Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Electronics Lab 1
Uploaded by
Rodge BalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Electronics Lab 1
Uploaded by
Rodge BalCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No.
1 MULTIMETERS FOR RESISTANCE MEASUREMENT GROUP MEMBERS: ______________________________ Date Performed: __________________ _________________________________ Grade: __________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ I. Objectives: 1. To be familiar with the functions of an analog VOM particularly its ohmmeter function. 2. To become acquainted with the color code of resistors. 3. To study the operation of potentiometer. 4. To become acquainted in using a breadboard in connecting resistors in series, parallel and series parallel combinations.
II. Equipment and Components (1) Volt-ohmmeter (VOM) (5) Assorted carbon resistors (1) Breadboard (1) Potentiometer
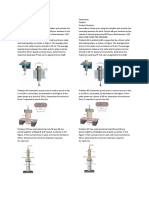
III. Schematic Diagrams Figure 1:
Figure 2:
Figure 3:
Figure 4:
Figure 5:
IV. Procedure VOM Familiarization
1. Familiarize yourself with the controls and scales of the Analog Voltmeter. 2. Fill-up Tables 2, 3 and 4.
Fixed Carbon Resistor 1. Determine the rated value of the five resistors. Refer to table 1. Table 1: Resistor Color Coding EIA Standards
2. Measure their resistances as shown in Figure 1 and compare it with the rated value. Determine their condition (good, open, shorted, out of range). Accomplish Tables 5 and 6. Resistors in Series, Parallel and Series-Parallel Connections 1. Connect the five resistors in series as shown in figure 3. Measure the total resistance between terminals 1 and 2 of the figure. Compare the computed value and the measured value and solve for the percent difference. 2. Connect the five resistors in parallel as shown in figure 4. Measure the equivalent resistance between terminals 1 and 2 of the figure. Compare the computed value and the measured value and solve for the percent difference. 3. Connect the five resistors in series-parallel connection as shown in figure 5. Measure the total resistance between terminals 1 and 2 of the figure. Compare the computed value and the measured value and solve for the percent difference. Potentiometer 1. With the shaft in front, designate the terminals for the potentiometer as terminal 1, 2 and 3, left to right. Turn the shaft complete counterclockwise. This is the 0 setting. 2. Measure and record in Table 7 the total resistance across terminals 1 and 3. This resistance will be designated as R13. 3. Connect the ohmmeter terminals across terminals 1 and 2. Measure the resistance and assign it as R12. Transfer the probe from terminal 1 to terminal 3 and measure the resistance. Designate it as R23. Record the data in Table 7.
4. Turn shaft , , until maximum limit 1 setting or one complete clockwise rotation. Correspondingly, record data for those settings as required in Table 7. V. Data VOM Controls and Scales Resistance Measurement
Table 2:
Range Settin g Rx1 R 10 Rx 100
Position B Reading ohms
Position C Reading ohms
Position D Reading ohms
Current Measurement
Range Settin Table 3: g amper es 50mA 250mA 10A
Position A Reading amperes 17mA 85mA 4.1A
Position B Reading amperes
Position C Reading amperes
Position D Reading amperes
Voltage Measurement
Table 4: Range Settin g 250 50 10
Position A Reading volts 145V 29V 6V
Position B Reading volts
Position C Reading volts
Position D Reading volts
Table 5: Rated Value 4
Resisto r R1 R2 R3 R4 R5
Color Bands 1 2 3
Tolerance %
Table 6:
Rated Resistor Value R1 R2 R3 R4 R5
Measured Condition Value
Percent Difference%
Series Connection RT (Computed) : __________ __________ Parallel Connection Req (Computed): _________ Req(Measured): ___________ Percent Difference: __________ RT (Measured): __________ Percent Difference:
Series-Parallel Connection Req (Computed): __________ Req(Measured): __________ Percent Difference: __________
Potentiometer Table 7:
Settings 0 1/4 1/2 3/4 1
R12
R23
R31
VI. Conclusion
You might also like
- Project PlanDocument12 pagesProject Plan1deakz4lu7geNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Wave Shaping CircuitsDocument9 pagesExperiment 2 Wave Shaping CircuitsMaria Abia Lapena50% (2)
- Electronics 2 Lab ManualDocument75 pagesElectronics 2 Lab ManualLuisa Marie Bernardo Rañada100% (1)
- ECE 460 Lab ReportDocument23 pagesECE 460 Lab Report01001110010100101100% (1)
- Lab#11 (Common Base Amplifier)Document8 pagesLab#11 (Common Base Amplifier)Faraz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - IC Logic FamilyDocument33 pagesChapter 7 - IC Logic Familyswathich6No ratings yet
- Lab Manual 3 Semester Basic Electronics - I: Lab Engineerer: Subject TeacherDocument21 pagesLab Manual 3 Semester Basic Electronics - I: Lab Engineerer: Subject TeacherOmer Sheikh100% (1)
- Experiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDenisse Torizo Olan100% (1)
- Laboratory Experiment 1Document14 pagesLaboratory Experiment 1John Bien VelascoNo ratings yet
- Automated Smoking Zone Monitoring & Alerting Project: Block DiagramDocument2 pagesAutomated Smoking Zone Monitoring & Alerting Project: Block DiagramIsraelPerezSanchez100% (1)
- EE Laws QuizDocument9 pagesEE Laws QuizJiever AustriaNo ratings yet
- EEE431 Module 2Document27 pagesEEE431 Module 2Victor ImehNo ratings yet
- (ELECS2) Exp3 - Darlington and Cascode Amplifier CircuitsDocument17 pages(ELECS2) Exp3 - Darlington and Cascode Amplifier CircuitsFrodolfre Reginald Lazo100% (2)
- Power Supply Filters and RegulatorsDocument13 pagesPower Supply Filters and RegulatorsYacine KhalidNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3,4 and 5Document10 pagesExperiment 3,4 and 5airaNo ratings yet
- Shockley Diode Working and AdvantagesDocument6 pagesShockley Diode Working and AdvantagesHaries GarciaNo ratings yet
- ECEN 20093 - Lesson 4 Unit 1-4 - Salamat, Andre Agassi DDocument1 pageECEN 20093 - Lesson 4 Unit 1-4 - Salamat, Andre Agassi DandreagassiNo ratings yet
- Proposal 1Document14 pagesProposal 1Engid100% (1)
- Ee Laws Codes and Professional Ethics Bsee 201a Ella Mae D. Detablan Le2 PDFDocument26 pagesEe Laws Codes and Professional Ethics Bsee 201a Ella Mae D. Detablan Le2 PDFMark Lawrence BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller: Minor Project PresentationDocument14 pagesMPPT Solar Charge Controller: Minor Project PresentationManikandan P Engineering EEENo ratings yet
- 0-12v Variable Power SupplyDocument19 pages0-12v Variable Power Supplygirigtr2010100% (1)
- Experiment 2 BJT SwitchDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 BJT Switchprop_kcp50% (2)
- Electromagnetic Fields & Waves (BEB20303) Chapter 1: Electrostatic FieldDocument32 pagesElectromagnetic Fields & Waves (BEB20303) Chapter 1: Electrostatic FieldAFiqah Nazirah JailaniNo ratings yet
- BJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseDocument29 pagesBJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseKrista JacksonNo ratings yet
- IEEE Format Vending Machine ReportDocument6 pagesIEEE Format Vending Machine ReportKarim I. Chevelwalla57% (7)
- Instrumentation (Finale)Document20 pagesInstrumentation (Finale)Jonathan BacusNo ratings yet
- Mdefbod Quiz 1Document1 pageMdefbod Quiz 1Heiro KeystrifeNo ratings yet
- CPE 004 Logic CircuitDocument48 pagesCPE 004 Logic CircuitkennethNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication With Arduino Uno BoardDocument3 pagesWireless Communication With Arduino Uno BoardDan M Stone100% (1)
- Experiment #01 (Measurement of AC Voltage With An Oscilloscope)Document9 pagesExperiment #01 (Measurement of AC Voltage With An Oscilloscope)NeilChristianBonillaNo ratings yet
- Linear Summing and Non-Linear MixingDocument14 pagesLinear Summing and Non-Linear MixingErven UmbaoNo ratings yet
- FET Amplifier: ECE20L-2Document10 pagesFET Amplifier: ECE20L-2Luch ÜNo ratings yet
- Group 11 Case Study 1 Ra 7920 ElectricalDocument9 pagesGroup 11 Case Study 1 Ra 7920 ElectricalHani NotorioNo ratings yet
- Ujt and PutDocument35 pagesUjt and Putisraeljumbo100% (1)
- LC Lab Print Me PlsDocument5 pagesLC Lab Print Me PlsMark Christian GapasNo ratings yet
- Efficient Automatic Plant Irrigation System Using ATMEGA MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesEfficient Automatic Plant Irrigation System Using ATMEGA MicrocontrollerSatyanarayan MahantaNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits: Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsDocument16 pagesAC Circuits: Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsHiếu Dương100% (1)
- Power Dissipation in Ac Circuits: Experiment No. 7Document11 pagesPower Dissipation in Ac Circuits: Experiment No. 7NicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 BJT Biasing and Thermal StabilizationDocument74 pagesChapter 5 BJT Biasing and Thermal Stabilizationshubhankar palNo ratings yet
- Eletronics Lab Report - Zener DiodesDocument3 pagesEletronics Lab Report - Zener DiodesThan Lwin Aung71% (7)
- Lab Manual All ExperimentDocument62 pagesLab Manual All ExperimentLIFE of PSNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1535596930012Document64 pagesOrca Share Media1535596930012Julia Latawan LasilasNo ratings yet
- DSP Project ProposalDocument6 pagesDSP Project ProposalAnees AbrolNo ratings yet
- 2.diode Clipper and ClamperDocument12 pages2.diode Clipper and ClamperMounika AllagaddaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Reduction of Multiple Subsystems BlockDocument21 pagesChapter 5 Reduction of Multiple Subsystems BlockRahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- 11 WattmeterDocument14 pages11 WattmeterislahidNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Power Supply Circuit (Paloma)Document16 pagesSimulation of Power Supply Circuit (Paloma)Emmanuel PalomaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory No. 1 - Familiarization of Electrical Measuring Instruments DevicesDocument11 pagesLaboratory No. 1 - Familiarization of Electrical Measuring Instruments DevicesJames Patrick Torres0% (1)
- MicroprocessorDocument7 pagesMicroprocessorEjay BildanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1A Basic Concepts PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 1A Basic Concepts PDFChristian MuliNo ratings yet
- BLOCKTRANSFERANDSEARCHDocument7 pagesBLOCKTRANSFERANDSEARCHNaomi Aira Gole CruzNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics Activity 2Document2 pagesPneumatics Activity 2Jay Mark BalaneNo ratings yet
- EC8553 Electron Devices and Circuits Question BankDocument24 pagesEC8553 Electron Devices and Circuits Question BankRaja PirianNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4Document4 pagesExperiment No. 4Archimedes R. OyangorenNo ratings yet
- DCExpt 3Document5 pagesDCExpt 3Eya CedillaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department: Logic Circuits and Switching Theory ManualDocument8 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineering Department: Logic Circuits and Switching Theory ManualFrodolfre Reginald LazoNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLab Reportnaveed sheikhNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document8 pagesExp 2Rohaan AhmedNo ratings yet
- LAB 2 OHMs Law and Resistor Color CodingDocument4 pagesLAB 2 OHMs Law and Resistor Color Codingrexel100% (1)
- Ohm's Law in The Lab: Laboratory Activity 2Document6 pagesOhm's Law in The Lab: Laboratory Activity 2CathyNo ratings yet
- JANUARY 22, 2017 Mt. Manalmon, San Miguel, Bulacan: Jay Umali: 0927-417-7863Document1 pageJANUARY 22, 2017 Mt. Manalmon, San Miguel, Bulacan: Jay Umali: 0927-417-7863Rodge BalNo ratings yet
- Student Consultation Log Sheet: 2nd Semester: SY 2014 - 2015Document1 pageStudent Consultation Log Sheet: 2nd Semester: SY 2014 - 2015Rodge BalNo ratings yet
- Ideal Weight ChartDocument2 pagesIdeal Weight ChartRodge BalNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine: Parts and FunctionsDocument40 pagesDiesel Engine: Parts and FunctionsRodge Bal100% (2)
- X Hybrid User ManualDocument55 pagesX Hybrid User ManualRodge BalNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Prob Set (Seph)Document23 pagesDynamics Prob Set (Seph)Rodge BalNo ratings yet
- Engineering DesignDocument6 pagesEngineering DesignRodge BalNo ratings yet
- Statics MathalinoDocument5 pagesStatics MathalinoRodge Bal100% (1)
- Bus InterconnectionDocument31 pagesBus InterconnectionAnonymous A72zb61100% (1)
- 4688 PDFDocument2 pages4688 PDFLucas PinonNo ratings yet
- I/O Buffer Megafunction (ALTIOBUF) User GuideDocument54 pagesI/O Buffer Megafunction (ALTIOBUF) User GuideSergeyNo ratings yet
- Infinity Pro IntraDocument16 pagesInfinity Pro IntraPaki2908No ratings yet
- LdoDocument13 pagesLdoThanhNhan DinhNo ratings yet
- HI 2160 RC Plus Quick TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesHI 2160 RC Plus Quick TroubleshootingtahaNo ratings yet
- DICA Lab Manual PDFDocument64 pagesDICA Lab Manual PDFssptc MagazineNo ratings yet
- 06 Appendix ADocument6 pages06 Appendix AING. RUBENSNo ratings yet
- Lenovo X270 NM-B061R04 Schematic PDFDocument100 pagesLenovo X270 NM-B061R04 Schematic PDFodie70No ratings yet
- WT8072Document5 pagesWT8072hectcandNo ratings yet
- GO - NA25 - E1 - 1 2G-3G Cell Reselection & HandoverDocument37 pagesGO - NA25 - E1 - 1 2G-3G Cell Reselection & HandoverAmitesh DasNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument8 pagesDatasheetStuxnetNo ratings yet
- Mt1000 Parts List and AccessoriesDocument14 pagesMt1000 Parts List and AccessoriespatatepoileNo ratings yet
- KPD285 Sibabangun - KPD978 Sibabangun Kota, MLCN-23Xu, 0.6, 50 MBPS, 1+0Document4 pagesKPD285 Sibabangun - KPD978 Sibabangun Kota, MLCN-23Xu, 0.6, 50 MBPS, 1+0lewgne08No ratings yet
- InteliNano NT Datasheet 2012-3 CPLENANODocument6 pagesInteliNano NT Datasheet 2012-3 CPLENANOsdiaman100% (1)
- Systems Theory and Management Information SystemsDocument393 pagesSystems Theory and Management Information SystemsWycliffNo ratings yet
- Riotronic XS - Uphole Tester - EngDocument2 pagesRiotronic XS - Uphole Tester - EngPedro Ramos PAchecoNo ratings yet
- AC Servo Motor Driver MINAS S-SeriesDocument133 pagesAC Servo Motor Driver MINAS S-SeriesIsmael 8877No ratings yet
- Yamaha DVRS 100Document144 pagesYamaha DVRS 100videosonNo ratings yet
- Haxorware ManualDocument23 pagesHaxorware ManualVivianandEnrique Garibay100% (1)
- Inductive Proximity Sensor Interfaced With ArduinoDocument6 pagesInductive Proximity Sensor Interfaced With ArduinoIJSTENo ratings yet
- Control Systems: GATE Objective & Numerical Type SolutionsDocument26 pagesControl Systems: GATE Objective & Numerical Type SolutionsFlat Mate67% (3)
- Configuring SDR33 To Leica TPSDocument3 pagesConfiguring SDR33 To Leica TPSVali ItuNo ratings yet
- Uc 51 DocuDocument61 pagesUc 51 DocuMohamed LazouriNo ratings yet
- CSS 8Document26 pagesCSS 8bernardocathlynnNo ratings yet
- MCQ Electrical CircuitsDocument81 pagesMCQ Electrical CircuitsAnonymous sENwj8nwq50% (2)
- Prx600 SeriesDocument36 pagesPrx600 SeriesaugustinhodjNo ratings yet
- 8051 SerialDocument10 pages8051 SerialnagarajNo ratings yet
- Transformer Lab ManualDocument68 pagesTransformer Lab ManualRolando Cruz100% (1)
- Esp-S3-12k Module Datasheet v1.0.0Document25 pagesEsp-S3-12k Module Datasheet v1.0.0vmsperandioNo ratings yet