Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 31a UCLA
Uploaded by
artecmkCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 31a UCLA
Uploaded by
artecmkCopyright:
Available Formats
sin
2
x + cos
2
x = 1
tan
2
x + 1 = sec
2
x
sin(2x) = 2 sinxcos x
cos(2x) = cos
2
x sin
2
x
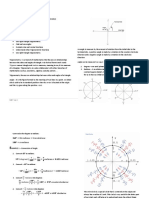
y = arctanx x = tany
arctan(0) = 0
arctan(1) = /4
0 /6 /4 /3 /2
sin 0 1/2
2/2
3/2 1
cos 1
3/2
2/2 1/2 0
tan 0
3/3 1
3 DNE
f
(x) = lim
h0
f(x + h) f(x)
h
= lim
ax
f(a) f(x)
a x
, y = f(a) + f
(a)(x a)
. .
tangent line at x = a
d
dx
_
x
a
_
= ax
a1
,
d
dx
_
sinx
_
= cos x,
d
dx
_
cos x
_
= sinx,
d
dx
_
tanx
_
= sec
2
x
d
dx
_
sec x
_
= sec xtanx,
d
dx
_
arctanx
_
=
1
1 + x
2
,
d
dx
_
f(x)g(x)
_
= f
(x)g(x) + f(x)g
(x)
d
dx
_
f(x)
g(x)
_
=
f
(x)g(x) f(x)g
(x)
_
g(x)
_
2
,
d
dx
_
f
_
g(x)
__
= f
_
g(x)
_
g
(x)
Implicit
derivatives
_
_
_
* take derivative of both sides
w.r.t. x (dont forget y
terms)
* rearrange and solve for y
Related
rates
_
_
* nd relationship between the
quantities that are changing
* take derivative of both sides w.r.t t
* use known values to solve
f f
(a)x or f(x) L(x) = f(a) + f
(a)(x a)
. .
Linear approximation
f
(c) = 0 f
(c) = DNE
. .
critical points
_
_
f
> 0 f increasing
f
< 0 f decreasing
f
> 0 f concave up
f
< 0 f concave down
Global
min/max
_
_
_
* list endpoints and critical points
* plug all values into the function
* largest=max, smallest=min
f
(c) =
f(b) f(a)
b a
. .
f continuous and dierentiable
Mean Value Theorem
Applied
optimization
_
_
* express quantity we are optimizing
as a function of a single variable
* take derivative and nd critical pts.
* use rst/second derivative test
if f(x) g(x)
_
b
a
f(x) dx
_
b
a
g(x) dx
_
b
a
f(x) dx =
_
c
a
f(x) dx +
_
b
c
f(x) dx,
_
b
a
f(x) dx =
_
a
b
f(x) dx,
_
a
a
f(x) dx = 0
_
x
a
dx =
1
a + 1
x
a+1
+ C (a = 1),
_
sinxdx = cos x + C,
_
cos xdx = sinx + C
_
sec
2
xdx = tanx + C,
_
sec xtanxdx = sec x + C,
_
1
1 + x
2
dx = arctanx + C
_
f
_
g(x)
_
g
(x) dx
. .
u=g(x), du=g
(x) dx
=
_
f(u) du,
d
dx
__
h(x)
g(x)
f(u) du
_
= f
_
h(x)
_
h
(x) f
_
g(x)
_
g
(x)
average
value
=
1
b a
_
b
a
f(x) dx,
area when
f(x) g(x)
=
_
b
a
_
f(x) g(x)
_
dx
volume of
revolution
:
_
b
a
_
(f(x))
2
(g(x))
2
_
dx (x-axis) or 2
_
b
a
x
_
f(x) g(x)
_
dx (y-axis)
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Precalculus With TrigonometryDocument864 pagesPrecalculus With Trigonometryrcpuram01100% (8)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Chapter 7 - Algebra Practice WorksheetDocument7 pagesChapter 7 - Algebra Practice WorksheetRahul KarnaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Mathmatics 1ggggggggg PDFDocument753 pagesMathmatics 1ggggggggg PDFZahid Ali Mughal100% (1)
- Goldstein 2nd Edition 2nd Chapter SolutionsDocument10 pagesGoldstein 2nd Edition 2nd Chapter SolutionsKarmakarışıkblog Blogspot67% (3)
- Trigbook PDFDocument264 pagesTrigbook PDFsouvikbesu89No ratings yet
- Concept of Stress and Strain AssignmentDocument17 pagesConcept of Stress and Strain AssignmentBirwa GandhiNo ratings yet
- Jee 2024Document8 pagesJee 2024Md ArabiNo ratings yet
- Geometric Figures: Secondary Math TwoDocument61 pagesGeometric Figures: Secondary Math TwoJonathan 2018100% (1)
- ENGINEERING DRAWING OBJECTIVE QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesENGINEERING DRAWING OBJECTIVE QUESTIONShiteshsoft75% (8)
- Topic 9 - TorsionDocument32 pagesTopic 9 - TorsionJane Docdoc100% (1)
- 1st Year Physics M.C.Q Sindh BoardDocument66 pages1st Year Physics M.C.Q Sindh BoardMudasir Soomro80% (15)
- Model Year MG SG Illustration Restrictions UPD: Et - bt1.frmDocument1 pageModel Year MG SG Illustration Restrictions UPD: Et - bt1.frmartecmkNo ratings yet
- Model Year MG SG Illustration Restrictions UPD: Et - bt1.frmDocument1 pageModel Year MG SG Illustration Restrictions UPD: Et - bt1.frmartecmkNo ratings yet
- Model Year MG SG Illustration Restrictions UPD: Et - bt1.frmDocument1 pageModel Year MG SG Illustration Restrictions UPD: Et - bt1.frmartecmkNo ratings yet
- Model Year MG SG Illustration Restrictions UPD: Et - bt1.frmDocument1 pageModel Year MG SG Illustration Restrictions UPD: Et - bt1.frmartecmkNo ratings yet
- Ne Treba (So Detali) Drzac Za Branik (Lim)Document3 pagesNe Treba (So Detali) Drzac Za Branik (Lim)artecmkNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Systems AccessoriesDocument4 pagesIrrigation Systems AccessoriesartecmkNo ratings yet
- Ne Treba (So Detali) Drzac Za Branik (Lim)Document3 pagesNe Treba (So Detali) Drzac Za Branik (Lim)artecmkNo ratings yet
- A3 Cooler and IntercoolerDocument1 pageA3 Cooler and IntercoolerartecmkNo ratings yet
- IPS Empress Direct PDFDocument8 pagesIPS Empress Direct PDFartecmkNo ratings yet
- Ariston AML 105Document12 pagesAriston AML 105artecmkNo ratings yet
- PFCSolnsDocument9 pagesPFCSolnsartecmkNo ratings yet
- Netafim-Venturi Injector 2014Document4 pagesNetafim-Venturi Injector 2014artecmkNo ratings yet
- Tanydy: Arctan X DXDocument9 pagesTanydy: Arctan X DXartecmkNo ratings yet
- PFASolnsDocument10 pagesPFASolnsartecmkNo ratings yet
- Lectures On BuildingsDocument8 pagesLectures On Buildingschaoxian82416No ratings yet
- Term 1 Mathematics Examination SheetDocument11 pagesTerm 1 Mathematics Examination SheetAkhssnnajaNo ratings yet
- Cam Mechanism Design FundamentalsDocument54 pagesCam Mechanism Design FundamentalsroshanijazNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document21 pagesCH 10MuhammadImranNo ratings yet
- Module 2 in Abe 215 Statics1 l1 5Document22 pagesModule 2 in Abe 215 Statics1 l1 5Cynel DelaNo ratings yet
- Maths Sample PaperDocument10 pagesMaths Sample PaperPonharish kumar.JNo ratings yet
- Geometric Algebra and Its Application To Computer Graphics: D. Hildenbrand, D. Fontijne, C. Perwass and L. DorstDocument49 pagesGeometric Algebra and Its Application To Computer Graphics: D. Hildenbrand, D. Fontijne, C. Perwass and L. DorstJuan José Ley RosasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AlgebraDocument12 pagesIntroduction To AlgebraRashee GoyalNo ratings yet
- 65-3 (Mathematics) PDFDocument8 pages65-3 (Mathematics) PDFayush guptaNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Document13 pagesJEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Kalyan MarutiNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Plane and Solid Geometry - Set 3Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 - Plane and Solid Geometry - Set 3Mark Lester LualhatiNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus-Quarter 3: Asseeement # 1Document6 pagesBasic Calculus-Quarter 3: Asseeement # 1Aiyu ChiseeNo ratings yet
- Solutionbank C2: Edexcel Modular Mathematics For AS and A-LevelDocument10 pagesSolutionbank C2: Edexcel Modular Mathematics For AS and A-LevelMaruf_007No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Worksheet SolutionsDocument2 pagesEngineering Mechanics Worksheet SolutionsLeul TesfuNo ratings yet
- Chapter. 2-Curvilinear Motion of Particles PDFDocument45 pagesChapter. 2-Curvilinear Motion of Particles PDFEng-Al Raie SaadNo ratings yet
- ED Acad Sheet Feb-Jun 2023Document4 pagesED Acad Sheet Feb-Jun 2023Akshita PillaiNo ratings yet
- Inmo PreparationDocument2 pagesInmo PreparationVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus For non-STEM (Algebra & TrigonometryDocument18 pagesPre-Calculus For non-STEM (Algebra & TrigonometryAlfeo DucejoNo ratings yet
- DLP 1 5 AttachmentsDocument6 pagesDLP 1 5 AttachmentsJay BeeNo ratings yet