanitidine HydrochlorideIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument2 pagesGentamicinMiguel Sanico0% (2)
- Drug Study - Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Magnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- 15 Drug StudyDocument1 page15 Drug StudyRuby PetalloNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin medication sheet for infectionsDocument3 pagesCephalexin medication sheet for infectionsCiera YoungNo ratings yet
- CelecoxibDocument2 pagesCelecoxibXtinegoNo ratings yet
- Icu Drug StudyDocument7 pagesIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyClarkEstacioNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole: (Oh Me' Pray Zol)Document3 pagesOmeprazole: (Oh Me' Pray Zol)Athea MelosantosNo ratings yet
- Tos Notes 3rd YrDocument4 pagesTos Notes 3rd YrDEEPAK SINGHNo ratings yet
- SP ARLACEL 170 MBAL PA (SG) - ES80360 - Product Information DossierDocument18 pagesSP ARLACEL 170 MBAL PA (SG) - ES80360 - Product Information DossierAsep Syaefun NazmiNo ratings yet
- Training For Handling Hazardous MaterialsDocument24 pagesTraining For Handling Hazardous Materialssyreiljude100% (3)
- Step 1 BiochemistryDocument12 pagesStep 1 Biochemistrylotusnelum7100% (2)
- Disinfect water with UV lightDocument16 pagesDisinfect water with UV lightsleonNo ratings yet
- Science: Revision Guide by MalaikaDocument7 pagesScience: Revision Guide by MalaikamalaikaNo ratings yet
- OTC 15275 Design Challenges of A 48-Inch Pipeline Subsea ManifoldDocument7 pagesOTC 15275 Design Challenges of A 48-Inch Pipeline Subsea Manifoldgvsha88No ratings yet
- Astm A240Document13 pagesAstm A240sukrisnoNo ratings yet
- Biomagnification 1Document9 pagesBiomagnification 1anjanakaveriNo ratings yet
- Criteria air pollutants: Sources, health effects and control of particulate matterDocument8 pagesCriteria air pollutants: Sources, health effects and control of particulate matterSumaiya ImamNo ratings yet
- Buckingham - Molecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical ApplicationsDocument479 pagesBuckingham - Molecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applicationsfakefacebook75891% (11)
- CPCB SOPs Utilization Spent Alkali Bromide Manufacturing Recovery BromineDocument11 pagesCPCB SOPs Utilization Spent Alkali Bromide Manufacturing Recovery Brominekrunal soniNo ratings yet
- Establishing A Coating Maintenance Plan PDFDocument11 pagesEstablishing A Coating Maintenance Plan PDFRicardo MendesNo ratings yet
- Crystal Appearance/Characteristics Clinical SignificanceDocument4 pagesCrystal Appearance/Characteristics Clinical SignificanceAngela LaglivaNo ratings yet
- BS EN 15408-2011 Solid Recovered Fuels - Determination of Sulphur (S), C...Document22 pagesBS EN 15408-2011 Solid Recovered Fuels - Determination of Sulphur (S), C...fadhil muhamadNo ratings yet
- Training The ABC's of Perfumery: Stephen V. Dowthwaite PerfumersWorldDocument27 pagesTraining The ABC's of Perfumery: Stephen V. Dowthwaite PerfumersWorldSteve100% (16)
- Wang and Helliwell (2001) Determination of Flavonols in Green and Black Tea LeavesDocument5 pagesWang and Helliwell (2001) Determination of Flavonols in Green and Black Tea LeavesYvonne TongNo ratings yet
- Softwood and Hardwood in Dissolving PulpDocument126 pagesSoftwood and Hardwood in Dissolving PulpAlan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Ryj Hvac CatalogDocument100 pagesRyj Hvac CataloganthonptbgNo ratings yet
- Id35 Honda GX630 GX660 GX690Document20 pagesId35 Honda GX630 GX660 GX690RodrigoChaves0% (1)
- Battery Basics: Cell Chemistry and DesignDocument40 pagesBattery Basics: Cell Chemistry and DesignAliNo ratings yet
- 3300 XL Ceramic Capped Probe 172932Document9 pages3300 XL Ceramic Capped Probe 172932Cecep AtmegaNo ratings yet
- Test - Molecular Spectroscopy - 30 Questions MCQ TestDocument15 pagesTest - Molecular Spectroscopy - 30 Questions MCQ Testsatish100% (1)
- Hosmane2017 Point Group BookDocument12 pagesHosmane2017 Point Group BookRenato EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Philippines Pharmacy Act PenaltiesDocument6 pagesPhilippines Pharmacy Act PenaltiesOdyNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicDocument60 pagesClass XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicBaljit Singh100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Intro To CellDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Intro To CellrexartoozNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-03: ElectrochemistryDocument6 pagesCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-03: ElectrochemistrySAKET TYAGI100% (1)
- SECTION 15081: Duct Insulation 15081Document5 pagesSECTION 15081: Duct Insulation 15081fatREVITNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Absorption Chillers ToDocument4 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Using Absorption Chillers Toأحمد صلاحNo ratings yet