Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluphenazine Drug Study!
Uploaded by
EmJay BalansagOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluphenazine Drug Study!
Uploaded by
EmJay BalansagCopyright:
Available Formats
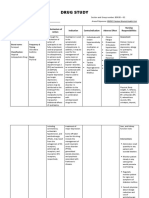
GENERIC/BRAND/ MECHANISM OF CLASSIFICATION ACTION Generic: Alters the effects of Fluphenazine dopamine in CNS.
Anticholinergic and alpha-adrenergic blocking activity. BRAND: Prolixin, Fluphenazine Decanoate
INDICATION Acute and chronic psychoses.
CONTRAINDICATION Hypersensitivity; crosssensitivity with other phenothiazines may exist; subcortical brain damage; severe CNS depression; coma; bone marrow depression; liver disease; hypersensitivity to sesame oil (decanoate salt); some products contain alcohol or tartrazine and should be avoided in clients with known intolerance; concurrent use of drugs that prolong QT interval.
ADVERSE REACTION CNS: NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME, extrapyramidal reactions, sedation, tardive dyskinesia. EENT: Blurred vision, dry eyes. CV: Hypertension, hypotension, tachycardia. GI: Anorexia, constipation, druginduced hepatitis, dry mouth, ileus, nausea, weight gain. GU: Urinary retention. Derm: Photosensitivity, pigment changes, rashes. Endo: Galactorrhea. Hemat: AGRANULOCYTOSIS, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Misc: Allergic reactions.
DOSAGE Usual: PO (Adults): 0.510 mg/day in divided doses every 68 hr (maximum dose = 40 mg/day). IM (Adults): 12.525 mg initially; may be repeated every 3 wk. Dosage may be slowly as needed (not to exceed 100 mg/dose).
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Assess patients mental status (orientation, mood, behavior) before and periodically throughout therapy. Monitor blood pressure (sitting, standing, lying), ECG, pulse, and respiratory rate before and frequently during the period of dosage adjustment. May cause Qwave and T-wave changes in ECG. Observe patient carefully when administering oral medication to ensure that medication is actually taken and not hoarded. Assess fluid intake and bowel function. Increased bulk and fluids in the diet help minimize constipation. Monitor patient for onset of akathisia (restlessness or desire to keep moving) and extrapyramidal side effects (parkinsoniandifficulty speaking or swallowing, loss of balance control, pill rolling, mask-like face,
RATIONALE
CLASSIFICATION: Antipsychotics
Actual:
Drug Image:
shuffling gait, rigidity, tremors; dystonicmuscle spasms, twisting motions, twitching, inability to move eyes, weakness of arms or legs) every 2 mo during therapy and 812 wk after therapy has been discontinued. Reduction in dosage or discontinuation of medication may be necessary. Trihexyphenidyl or diphenhydramine may be used to control these symptoms. Monitor for tardive dyskinesia (uncontrolled rhythmic movement of mouth, face, and extremities; lip smacking or puckering; puffing of cheeks; uncontrolled chewing; rapid or worm-like movements of tongue). Report immediately; may be irreversible. Monitor for development of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (fever, respiratory distress, tachycardia, seizures, diaphoresis, hypertension or hypotension, pallor, tiredness, severe muscle stiffness, loss of bladder control). Report
immediately. Lab Test Considerations: CBC, liver function tests, and ocular examinations should be evaluated periodically during therapy. May cause decreased hematocrit, hemoglobin, leukocytes, granulocytes, and platelets. May cause elevated bilirubin, AST, ALT, and alkaline phosphatase. Agranulocytosis may occur after 410 wk of therapy with recovery 12 wk after discontinuation. May recur if medication is restarted. Liver function abnormalities may require discontinuation of therapy. May cause false-positive or false-negative pregnancy tests and false-positive urine bilirubin test results.
You might also like
- GENERIC/BRAND MECHANISM OF CLASSIFICATION ACTIONDocument3 pagesGENERIC/BRAND MECHANISM OF CLASSIFICATION ACTIONEmJay Balansag100% (5)
- FluphenazineDocument3 pagesFluphenazineKaren T. CeletariaNo ratings yet
- FluphenazineDocument4 pagesFluphenazineimthebossNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJezzy Ann F. SarrozaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CLOZAPINEDocument6 pagesDrug Study CLOZAPINESandra ManzanoNo ratings yet
- ChlorpromazineDocument3 pagesChlorpromazineMarinel AgultoNo ratings yet
- DS HaloperidolDocument3 pagesDS HaloperidolbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayDocument4 pagesQuetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Psych Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- School of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeDocument3 pagesSchool of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeMiggsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ZiprasidoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study ZiprasidoneArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LamotrigineDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY LamotrigineP B0% (2)
- Biperiden (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBiperiden (Drug Study)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Clozapine (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClozapine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (3)
- Divalproex Sodium (Depakote ER)Document1 pageDivalproex Sodium (Depakote ER)karenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- Escitalopram Uses, Dosage, Side Effects and Nursing InterventionsDocument3 pagesEscitalopram Uses, Dosage, Side Effects and Nursing InterventionsPao HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesQuetiapine Drug StudyEula Angelica Oco100% (1)
- Drug Study (Olanzapine)Document1 pageDrug Study (Olanzapine)Eden Marie Francisco100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyTarquin Tomada100% (2)
- FluoxetineDocument3 pagesFluoxetineArnzz Agbulos100% (1)
- Clorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Valproic AcidDocument2 pagesValproic AcidRoshleen Ann De PedroNo ratings yet
- Olanzapine Drug StudyDocument1 pageOlanzapine Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- Chlorpromazine drug infoDocument2 pagesChlorpromazine drug infoevalyn dane50% (2)
- RisperidoneDocument2 pagesRisperidoneKeij Araneta0% (1)
- Effectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorDocument4 pagesEffectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyjennachristy03100% (3)
- BiperidenDocument3 pagesBiperidenKaren T. Celetaria100% (1)
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 pagesCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Drug Study ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Biperiden Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBiperiden Drug StudyMelissa Fatima Laurente Dosdos100% (1)
- Drug Study-ChlorpromazineDocument1 pageDrug Study-ChlorpromazineMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesChlorpromazine Drug StudyPeyjey100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTeZza_Enano_2209100% (1)
- Lithium Carbonate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesLithium Carbonate Drug Studynot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HaloperidolDocument2 pagesDrug Study HaloperidolRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRisperidone Drug StudyNajmah Saaban77% (13)
- BIPERIDEN (Akineton)Document2 pagesBIPERIDEN (Akineton)karenmichellelecaroz100% (5)
- Anti-Depressants: Sertraline, Flouxetine, MitrazapineDocument20 pagesAnti-Depressants: Sertraline, Flouxetine, MitrazapineBobbie Sison67% (3)
- Drug study on Biperiden for ParkinsonismDocument2 pagesDrug study on Biperiden for ParkinsonismMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid Drug Data SheetDocument4 pagesValproic Acid Drug Data SheetJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- Drug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)Document5 pagesDrug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)kuro hanabusa100% (2)
- QuetiapineDocument1 pageQuetiapineHanna Se100% (1)
- ClonazepamDocument2 pagesClonazepamjhezelle05100% (2)
- Lithium CarbonateDocument2 pagesLithium CarbonateArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- HALOPERIDOL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHALOPERIDOL Drug Studyanreilegarde89% (9)
- Biperiden Drug StudyDocument1 pageBiperiden Drug StudyMill Jan CruzNo ratings yet
- Olanzapine Nursing Care GuideDocument3 pagesOlanzapine Nursing Care GuideBarbara Detaro100% (2)
- Lithium drug information and nursing responsibilitiesDocument2 pagesLithium drug information and nursing responsibilitiesShedrann Johan100% (1)
- Drug Study-Grand Case PresDocument8 pagesDrug Study-Grand Case PresLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Considerations for BenzodiazepinesDocument4 pagesNursing Considerations for BenzodiazepinesKuro Hanabusa100% (2)
- DivalproexDocument2 pagesDivalproexeefrheelNo ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrilDocument2 pagesGENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrildanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ClonazepamDocument3 pagesDrug Study ClonazepamJohn Rey AbadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Thiothixene and OlanzapineDocument3 pagesDrug Study For Thiothixene and OlanzapineHARVEY SELIMNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies PsychDocument12 pagesDrug Studies PsychAnna Mendiola-BasbasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyMeraflor BahonsuaNo ratings yet
- Carbidopa-Levodopa (SINEMET CR)Document1 pageCarbidopa-Levodopa (SINEMET CR)Amanda CoadNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NameJhennyvie Dueñas ArcoirezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMariCris CaronanNo ratings yet
- Flupentixol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFlupentixol Drug StudyEmJay Balansag0% (1)
- Ischemic CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesIschemic CardiomyopathyEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Isolation Precaution Airborne Droplet ContactDocument1 pageIsolation Precaution Airborne Droplet ContactEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Blood Dyscrasias: Iron Deficiency Anemia Sickle Cell Anemia Hemophilia LeukemiaDocument2 pagesBlood Dyscrasias: Iron Deficiency Anemia Sickle Cell Anemia Hemophilia LeukemiaEmJay Balansag100% (1)
- Spread To The Surrounding Tissues in The Breast or Other Parts of The BodyDocument6 pagesSpread To The Surrounding Tissues in The Breast or Other Parts of The BodyEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Staff Nurse Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesStaff Nurse Job DescriptionEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Patients Profile I. Biographic DataDocument18 pagesPatients Profile I. Biographic DataEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Davao Doctors College: Gen. Malvar ST., Davao CityDocument1 pageDavao Doctors College: Gen. Malvar ST., Davao CityEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- READDocument51 pagesREADEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- IV ComplicaitonDocument2 pagesIV ComplicaitonEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- I Am SamDocument4 pagesI Am SamEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Patients Profile I. Biographic DataDocument18 pagesPatients Profile I. Biographic DataEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Head NurseDocument2 pagesHead NurseEmJay Balansag100% (1)
- 9172Document5 pages9172EmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Ischemic CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesIschemic CardiomyopathyEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- The Information Processing Approach To CognitionDocument8 pagesThe Information Processing Approach To CognitionEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Our New Era Has Charted New Discoveries Through SCDocument1 pageOur New Era Has Charted New Discoveries Through SCEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- I Am SamDocument4 pagesI Am SamEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Michael Jones GDocument2 pagesMichael Jones GEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- PArtial COmplete Baxh Nalng KulangDocument18 pagesPArtial COmplete Baxh Nalng KulangEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- MENTAL STATUS EXAM ELDERLY MANDocument8 pagesMENTAL STATUS EXAM ELDERLY MANEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Problem Scientific Basis Goals Interventions RationaleDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Problem Scientific Basis Goals Interventions RationaleEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- DAY 2 - Inflam and Immuno 2Document61 pagesDAY 2 - Inflam and Immuno 2EmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis of Tuberculosis Spondylitis (Pott's DiseaseDocument2 pagesCase Analysis of Tuberculosis Spondylitis (Pott's DiseaseEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- CASE Study. RecopiedDocument4 pagesCASE Study. RecopiedEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- PRA SA MONDAY With New Personal DataDocument27 pagesPRA SA MONDAY With New Personal DataEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- SheDocument4 pagesSheEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- MENTAL STATUS EXAM ELDERLY MANDocument8 pagesMENTAL STATUS EXAM ELDERLY MANEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
- ASUSTeK TECHNICAL SUPPORT REQUEST FORM DATEDocument2 pagesASUSTeK TECHNICAL SUPPORT REQUEST FORM DATEEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
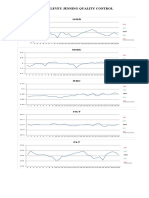
- Grafik Levey Jenning Quality ControlDocument5 pagesGrafik Levey Jenning Quality Controluyun cahyaNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease: Overview of The LiverDocument6 pagesLiver Disease: Overview of The LiverMustafa AlmasoudiNo ratings yet
- Interpret ECG & Ask Risk Questions for AF PatientDocument20 pagesInterpret ECG & Ask Risk Questions for AF PatientLorenzoChi100% (3)
- Mirizzi Syndrome: An Unusual Presentation of CholecystitisDocument16 pagesMirizzi Syndrome: An Unusual Presentation of CholecystitisAnn Alegre ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- 0089511-HLH PHS-2-0321-11694: Lab No: Patient NoDocument4 pages0089511-HLH PHS-2-0321-11694: Lab No: Patient NoSyed Abid Rais ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cirrhosis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesCardiac Cirrhosis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfKardiologi ManadoNo ratings yet
- Lab Result Chart With Normal Range, Purpose, Reason For High/low Results (Nursing)Document5 pagesLab Result Chart With Normal Range, Purpose, Reason For High/low Results (Nursing)Linsey Bowen100% (6)
- PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL TERMINOLOGYDocument4 pagesPRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL TERMINOLOGYTimotheé KensukeNo ratings yet
- Pathology & Clinical Laboratory (M) SDN - BHD (37363-K) : HaematologyDocument4 pagesPathology & Clinical Laboratory (M) SDN - BHD (37363-K) : HaematologyKukuru HiruNo ratings yet
- Urea/ Ammonia Tests: Primary Liver Function TestsDocument6 pagesUrea/ Ammonia Tests: Primary Liver Function TestsMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Module14 Content Nursing Care Management of AdultDocument21 pagesModule14 Content Nursing Care Management of AdultFranceska AntonioNo ratings yet
- CLL PatientReportDocument7 pagesCLL PatientReportHassan Sarfraz AliNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests... ROHITDocument61 pagesLiver Function Tests... ROHITJr Jc Rohit SahNo ratings yet
- Hepatoprotector Activities of 'A' Apple Vinegar To SGOT and SGPT Serum in Wistar Rats Induced by Toxic Dose of ParacetamolDocument5 pagesHepatoprotector Activities of 'A' Apple Vinegar To SGOT and SGPT Serum in Wistar Rats Induced by Toxic Dose of ParacetamolWaode Cahaya Widya PutriNo ratings yet
- S2 Sample4Document5 pagesS2 Sample4ZH. omg sarNo ratings yet
- The Full Moon Parasite Cleanse ProtocolDocument49 pagesThe Full Moon Parasite Cleanse ProtocolparthvarandaniNo ratings yet
- Revised HS360 ICICI Lombard Health Insurance PlanDocument29 pagesRevised HS360 ICICI Lombard Health Insurance PlanrbitrackerNo ratings yet
- Swift River Medication AdministrationDocument4 pagesSwift River Medication AdministrationmattNo ratings yet
- Minmed Health Screeners: Executive Health Screening That You DeserveDocument7 pagesMinmed Health Screeners: Executive Health Screening That You DeserveNicky LimNo ratings yet
- Year 2: PBL 2: JaundiceDocument74 pagesYear 2: PBL 2: JaundiceyaneemayNo ratings yet
- Data Interpretation For Medical Students, 2e (Pastest)Document642 pagesData Interpretation For Medical Students, 2e (Pastest)Test MRCP100% (1)
- Webb 2018 Hepatic Lipidosis Clinical Review Drawn From Collective EffortDocument11 pagesWebb 2018 Hepatic Lipidosis Clinical Review Drawn From Collective EffortJulia Maria dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests SummaryDocument2 pagesLiver Function Tests SummaryAdrian CastroNo ratings yet
- Acasestudyoncirrhosisofliver 160424143748Document48 pagesAcasestudyoncirrhosisofliver 160424143748michelleNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kinerja Lab Per Pasien Pemeriksaan 2022-07-24 S - D 2022-07-24Document48 pagesLaporan Kinerja Lab Per Pasien Pemeriksaan 2022-07-24 S - D 2022-07-24LaboratoriumNo ratings yet
- Blood Chemistry TestsDocument3 pagesBlood Chemistry TestsMarcelina ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Enzyme TestsDocument12 pagesEnzyme TestsgireeshsachinNo ratings yet
- Lab Request FormDocument2 pagesLab Request FormVanny JoyceNo ratings yet
- Althea NCM 116aDocument192 pagesAlthea NCM 116aspain michaelisNo ratings yet
- Vettest Operators Guide enDocument132 pagesVettest Operators Guide enLisbeth R Duran ChaparroNo ratings yet