Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maternal and Child Care
Uploaded by
Trixie Al MarieCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maternal and Child Care
Uploaded by
Trixie Al MarieCopyright:
Available Formats
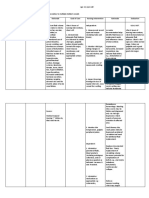
Terminology Gestation - Number of weeks of pregnancy Abortion - Birth that occurs before the end of 20 wks.
Gestation Term - The normal duration of pregnancy Preterm - Delivery that occurs after 20th wks but before completion of 37th weeks Post term - Labor that occurs after 42 wks Gravida - Any Pregnancy, regardless of duration. Nulligravida - Never been pregnant Primigravida - First time Multigravida - Second or more pregnancy Para- Birth after 20 wks gestation regardless of wheteher the infant is alive or dead. Nullipara - A woman who has had no births at more than 20 wks gestation Primipara - A woman whon has had 1 birth at more than 20 wks of gestation Antepartum - Between conception and the onset of labor Intrapartum - From the onset of true labor until birth of infant and placenta Postpartum - From the delivery of placenta until the return of womans body to a non pregnant condition Fertilization - UNion of the ovum and spermatozoon, impregnation or fecundation Implantation - contact between the growing structure and uterine endometrium, occurs 8-10 days after fertilization Apostion - Processby which the blastocyst brushes with the uterine endometrium Adhesion - PRocess by which the blastocyst attaches to the surface of the endometrium Invasion - Process wherein blastocyst settles down into endometrium's soft lining Factors in fertilizarion Maturation of both sperm and ovum Ability of sperm to reach the ovum Sperm agility Ability of sperm to penetrate the zona pellucida and cell membrane Capacitation and enough amount of enzyme Hyaluronidaseto dissolve corona radiata Sperm count (200 - 400 million/ejaculation) Labor and Delivery TYPES: 3 Major Components of Labor 1.) Passage - The passageway through which the fetus exits the body. Maternal pelvis and soft tissues, affected by the shape of the inlet, structure of the pelvis, and pelvic diameters. 2.) Passenger - The fetus and its ability to move through the passage. Affected by: *the skull *the lie (relationship of the long axis(spine) of the fetus to the long axis to the mother *the presentation (proportion of the fetus that enters the pelvic passageway fisrt *position (relationshio of the presentation part of the fetus to the front, back, and sides of the maternal pelvis) *attitude - the fetal head's ability to flex or extend 5 degrees and rotate 180 degrees, allowing it smallest diameters to move down the birth canal and pass theough the maternal pelvis.
3.) Power - Refers to s Types of Pelvis *Gynecoid - 50% -slightly ovoid -transvbersely rounded -subpubic arch wide -side walls straight -vaginal spontaneous *Android - 23% -Heart shapeed -deep -side walls convergent -narrow subpubic arch -C/section vaginal difficult with forceps *Anthropoid - 24% -Oval -Wider anterior -Staight side walls -Narrow subpubic arch -forceps/spontaneous if occipitosterior or occipoanterior *Platypelloid - 3% -Flattened anteroposteriosity -Wide transversely -straight side walls -Wide subpubic Stages of Labor First stage -Begins with the first true labor contractions and ends with complete effacement and dilation of the cervix (10 cm dilated) -Average: 13 hr (primi), 7.5 hr (multi) *Latent Phase (early) -Dilates from 0-3 cm -Contractions 2-5 mins, 30-50 secs; mild moderate intensity ans establisg a regular pattern *Active Phase -Dilates from 4-7 cm -Contractions 2-5 mins, 30-5- secs; mild moderate intensity -Dilatation ace: 1.2 cm / hr.-primi, 1.5 cm/hr-multi *Transitional phase -Dilations 8-10 cm -Contractions 2-3 mins, 30-50 secs -Dilation rate:
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- A Reaction Paper On Movie: A Beautiful MindDocument4 pagesA Reaction Paper On Movie: A Beautiful MindTrixie Al Marie100% (2)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- XVI. Nursing Care Plan 3Document3 pagesXVI. Nursing Care Plan 3Trixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- XVIII. Discharge PlanDocument1 pageXVIII. Discharge PlanTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- XVII. Health Teaching/RecommendationDocument2 pagesXVII. Health Teaching/RecommendationTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- XVI. Nursing Care Plan 4Document2 pagesXVI. Nursing Care Plan 4Trixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- XVI. Nursing Care Plan 4Document2 pagesXVI. Nursing Care Plan 4Trixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- XVI. Nursing Care Plan 5Document2 pagesXVI. Nursing Care Plan 5Trixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- XVI. Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesXVI. Nursing Care Plan 2Trixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- XIII. Diagnostic ExamDocument4 pagesXIII. Diagnostic ExamTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- XIV. Drug StudyDocument3 pagesXIV. Drug StudyTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- XV. Nursing TheoriesDocument3 pagesXV. Nursing TheoriesTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- XVI. Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesXVI. Nursing Care PlanTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- X. SymptomatologyDocument1 pageX. SymptomatologyTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- XII. Doctors OrderDocument5 pagesXII. Doctors OrderTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- IX. EtiologyDocument2 pagesIX. EtiologyTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- III. Patient DataDocument1 pageIII. Patient DataTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- V. Developmental DataDocument6 pagesV. Developmental DataTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- VIII. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesVIII. Anatomy and PhysiologyTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Vii RecDocument4 pagesVii RecTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- IV. Family BackgroundDocument2 pagesIV. Family BackgroundTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument1 pageAcknowledgementTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- ObjectivesDocument2 pagesObjectivesTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- I. IntroductionDocument2 pagesI. IntroductionTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument3 pagesHyperthermia NCPkaylejordan_29100% (2)
- NCP For HemothoraxDocument12 pagesNCP For HemothoraxroseonabreezeNo ratings yet
- Laennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesLaennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyTrixie Al Marie100% (3)
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Male DisorderDocument2 pagesMale DisorderTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Malposition of The UterusDocument1 pageMalposition of The UterusTrixie Al MarieNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pijatan Perineum Dan Senam Kegel Terhadap Pengurangan Ruptur Perineum Pada Ibu BersalinDocument7 pagesPengaruh Pijatan Perineum Dan Senam Kegel Terhadap Pengurangan Ruptur Perineum Pada Ibu BersalinPristika wiyarnaNo ratings yet
- Sakala Step 2 CK GYN 2018 Color Handout 2 - PageDocument12 pagesSakala Step 2 CK GYN 2018 Color Handout 2 - PageJurian F. Kaunang100% (1)
- Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument35 pagesFemale Reproductive AnatomySasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- American Society For Reproductive MedicineDocument3 pagesAmerican Society For Reproductive MedicineShanti Natalia NababanNo ratings yet
- 2.reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals 1Document29 pages2.reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals 1nileshmpharmNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument6 pagesMenstrual CycleKyndra Maxynne CamachoNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Care After Normal DeliveryDocument7 pagesPostpartum Care After Normal DeliveryJennifer MagzNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System LessonDocument3 pagesReproductive System LessonmargemunozNo ratings yet
- A&P Crash Course Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesA&P Crash Course Reproductive SystemAdan MantriNo ratings yet
- DLP Grade10 Feedback MechanismDocument8 pagesDLP Grade10 Feedback MechanismJoy MonteroNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Uterine Rupture: A Catastrophic Obstetric Emergency: OriginalDocument4 pagesUterine Rupture: A Catastrophic Obstetric Emergency: OriginalBogdan CăpățînăNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesDocument45 pagesAnatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesMesk BanatNo ratings yet
- ComparisonDocument7 pagesComparisonpurnoor abidNo ratings yet
- Feminism, Feminist Theory and Femisnist Literary CriticismDocument2 pagesFeminism, Feminist Theory and Femisnist Literary CriticismAndrea Verónica GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Checklist Female GenitaliaDocument2 pagesChecklist Female GenitaliaJessoliver GalvezNo ratings yet
- Feminism EssayDocument4 pagesFeminism EssayAnnaocap2016No ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 19Document3 pagesLab Exercise 19Yeong-Ja KwonNo ratings yet
- Agenda Rapat Bagian: Rabu, 12 Desember 2018Document10 pagesAgenda Rapat Bagian: Rabu, 12 Desember 2018Puspitasari NotohatmodjoNo ratings yet
- Puberty Below: Role of HormonesDocument3 pagesPuberty Below: Role of HormonesCyril CauilanNo ratings yet
- Myths and Misconceptions About SexualityDocument33 pagesMyths and Misconceptions About Sexualityprecious maningasNo ratings yet
- Labour Room LayoutDocument1 pageLabour Room LayoutRana Vandana100% (2)
- Amandeep Kaur Nursing Demonstrator Ionurc, Goindwal Sahib, PunjabDocument20 pagesAmandeep Kaur Nursing Demonstrator Ionurc, Goindwal Sahib, PunjabSanjay Kumar SanjuNo ratings yet
- CMCA ASSIGNMENT #1b PDFDocument3 pagesCMCA ASSIGNMENT #1b PDFAyanami PascuaNo ratings yet
- MCP NCP Benefits SlidesDocument13 pagesMCP NCP Benefits SlidesJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- Wid Wad GadDocument14 pagesWid Wad GadICT Fortune TowneNo ratings yet
- GynecologyDocument42 pagesGynecologyYa MaNo ratings yet
- Handout and Questions of HysterosalpingDocument12 pagesHandout and Questions of Hysterosalpingahmad shaltout100% (2)
- K - (0gq I5) U U!$g.qDocument64 pagesK - (0gq I5) U U!$g.qKristel AnneNo ratings yet
- Endometrium in Surgical PathologyDocument129 pagesEndometrium in Surgical PathologyleartaNo ratings yet
- Checklist (PapSmear)Document5 pagesChecklist (PapSmear)Sinung BawonoNo ratings yet
- What to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)From EverandWhat to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Labor with Hope: Gospel Meditations on Pregnancy, Childbirth, and MotherhoodFrom EverandLabor with Hope: Gospel Meditations on Pregnancy, Childbirth, and MotherhoodRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (28)
- The Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeFrom EverandThe Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- ADHD Women: A Holistic Approach To ADHD ManagementFrom EverandADHD Women: A Holistic Approach To ADHD ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.From EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (124)
- All in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayFrom EverandAll in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Healing PCOS: A 21-Day Plan for Reclaiming Your Health and Life with Polycystic Ovary SyndromeFrom EverandHealing PCOS: A 21-Day Plan for Reclaiming Your Health and Life with Polycystic Ovary SyndromeNo ratings yet
- The Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouFrom EverandThe Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouNo ratings yet