Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Sarie LevitaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Sarie LevitaCopyright:
Available Formats
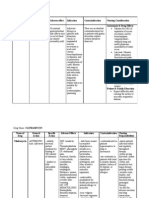
NAME OF DRUG
CLASSIFICATIO N
DOSAGE/ FREQUENCY/ ROUTE 1 ampule OD IV
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATIONS/ CONTRAINDICATIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Metoclopramide
Antiemetic GI stimulant
Stimulates motility of upper GI tract without stimulating gastric, biliary, or pancreatic secretions; appears to sensitize tissues to action of acetylcholine; relaxes pyloric sphincter, which, when combined with effects on motility, accelerates gastric emptying and intestinal transit, little effect on gallbladder or colon motility; increases lower esophageal sphincter pressure; has sedative properties; induces release of prolactin.
-short- term therapy for adults with GERD -parenteral: prevention of nausea and vomiting -prophylaxis of postoperative nausea and vomiting when nasogastric suction is undesirable -treatment of nausea and vomiting of a variety of etiologies -contraindicated with allergy to metoclopramide, GI hemorrhage, mechanical obstruction or perforation, epilepsy. -use cautiously with previously detected breast cancer, lactation, pregnancy
CNS: restlessness, drowsiness, fatigue, insomnia, dizziness, anxiety CV: transient hypertension GI: nausea, diarrhea
-monitor BP carefully during IV administration -keep diphenhydramine injection readily available in case extrapyramidal reactions occur -have phenotolamine readily available in case of hypertensive crisis -take drug exactly as prescribed -use of alcohol, sleep remedies, or sedatives can cause serious sedation. -report involuntary movement of the face, eyes, and limbs
NAME OF DRUG
CLASSIFICATION
DOSAGE/ FREQUENC/ ROUTE 1 Tab OD PO
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATIONS/ CONTRAINDICATIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Bisacodyl
Increases peristalsis & motor activity of the small intestines by acting directly on the smooth muscles.
Constipation, relief of evacuation in hemorrhoids, prep for barium enema, pre and post-op
Occasional abdominal discomfort, soreness in anal region
-monitor frequency & character of stool -monitor occurrence of adverse rxn -swallow the tablet whole, do not crush or chew
NAME OF DRUG
CLASSIFICATION
DOSAGE/ FREQUENC/ ROUTE 400/tab OD PO
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATIONS/ CONTRAINDICATIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
OFLOXACIN
Antibiotic
Ofloxacin is an antibiotic that is used to treat bacterial infections. It belongs to the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics. Ofloxacin stops the multiplication of bacteria by inhibiting the reproduction and repair of their genetic material (DNA).
-Ofloxacin is used to treat pneumonia and bronc hitiscaused by Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococ cus pneumoniae. It also is used in treating skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, andStreptococcus pyogenes bacteria. -Ofloxacin is used to treat sexually transmitted diseases. -Ofloxacin is used often to treat urinary infections and prostate infections caused by E. Coli. -Ofloxacin should be avoided during pregnancy because it is secreted in breast milk and can cause adverse events in the infant. - Ofloxacin should be avoided in nursing mothers, as safe use has not been established. - Ofloxacin should be used with caution in patients with central nervous system diseases such as seizures because rare seizures have been reported in patients receiving this medication. -Ofloxacin should be avoided in children and adolescents under 18
nausea,vomiti ng, diarrhea, insomnia, hea dache, dizziness, itching, and vaginitis in women.
years of age, as safe use in these patients have not been established. -Ofloxacin should not be used in patients with myasthenia gravis because it can increase muscle weakness.
NAME OF DRUG
CLASSIFICATION
DOSAGE/ FREQUENC/ ROUTE 25mg/tab OD PO
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATIONS/ CONTRAINDICATIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
hydroxyzine hydrochloride
Anxiolytic Antihistamine Antiemetic
Mechanisms of action not understood; actions may be due to suppression of subcortical areas of the CNS; has clinically demonstrated antihistaminic, analgesic, antispasmodic, antiemetic, mild antisecretory, and bronchodilator activity
-Symptomatic relief of anxiety and tension associated with psychoneurosis; adjunct in organic disease states in which anxiety is manifested; alcoholism and asthma; prior to dental procedures -Management of pruritus due to allergic conditions, such as chronic urticaria, atopic and contact dermatosis, and in histamine-mediated pruritus -Sedation when used as premedication and following general anesthesia -Control of nausea and vomiting and as adjunct to analgesia preoperatively and postoperatively (parenteral) to allow decreased opioid dosage
CNS: Drowsines s, involuntar y motor activity, including tremor and seizures GI: Dry mouth Hypersensitiv ity: Wheezing, dyspnea, chest tightness
- Take this drug as prescribed. Avoid excessive dosage. - Report difficulty breathing, tremors, loss of coordination, sore muscles, or muscle spasms.
-Contraindicated with allergy to hydroxyzine, pregnancy, lactation. -Use cautiously with uncomplicated vomiting in children (may contribute to Reye's syndrome or unfavorably influence its outcome; extrapyramidal effects may obscure diagnosis of Reye's syndrome).
NAME OF DRUG . Tranexamic Acid
CLASSIFICATION
DOSAGE/ FREQUENC/ ROUTE 500mg/cap TID PO
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATIONS/ CONTRAINDICATIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
produces an antifibrinolytic effect by competitively inhibiting the activation of plasminogen to plasmin. It is also a weak noncompetitive inhibitor of plasmin
-Hereditary angioneurotic edema -Increased local fibrinolysis when the diagnosis is indicative of hyperfibrinolysis -Patients with a history or risk of thrombosis -Patients with acquired disturbances of color vision
-Pale skin -Troubled breathing with exertion - Unusual bleeding or bruising -Unusual tiredness or weakness -Difficulty with moving -Fever - Flushing
-Monitor closely in disseminated intravascular coagulation -Advise patient to report side effects associated with the drug -Discontinue if disturbance in colour vision occurs
NAME OF DRUG
CLASSIFICATION
DOSAGE/ FREQUENCY/ ROUTE 200mg/sachet OD PO
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATIONS/ CONTRAINDICATIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Acetylcysteine
Mucolytic agent
Exerts mucolytic action through its free sulfhydryl group which opens up the disulfide bonds in the mucoproteins thus lowering mucous viscosity. The exact mechanism of action in acetaminophen toxicity is unknown. It is thought to act by providing substrate for conjugation with the toxic metabolite.
-Treatment of respiratory affections characterized by thick and viscous hypersecretions: acute bronchitis, chronic bronchitis and its exacerbations; pulmonary emphysema, mucoviscidosis and bronchiectasis. - MAO inhibitor therapy within 14 days initiating therapy; severe hypertension; severe. Coronary artery disease, hypersensitivity to pseudoedephrine, acrivastine or any component; renal impairment.
bronchospasm , angioedema, rashes and pruritus, nausea and vomiting, fever, syncope, sweating, arthralgia, blurred vision, disturbances of liver function
- Monitor effectiveness of therapy and advent of adverse/allergic effects. Instruct patient in appropriate use and adverse effects to report.
NAME OF DRUG
CLASSIFICATION
DOSAGE/ FREQUENCY/ ROUTE 8cc 6 doses Via epidural catheter
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATIONS/ CONTRAINDICATIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Morphine Sulfate
Opioid agonist analgesic
Principal opium alkaloid; acts as agonist at specific opioid receptors in the CNS to produce analgesia, euphoria, sedation; the receptors mediating these effects are thought to be the same as those mediating the effects of endogenous opioids (enkephalins, endorphins).
-Relief of moderate to severe acute and chronic pain -Preoperative medication to sedate and allay apprehension, facilitate induction of anesthesia, and reduce anesthetic dosage -Analgesic adjunct during anesthesia -Component of most preparations that are referred to as Brompton's cocktail or mixture, an oral alcoholic solution that is used for chronic severe pain, especially in terminal cancer patients -Intraspinal use with microinfusion devices for the relief of intractable pain -Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to opioids; diarrhea caused by poisoning until toxins are eliminated; during labor or delivery of a premature infant (may cross immature bloodbrain barrier more readily); after biliary tract surgery or following surgical anastomosis; pregnancy; labor (respiratory depression in neonate; may prolong labor). - Use cautiously with head injury and increased
dry mouth, constipation. Tissue irritation and induration (SC injection). sweating,physi cal tolerance and dependence, psychological dependence
-Dilute and administer slowly IV to minimize likelihood of adverse effects. -Tell patient to lie down during IV administration. -Keep opioid antagonist and facilities for assisted or controlled respiration readily available during IV administration. -Use caution when injecting SC or IM into chilled areas or in patients with hypotension or in shock; impaired perfusion may delay absorption; with repeated doses, an excessive amount may be absorbed when circulation is restored. Reassure patients that they are unlikely to become addicted; most patients who receive opioids for medical reasons do not develop dependence syndromes
intracranial pressure; acute asthma, COPD, cor pulmonale, preexisting respiratory depression, hypoxia, hypercapnia (may decrease respiratory drive and increase airway resistance); acute abdominal conditions, CV disease, supraventricular tachycardias, myxedema, seizure disorders, acute alcoholism, delirium tremens, cerebral arteriosclerosis, ulcerative colitis, fever, kyphoscoliosis, Addison's disease, prostatic hypertrophy, urethral stricture, recent GI or GU surgery, toxic psychosis, renal or hepatic dysfunction.
NAME OF DRUG Arcoxia
CLASSIFICATION
DOSAGE/ FREQUENCY/ ROUTE
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATIONS/ CONTRAINDICATIONS
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Medication AdministrationDocument34 pagesMedication AdministrationSarie Levita100% (2)
- Medication AdministrationDocument34 pagesMedication AdministrationSarie Levita100% (2)
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- IVIS Guide To Hematology in Dog and CatDocument63 pagesIVIS Guide To Hematology in Dog and CatFaqih100% (1)
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboDocument7 pagesNursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboAlexa Abidin Oldenborg100% (8)
- Types of AnemiaDocument11 pagesTypes of AnemiaCHRISTIE MONTANO50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudysarahtotNo ratings yet
- Medication ListDocument14 pagesMedication ListMarie LeyvaNo ratings yet
- Sample - Drug Index DatabaseDocument12 pagesSample - Drug Index DatabaseEubert John VenturinaNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument11 pagesDrugrihamNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin drug infoDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacin drug infoRosalie Delfin89% (9)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Isoxsuprine and Amoxicillin TreatmentsDocument3 pagesIsoxsuprine and Amoxicillin TreatmentsRia Nicole100% (1)
- Metronidazole drug information summaryDocument4 pagesMetronidazole drug information summaryKaloy AnneNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFritzie Beatrice NomusNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicDocument7 pagesGeneric Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Work in Team EnvironmentDocument50 pagesWork in Team EnvironmentMercy Dadulla - ElvinaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Disorders, PowerpointDocument63 pagesUrinary Tract Disorders, Powerpointmutia mutia100% (4)
- Compliled DrugstudyDocument15 pagesCompliled DrugstudyApril Jan D. Alagon0% (1)
- Calcium Carbonate for Bone HealthDocument14 pagesCalcium Carbonate for Bone HealthBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- VPT 411 Veterinary Chemotherapy Tanuvas Lecture NotesDocument94 pagesVPT 411 Veterinary Chemotherapy Tanuvas Lecture NotesSunil100% (41)
- Ofloxacin Drug Class and Mechanism of ActionDocument5 pagesOfloxacin Drug Class and Mechanism of ActionSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Drug Classification: Drug:: MedicationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Drug Classification: Drug:: MedicationsCharmaigne Aurdane PajeNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Drug Study - CaseDocument9 pagesDrug Study - CaseMay EvelynNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyDocument7 pagesNeuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyJomabee TuArNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocument6 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ventolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefDocument10 pagesVentolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefmidskiescreamzNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medications ReviewDocument4 pagesRespiratory Medications ReviewKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- LIVOLIN FORTE ACTIONS AND USESDocument5 pagesLIVOLIN FORTE ACTIONS AND USESDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument42 pagesAntifungal AgentsOluwatobi AyomideNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate, antibiotics, and postoperative careDocument13 pagesNursing responsibilities for magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate, antibiotics, and postoperative careabrokenheartedgirlNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyDocument9 pagesParacetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Pentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GanDocument34 pagesPentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GankotonashiNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoDocument10 pagesAmpicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document PDFDocument3 pagesUntitled Document PDFdzmtz02No ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesAmoxicillindheng05No ratings yet
- PARACETAMOLDocument2 pagesPARACETAMOLMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Adults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YDocument2 pagesAdults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YFildehl Janice Bomediano Catipay100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJannefer HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRoselle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaAngelica Tresha RaonNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsElisa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Uterine ProlapseDocument9 pagesDrug Study-Uterine ProlapseANNA V. LARITANo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument6 pagesDrugs StudyMark_Rebibis_8528No ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Morphine SulfateDocument2 pagesMorphine SulfategreynabNo ratings yet
- Fluimucil 300mg / 3mlDocument3 pagesFluimucil 300mg / 3mlRezti PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism Use Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ImplicationsDocument3 pagesDrug Mechanism Use Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Implicationshendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate InjectionDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate InjectionIrawanMarlyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- DRug StudyDocument6 pagesDRug StudyRochell Torres ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Non-opioid analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugsDocument33 pagesNon-opioid analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugsKristine AnaenNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument17 pagesName of DrugAllan DiazNo ratings yet
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocument19 pagesAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Indications: Adult 750 MG IM or IV Tid. More Severe Infections 1.5 G IV Tid. Childn & Infant 30-100Document14 pagesIndications: Adult 750 MG IM or IV Tid. More Severe Infections 1.5 G IV Tid. Childn & Infant 30-100thangentNo ratings yet
- Drugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- HIV/AIDSDocument11 pagesHIV/AIDSSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument4 pagesDialysisSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Iron Supplement for PregnancyDocument8 pagesIron Supplement for PregnancySarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Pacific RimDocument10 pagesPacific RimSarie Levita100% (1)
- Health EcoDocument1 pageHealth EcoSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument14 pagesCHNSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- N IDocument1 pageN ISarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Case Assigntment - OsteoporosisDocument7 pagesCase Assigntment - OsteoporosisYasser HoldarNo ratings yet
- EosinophiliaDocument8 pagesEosinophiliajohnNo ratings yet
- Bookshelf NBK236643 PDFDocument320 pagesBookshelf NBK236643 PDFarumNo ratings yet
- Coxsackievirus: Presented By: LKCDocument18 pagesCoxsackievirus: Presented By: LKCLeang KarichakNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activities of Ethanol Extracts ofDocument9 pagesAntibacterial Activities of Ethanol Extracts ofGenesis JoseNo ratings yet
- Scott-Sinema Medicare Advantage LetterDocument2 pagesScott-Sinema Medicare Advantage LetterRachel CohrsNo ratings yet
- II-Vocab of Hospital DeptDocument1 pageII-Vocab of Hospital DeptAdhwaNo ratings yet
- Rule: Medicare: Physician Fee Schedule (CY 2007) Payment Policies and Relative Value UnitsDocument629 pagesRule: Medicare: Physician Fee Schedule (CY 2007) Payment Policies and Relative Value UnitsJustia.com100% (1)
- Barriers To Eye Care ForDocument1 pageBarriers To Eye Care ForEunice DichosoNo ratings yet
- 1st IBRO UM5 School ProgramDocument9 pages1st IBRO UM5 School ProgramInternational Brain Research OrganizationNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guide GIP VersionDocument22 pagesClinical Guide GIP Versionsireesha gandrotuNo ratings yet
- CFPC 99 Topics Starter Study DocumentDocument372 pagesCFPC 99 Topics Starter Study DocumentaayceeNo ratings yet
- The Lancet, 2018Document70 pagesThe Lancet, 2018dessyNo ratings yet
- COPD LeafletDocument2 pagesCOPD LeafletAN KnEeNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Innovation AgendaDocument13 pagesHealthcare Innovation AgendaPradeep PandeyNo ratings yet
- Government Initiatives in Health and Nutrition: Vinod PaulDocument29 pagesGovernment Initiatives in Health and Nutrition: Vinod PaulMani KandanNo ratings yet
- New Patient Forms PacketDocument4 pagesNew Patient Forms PacketCarrboro Family MedicineNo ratings yet
- Naranjo AlgorithmDocument3 pagesNaranjo AlgorithmmilkymilkyNo ratings yet
- Photovoice Paper HLTH 102Document7 pagesPhotovoice Paper HLTH 102api-625678417No ratings yet
- Don't let knee pain slow you downDocument2 pagesDon't let knee pain slow you downrajagopal_k@vsnl.netNo ratings yet
- Multinodular Goitre Case PresentationDocument19 pagesMultinodular Goitre Case PresentationTamilNo ratings yet
- List Cebu AFFIL PHYSICIANS1 (Wo Neuro) - As of 09012011Document6 pagesList Cebu AFFIL PHYSICIANS1 (Wo Neuro) - As of 09012011Irish BalabaNo ratings yet
- Non Adherence and Its Contributing Factors Among Ambulatory Type Two Diabetic Patients in Bishoftu General Hospital, South East, EthiopiaDocument15 pagesNon Adherence and Its Contributing Factors Among Ambulatory Type Two Diabetic Patients in Bishoftu General Hospital, South East, EthiopiaIjupbs IjupbsNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 - Case StudyDocument2 pagesActivity 5 - Case StudyMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- BJOG - 2022 - Girling - Green Top Guideline No 43 June 2022Document20 pagesBJOG - 2022 - Girling - Green Top Guideline No 43 June 2022Kalaivathanan VathananNo ratings yet