Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mish Chickenpox Report
Uploaded by
Mish Abo-aboOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mish Chickenpox Report
Uploaded by
Mish Abo-aboCopyright:
Available Formats
CHICKENPOX
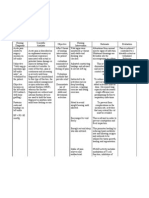
I. Synonym (varicella) II. Definition It is an acute and highly contagious disease of viral etiology that is characterized by vesicular eruptions on the skin and mucous membrane with mild constitutional symptoms. III. Etiologic agent Herpesvirus varicellae- a DNAcontaining virus 1. Human beings are the only source of infection. 2. This is closely related or identical to herpes zoster virus. IV. Mode of Transmission 1. Direct contact that sheds the virus from the vesicles. 2. Indirect contact, trough linens or fomites. 3. Airborne, or spread by aerosolized droplets from the nasopharyx of ill individuals. 4. High viral titers are found in the vesicles of chickenpox; thus, viral transmission may also occur through direct contact with these vesicles, although the risk is lower. 5. Following primary infection there is usually lifelong protective immunity from further episodes of chickenpox. V. Incubation Period The incubation period is 10-21 days or may be prolonged after passive immunization against chickenpox. VIII. Diagnostic Procedure Blood and laboratory tests to identify the varicella zoster virus (VZV). IX. Drug of choice 1. Oral Acyclovir 800mg 3x/day for five days must also be given. 2. Oral antihistamine can be taken to symptomatic pruritus. 3. Calamine lotion eases itchiness. 4. Antipyretic might be given for fever. X. Immunization Chickenpox (Varicella) vaccine XI. Prevent and control 1. Active immunization with live, attenuated varicella vaccine is necessary. 2. Avoid exposure as much as possible to infected persons. 3. Patients must be isolated to avoid transmission of organism to other members of the family. XII. Nursing Management 1. Respiratory isolation is a must until all vehicles have crusted. VI. Signs and Symptoms 1. 2. 3. 4. Fever Headache Sore throat Chicken pox rash after the first symptoms appear.
VII. Pathognomonic sign Vesiculopapular lesions.
41
2. Prevent secondary infection of the skin lesions through hygienic care of the patient. 3. Attention should be given to nasopharyngeal secretions and discharges. Linens must be disinfected under the sunlight or through boiling. 4. Cut fingernails short and wash hands more often to minimize bacterial infections that may be introduced by scratching. 5. A child must wear mittens. 6. Provide activities to keep child occupied to lessen pruritus. 7. Observe oral and nasal care as rashes may appear in the buccal cavity. XIII. Possible Nursing Diagnosis 1. Hyperthermia related to viral infection
SUBMITTED BY: ABO-ABO, JAIME JOYCE DARLENE M. Pamantasan ng Cabuyao, Cabuyao City SUBMITTED TO: Mr. Armando A. delos Santos RN, MAN. (Clinical Instructor)
42
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Case Study - Genetic DisordersDocument3 pagesCase Study - Genetic Disordersapi-340003532100% (1)
- Human Sexual Response Physiology PhasesDocument2 pagesHuman Sexual Response Physiology PhasesLovely HerreraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Uterine FibroidsDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Uterine FibroidsDoctor JitNo ratings yet
- College of Medicine & Health SciencesDocument56 pagesCollege of Medicine & Health SciencesMebratu DemessNo ratings yet
- Things of Boundaries. Andrew AbbottDocument27 pagesThings of Boundaries. Andrew AbbottDaniel SotoNo ratings yet
- Remote Working A Dream Job British English Advanced c1 c2 GroupDocument5 pagesRemote Working A Dream Job British English Advanced c1 c2 GroupNick ManishevNo ratings yet
- NurseCorps Part 8Document24 pagesNurseCorps Part 8smith.kevin1420344No ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain - FractureDocument1 pageNCP - Acute Pain - Fracturemawel73% (22)
- Pta ResumeDocument2 pagesPta Resumeapi-669470996No ratings yet
- الورقة الثالثة- القبالة-2Document4 pagesالورقة الثالثة- القبالة-2Habebt MusabNo ratings yet
- Prevention Strategies For Periodontal Disease - Chapter 16Document10 pagesPrevention Strategies For Periodontal Disease - Chapter 16Daniah MNo ratings yet
- Reiki Tummo Brochure 2013Document2 pagesReiki Tummo Brochure 2013Alicia TerryNo ratings yet
- Table : Number of Population, Hospitals and Beds in All Over JordanDocument8 pagesTable : Number of Population, Hospitals and Beds in All Over JordanjNo ratings yet
- Package List Swasthysathi 2018-Grade BDocument150 pagesPackage List Swasthysathi 2018-Grade BKuntal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Bams Private Colleges Fess.Document2 pagesMaharashtra State Bams Private Colleges Fess.Bhavesh RajpurohitNo ratings yet
- Respiration 3... Pulmonary Function TestsDocument26 pagesRespiration 3... Pulmonary Function Testsapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Stefan White, Andrew Sinclair (Auth.), John M. Hutson, Garry L. Warne, Sonia R. Grover (Eds.) - Disorders of Sex Development_ an Integrated Approach to Management-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (20Document327 pagesStefan White, Andrew Sinclair (Auth.), John M. Hutson, Garry L. Warne, Sonia R. Grover (Eds.) - Disorders of Sex Development_ an Integrated Approach to Management-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (20Aakanksha MehtaNo ratings yet
- Methodology Tapping Methodology of WaterlineDocument15 pagesMethodology Tapping Methodology of WaterlineBryNo ratings yet
- Complete VaccinationDocument2 pagesComplete VaccinationNgoo NwosuNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biomechanics in Implant DentistryDocument36 pagesClinical Biomechanics in Implant DentistryMahadevan Ravichandran100% (4)
- Nursing Assignment SampleDocument12 pagesNursing Assignment Sampleswetha swethaNo ratings yet
- hdf492 Portfolio PresentationDocument14 pageshdf492 Portfolio Presentationapi-403412647No ratings yet
- Hse in Drilling OperationsDocument13 pagesHse in Drilling OperationsSamad Ali Siddiqui100% (2)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology Question PapersDocument22 pagesObstetrics and Gynecology Question Papersprinceej83% (18)
- 4020 Assessment 4 Instructions - Improvement Plan Tool Kit - ..Document4 pages4020 Assessment 4 Instructions - Improvement Plan Tool Kit - ..Sabahat BashirNo ratings yet
- UV-VIS Method for Estimating Fat-Soluble Vitamins in MultivitaminsDocument6 pagesUV-VIS Method for Estimating Fat-Soluble Vitamins in MultivitaminsTisenda TimiselaNo ratings yet
- Bmjopen 2017 016402Document6 pagesBmjopen 2017 016402Ćatke TkećaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Wastewater Collection and PumpingDocument84 pagesIntro To Wastewater Collection and PumpingMoh'd KhadNo ratings yet
- Storage Tanks Selection and Sizing: Richardhaw@sympatico - CaDocument50 pagesStorage Tanks Selection and Sizing: Richardhaw@sympatico - CamanojjuvaliNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Quarter 1 - Module 4: CaregivingDocument20 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Quarter 1 - Module 4: CaregivingIrine Irine100% (1)