Professional Documents
Culture Documents
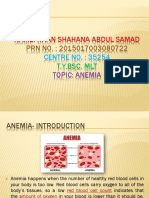
Anemia
Uploaded by
vincesumergidoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anemia
Uploaded by
vincesumergidoCopyright:
Available Formats
New Mexico
AIDS InfoNet
www.aidsinfonet.org
Fact Sheet Number 552
ANEMIA
WHAT IS ANEMIA?
Anemia is a shortage of hemoglobin (HGB). HGB is a protein in red blood cells. It carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. Anemia causes fatigue and shortness of breath. People with anemia dont feel as good as people with a normal level of HGB. They find it harder to work. This is called having a lower quality of life. HGB levels are measured as part of a complete blood count (CBC.) See Fact Sheet 106 for more information on these laboratory tests. HGB is measured as grams per deciliter, the amount in a specific volume of blood. Anemia is defined by the level of HGB. Most doctors agree that HGB levels below 6.5 indicate life-threatening anemia. Normal levels are at least 12 for women and at least 14 for men. Overall, women have lower levels of HGB. So do very old and very young people. More African-Americans have anemia than people in other ethnic groups. HIV infection can cause anemia. So can many opportunistic infections (see fact sheet 500) related to HIV disease. Many drugs that are commonly used to treat HIV and related infections can cause anemia. medications that cause anemia. Two additional treatments are transfusions, and injections of EPO. Blood transfusion used to be the only treatment for severe anemia. However, transfusions can cause infection and suppress the immune system. They appear to cause faster progression of HIV disease and to increase the risk of death for HIV patients. EPO (erythropoietin) stimulates the production of red blood cells. In 1985, scientists learned how to make synthetic EPO. It is injected under the skin, usually once a week. A large study of people with HIV found that transfusions seemed to increase the risk of death, while EPO injections decreased it. Because of the risks of transfusions, they are rarely used to treat anemia.
ANEMIA AND HIV
Serious anemia used to be much more common. Over 80% of people with an AIDS diagnosis had some degree of anemia. People with more advanced HIV disease, or a lower CD4 count, had higher rates of anemia. The rate of anemia went down when people started using highly active antiviral therapy (HAART.) Severe anemia has become rare. However, HAART has not eliminated anemia. A large study found that about 46% of patients had mild or moderate anemia, even after one year of HAART. Several factors are linked to a higher rate of anemia in people with HIV: Lower CD4 cell counts (see fact sheet 412). Higher viral load (fact sheet 413) Taking AZT (Retrovir, fact sheet 420) Being African-American Being a woman HIV disease progression is about 5 times more common in people with anemia. Anemia is also linked to a higher risk of death. Treatment of anemia seems to eliminate these risks.
THE BOTTOM LINE
Anemia has always been a problem for people with HIV and AIDS. The rate of serious anemia has dropped considerably since people started using HAART. However, almost half of people with HIV still have mild or moderate anemia. Anemia increases fatigue and makes people feel bad. It increases the risk of disease progression and death. It can be caused by HIV infection or other diseases. Many drugs used to treat HIV and related infections also cause anemia. Treating anemia improves the health and survival of people with HIV. Correcting bleeding or shortages of iron, or vitamins are the first steps. If possible, medications that cause anemia should be stopped. If necessary, the patient should be treated with erythropoietin, or, in rare cases, with a blood transfusion.
WHAT CAUSES ANEMIA?
The bone marrow produces red blood cells. This process requires iron, the vitamins B12 and folic acid (or folate.) Erythropoietin (EPO) stimulates the production of red blood cells. EPO is a hormone made by the kidneys. Anemia can be caused by low production of red blood cells. It is also caused by their loss or destruction. Several factors can cause anemia: Too little iron, vitamin B12 or folate. A shortage of folate can cause megaloblastic anemia with large, pale red blood cells (see Fact Sheet 106) Damage to bone marrow or kidneys Blood loss from internal bleeding or a womans menstrual cycle Destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia)
HOW IS ANEMIA TREATED?
Treating anemia depends on its cause. First, treat any chronic bleeding. This could be internal bleeding, hemorrhoids, or even frequent nosebleeds. Next, correct any shortages of iron, vitamin B12 or folate. Stop using, or reduce the doses of medications that cause anemia. These approaches might not work. It may not be possible to stop using all
Revised March 15, 2002
Partially funded by the National Library of Medicine and the New Mexico Department of Health Fact Sheets can be downloaded from the Internet at http://www.aidsinfonet.org
You might also like
- Anemia and Chronic Kidney Disease: What You Need To Know AboutDocument8 pagesAnemia and Chronic Kidney Disease: What You Need To Know AboutyehezkieldwardNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Arranged By: Mishael Immanuel Dae Pany (2014.03.010) Firman Syalasah (2014.03.006)Document13 pagesAnemia: Arranged By: Mishael Immanuel Dae Pany (2014.03.010) Firman Syalasah (2014.03.006)kharisma restuNo ratings yet
- Inf1268 3 Feb 2021 Anaemia Patient InformationDocument5 pagesInf1268 3 Feb 2021 Anaemia Patient InformationDavis JermacansNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide on Anemia: Learn Anemia Symptoms, Anemia Causes, and Anemia Treatments. Anemia types covered in full details: Iron-deficiency, Microcytic, Autoimmune Hemolytic, Sideroblastic, and Normocytic AnemiaFrom EverandThe Complete Guide on Anemia: Learn Anemia Symptoms, Anemia Causes, and Anemia Treatments. Anemia types covered in full details: Iron-deficiency, Microcytic, Autoimmune Hemolytic, Sideroblastic, and Normocytic AnemiaRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- Anemia in Kidney Disease and DialysisDocument6 pagesAnemia in Kidney Disease and DialysiscopiimeiNo ratings yet
- Anemia in CKDDocument36 pagesAnemia in CKDmaymawziNo ratings yet
- Review Jurnal Anfisman Grup G English VersionDocument11 pagesReview Jurnal Anfisman Grup G English VersionKayla NikenNo ratings yet
- ANEMIADocument5 pagesANEMIAIfèNo ratings yet
- Types of AnaemiaDocument5 pagesTypes of AnaemiaSrivatsav BhoopathyNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America Volume Issue 2014 (Doi 10.1016 - J.emc.2014.04.007) Vieth, Julie T. Lane, David R. - AnemiaDocument16 pagesEmergency Medicine Clinics of North America Volume Issue 2014 (Doi 10.1016 - J.emc.2014.04.007) Vieth, Julie T. Lane, David R. - AnemiaJeffrey Stefan Pal RiveraNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument92 pagesAnemiasangeetachatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Abstract Cardiovascular Complications Caused by An Accelerated Atherosclerotic Disease ConsistDocument5 pagesAbstract Cardiovascular Complications Caused by An Accelerated Atherosclerotic Disease Consistsandhu2020No ratings yet
- GGFHGFJKL KJKHGFDGHJKLDocument14 pagesGGFHGFJKL KJKHGFDGHJKLVania Millenia MelindaNo ratings yet
- A Case Analysis of Anemia2Document11 pagesA Case Analysis of Anemia2Recca Guirigay100% (1)
- Biology: Investigatory Project OnDocument24 pagesBiology: Investigatory Project OnManish KarnaniNo ratings yet
- PIL - What Is Anaemia (A5)Document8 pagesPIL - What Is Anaemia (A5)Hassan ShahNo ratings yet
- Anemia in Kidney Disease and Dialysis: EmailDocument9 pagesAnemia in Kidney Disease and Dialysis: EmailBenantoNo ratings yet
- Presenting Problems in Blood Disease and Clinical Examination of PatientsDocument31 pagesPresenting Problems in Blood Disease and Clinical Examination of Patientsساره عدي مصطفىNo ratings yet
- Why Get Tested?: AnaemiaDocument4 pagesWhy Get Tested?: Anaemiashasha009No ratings yet
- Fatigue: What Is Anemia?Document3 pagesFatigue: What Is Anemia?Annapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Anemia IntroductionDocument15 pagesAnemia IntroductionNitesh Kotian100% (1)
- Anemia Pres OrginalDocument61 pagesAnemia Pres OrginalenooNo ratings yet
- Aplastic Anemia InfoDocument5 pagesAplastic Anemia InfoSareno PJhēaNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument13 pagesAnemiaharizmnNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaLazeh MeNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid Deficiency AnemiaDocument15 pagesFolic Acid Deficiency Anemiafam111222No ratings yet
- Anemia For The Primary Care PhysicianDocument16 pagesAnemia For The Primary Care PhysicianAbdón Guerra FariasNo ratings yet
- Princess Durru Shehvar College of Nursing B.SC Nursing 2 Year Online Coaching Community Health Nursing - I AnemiaDocument6 pagesPrincess Durru Shehvar College of Nursing B.SC Nursing 2 Year Online Coaching Community Health Nursing - I AnemiaAnonymous hYMWbA100% (1)
- Bleeding DisordersDocument6 pagesBleeding DisorderslouisNo ratings yet
- Normocytic AnemiaDocument16 pagesNormocytic AnemiaPaula ArayaNo ratings yet
- AnaemiaDocument33 pagesAnaemiaShivam SoniNo ratings yet
- Blood Disorders in GeriatricDocument29 pagesBlood Disorders in GeriatricdheaNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic AnemiaDocument18 pagesHemolytic AnemiaAdisurya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Anemia of Chronic Disease in The ElderlyDocument7 pagesAnemia of Chronic Disease in The ElderlyAkbarNo ratings yet
- Anemia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, TreatmentsDocument1 pageAnemia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, TreatmentsBellaNo ratings yet
- Salinan Terjemahan 307211717 Laporan Pendahuluan AnemiaDocument16 pagesSalinan Terjemahan 307211717 Laporan Pendahuluan AnemiaRidho HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- HCA 240 WK 4 Blood DisordersDocument6 pagesHCA 240 WK 4 Blood Disordersmarilyn1221_55503248No ratings yet
- Update On (Approach To) Anemia1 (Changes)Document39 pagesUpdate On (Approach To) Anemia1 (Changes)Balchand KukrejaNo ratings yet
- AnemiaFactSheet ANNADocument5 pagesAnemiaFactSheet ANNARahmad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Anemia NevinDocument69 pagesAnemia NevinAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition AnemiaDocument5 pagesNutrition AnemiaPratiwi Raissa WindianiNo ratings yet
- Child With Blood Disorders PPT PRDocument114 pagesChild With Blood Disorders PPT PRchaarviNo ratings yet
- NCP - AnemiaDocument7 pagesNCP - AnemiaJulian Ivaran Naceda90% (10)
- Yyyy Y Yyyy Y Y Y Yyyy YY YYY YY: C C Y CyDocument5 pagesYyyy Y Yyyy Y Y Y Yyyy YY YYY YY: C C Y CyPrincess PlateroNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Anemia Bahasa InggrisDocument9 pagesJurnal Anemia Bahasa InggrisonyourmargotNo ratings yet
- What Is Anemia?Document11 pagesWhat Is Anemia?myacob_5No ratings yet
- What Is AnemiaDocument3 pagesWhat Is AnemiaPalakang PetotNo ratings yet
- When To See A DoctorDocument4 pagesWhen To See A DoctorIlmiyah Kisya El-FarrohNo ratings yet
- Anemia Report1Document2 pagesAnemia Report1Yhan-yhan Rodriguez KhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 49Document6 pagesChapter 49Melissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- Types Of Hemolytic Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandTypes Of Hemolytic Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fresh Frozen Plasma: Plasma Is The Clear, Pale-Yellow Liquid Part of BloodDocument5 pagesFresh Frozen Plasma: Plasma Is The Clear, Pale-Yellow Liquid Part of BloodsashaNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument11 pagesAplastic AnemiaToni Shiraishi-Aque RuizNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanHikaru TakishimaNo ratings yet
- Anemia and Chronic Kidney Disease: Stages 1-4Document16 pagesAnemia and Chronic Kidney Disease: Stages 1-4Pearl Raiza HadaniNo ratings yet
- 209-Hematology Review - Case StudiesDocument129 pages209-Hematology Review - Case StudiesKhalid Khalidi100% (2)
- Student's Name Institution Course DateDocument7 pagesStudent's Name Institution Course DateStephen NdireNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders: Vascular Defects & Coagulation FactorsDocument11 pagesBleeding Disorders: Vascular Defects & Coagulation FactorslouisNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DisordersDocument108 pagesHematologic DisordersEmma IntiaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Anemia, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Anemia, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Trauma Sellick's ManoeuvreDocument4 pagesTrauma Sellick's ManoeuvrevincesumergidoNo ratings yet
- Your Guide To Certification.6Document1 pageYour Guide To Certification.6vincesumergidoNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Extravasation, Management and PreventionDocument2 pagesPeripheral Extravasation, Management and PreventionvincesumergidoNo ratings yet
- Adam Glaser Slides 28 MarchDocument13 pagesAdam Glaser Slides 28 MarchvincesumergidoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcers The Stakes Just Got HigherDocument3 pagesPressure Ulcers The Stakes Just Got HighervincesumergidoNo ratings yet
- A (H1N1)Document3 pagesA (H1N1)vincesumergidoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Assessment For ElderlyDocument10 pagesNutrition Assessment For Elderlyvincesumergido100% (1)
- HDMI To MIPI and LVDS To MIPI Converter Rotator Board Solutions From Q VioDocument2 pagesHDMI To MIPI and LVDS To MIPI Converter Rotator Board Solutions From Q VioSubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Drinking Water Treatment Unit Scheme Ver 2Document31 pagesDrinking Water Treatment Unit Scheme Ver 2josephsedNo ratings yet
- 9.LearnEnglish Writing A2 Instructions For A Colleague PDFDocument5 pages9.LearnEnglish Writing A2 Instructions For A Colleague PDFوديع القباطيNo ratings yet
- A Cultura-Mundo - Resposta A Uma SociedDocument7 pagesA Cultura-Mundo - Resposta A Uma SociedSevero UlissesNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Measurement: Part 2: Measurement of National IncomeDocument13 pagesMacroeconomics Measurement: Part 2: Measurement of National IncomeManish NepaliNo ratings yet
- Yemen Companies Contact DetailsDocument5 pagesYemen Companies Contact DetailsYAGHMOURE ABDALRAHMAN78% (9)
- Research InstrumentsDocument28 pagesResearch InstrumentsAnjeneatte Amarille AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Fruit Brearing CropsDocument177 pagesFruit Brearing CropsJoshua G. Sapin100% (1)
- Ottawa County May ElectionDocument7 pagesOttawa County May ElectionWXMINo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory Manual: by Dr. N. Kumara SwamyDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory Manual: by Dr. N. Kumara SwamyMD Mahmudul Hasan Masud100% (1)
- Product Management Mcnaughton - 0Document4 pagesProduct Management Mcnaughton - 0Andrey MatusevichNo ratings yet
- 01 Childrenswear Safety Manual 2009 - ClothingDocument57 pages01 Childrenswear Safety Manual 2009 - Clothingmorshed_mahamud705538% (8)
- Banking Adbl EnglishDocument74 pagesBanking Adbl Englishdevi ghimireNo ratings yet
- AM2020-AFP1010 Installation Programming OperatingDocument268 pagesAM2020-AFP1010 Installation Programming OperatingBaron RicthenNo ratings yet
- SCI Annual Report 2017Document32 pagesSCI Annual Report 2017The Seamen's Church Institute100% (2)
- Soil ResistivityDocument6 pagesSoil ResistivityAnonymous EP0GKhfNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Financial AccountingDocument3 pagesSyllabus Financial AccountingHusain ADNo ratings yet
- 1. Mạch điện đồng hồ santafe 2014-2018Document5 pages1. Mạch điện đồng hồ santafe 2014-2018PRO ECUNo ratings yet
- ITR-C (Instrument) 16cDocument1 pageITR-C (Instrument) 16cMomo ItachiNo ratings yet
- Zencrack Installation and ExecutionDocument48 pagesZencrack Installation and ExecutionJu waNo ratings yet
- SOLIDWORKS 2022 Whitepaper UsingDesignAutomationtoReduceCostsIncreaseProfitability FinalDocument10 pagesSOLIDWORKS 2022 Whitepaper UsingDesignAutomationtoReduceCostsIncreaseProfitability FinalAlba R.No ratings yet
- Alburg-Caldwell Manor 1784-1826 Draft by Fay YoungDocument3 pagesAlburg-Caldwell Manor 1784-1826 Draft by Fay YoungNancy Cunningham100% (1)
- Welcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Document4 pagesWelcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Niño Jay C. GastonesNo ratings yet
- Revised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Document79 pagesRevised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Rodel D. LuyaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Customer Service SkillsDocument90 pagesBasic Customer Service SkillsGillian Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- 2 Issues in Language LearningDocument30 pages2 Issues in Language LearningEva JakupcevicNo ratings yet
- TV ExplorerDocument2 pagesTV Explorerdan r.No ratings yet
- Alma Matter SpeechDocument1 pageAlma Matter Speechlariza gallegoNo ratings yet
- Osssc JR Clerk Odia Paper 2015 - 20171207 - 0001Document7 pagesOsssc JR Clerk Odia Paper 2015 - 20171207 - 0001songspk100No ratings yet