Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy Optimizing Furnace
Uploaded by
sourajpatelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy Optimizing Furnace
Uploaded by
sourajpatelCopyright:
Available Formats
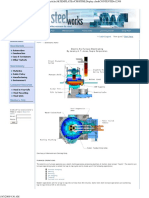
ENERGY OPTIMIZING FURNACE Main parts of EOF
1. Oxygen Lancing 2. EBT 3. Slag Door 4. Coke Injection System 5. Charging Door 6. Furnace Exhaust System
1. Oxygen LancingA. for oxygen lancing three co-jet systems is arranged in EOF. In each co-jet system coherent jet blow by different nozzle. For oxygen gas one hole is used and diameter of the hole 22.4 mm, oxygen gas penetration depth is 1.4 mm and the purity of oxygen is 99.9%, blowing pressure is 22 kg/cm2 and oxygen consumption 2200 nm3/heat. B. Propane (C3H8) gas used for producing the cloud over the oxygen jet which prevent the reaction of oxygen with refractory wall and also prevent the wear of refractory wall as well as to help for deep penetration, the propane gas pressure 8 kg/cm2 and the diameter is 4 mm. C. Shroud oxygen used due to high utilization of main oxygen gas and deep penetration of main oxygen and pressure of shroud oxygen 3-4 kg/cm2 and nozzle diameter is 8 mm. D. The three oxygen lance are placed at position 120 deg. and two are inclined at 45 deg. and one is inclined at 55 deg.
2. EBT- the full form of the EBT is eccentric bottom tap and their diameter is 130 mm. the
main function of EBT are slag free tapping and good alloy recovery in further process, and to reduce the process time.
3. Slag Door- slag door is used to tap continuously foamy slag to refine the steel.
foam has been defined as a medium consisting of gas bubbles in a liquid, e.g. soap bubbles in water. Principle of foamy slag in steel making the generation of CO during the refining can lead to foam formation if the slag is viscous enough. Reaction of Foamy slag Practice-
Foamy Slag Practice-
(FeO) + C = Fe + CO (g)
4. Coke Injection System- for the injection of fines coke (3-6 mm) two hoppers are
used. Purpose1. To safe refractory lining 2. for better foamy slag practice 3. for better recovery of oxygen 4. and also prevent the metal Fe is not form FeO more
5. Charging Door- through the pan feeder the raw material of EOF is charge in charging
door of furnace. Mainly bottom charging is done by pan feeder. Bottom charging used because it prevent the wear of refractory lining from hot metal charging. Bottom chargingLime Dolomite DRI Fines Scrap -500 Kg - 500 Kg - 1500 Kg - 500 Kg
Purpose of charging materialsLime- use for Slag making Dolomite- use for slag making as well as refractory lining safety by coating of Mgo DRI For temperature maintenance as a coolant.
6. Fume Extraction System (FES)- During the furnace operation large amount of
CO gas are generates which are used as main refining gas but some amount of CO gas are unutilized which are come out through FES, this CO gar are very harmful for our environment therefore this CO gar are converted into CO2 by combustion of air. When the CO gas come out from furnace which are burn in combustion chamber by air. The air suction amount operate by elbow duct if the distance of moving sleeve increase air suction is increase.
After burning of CO gas which are convert into CO2 gas, these CO2 gas goes for cooling in forced air cooler (FAC) than finally goes in bay house for removal of solid dust and now solid free CO2 gas come out through ID fan.
PROCESS OF ENERGY OPTIMIZING FURNACEEOF process done in 40 T capacity furnace the raw materials are 1. Hot metal composiion C- 3.5-4.2%, Mn- 0.1-0.5%, S- 0.06% (max), 2. Lime 3. Dolomite 4. Coke 5. DRI 6. Scrap Steel making is a oxidation process, in EOF heat generate by exothermic reaction. Operating temperature of EOF is 1580 deg. C and tapping temperature is 1620 deg. C. Color of oxidizing slag is black and FeO % in slag 20% In steel making process the impurities are remove in following sequence Si , Mn, C, P. For the removal of P, the temperature maintain between 1540 deg.C-1580 deg.C because above that temperature bond of P2O5 has break& P again diffused in hot metal Removal of P and S are very important because it form the non-metallic inclusion which are create the problem for further processing. Phosphorus Create Cold shortness Sulfur Create Hot shortness Si- 0.8-1.2% P- 0.12(max) Fe- 93-94%
Mainly two process are done in EOF1. De-carburization- it is a process of removal of carbon by O2 Blowing . 2. De-phophorisation- it is process of removal of P by O2 blowing and maintaining basicity. De-phophorisation condition are-
1. High basicity 2.5-3 2. Low temperature-1540 C-1580 deg. C 3. Oxidizing atmosphere oxygen blowing Basicity- it is a ratio of basic slag and acid slag Basicity = Basic slag/acid slag, CaO/SiO2 = 2.5-3 The Principle Reactions of steel making are1. (FeO) = [Fe] + [O] Oxygen dissolved in the melt oxidizes carbon, phosphorous, silicon and manganese: 2. [C] + [O] = {CO} 3. [Si] + {O2} = (SiO2) 4. [Mn] + 1/2{O2} = (MnO) 5. 2[P] + 5/2{O2} = (P2O5) 6. [S] + (CaO) = (CaS) + [O] reducing atmosphere
You might also like
- Indian Steel Making ProcessesDocument10 pagesIndian Steel Making ProcessesSarbajitManna100% (1)
- Iron MakingDocument26 pagesIron Makingsumit ranjanNo ratings yet
- THE EFFECT OF FOAMY SLAG IN THE ELECTRIC ARC FURNACES ON ELECTRIC Energy Consumption PDFDocument10 pagesTHE EFFECT OF FOAMY SLAG IN THE ELECTRIC ARC FURNACES ON ELECTRIC Energy Consumption PDFManojlovic VasoNo ratings yet
- Ironmaking and Steelmaking Theory and PracticeDocument9 pagesIronmaking and Steelmaking Theory and PracticeRasul BzNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pulverized Coal Injection Technology and Blast Furnace OperationFrom EverandAdvanced Pulverized Coal Injection Technology and Blast Furnace OperationK. IshiiNo ratings yet
- Combustion of Pulverised Coal in a Mixture of Oxygen and Recycled Flue GasFrom EverandCombustion of Pulverised Coal in a Mixture of Oxygen and Recycled Flue GasNo ratings yet
- Steel Processing in Energy Optimizing Furnace: 4.1 Preparation of EofDocument8 pagesSteel Processing in Energy Optimizing Furnace: 4.1 Preparation of EofRitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual FurnaceDocument21 pagesOperation Manual FurnaceAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Pig Iron - Blast Furnace RouteDocument3 pagesPig Iron - Blast Furnace RouteRaden Pambudi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Modern Steelmaking Processes: Basic Oxygen Process DesignDocument14 pagesModern Steelmaking Processes: Basic Oxygen Process DesignMir Rafsan100% (1)
- Cupola Furnace: Types, Parts, Working and ApplicationsDocument23 pagesCupola Furnace: Types, Parts, Working and Applicationssayan halderNo ratings yet
- Embr 1 PDFDocument32 pagesEmbr 1 PDFKamod RanjanNo ratings yet
- Ladle Refining FurnaceDocument3 pagesLadle Refining FurnaceBibhudutta mishraNo ratings yet
- Mill ScaleDocument6 pagesMill ScaleJhovanny RendónNo ratings yet
- How Cupola Furnaces Melt Cast IronDocument13 pagesHow Cupola Furnaces Melt Cast IronRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Iron and Steel Making Lecture 1: Introduction: Prof. Dr. Hafiz A. Ahmed Dr. Lamiaa Z. MohamedDocument7 pagesIron and Steel Making Lecture 1: Introduction: Prof. Dr. Hafiz A. Ahmed Dr. Lamiaa Z. Mohamedيوسف عادل حسانينNo ratings yet
- Production of IronDocument15 pagesProduction of IronMassy KappsNo ratings yet
- Cupola Furnace Project ReportDocument32 pagesCupola Furnace Project Reportadelina ednandaNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation in Cupola FurnaceDocument32 pagesEnergy Conservation in Cupola Furnacenayan patel100% (1)
- Blast Furnace Gas CleaningDocument25 pagesBlast Furnace Gas CleaningSalil JainNo ratings yet
- Brief Description On Electric Arc FurnaceDocument28 pagesBrief Description On Electric Arc FurnaceVishwanath HunagundNo ratings yet
- Strollberg LEO WorkshopDocument54 pagesStrollberg LEO WorkshopBinod Kumar PadhiNo ratings yet
- Bee - Hive Metallurgical CokeDocument4 pagesBee - Hive Metallurgical Coke124swadeshiNo ratings yet
- Mass and Heat Balance of Steelmaking in Bof As Compared To Eaf ProcessesDocument15 pagesMass and Heat Balance of Steelmaking in Bof As Compared To Eaf ProcessesAgil Setyawan100% (1)
- First Movable KR in India Has Successfully Started Up in JSW Steel at VijayanagarDocument10 pagesFirst Movable KR in India Has Successfully Started Up in JSW Steel at VijayanagarJJNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Steel Making ProcessesDocument78 pagesOxygen Steel Making ProcessesDwy IconAceNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel AOD Operation and Slag Optimisation PDFDocument41 pagesStainless Steel AOD Operation and Slag Optimisation PDFPrakash MishraNo ratings yet
- Carbon Pick-Up IF Steels PDFDocument3 pagesCarbon Pick-Up IF Steels PDFAnonymous jYdzzw6No ratings yet
- Improvement of Surface Quality of Continuously Cast Steel Control PDFDocument130 pagesImprovement of Surface Quality of Continuously Cast Steel Control PDFChrist ChristiNo ratings yet
- Reverberatory Furnace: By: Walid Khalid AbdulkaderDocument9 pagesReverberatory Furnace: By: Walid Khalid Abdulkaderanon_665535262No ratings yet
- State of The Art and Future of The Blast FurnaceDocument16 pagesState of The Art and Future of The Blast Furnacesaibal_silNo ratings yet
- Nmd-Atm-2018r-00405 - Arghya Majumder - RinlDocument18 pagesNmd-Atm-2018r-00405 - Arghya Majumder - RinlArghya MajumderNo ratings yet
- Iron Making PPT 1Document35 pagesIron Making PPT 1SHUBHAM VERMANo ratings yet
- Tecnored Process - High Potential in Using Different Kinds of Solid FuelsDocument5 pagesTecnored Process - High Potential in Using Different Kinds of Solid FuelsRogerio CannoniNo ratings yet
- The Basic Oxygen SteelmakingDocument15 pagesThe Basic Oxygen SteelmakingM. Didik Suryadi100% (1)
- Desulfurization of SteelDocument69 pagesDesulfurization of SteelPouria Homayoun100% (2)
- Steeelmaking 130109095431 Phpapp02Document251 pagesSteeelmaking 130109095431 Phpapp02Debasish Chatterjee ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- OTE Outotec Pallet Cars For Sintering and PelletizDocument4 pagesOTE Outotec Pallet Cars For Sintering and PelletizShukla SuyashNo ratings yet
- Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking by Jeremy A. T. Jones, Nupro CorporationDocument9 pagesElectric Arc Furnace Steelmaking by Jeremy A. T. Jones, Nupro CorporationGilson JuniorNo ratings yet
- Electric Arc Furnace Injection System For OxygenDocument7 pagesElectric Arc Furnace Injection System For OxygenIcilma LiraNo ratings yet
- Steel MakingDocument28 pagesSteel Makingsatish_trivediNo ratings yet
- The Behaviour of The Secondary Metallurgy Slag Into The EAF. How To Create A Good Foamy Slag With The Appropriate Basicity Using A Mix of Lime and Recycled Ladle Slag As EAF Slag FormerDocument1 pageThe Behaviour of The Secondary Metallurgy Slag Into The EAF. How To Create A Good Foamy Slag With The Appropriate Basicity Using A Mix of Lime and Recycled Ladle Slag As EAF Slag FormerRavindra Kashyap0% (1)
- What is a Blast Furnace? The Extraction of IronDocument10 pagesWhat is a Blast Furnace? The Extraction of IronSapan KansaraNo ratings yet
- AmiimDocument9 pagesAmiimRanjan SahooNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction of The Blast Furnace ProcessDocument9 pages1 Introduction of The Blast Furnace Processhemant patilNo ratings yet
- Blast Furnace Tap Hole and Tapping of The FurnaceDocument11 pagesBlast Furnace Tap Hole and Tapping of The Furnaceprashant mishraNo ratings yet
- Tap Hole ClaysDocument1 pageTap Hole ClaysNishant BandaruNo ratings yet
- Blast Furnace: How Iron is ExtractedDocument17 pagesBlast Furnace: How Iron is ExtractedAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- 021-Integration of Midrex Technologies in North America Steel Plants - Evaluation of Economical and CO2 ImpactsDocument10 pages021-Integration of Midrex Technologies in North America Steel Plants - Evaluation of Economical and CO2 ImpactscornNo ratings yet
- Cupola Furnace eDocument5 pagesCupola Furnace eAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- What Is SteelDocument10 pagesWhat Is SteelKristo Ver TamposNo ratings yet
- How's Steel Manufactured?: Raw Materials For IronmakingDocument6 pagesHow's Steel Manufactured?: Raw Materials For IronmakingUpendra93No ratings yet
- Design, Manufacturing and Testing of Induction Furnace: Submitted byDocument65 pagesDesign, Manufacturing and Testing of Induction Furnace: Submitted byGuru ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- IRREGULARITIES AND REMEDIES IN BLAST FURNACESDocument2 pagesIRREGULARITIES AND REMEDIES IN BLAST FURNACESSk BeheraNo ratings yet
- Blast FurnaceDocument28 pagesBlast Furnaceavanisharma_1991No ratings yet
- STEEL TITLEDocument23 pagesSTEEL TITLEMahadi HasanNo ratings yet
- Fluxes For MetallurgyDocument15 pagesFluxes For Metallurgyramau619No ratings yet
- Coke Quality and Thermal Reserve Zone PDFDocument6 pagesCoke Quality and Thermal Reserve Zone PDFhalder_kalyan9216No ratings yet
- 2011 Steelmaking Ch12Document56 pages2011 Steelmaking Ch12Thapelo LesameNo ratings yet
- Roll Cooling Report2Document7 pagesRoll Cooling Report2sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Ø72 04.05.23 PDFDocument1 pageØ72 04.05.23 PDFsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Tax Saving (ELSS) Statement: Souraj Ranjan PatelDocument2 pagesTax Saving (ELSS) Statement: Souraj Ranjan PatelsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Roll Cooling Report2Document7 pagesRoll Cooling Report2sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Mill Operation Shift Schedule1Document32 pagesMill Operation Shift Schedule1sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Ø72 04.05.23 PDFDocument1 pageØ72 04.05.23 PDFsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Cont BillDocument17 pagesCont BillsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Ø72 04.05.23 PDFDocument1 pageØ72 04.05.23 PDFsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- GuidingDocument1 pageGuidingsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- IDL EL Interview Application FormDocument4 pagesIDL EL Interview Application FormsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Dismentling ProcedureDocument4 pagesDismentling ProceduresourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Aarti Steels Limited Roll Shop Process Chart: Stock Size From BD Mill - 127 X 128 MMDocument1 pageAarti Steels Limited Roll Shop Process Chart: Stock Size From BD Mill - 127 X 128 MMsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Fiche Technique Steel Bronze - Anglais - Site - 2 1Document1 pageFiche Technique Steel Bronze - Anglais - Site - 2 1sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Spec. For Cranes (TATA)Document34 pagesElectrical Spec. For Cranes (TATA)sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- RHF Log Books-New (10494)Document2 pagesRHF Log Books-New (10494)sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Plain Bearing FailuresDocument7 pagesPlain Bearing FailuressourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Ø72 04.05.23 PDFDocument1 pageØ72 04.05.23 PDFsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Final Sheet (Rolled Size) - 24122019Document17 pagesFinal Sheet (Rolled Size) - 24122019sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Aarti Steels-23-4-2022Document10 pagesAarti Steels-23-4-2022sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Final Sheet (Rolled Size)Document12 pagesFinal Sheet (Rolled Size)sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Fichetechnique-White-Metal Anglais Site 2Document1 pageFichetechnique-White-Metal Anglais Site 2sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System Work Instruction for Roll AssemblyDocument2 pagesQuality Management System Work Instruction for Roll AssemblysourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Work Instructionfor MISReports 9980Document1 pageWork Instructionfor MISReports 9980sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System: Work Instruction For Person Working in RHF AreaDocument2 pagesQuality Management System: Work Instruction For Person Working in RHF AreasourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System: Work Instruction For Roll Inspection and Turning A. New Rolls: InspectionDocument2 pagesQuality Management System: Work Instruction For Roll Inspection and Turning A. New Rolls: InspectionsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System: Work Instruction For Person Working in RHF AreaDocument2 pagesQuality Management System: Work Instruction For Person Working in RHF AreasourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System Work Instruction for Roll AssemblyDocument2 pagesQuality Management System Work Instruction for Roll AssemblysourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System: Work Instruction For Operator, Fitters & Helpers in BDM StandDocument2 pagesQuality Management System: Work Instruction For Operator, Fitters & Helpers in BDM StandsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Work Instructionfor MISReports 9980Document1 pageWork Instructionfor MISReports 9980sourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System: Work Instruction For Roll Inspection and Turning A. New Rolls: InspectionDocument2 pagesQuality Management System: Work Instruction For Roll Inspection and Turning A. New Rolls: InspectionsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Skoda Yeti Brake Systems EngDocument174 pagesSkoda Yeti Brake Systems EngJonattan Javier Ramirez BolañosNo ratings yet
- Educational Leadership and Management: Lecturer: Ms. Janet Au YeungDocument22 pagesEducational Leadership and Management: Lecturer: Ms. Janet Au YeungTamamaNo ratings yet
- 48 Essential Life Skills Everyone Should Learn (S.a.)Document39 pages48 Essential Life Skills Everyone Should Learn (S.a.)Roman CooperNo ratings yet
- Seton Hall Univ Graphics ManualDocument39 pagesSeton Hall Univ Graphics ManualArung MabessaNo ratings yet
- History UNIT 2 Class NotesDocument15 pagesHistory UNIT 2 Class NotesVANSHIKA CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- How To Model A Square Foundation On PlaxisDocument4 pagesHow To Model A Square Foundation On Plaxisomarrashad84No ratings yet
- Regulating Admin AccountsDocument5 pagesRegulating Admin Accountsami pritNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Harga Vskepuasan Pelanggan Vs Loyalitas PelangganDocument13 pagesJurnal Harga Vskepuasan Pelanggan Vs Loyalitas PelangganSyahrin AsmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Professional Ethics & Code of ConductDocument97 pagesUnit 2 - Professional Ethics & Code of ConductPradiba Raajkumaar25% (4)
- Model Operator'S Manual: Non Contact TonometerDocument100 pagesModel Operator'S Manual: Non Contact TonometerRitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Election Laws (Nachura, de Leon, Bernas, Valencia) (2022)Document101 pagesElection Laws (Nachura, de Leon, Bernas, Valencia) (2022)Aimee VenterosoNo ratings yet
- Hyper 66 Hammer Brochure Ql60Document2 pagesHyper 66 Hammer Brochure Ql60Vasu KapoorNo ratings yet
- ACEA Regulatory Guide 2022Document197 pagesACEA Regulatory Guide 2022Reinaldo RamírezNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Corporations IDocument13 pagesAccounting For Corporations Iibrahim mohamedNo ratings yet
- Tugas Contoh 3 Jurnal Nasional - Muhammad Habib - 217312040005Document73 pagesTugas Contoh 3 Jurnal Nasional - Muhammad Habib - 217312040005abibardaya desain3No ratings yet
- IPS-ENERGY - Available Relay ModelsDocument597 pagesIPS-ENERGY - Available Relay Modelsbrahim100% (2)
- The Chairman, Railway Board & Ors. V Chandrima Das PDFDocument11 pagesThe Chairman, Railway Board & Ors. V Chandrima Das PDFSandeep Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Full Course NotesDocument33 pagesFull Course Notesukxgerard100% (11)
- How To Use Automotive Diagnostic Scanners (2015) PDFDocument203 pagesHow To Use Automotive Diagnostic Scanners (2015) PDFAntonio M Palma89% (9)
- English For The Workplace: The Importance of English Language Skills For Effective PerformanceDocument16 pagesEnglish For The Workplace: The Importance of English Language Skills For Effective Performanceบี'โอ' วายNo ratings yet
- TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES PRE BOARD EXAM DAY 3Document12 pagesTECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES PRE BOARD EXAM DAY 3ZZROTNo ratings yet
- Cosmetic Stability TestingDocument10 pagesCosmetic Stability Testingshivampharma100% (3)
- Dow Corning Success in ChinaDocument24 pagesDow Corning Success in ChinaAnonymous lSeU8v2vQJ100% (1)
- Tkinter Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesTkinter Cheat Sheetphanina01No ratings yet
- Canapele-Coltare Decart SchneiderDocument91 pagesCanapele-Coltare Decart SchneiderLibelulaNeagraNo ratings yet
- Welding Symbol Modul 1Document52 pagesWelding Symbol Modul 1bheghe100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Cultural Foods PlanningDocument8 pagesFactors Affecting Cultural Foods PlanningRegie Atienza50% (4)
- (Doc24.vn) De-Thi-Vao-10-Mon-Tieng-Anh-Thpt-Chuyen-Tp-Ho-Chinh-Minh-Nam-2014-2015-Co-Loi-GiaiDocument20 pages(Doc24.vn) De-Thi-Vao-10-Mon-Tieng-Anh-Thpt-Chuyen-Tp-Ho-Chinh-Minh-Nam-2014-2015-Co-Loi-GiaiThao AnhNo ratings yet
- Naukri ANANDKUMARCHANDRAKANTPANDYAMCA (25y 0m)Document5 pagesNaukri ANANDKUMARCHANDRAKANTPANDYAMCA (25y 0m)Kewal DNo ratings yet
- OSV Part 4Document664 pagesOSV Part 4devbsl123No ratings yet