Professional Documents
Culture Documents
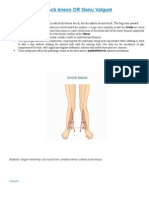
Genu Varum and Genu Valgum Ganger 20.05.2011
Uploaded by
Istianah EsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genu Varum and Genu Valgum Ganger 20.05.2011
Uploaded by
Istianah EsCopyright:
Available Formats
Genu varum and Genu valgum
Etiology Incidence Diagnosis
R. Ganger, MD, PhD
Orthopaedic Hospital Vienna Speising (www.oss.at) Department of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery (F. Grill)
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane alignment:
Physiologic variations: the range of normal knee angles changes with age
Account for the greatest number of referrals (including torsional problems) of children to orthopaedists
- Genu varum: bow legs
- Genu valgum: knock knees
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane alignment:
Genu varum: bow legs Genu valgum: knock knees
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane alignment:
Genu varum: bow legs Genu valgum: knock knees
Newborn
6 months
18 months
30 months
4-6 years
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane deformities:
Genu varum or Genu valgum outside normal range (+/- 2 SD) Normal or abnormal History: inquire about the onset was there an injury, illness or infection? is the deformity progressing? is the general health good? are other familiy members affected?
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane deformities:
Genu varum or Genu valgum outside normal range (+/- 2 SD) Normal or abnormal?
- Body height and body proportion - Other present deformities - Unilateral or bilateral - Leg length difference
- Laboratory examination: metabolic?
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane deformities:
Genu varum or Genu valgum outside normal range (+/- 2SD) Warnings:
- Asymmetrical deformity
- Progression
- Pain
- Leg length difference
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane alignment:
Standard imaging: AP-long leg standing radiogram, patella pointing straight forward
incorrect
correct
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane alignment:
Standard imaging: Teleradiogram
Normal alignment but LLD: left side: - 3 cm
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane alignment:
The majority of children with bow legs before age of 2 yrs. and knock knees presenting before 6 yrs. will resolve spontaneously
Natural history: benign selfcorrecting deformity Correction devices (twister cables, night splints, shoe wedges) are unnecessary. Anual clinical checks are recommended.
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane malalignment:
The minority of children with unilateral deformity, progression, leg length discrepancy and pain need further investigation.
Pathological genu varum / valgum: M. Blount Rickets, Vit.D - resistent rickets, Deformities after infection, trauma, tumor.
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane malalignment:
M. Blount
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane malalignment:
Epi-, metaphyseal dysplasia:
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane malalignment:
Pseudoachondroplasia:
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane malalignment:
posttraumatic:
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane malalignment:
after infection:
Lower Limb Development
Frontal plane alignment:
Goal:
Physiological deformities are best observed Pathological deformities are treated surgically to achieve straight legs at same length
Lower Limb Development
Normal lower limb alignment: Diagnosis
Frontal plane:
Mechanical axis
Lower Limb Development
Normal lower limb alignment: Diagnosis
Frontal plane:
Anatomical axis
Lower Limb Development
Normal lower limb alignment:
Frontal plane:
Mechanical axis
versus
Femur: difference of 6
Anatomical axis
Tibia: same
Lower Limb Development
Normal lower limb alignment:
Sagittal plane:
Lower Limb Development
Lower limb malalignment: Diagnosis
Deformity analysis:
Frontal plane: Varus, valgus, translation
Sagittal plane: Antecurvation, recurvation, translation Axial plane: Rotation, lengthening or shortening
Lower Limb Development
Malalignment test acc. to Paley and Herzenberg:
Identify the source(s) of the mechanical axis deviation
Femoral deformity
Lower Limb Development
Malalignment test:
Identify the source(s) of the mechanical axis deviation
Tibial deformity
Lower Limb Development
Malalignment test:
Identify the source(s) of the mechanical axis deviation
Femoral and tibial deformity
Lower Limb Development
Tibial mechanical axis planning:
Frontal plane:
Lower Limb Development
Tibial mechanical axis planning:
Frontal plane:
Lower Limb Development
Tibial mechanical axis planning:
Frontal plane:
Digital planning
with
TraumaCad program
Lower Limb Development
Tibial mechanical axis planning:
Frontal plane:
Digital planning
with
TraumaCad program
Lower Limb Development
Tibial mechanical axis planning:
Frontal plane:
Digital planning
with
TraumaCad program
Deformity: 4 Correction: 8.5 With Auto Alignment: MAD 7mm med Individual Alignment: MAD 1mm med
Lower Limb Development
Tibial mechanical axis planning:
Frontal plane:
Digital planning
with
TraumaCad program
Lower Limb Development
Tibial mechanical axis planning:
Frontal plane:
Digital planning
with
TraumaCad program
Thank you for your attention!
You might also like
- Adolescent Idiopathic ScoliosisDocument29 pagesAdolescent Idiopathic ScoliosisfenskaNo ratings yet
- Genu Valgus Genu VarusDocument35 pagesGenu Valgus Genu VarusRatu FaniaNo ratings yet
- ACL Injury: Everything You Need to Know to Make the Right Treatment Decision: - What the ACL does and why it is so important - Treatment options for partial and complete ACL tears - Surgery: graft options, how it is done, what to expect - How to prepare for surgery - What to dFrom EverandACL Injury: Everything You Need to Know to Make the Right Treatment Decision: - What the ACL does and why it is so important - Treatment options for partial and complete ACL tears - Surgery: graft options, how it is done, what to expect - How to prepare for surgery - What to dNo ratings yet
- Genu ValgumDocument2 pagesGenu ValgumPurohit_R0% (1)
- Biceps Brachii Rupture FinalDocument27 pagesBiceps Brachii Rupture Finalapi-282332260No ratings yet
- Jurnal Shoulder Dislocation - PendekDocument84 pagesJurnal Shoulder Dislocation - PendekCliff LewisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Bio Mechanics of The KneeDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Bio Mechanics of The KneeaimanshalpyNo ratings yet
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPosterior Cruciate Ligament Injury, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ankle Foot OrthosisDocument4 pagesAnkle Foot Orthosis楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Ortho Lec Knee OrthopaedicsDocument45 pagesOrtho Lec Knee OrthopaedicsNadeen GhazalNo ratings yet
- Total Hip Replacement PPDocument22 pagesTotal Hip Replacement PPAnonymous dGfXuDd5No ratings yet
- Ankle Sprain Rehabilitation ProtocolDocument3 pagesAnkle Sprain Rehabilitation ProtocolMuhammad Luqmanulhakim Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction Into Orthopaedic ImplantsDocument20 pagesA Brief Introduction Into Orthopaedic ImplantsLuisAngelPonceTorresNo ratings yet
- Hip Joint 1Document22 pagesHip Joint 1foziiiii100% (2)
- Kyphosis - Causes, Treatments & RisksDocument8 pagesKyphosis - Causes, Treatments & Riskstarun72ceeNo ratings yet
- IC SocketDocument307 pagesIC SocketChandan Mahapatra100% (1)
- ACL Injury PresentationDocument36 pagesACL Injury Presentationmail_rajibNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Knee OrthosesDocument50 pagesLecture 1 Knee OrthosesAlfred JacksonNo ratings yet
- Genu Valgum Treatment & SurgeryDocument17 pagesGenu Valgum Treatment & SurgeryRanadaPrasadSahaNo ratings yet
- Acl Injury Surgery - Orthoinfo - AaosDocument15 pagesAcl Injury Surgery - Orthoinfo - Aaosapi-228773845No ratings yet
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery: Trauma & Orthopaedic DirectorateDocument38 pagesAnterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery: Trauma & Orthopaedic DirectorateSzilvia MartonosNo ratings yet
- Vivek Sharm Acl ReconstructionDocument7 pagesVivek Sharm Acl ReconstructionJuan Pablo FuentesNo ratings yet
- BankartDocument14 pagesBankartshayneberry25No ratings yet
- MCL Injury PaperDocument6 pagesMCL Injury Paperapi-268835137No ratings yet
- Shoulder ArthroplastyDocument53 pagesShoulder ArthroplastyWijaya X PutriNo ratings yet
- Bahan Kuliah Fractures in ElderlyDocument27 pagesBahan Kuliah Fractures in ElderlyhazelelNo ratings yet
- Clubfoot Book PDFDocument626 pagesClubfoot Book PDFJefryan SofyanNo ratings yet
- Below Knee and Through Knee ProsthesisDocument4 pagesBelow Knee and Through Knee ProsthesisClang TejadaNo ratings yet
- Acl RehabDocument3 pagesAcl RehabMark RausaNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: Degenerative & IdiopathicDocument34 pagesScoliosis: Degenerative & IdiopathicClaudia MariscaNo ratings yet
- KyphosisDocument32 pagesKyphosisBeniamin CostinașNo ratings yet
- Anterior Shoulder DislocationDocument121 pagesAnterior Shoulder DislocationAnupama SNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The Anterior Cruciate LigamentDocument37 pagesBiomechanics of The Anterior Cruciate LigamentRoshynta Linggar Andatu100% (1)
- Presentation ACL and PCLDocument38 pagesPresentation ACL and PCLMuhammad Haekal HasryNo ratings yet
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament InjuriesDocument35 pagesAnterior Cruciate Ligament InjuriesAhmad Hakim Al-ashrafNo ratings yet
- Biomech of Hip JointDocument68 pagesBiomech of Hip JointkashifNo ratings yet
- Genu VarumDocument3 pagesGenu VarumPurohit_RNo ratings yet
- DislocationDocument46 pagesDislocationShaa ShawalishaNo ratings yet
- Clavicle AO Surgery Reference (2023)Document399 pagesClavicle AO Surgery Reference (2023)Wael GabrNo ratings yet
- Hip Fractures-Orthoinfo - AaosDocument9 pagesHip Fractures-Orthoinfo - Aaosapi-228773845No ratings yet
- Applied Biomechanics Arthroplasty: DR Abda ShaikhDocument42 pagesApplied Biomechanics Arthroplasty: DR Abda ShaikhAbida ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Reinold - Glenohumeral and Scapulothoracic RehabDocument45 pagesReinold - Glenohumeral and Scapulothoracic Rehabshivnair100% (2)
- Legg Calvé Perthes DiseaseDocument11 pagesLegg Calvé Perthes DiseaseronnyNo ratings yet
- Acl Rehab ProgrammeDocument8 pagesAcl Rehab ProgrammePengintaiNo ratings yet
- Kyphosis - Lecture 2013Document70 pagesKyphosis - Lecture 2013Dibyendunarayan BidNo ratings yet
- Gpe - 017.1 - Orthopaedic ExaminationDocument3 pagesGpe - 017.1 - Orthopaedic ExaminationImiey Eleena HanumNo ratings yet
- Common CasesDocument44 pagesCommon CasesRebecca WongNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Tendinitis PDFDocument56 pagesShoulder Tendinitis PDFMajda BajramovićNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Foot DeformitiesDocument27 pagesPediatric Foot DeformitieszeshmaNo ratings yet
- Fracture of Radius and Ulna 3Document38 pagesFracture of Radius and Ulna 3Noor Al Zahraa AliNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Foot Examination PDFDocument16 pagesAnkle and Foot Examination PDFainizatiNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic: Dislocations of The Hip JointDocument16 pagesOrthopedic: Dislocations of The Hip JointAnmarNo ratings yet
- Shoulder PathologiesDocument33 pagesShoulder PathologiesjermaineNo ratings yet
- Transtibial Prosthetics 1 PDFDocument64 pagesTranstibial Prosthetics 1 PDFAlfionita Wika100% (1)
- Floor Reaction OrthosisDocument22 pagesFloor Reaction Orthosischinmayghaisas50% (2)
- Diagnostic Challenges in Musculoskeletal Radiology PDFDocument182 pagesDiagnostic Challenges in Musculoskeletal Radiology PDFphuong mai leNo ratings yet
- CTEVDocument61 pagesCTEVSylvia LoongNo ratings yet
- Forearm Fractures, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandForearm Fractures, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Improved Access To Comprehensive Emergency Obstetric Care and Its Effect On Institutional Maternal Mortality in Rural MaliDocument9 pagesImproved Access To Comprehensive Emergency Obstetric Care and Its Effect On Institutional Maternal Mortality in Rural MaliIstianah EsNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Herpes PDFDocument9 pagesJurnal Herpes PDFIstianah EsNo ratings yet
- Time To Learn. Understanding Patient Centered CareDocument7 pagesTime To Learn. Understanding Patient Centered CareIstianah EsNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Herpes PDFDocument9 pagesJurnal Herpes PDFIstianah EsNo ratings yet
- Guideline Antibiotic RationalDocument35 pagesGuideline Antibiotic RationalIstianah EsNo ratings yet
- Drug Interaction Can Be Defined As TheDocument34 pagesDrug Interaction Can Be Defined As TheIstianah Es100% (1)
- Drug Interaction Can Be Defined As TheDocument34 pagesDrug Interaction Can Be Defined As TheIstianah Es100% (1)
- Codman's Pendulum ExercisesDocument1 pageCodman's Pendulum ExercisesIstianah EsNo ratings yet
- MiracleDocument11 pagesMiracleJonatasCostaNo ratings yet
- (Doc24.vn) Bai-Tap-Tieng-Anh-10-Thi-Diem-Co-Dap-AnDocument14 pages(Doc24.vn) Bai-Tap-Tieng-Anh-10-Thi-Diem-Co-Dap-AnTạ Quang ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Vortex Laser Reiki 1Document17 pagesVortex Laser Reiki 1Volkan VVolkan100% (3)
- 49-Emotional-Conditions and Their RemediesDocument6 pages49-Emotional-Conditions and Their RemediesgcmakrisNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP VỀ ĐỌC HIỂUDocument7 pagesBÀI TẬP VỀ ĐỌC HIỂUNguyễn Việt HảiNo ratings yet
- Report On DR.B.R.K.R Govt - Ayurvedic College & Hospital, Erragadda, HyderabadDocument22 pagesReport On DR.B.R.K.R Govt - Ayurvedic College & Hospital, Erragadda, HyderabadRavindra Singh PalNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnanciesDocument27 pagesHigh Risk PregnanciesMochammad Adam EldiNo ratings yet
- Griffith 1898 PlatesDocument180 pagesGriffith 1898 PlateshaleliNo ratings yet
- HLH BloodDocument13 pagesHLH BloodOmyRojasNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Questions With RationaleDocument8 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Questions With RationaleLes ChiensNo ratings yet
- Push Up Fact SheetDocument1 pagePush Up Fact SheetNor AmalinaNo ratings yet
- FORM LPLPO & Permintaan TRIBULANDocument640 pagesFORM LPLPO & Permintaan TRIBULANMARTININo ratings yet
- Open Bite: A Review of Etiology and Management: Peter Ngan, DMD Henry W. Fields, DDS, MS, MSDDocument8 pagesOpen Bite: A Review of Etiology and Management: Peter Ngan, DMD Henry W. Fields, DDS, MS, MSDAzi Pertiwi HussainNo ratings yet
- Promotion MCQDocument17 pagesPromotion MCQssamaddNo ratings yet
- FrequencyDocument120 pagesFrequencyp100% (1)
- Paulding Progress May 27, 2015Document16 pagesPaulding Progress May 27, 2015PauldingProgressNo ratings yet
- AyaskritiDocument2 pagesAyaskritidrbhaveshpNo ratings yet
- MPT NeurologyDocument22 pagesMPT NeurologyDevasyaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Occlusal Radiography - Pocket DentistryDocument5 pages11 - Occlusal Radiography - Pocket DentistryDeysi AguaguiñaNo ratings yet
- Discourse Community EthnographyDocument6 pagesDiscourse Community Ethnographyapi-294418947No ratings yet
- COVID 19 Consent FormDocument2 pagesCOVID 19 Consent FormfvdssfdNo ratings yet
- Operator Manual AXIOM Artis: ListsDocument606 pagesOperator Manual AXIOM Artis: ListsHelen Cid Acevedo100% (2)
- General Abbreviations For Medical RecordsDocument9 pagesGeneral Abbreviations For Medical Recordsjainy12No ratings yet
- Common Pediatric Illnesses in The Er UrgentDocument46 pagesCommon Pediatric Illnesses in The Er UrgentDr mohamedNo ratings yet
- Faktor Risiko Kejadian Arthritis Gout Pada Pasien Rawat Jalan Di Rumah Sakit Dr. Wahidin Sudirohusodo, MakassarDocument8 pagesFaktor Risiko Kejadian Arthritis Gout Pada Pasien Rawat Jalan Di Rumah Sakit Dr. Wahidin Sudirohusodo, MakassarEster DewNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: The Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - An UpdateDocument12 pagesNIH Public Access: The Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - An UpdateYessicaMariñosKirosNo ratings yet
- Theologus Autodidact Us of Ibn Al-NafisDocument77 pagesTheologus Autodidact Us of Ibn Al-NafisMujahid Asaadullah Abdullah100% (2)
- Triclosan USP..Document2 pagesTriclosan USP..Arun Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Magnesium ReplacementDocument4 pagesMagnesium ReplacementArvenaa SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Current Scenario: Knowledge of Basic Life Support in Medical CollegeDocument3 pagesCurrent Scenario: Knowledge of Basic Life Support in Medical CollegeaminNo ratings yet