Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Normal Values of Vital Signs
Uploaded by
Mela VincoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Normal Values of Vital Signs
Uploaded by
Mela VincoCopyright:
Available Formats
Pulse Descriptors: regular, irregular, strong or weak Adult 60 to 100 beats per minute Children - age 1 to 8 years 80 to 100
Infants - age 1 to 12 months 100 to 120 Neonates - age 1 to 28 days 120 to 160 Top of the Page Blood pressure Systolic Adult 90 to 140 mmHg Children - age 1 to 8 years 80 to 110 mmHg Infants - age 1 to 12 70 to 95 mmHg months Neonates - age 1 to 28 days >60 mmHg Diastolic 60 to 90 mmHg
Top of the Page Respirations Descriptors: normal, shallow, labored, noisy, Kussmaul Adult (normal) 12 to 20 breaths per minute Children - age 1 to 8 years 15 to 30 Infants - age 1 to 12 months 25 to 50 Neonates - age 1 to 28 days 40 to 60 Top of the Page Vital signs by age Adult vital signs Pulse Blood pressure Respirations 60 to 100 beats per minute 90 to 140 mmHg (systolic) 60 to 90 mmHg (diastolic) 12 to 20 breaths per minute
Child vital signs (age 1 to 8 years) Pulse 80 to 100 beats per minute Blood pressure 80 to 110 mmHg systolic Respirations 15 to 30 breaths per minute Infant vital signs Pulse Blood pressure Respirations 100 to 140 beats per minute 70 to 95 mmHg systolic 25 to 50 breaths per minute
Neonatal vital signs (full-term, <28 days) Pulse 120 to 160 beats per minute Blood pressure >60 mmHg systolic Respirations 40 to 60 breaths per minute Top of the Page Lung sounds Crackles or rales Wheezing Stridor Rhonchi crackling or rattling sounds high-pitched whistling expirations harsh, high-pitched inspirations coarse, gravelly sounds Top of the Page Pulse oximetry Range Normal Mild hypoxia Moderate hypoxia Severe hypoxia Value 95 to 100% 91 to 94% 86 to 90% < 85% Treatment None or placebic Give oxygen Give 100% oxygen Give 100% oxygen w/ positive pressure Top of the Page Glasgow Coma Scale ADULT Eye opening Spontaneous To speech To pain No response Best motor response Obeys verbal command Localizes pain Flexion - withdraws from pain Flexion - abnormal Extension No response Best verbal response Oriented and converses Disoriented and converses E 4 3 2 1 M 6 5 4 3 2 1 V 5 4 INFANT Eye opening Spontaneous To speech To pain No response Best motor response Normal movements Localizes pain Withdraws from pain Flexion - abnormal Extension No response Best verbal response Coos, babbles Cries but consolable
Inappropriate words Incomprehensible sounds No response
3 2 1
Persistently irritable Grunts to pain/restless No response
E + M + V = 3 to 15 90% less than or equal to 8 are in coma Greater than or equal to 9 not in coma 8 is the critical score Less than or equal to 8 at 6 hours - 50% die 9-11 = moderate severity Greater than or equal to 12 = minor injury
Coma is defined as not opening eyes, not obeying commands, and not uttering understandable words.
Additional references: Traumatic Brain Injury Resource Guide and House of DeFrance.
Top of the Page Apgar Scale (evaluate @ 1 and 5 minutes postpartum) Sign 2 A Activity (muscle Active tone) P Pulse >100 bpm G Grimace (reflex Sneezes, irritability) coughs, pulls away A Appearance Normal over (skin color) entire body R Respirations Good, crying 1 0 Arms and legs Absent flexed <100 bpm Absent Grimaces No response Normal except Cyanotic or pale extremities all over Slow, irregular Absent Top of the Page
Pain scale The 0-10 pain scale is becoming known as the "fifth vital sign" in hospital, pre-hospital and outpatient care. Patients are asked to rate their pain from 0 (no pain) to 10 (the most intense pain imaginable), and a quantitative measure is taken.
You might also like
- Dictionary of American History 3rd Vol 08 PDFDocument603 pagesDictionary of American History 3rd Vol 08 PDFaNo ratings yet
- Payward Drug Study and FdarDocument10 pagesPayward Drug Study and FdarMico SantosNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Learning Filipino StyleDocument8 pagesStrategic Management Learning Filipino StyleMela Vinco100% (2)
- Normal Vital Signs Guidelines For EmsDocument2 pagesNormal Vital Signs Guidelines For Emsisabelo_laguraNo ratings yet
- APGAR Score and Ballard Score: K. C. JanakDocument41 pagesAPGAR Score and Ballard Score: K. C. JanakJanak Kc100% (1)
- Fdar Charting Date & Time Focus Progress Notes: DataDocument2 pagesFdar Charting Date & Time Focus Progress Notes: DataElaine dadaNo ratings yet
- Module 12 of Child and Adolescence DevelopmentDocument3 pagesModule 12 of Child and Adolescence DevelopmentMakki Andre Antonio75% (4)
- IV ComputationDocument12 pagesIV Computationapi-300218860100% (1)
- Vitals Pocket ChartDocument4 pagesVitals Pocket ChartAli MullaNo ratings yet
- Weaning Food PPT & Health TalkDocument26 pagesWeaning Food PPT & Health Talkkrishna chandrakani81% (32)
- Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MAN: Maternal and Child Nursing BulletsDocument10 pagesMark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MAN: Maternal and Child Nursing BulletsMark DaenosNo ratings yet
- IV ComputationDocument11 pagesIV ComputationSheniel VariacionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Compartment Sydnrome)Document6 pagesNursing Care Plan (Compartment Sydnrome)Zyiv BalogalNo ratings yet
- Instruments in The Delivery RoomDocument6 pagesInstruments in The Delivery RoomRenea Joy Arruejo0% (1)
- Vital Signs TableDocument5 pagesVital Signs Tableneleh grayNo ratings yet
- Normal Vital SignsDocument2 pagesNormal Vital SignsEunice Domingo AlipioNo ratings yet
- Life Span Development Notes-Chapter 4Document13 pagesLife Span Development Notes-Chapter 4Kayelita Wu100% (1)
- Wong Worksheet PediaDocument3 pagesWong Worksheet PediaLecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Nurses Progress Notes Name of Patient Attending Physician Room/Ward Hospital NoDocument1 pageNurses Progress Notes Name of Patient Attending Physician Room/Ward Hospital NoMr rawrNo ratings yet
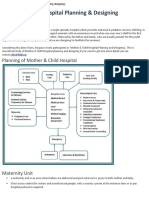
- Mother & Child Hospital Planning & Designing: Info@hhbc - inDocument8 pagesMother & Child Hospital Planning & Designing: Info@hhbc - inwrightwoman100% (1)
- 205 CS - Dengue FeverDocument39 pages205 CS - Dengue FeverMarielle Mae TanNo ratings yet
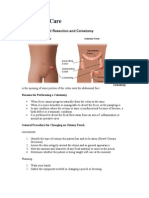
- Colostomy CareDocument13 pagesColostomy CareLord Pozak MillerNo ratings yet
- 10 CaritosDocument3 pages10 CaritosDARREN EDMARK100% (4)
- IVF ComputationDocument31 pagesIVF ComputationDuran JustineNo ratings yet
- Focus Data ChartingDocument3 pagesFocus Data ChartingcattleyaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Admin Answer-4Document3 pagesDrugs Admin Answer-4June Dumdumaya0% (1)
- Examination of The Newborn An Evidence Based Guide PDFDocument2 pagesExamination of The Newborn An Evidence Based Guide PDFPhilNo ratings yet
- DR Notes at Benguet General HospitalDocument1 pageDR Notes at Benguet General HospitalTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Normal Vital Signs Guidelines For EmsDocument4 pagesNormal Vital Signs Guidelines For EmsJonathan delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development: Infancy Early Childhood Middle Childhood AdolescentDocument47 pagesGrowth and Development: Infancy Early Childhood Middle Childhood AdolescentJamna MaharajNo ratings yet
- Nursing Progress Note.Document2 pagesNursing Progress Note.Art Christian RamosNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan For BreastfeedingDocument2 pagesTeaching Plan For BreastfeedingEmerson Sambo100% (6)
- Incompetent CervixDocument5 pagesIncompetent CervixNaidin Catherine De Guzman-Alcala100% (1)
- Structure of An Ovum Structure and Function of A SpermDocument25 pagesStructure of An Ovum Structure and Function of A SpermTiffany Joy QuiliopeNo ratings yet
- CEUFast Infection Control and Barrier PrecautionsDocument90 pagesCEUFast Infection Control and Barrier PrecautionsMeg GalauranNo ratings yet
- Final Course in The WardDocument4 pagesFinal Course in The WardMichael Boado100% (1)
- NCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Document3 pagesNCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Anne DyNo ratings yet
- 51 100Document18 pages51 100Jaessa Feliciano100% (1)
- PrefixDocument8 pagesPrefixleian28No ratings yet
- Soapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINDocument7 pagesSoapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINAna100% (2)
- Case Study of PNEUMONIADocument12 pagesCase Study of PNEUMONIAAriaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolDocument3 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Goals and Objectives Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Goals and Objectives Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCrissa AngelNo ratings yet
- BSN 215 Reflection Essay - LagoDocument2 pagesBSN 215 Reflection Essay - LagoAlliahkherzteen LagoNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument9 pagesNCP Impaired Physical MobilityChristian Apelo SerquillosNo ratings yet
- Case Study #117: Intrapartal CareDocument21 pagesCase Study #117: Intrapartal CareDudong SasakiNo ratings yet
- Nurses Notes SurgeryDocument3 pagesNurses Notes SurgeryLouie ParillaNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy O.R. Write UpDocument11 pagesAppendectomy O.R. Write UpJessica Christine Datuin GustiloNo ratings yet
- ARTHROCENTESISDocument3 pagesARTHROCENTESISleroux2890No ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument4 pagesConcept MapgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Case Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNDocument5 pagesCase Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNRogelio Saupan Jr100% (1)
- Im Case Study 04Document49 pagesIm Case Study 04Shaine BalverdeNo ratings yet
- Operating Room WriteDocument2 pagesOperating Room WritemodiNo ratings yet
- Criteria Good Fair Poor Rationale Justification XDocument3 pagesCriteria Good Fair Poor Rationale Justification XJaye DangoNo ratings yet
- Head NurseDocument11 pagesHead Nursejannet20No ratings yet
- Patient Endorsement SheetDocument1 pagePatient Endorsement SheetKim Caitlin Carbolico ClasieteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNKristina Marie Parulan RnNo ratings yet
- Individual Activity 3 PDFDocument11 pagesIndividual Activity 3 PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Plan of Activities For Surgery WardDocument4 pagesPlan of Activities For Surgery WardFrances DaeNo ratings yet
- Case Study StabDocument7 pagesCase Study StabMari Jasmeen Estrada Noveda100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: OSTEOPOROSIS DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: OSTEOPOROSIS DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy - Asynchronous ActivityDocument2 pagesIV Therapy - Asynchronous ActivityNicole Chloe OcanaNo ratings yet
- Sample Charting orDocument1 pageSample Charting orKatherine Ibarra100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument25 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurejohnleeeNo ratings yet
- Child - Major Burn PDFDocument3 pagesChild - Major Burn PDFAldith GrahamNo ratings yet
- COLLEGE OF ST. JOHN - ROXAS Member: Association ofDocument6 pagesCOLLEGE OF ST. JOHN - ROXAS Member: Association ofCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Personal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesDocument15 pagesPersonal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesteuuuuNo ratings yet
- V/S TableDocument4 pagesV/S TableBenj VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- FON Information موشتاقDocument3 pagesFON Information موشتاقzaetwnnawzad2004No ratings yet
- Vital Signs in Children: Heart Rate (Rate/min) Age Awake Rate Sleeping RateDocument3 pagesVital Signs in Children: Heart Rate (Rate/min) Age Awake Rate Sleeping RateGhina KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Normal Vital Signs Guidelines For EmsDocument2 pagesNormal Vital Signs Guidelines For EmsMichael WijayaNo ratings yet
- Admission ChecklistDocument2 pagesAdmission ChecklistMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Private Patients Pati: Service PatientsDocument2 pagesPrivate Patients Pati: Service PatientsMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Flowchart AdmissionDocument1 pageFlowchart AdmissionMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Flowchart AdmissionDocument1 pageFlowchart AdmissionMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Admission ChecklistDocument2 pagesAdmission ChecklistMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Inform The Name, Age, AP, Classification, Diagnosis, Contraptions and To Where Will Be The Patient Will Be Transferred (E.g Isolation or Icu)Document1 pageInform The Name, Age, AP, Classification, Diagnosis, Contraptions and To Where Will Be The Patient Will Be Transferred (E.g Isolation or Icu)Mela VincoNo ratings yet
- INTRA-PARTAL COMPETENCY (Summary of Evaluation)Document3 pagesINTRA-PARTAL COMPETENCY (Summary of Evaluation)Mela VincoNo ratings yet
- Useful VocabularyDocument3 pagesUseful VocabularyMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Remarks: ST NDDocument1 pageRemarks: ST NDMela VincoNo ratings yet
- DANCE PPTRTTDocument24 pagesDANCE PPTRTTMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Gordons QMMCDocument3 pagesGordons QMMCMela VincoNo ratings yet
- OligoDocument3 pagesOligoMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Nclex Cram GuideDocument11 pagesNclex Cram GuideMela VincoNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS Communicable DseDocument62 pagesHANDOUTS Communicable DseMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Types of ArrhythmiaDocument2 pagesTypes of ArrhythmiaMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Managemerrtrrnt Learning Filipino StyleDocument3 pagesStrategic Managemerrtrrnt Learning Filipino StyleMela VincoNo ratings yet
- AccreditationretrtDocument36 pagesAccreditationretrtMela VincoNo ratings yet
- VcapDocument17 pagesVcapMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Types of ArrhythmiaDocument2 pagesTypes of ArrhythmiaMela VincoNo ratings yet
- NCP QMMCDocument2 pagesNCP QMMCMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Rupture of The Membranes Is The Most Common Cause of OligohydramniosDocument1 pageRupture of The Membranes Is The Most Common Cause of OligohydramniosMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Physical Assesspent VMMCDocument3 pagesPhysical Assesspent VMMCMela VincoNo ratings yet
- RRL MelaDocument9 pagesRRL MelaMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Physical Assesspent VMMCDocument3 pagesPhysical Assesspent VMMCMela VincoNo ratings yet
- OncoDocument4 pagesOncoMela VincoNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument3 pagesJournalMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Journal About Renal DialysisDocument8 pagesJournal About Renal DialysisMela VincoNo ratings yet
- IV OsmolarityDocument1 pageIV OsmolarityMela VincoNo ratings yet
- RRL MelaDocument9 pagesRRL MelaMela VincoNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Practice: Unit OneDocument25 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Practice: Unit OneZheefNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Case Study of Music Interactions Between Mothers and InfantsDocument16 pagesA Comparative Case Study of Music Interactions Between Mothers and InfantsGiacomo Detto Anche PiazzaNo ratings yet
- Stamp ToolDocument20 pagesStamp ToolIlmia FahmiNo ratings yet
- Situation 1Document18 pagesSituation 1Maler De VeraNo ratings yet
- Maria Dalisay C. Caponpon, Man, RN, RM, BSM Member APSOM Group of TrainersDocument63 pagesMaria Dalisay C. Caponpon, Man, RN, RM, BSM Member APSOM Group of Trainersjamaica cabrigaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Document10 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Najia Sajjad KhanNo ratings yet
- Growth and Developments PDFDocument3 pagesGrowth and Developments PDFAlok SharmaNo ratings yet
- 07a How To Use This Competency-Based Learning MaterialDocument4 pages07a How To Use This Competency-Based Learning MaterialNonaNo ratings yet
- Course RequirementDocument27 pagesCourse RequirementCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychological Assessment: JA Hofheimer, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, United StatesDocument15 pagesNeuropsychological Assessment: JA Hofheimer, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, United StatesRealidades InfinitasNo ratings yet
- COPARDocument118 pagesCOPARleemeiOO100% (1)
- Equivalent To Caffeine 5mg/ml Equivalent To Caffeine 5mg/mlDocument2 pagesEquivalent To Caffeine 5mg/ml Equivalent To Caffeine 5mg/mlatawa1No ratings yet
- Atty. Rizza - Philippine Nursing LawsDocument44 pagesAtty. Rizza - Philippine Nursing LawsDENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Rhubarb May 2018 Edition 77Document11 pagesRhubarb May 2018 Edition 77Giedrė SkaisgirytėNo ratings yet
- Infant and Child Nutrition: Key PointsDocument4 pagesInfant and Child Nutrition: Key PointsseptiNo ratings yet
- Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument25 pagesFetal Growth and Developmentniogan anthonyNo ratings yet
- Baby and Pregnancy 2016 EneroDocument132 pagesBaby and Pregnancy 2016 EneroMariie CupcakeeNo ratings yet
- The Effect and Implication of Developmental Supportive Care Practices in Preterm BabiesDocument23 pagesThe Effect and Implication of Developmental Supportive Care Practices in Preterm BabiesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- q2 Health - 8 M 4 Revised PDFDocument24 pagesq2 Health - 8 M 4 Revised PDFGemarie CallosaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing All India Instutite of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh (Uttarakhand) B.Sc. (Hons) Nursing 3 Year Batch - 2016 End Term Examination - 2019 Subject - Maternal Health NursingDocument24 pagesCollege of Nursing All India Instutite of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh (Uttarakhand) B.Sc. (Hons) Nursing 3 Year Batch - 2016 End Term Examination - 2019 Subject - Maternal Health NursingRajaNo ratings yet