Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neurotransmitter
Uploaded by
abrar_998455740Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Neurotransmitter
Uploaded by
abrar_998455740Copyright:
Available Formats
NEUROTRANSMITTERS are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body.
They relay signals between nerve cells, called neurons. The brain uses neurotransmitters to tell your heart to beat, your lungs to breathe, and your stomach to digest. They can also affect mood, sleep, concentration, weight, and can cause adverse symptoms when they are out of balance. Neurotransmitter levels can be depleted many ways. As a matter of fact, it is estimated that 86% of Americans have suboptimal neurotransmitter levels. Stress, poor diet, neurotoxins, genetic predisposition, drug (prescription and recreational), alcohol and caffeine usage can cause these levels to be out of optimal range. There are two kinds of neurotransmitters INHIBITORY and EXCITATORY. Excitatory neurotransmitters are not necessarily exciting they are what stimulate the brain. Those that calm the brain and help create balance are called inhibitory. Inhibitory neurotransmitters balance mood and are easily depleted when the excitatory neurotransmitters are overactive.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
SEROTONIN is an inhibitory neurotransmitter which means that it does not stimulate the brain. Adequate amounts of serotonin are necessary for a stable mood and to balance any excessive excitatory (stimulating) neurotransmitter firing in the brain. If you use stimulant medications or caffeine in your daily regimen it can cause a depletion of serotonin over time. Serotonin also regulates many other processes such as carbohydrate cravings, sleep cycle, pain control and appropriate digestion. Low serotonin levels are also associated with decreased immune system function. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that is often referred to as natures VALIUM-like substance. When GABA is out of range (high or low excretion values), it is likely that an excitatory neurotransmitter is firing too often in the brain. GABA will be sent out to attempt to balance this stimulating over-firing. DOPAMINE is a special neurotransmitter because it is considered to be both excitatory and inhibitory. Dopamine helps with depression as well as focus, which you will read about in the excitatory section.
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
DOPAMINE is our main focus neurotransmitter. When dopamine is either elevated or low we can have focus issues such as not remembering where we put our keys, forgetting what a paragraph said when we just finished reading it or simply daydreaming and not being able to stay on task. Dopamine is also responsible for our drive or desire to get things done or motivation. Stimulants such as medications for ADD/ADHD and caffeine cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved. Unfortunately, stimulating dopamine consistently can cause a depletion of dopamine over time. NOREPINEPHRINE is an excitatory neurotransmitter that is responsible for stimulatory processes in the body. Norepinephrine helps to make epinephrine as well. This neurotransmitter can cause ANXIETY at elevated excretion levels as well as some MOOD DAMPENING effects. Low levels of norepinephrine are associated with LOW ENERGY, DECREASED FOCUS ability and sleep cycle problems.
EPINEPHRINE is an excitatory neurotransmitter that is reflective of stress. This neurotransmitter will often be elevated when ADHD like symptoms are present. Long term STRESS or INSOMNIA can cause epinephrine levels to be depleted (low). Epinephrine also regulates HEART RATE and BLOOD PRESSURE.
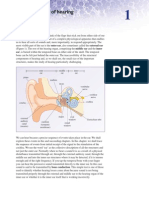
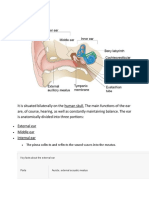
Q.1) This collects acoustic sounds and funnels it to the eardrum...
A.inner ear B.middle ear C.outer ear
Q.2) What is the most severe type of hearing loss you can get from cerumen impaction?
A.severe sensorineural B.moderate conductive C.severe conductive D.profound conductive
Q.3) What are the 3 functions of the external ear?
A.Impedance matching, Localization, Protection B.Protection, Amplification, Localization C.Protection, Amplification, Pressure Equalization
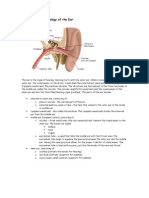
Q.4) A small air filled cavity lined with a mucous membrane....
( 2 words )
Q.5) Where are the ME and IE housed?
( 6 words )
Q.6)
What is a concave, disk-like structure with invaginated portion pointed in toward the middle ear space?
A.mastoid B.stapes C.tympanic membrane D.scala vestibuli
Q.7) What is the order of the TM layers, outer to inner?
( 3 words )
Q.8) Largest bone in the ME Q.9) What is the ring-shaped ligament that holds the footplate of the stapes in the oval window?
A.Axial ligament B.Tensor tympani C.Annular ligament D.Stapedius
Q.10) What do the axial ligaments do?
A.hold the footplate of the stapes B.pulls malleus medially and anteriorly, tensing the TM C.suspends the ossicles in the tympanic cavity
D.pulls stapes in a posterior direction
Q.11) The passageway leading from the nasopharynx to the anterior wall of the ME is
( 2 words )
Q.12) The Eustachian tube is usually Q.13) What are the functions of the middle ear?
A.Amplification, Protection, Impedance matching B.Protection, Impedance matching, Pressure Equalization C.Protection, Localization, Impedance matching
Q.14) How many decibels does the ME compensate for? Q.15) The area difference btwn the TM and footplate of the stapes is...
A.17:1 B.13:1 C.20:1 D.30:1
Q.16) The ratio of the lever action of the ossicular chain is Q.17) Higher mass equals
A.higher frequency B.lower frequency
Q.18) Higher stiffness equals
A.higher frequency B.lower frequency
Q.19) If the TM retracts due to negative pressure in the ME,what happens?
( 3 words )
Q.20) If fluid builds up in the ear, what happens?
( 3 words )
Q.21) How does the ME protect?
( 2 words )
Q.22) The acoustic reflex can reduce how many decibels of loud sounds?
A.70-80 B.50-60 C.10-30 D.20-40
Q.23) What is the structure comprising of the sensory organs for hearing and balance?
A.Tympanic membrane B.middle ear C.inner ear
Q.24) What is the auditory portion of the inner ear? Q.25) The base of the cochlea deals with...
A.high frequencies B.low frequencies
Q.26)
What is the membrane covered opening in the labyrinthine wall of the ME space, leading in the scala tympani?
A.oval window B.round window C.scala media
Q.27)
The opening in the labyrinthine wall of the ME space, leading into the scala vestibuli of the cochlea, into which the footplate of the stapes fits is
( 2 words )
Q.28) Which is filled with endolymph?
A.scala vestibuli B.scala tympani C.scala media
Q.29) Perilymph is not only similar to CSF, but also...
A.high in potassium B.high in sodium
Q.30) The base of the basilar membrane is for
A.high frequencies B.low frequencies
Q.31) How many rows of outer hair cells are there? Totally in what?
A.5 or 6, totaling in 12,000 B.3 or 4, totaling in 13,000 C.3 or 4, totaling in 12,000 D.5 or 6, totaling in 3,500 E.3 or 4, totaling in 3,500
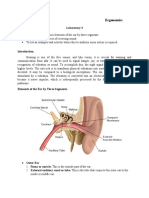
1. Synonyms of middle ear include
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Tympanum Protympanum Eustachean tube Epitympanum
2. Lateral wall of tympanum is formed by
A. B. C.
? ? ?
Eustachean tube Tympanic membrane Promontry
D.
Cochlea
3. Lateral wall of epitympanum is formed by
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Pars tensa of ear drum Pars flaccida of ear drum Promontory Cochlea
4. Scutum is also known as the
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Eustachean tube bony portion COG Tensor tympani projection Outer attic wall
5. The difference between pars tensa and pars flaccida is
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
The lack of external squamous layer in pars tensa The lack of inner mucousal layer in pars tensa Lack of middle fibrous layer in pars flaccida Lack of middle fibrous layer in pars tensa
6. Posterior canaliculus for corda tympani nerve is seen
A. B. C.
? ? ?
At the junction between lateral and posterior walls of tympanic cavity At the junction between anterior and medial walls of tympanic cavity At the junction of posterior and medial walls of tympanic cavity
D.
At the medial wall of tympanic cavity
7. Glaserian fissure is also known as
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Squamotympanic fissure Petromastoid fissure Petrotympanic fissure Squamomastoid fissure
8. Important content of Glasserian fissure is
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Facial nerve Chordatympani nerve Eustachean tube Anterior malleolar ligament
9. Glaserian fissure transmits
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Chorda tympni nerve Facial nerve Labyrinthine artery Anterior tympanic branch of maxillary artery
10. Canal of Hugier contains
A. B. C.
? ? ?
Facial nerve Anterior tympanic artery Chordatympani nerve
D.
Anterior malleolar ligament
11. Canal of Hugier lies
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Medial to glasserian fissure Lateral to glasserian fissure Lateral to petrotympanic fissure Superior to Glasserian fissure
12. Roof of the middle ear cavity is formed by
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Mastoid process Tegment tympani Promontory Cog
13. Petrosquamous suture line is seen in
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
The roof of the middle ear cavity Medial wall of middle ear cavity Close to the ear drum Labyrinth
14. Anterior wall of middle ear is formed by
A. B. C.
? ? ?
Convergence of medial and lateral walls Promontory Aditus
D.
Short process of incus
15. Lower portion of the middle ear anterior wall is related to
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Mastoid antrum Aditus Internal carotid artery Maxillary artery
16. Carotico tympanic nerves enter middle ear cavity via
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Medial wall Posterior wall Roof Anterior wall
17. Number of caroticotympanic nerves which enter the middle ear cavity are
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
one in number Three in number Two in number Four in number
18. Upper portion of the anterior wall of middle ear cavity is related to
A. B. C.
? ? ?
Internal carotid artery Carotico tympanic nerves Eustachean tube
D.
Promontory
19. Medial wall of middle ear cavity is formed by
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Mastoid air cells Antrum Promontory Eustachean tube
20. Promontory is formed by
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Lateral semicircular canal Utricle Saccule Basal turn of cochlea
21. Grooves on the promontory contain
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Lymphatics air cells Tympanic plexus Branches of internal auditory artery
22. Above and slightly behind the promontory lies
A. B. C.
? ? ?
Oval window Round window Stapedial tendon
D.
Pyramid
23. Inferior border of oval window is
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Convex Concave Straight linear
24. Above the oval window lies
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Promontory Horizontal portion of facial nerve Vertical portion of facial nerve Facial recess
25. Tunnel for tensor tympani muscle lies
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
In the medial wall of middle ear In the anterior wall of middle ear In the lateral wall of middle ear In the posterior wall of middle ear
26. Round window membraneis made up of
A. B. C.
? ? ?
One layer Two layers Three layers
D.
Four layers
27. Secondary tympanic membrane provides a reliable landmark for
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Cochlear nerve Singular nerve Facial nerve Chorda tympani nerve
28. The closest vestibular structure to the secondary tympanic membrane is
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Lateral canal Superior canal Ampulla of posterior canal Utricle
29. The oval and round windows are separated by
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Ponticulous Chorda tympani nerve Subiculum Eustachean tube
30. Round window niche is __________ in shape
A. B. C.
? ? ?
Circular Oval Triangular
D.
Ovoid
31. Sinus tympani lies under
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Pyramid Cog Eustachean tube Malleus
32. Posterior wall of middle ear cavity is
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Of the same size along the entire length of the middle ear Is wider above than below Is wider below than above The communication of middle ear to the eustachean tube
33. Overall length of the malleus is
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
2-4 mm 1-2 mm 15 mm 7.5 - 9 mm
34. Tendon of tensor tympani inserts into
A. B. C.
? ? ?
Anterior process of handle of malleus Medial surface of the handle of malleus Head of the malleus
D.
Close to the articular facet of the malleus
35. Commonest portion of ossicle which easily undergoes necrosis is
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Head of malleus Handle of malleus Crura of stapes Long process of incus
36. Stapedial muscle is supplied by
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Mandibular nerve Chorda tympani nerve Facial nerve Trigeminal nerve
37. Taste fibres travelling via chorda tympani nerve supplies
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
The entire tongue Posterior 1/3 of tongue Lateral surface of tongue Anterior third of tongue
38. Tympanic plexus is seen over
A. B. C.
? ? ?
Lateral surface of ear drum Medial surface of ear drum Promontory
D.
Attic region
39. Mucosal lining of attic region is
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Ciliated columnar Cuboidal Squamous Pavement
40. Type of mucosa lining hypotympanum is
A. B. C. D.
? ? ? ?
Pavement epithelium Ciliated columnar epithelium Squamous epithelium Cuboidal epithelium
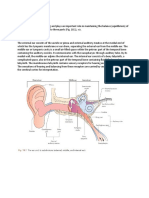
1. Lately I have seen many young adults with a pierced tragus. It
also has the tendency to be hairy. The English translation of tragus is what? Goat Hair Shave Mammal
2. A portion of the mandible which protrudes into the ear canal is
called what? condyle mandibular portion isthmus wisdom tooth
3. A pathology in the outer and/or middle ear causes which type of
hearing loss? sensorineural mixed wax blockage conductive
4. Two cranial nerves course parallel in the internal auditory
meatus. Which are they? Auditory and Trigeminal Facial and Optic Facial and Auditory Optic and Auditory
5. A perforation in the tympanic membrane will cause which type
of hearing loss? cochlear conductive conductive sensorineural
mixed
6. What are the correct anatomical names for the bones in the
middle ear? vice, anvil, cochlea malleus, incus, stapes tympani,eustachian, stapes cochlea, vestibule, incus
7. The anatomical feature of the ear responsible for pressure
equalization is known as what? tympanic membrane eustachian tube nasopharynx cochlear tube
8. The end organ of hearing is known as what?
organ of Corti scala media cochlea inner hair cells
9. The vestibular portion of the inner ear controls balance. What
are the main antatomical features of the vestibular apparatus? semicircular canals; saccule and utricle
vestibule, cochlear canals, utricle cochlea, semicircular canals, vestibule semicircular canals, eustachian tube, vestibule
10. Which bone houses and protects the cochlea?
temporal occipital frontal parietal
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing in the EarDocument15 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing in the EariwanNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of HearingDocument13 pagesThe Mechanics of HearingDustin NguyenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Ent-OrgansDocument52 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Ent-OrgansdrghassanNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Hearing: Ear Is Buried Within The Temporal Bone On Either Side of The Skull. The Temporal BoneDocument14 pagesThe Mechanics of Hearing: Ear Is Buried Within The Temporal Bone On Either Side of The Skull. The Temporal Bonereal_yooriNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of EarDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of EarAriguna WijayaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear. AreteDocument12 pagesAnatomy of The Ear. AreteBrandon AreteNo ratings yet
- Ear Nose and Throat QuizDocument6 pagesEar Nose and Throat QuizParsaant SinghNo ratings yet
- By DR Manah Chandra Changmai MBBS MSDocument31 pagesBy DR Manah Chandra Changmai MBBS MSKalaivaany RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Potongan CSOM Part 2Document12 pagesPotongan CSOM Part 2Athanasius WrinNo ratings yet
- Otic Disease and Ear Disorder MAINDocument27 pagesOtic Disease and Ear Disorder MAINJames AchuNo ratings yet
- Otorhea 3Document17 pagesOtorhea 3LutfiAnny Rahman HakimNo ratings yet
- Auditory SenseDocument3 pagesAuditory SenseFranchezka GuintoNo ratings yet
- EarDocument10 pagesEarfatimaawan8989No ratings yet
- Hayes Et AlDocument21 pagesHayes Et Aleka dharmaNo ratings yet
- Special Senses (EAR) : Sumera AfzalDocument74 pagesSpecial Senses (EAR) : Sumera AfzalAmbreen GhafoorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Ear FinalDocument61 pagesAnatomy of Ear FinalRavi KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media AkutDocument24 pagesOtitis Media AkutBethari K AbiantiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the EarDocument13 pagesAnatomy of the EarOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- Auditory PhoneticsDocument8 pagesAuditory PhoneticsمثنىالبريطانيNo ratings yet
- OAE Pediatrician BookletDocument22 pagesOAE Pediatrician BookletKalpana ParajuliNo ratings yet
- The Vestibulocochlear Organ: China Medical UniversityDocument30 pagesThe Vestibulocochlear Organ: China Medical UniversityDONALD UNASHENo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument196 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarChalsey Jene LorestoNo ratings yet
- 03 Friggeri 238174Document11 pages03 Friggeri 238174ffontanesiNo ratings yet
- Ear PerceptionDocument5 pagesEar PerceptionMaryam GhaffarNo ratings yet
- Mock TeachingDocument34 pagesMock TeachingMenaga IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- 10 - Anatomy of The Ear (Edited)Document26 pages10 - Anatomy of The Ear (Edited)Enlighten usNo ratings yet
- The Physics of HearingDocument4 pagesThe Physics of HearingSaadia HumayunNo ratings yet
- BellDocument79 pagesBellvijay1234568883No ratings yet
- Auditory SenseDocument15 pagesAuditory SenseSalma AslamNo ratings yet
- 2d Facial Nerve-Dr GosaiDocument6 pages2d Facial Nerve-Dr GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ReadingDocument32 pagesJurnal ReadingEva Ratnasari DinNo ratings yet
- Report 2 EMM352 - Muhammad Aiman Danial Bin YatimDocument3 pagesReport 2 EMM352 - Muhammad Aiman Danial Bin YatimAiman D.No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarrizzarNo ratings yet
- Share THE SENSORY SYSTEMS (Auditory Sense)Document19 pagesShare THE SENSORY SYSTEMS (Auditory Sense)kelvin ambazaNo ratings yet
- The Ear and HearingDocument55 pagesThe Ear and Hearingc3rberussNo ratings yet
- Dissection 33 - Ear and Nasal CavityDocument26 pagesDissection 33 - Ear and Nasal CavityLeonard EllerbeNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EarDocument20 pagesPhysiology of EarChippy SinghNo ratings yet
- Esp EnglishDocument5 pagesEsp EnglishCahyaa NingsiihNo ratings yet
- DR Karel JindrakDocument35 pagesDR Karel Jindrakpost2vishalNo ratings yet
- Aranilla - Laboratory No. 3Document4 pagesAranilla - Laboratory No. 3Mamamo157No ratings yet
- Ears Lecture GuideDocument56 pagesEars Lecture GuidemajNo ratings yet
- Exterior and Middle EarDocument26 pagesExterior and Middle EarAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Group 2: Amaliani Laraswati Dewi Andini Fifi Kurniawati Gita Rianti Nelly Marta Nadeak Nury Andriani Nur AnisahDocument15 pagesGroup 2: Amaliani Laraswati Dewi Andini Fifi Kurniawati Gita Rianti Nelly Marta Nadeak Nury Andriani Nur Anisahjihan salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory Systemtarunesh1No ratings yet
- Organs of Head&neckDocument143 pagesOrgans of Head&neckraphaelyohana140No ratings yet
- Grand Test 166.. 2019 PDFDocument116 pagesGrand Test 166.. 2019 PDFPandey AyushNo ratings yet
- Anatomy EarDocument35 pagesAnatomy EarPutri Noviarin IrhamnaNo ratings yet
- 04sensory Org-EarDocument9 pages04sensory Org-Earapi-19641337No ratings yet
- 1 M2XEmNdWyU0UgSsb6l-b1bJW4m4gPWADocument7 pages1 M2XEmNdWyU0UgSsb6l-b1bJW4m4gPWAmdikwamihlaliiNo ratings yet
- HA Eyes Ears NoseDocument21 pagesHA Eyes Ears NoseBeverly LavillaNo ratings yet
- Ent and OptalmologyDocument138 pagesEnt and OptalmologyFan Eli100% (3)
- Parkinsons Disease and Hearing LossDocument8 pagesParkinsons Disease and Hearing LossJohn OmandacNo ratings yet
- A. The External Ear, C. The Inner EarDocument3 pagesA. The External Ear, C. The Inner EarLili M.No ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument88 pagesUntitled Presentationmalar kumuthaNo ratings yet
- Auditory System: Human Outer Ear and CultureDocument5 pagesAuditory System: Human Outer Ear and CulturejennyrosepamatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy / Physio of The EarDocument58 pagesAnatomy / Physio of The EarRA100% (1)
- Anatomy of The EarDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The EarDarkAngelNo ratings yet
- LO SSS Week 5Document8 pagesLO SSS Week 5Tony StarkNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument19 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectAnsalAshutosh80% (5)
- PHILIPPINES Asthma Consensus Guidelines 2009Document134 pagesPHILIPPINES Asthma Consensus Guidelines 2009Sirias_black50% (2)
- Muscular SystemDocument20 pagesMuscular SystemAltaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- ANENCEPHALYDocument10 pagesANENCEPHALYSharmaine SimonNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Classification of NeoplasmsDocument31 pagesCharacteristics and Classification of Neoplasmsjpanay100% (1)
- MPL6Document2 pagesMPL6Daniel AgustinNo ratings yet
- Nutrients 08 00068Document29 pagesNutrients 08 00068Goran TomićNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Thomas Wieland - Next-Generation Sequencing Data AnalysisDocument143 pagesDissertation Thomas Wieland - Next-Generation Sequencing Data AnalysisatpowrNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument354 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemsPrecious RubaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System and Reflex Arc (GCSE)Document35 pagesThe Nervous System and Reflex Arc (GCSE)Raja UsamaNo ratings yet
- NEURULATION N Derivatives FDocument70 pagesNEURULATION N Derivatives Ffilza farheenNo ratings yet
- Excretion and HomeostasisDocument31 pagesExcretion and HomeostasiscsamarinaNo ratings yet
- SMRT Radiation Therapy IntroDocument18 pagesSMRT Radiation Therapy IntroDar WebNo ratings yet
- Anca VasculitisDocument12 pagesAnca Vasculitisatul_desai_3100% (2)
- 4 Other Blood Group SystemsDocument162 pages4 Other Blood Group SystemsFuentes, Jade Andrey R. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- Cholesterol Blt00034 35 36 ADocument2 pagesCholesterol Blt00034 35 36 AKERSYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Power PointDocument49 pagesChapter 16 Power PointJeff SzerykNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Microbiology Specimen ProcessingDocument48 pagesGuidelines for Microbiology Specimen ProcessingAl- ImanuddinNo ratings yet
- Your Health Today Choices in A Changing Society 5th Edition Teague Test BankDocument29 pagesYour Health Today Choices in A Changing Society 5th Edition Teague Test Banktaylorruiznqfpogxske100% (17)
- Harr. Cap 114Document7 pagesHarr. Cap 114tkovats.lopes2No ratings yet
- Causes and prevention of cancerDocument4 pagesCauses and prevention of cancerosamaNo ratings yet
- About Inflammation and InfectionDocument2 pagesAbout Inflammation and InfectionHAZRULNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers with Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsDocument28 pagesTreatment of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers with Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsSameer FasihNo ratings yet
- Omics-Based On Science, Technology, and Applications OmicsDocument22 pagesOmics-Based On Science, Technology, and Applications OmicsAlex Yalew0% (1)
- Gen Bio 1 - Mitosis and MeiosisDocument22 pagesGen Bio 1 - Mitosis and MeiosisQuiel Tangonan Jr.No ratings yet
- Oncology Revision Environmental Factors ScreeningDocument299 pagesOncology Revision Environmental Factors ScreeningMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument8 pagesDengue FevervikasmaeNo ratings yet
- Movement Disorders Movement DisordersDocument32 pagesMovement Disorders Movement Disordersreddyrajiv1526No ratings yet
- People of AppalachianDocument17 pagesPeople of AppalachianNestor BalboaNo ratings yet