Professional Documents
Culture Documents
70-236 Lesson01 IG 030609
Uploaded by
Nolan HiltonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
70-236 Lesson01 IG 030609
Uploaded by
Nolan HiltonCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1
Lesson 1 Exchange Server 2007 Basics
Learning Objectives
Students will learn to: Identify the purpose and usage of Exchange Server 2007. Describe standard email terminology. Understand email relay and DNS MX record usage. Explain the various types and uses of email protocols. Identify previous versions of Exchange Server and their features. List the new features introduced in Exchange Server 2007. Describe the function and usage of Exchange Server 2007 server roles.
Key Terms
Active Directory (AD) Microsofts directory service that automates network authentication, management, and security. ActiveSync A protocol used to synchronize email and other items between a smartphone device and Microsoft Exchange Server. Client Access Server (CAS) An Exchange Server 2007 server role that allows email clients to interact with Exchange Server 2007 to send and receive email and other information. Cmdlets Commands that can be executed within the Exchange Management Shell. A system that associates IP address to Fully Qualified
Domain Name System (DNS) Domain Names and vice versa.
Edge Transport Role (Edge) An Exchange Server 2007 server role that provides security for all inbound and outbound email for an organization. EdgeSync The protocol used to transfer configuration information from the Hub role servers to the Edge roles within your organization. Exchange Management Console (EMC) The graphical Microsoft Management Console snap-in utility used to manage Exchange Server 2007. Exchange Management Shell (EMS) Exchange Server 2007 using cmdlets. The command-line utility used to manage
3-1
Lesson 1
Extended Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (ESMTP) The latest protocol used to relay email messages from POP3 and IMAP4 to email servers, as well as from email servers to other email servers across the Internet. Hub Transport Role (Hub) An Exchange Server 2007 server role that is responsible for relaying email within an Exchange Organization. Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) The protocol used to display web pages.
Internet Message Access Protocol Version 4 (IMAP4) A common email access protocol that email clients can use to obtain email from an email server using a persistent connection. Mail Delivery Agent (MDA) The X.400 component that receives email from other email servers and delivers it to a recipients mailbox. Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) email server to another. The X.400 component that transfers email from one
Mail User Agent (MUA) The X.400 component that allows a client computer access to email on an email server. Mailbox Role An Exchange Server 2007 server role that stores mailbox and public folder databases as well as provides access to their contents. MAPI Clients Client computers that run software (such as Microsoft Outlook and Entourage) and can connect to Exchange Server 2007 using the MAPI protocol. Messaging Application Programming Interface (MAPI) The RPC-based, Microsoft-specific client access protocol designed to integrate Microsoft Outlook and Entourage with advanced features in Exchange Server 2007. It is often referred to as MAPI RPC. Messaging Records Management (MRM) An Exchange Server 2007 feature that allows organizations to easily store and archive messages for periods of time as required by law. Outlook Anywhere A protocol that allows MAPI clients to obtain email from their Exchange Server 2007 computer from across the internet using HTTPS. It is also called RPC over HTTP/HTTPS. Outlook Web Access (OWA) A Web site and related services that are hosted by a CAS role server to provide access to email via a web browser.
3-2
Lesson 1
Post Office Protocol Version 3 (POP3) A common email access protocol that can be used to download email from an email server. PowerShell A Windows command line management and scripting utility.
Public Folder A folder that can be used to store email, posts, tasks, notes, memos, calendars, and journal items. Round Robin The process whereby a list of multiple DNS A records for a host are rotated for each name resolution request. RPC over HTTP/HTTPS A protocol that allows MAPI clients to obtain email from their Exchange Server 2007 computer from across the internet using HTTPS. It is often called Outlook Anywhere in Exchange Server 2007. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) A technology used to provide encryption for a wide range of Internet protocols such as HTTP. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) The legacy protocol used to relay email messages from POP3 and IMAP4 to email servers, as well as from email servers to other email servers across the Internet. Smart Host A third-party email server that queues and filters email.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) A security technology based on SSL that can be used to secure a wide range of network protocols such as SMTP and ESMTP. Unified Messaging (UM) The Exchange Server 2007 component that allows for integration with an organizations PBX.
Lesson 1 Exchange Server 2007 Basics
Knowledge Assessment Fill in the Blank
Complete the following sentences by writing the correct word or words in the blanks provided. 1. The program used to send email on an email client is also called a Mail User Agent (MUA).
3-3
Lesson 1 2.Microsoft Outlook and Entourage typically connect to Exchange Server 2007 using RPCbased connections and MAPI. 3.The HTTP and HTTPS protocols are often used to access email using a Web browser. 4.An email server uses MX and A records in DNS to determine the target email server to relay email to. 5.The Edge server role must be installed on its own Exchange server and cannot co-exist with other server roles. 6.The Exchange Server 2007 feature that integrates voice mail and fax into an email system is called Unified Messaging (UM). 7.RPC over HTTP/HTTPS is called Outlook Anywhere in Exchange Server 2007. 8.Local Continuous Replication (LCR) is a new type of clustering in Exchange Server 2007 that can be used to perform continuous backups of data to a local hard drive. 9.If a DNS server returns several MX records with different priorities, the one with the Lowest priority is contact first. 10. Exchange Management Shell is a command-based administration tool in Exchange Server 2007 that is based on PowerShell.
Multiple Choice
Circle the letter that corresponds to the best answer. 1.Which of the following server roles in Exchange Server 2007 handles POP3 connections from client computers? a. b. c. d. CAS Hub Mailbox Edge
The CAS role provides client email access. 2.Outlook Web Access (OWA) relies on the ____________ component of Windows. a. b. c. d. Site PowerShell IIS RPC
OWA is a component of both IIS and Exchange Server 2007. 3.Which of the following email protocols encrypts data during transfer? a. b. c. d. ESMTPS IMAP4 HTTP RPC
ESMTPS encrypts data using SSL/TLS. 4.What DNS feature rotates the order of MX records before they are given to the email server that requested them? a. Failover
3-4
Lesson 1 b. c. d. MX ordering Priorities Round robin
DNS uses round robin to rotate multiple records in DNS queries. 5.Which of the following is not a valid email message format? a. b. c. d. plain text RPC HTML Rich Text
RPC is an email protocol and not an email message format. 6.Which of the following protocols can be used to obtain email from an email server? (Choose all that apply.) a. b. c. d. SMTP MAPI RPC POP3 IMAP4
SMTP can only be used to send emails. 7.Which of the following priority numbers will most likely be assigned to the DNS MX record that is used to identify a smart host? a. b. c. d. 10 255 99 5
The lowest priority number is typically assigned to a smart host MX record in DNS. 8.Which of the following is not a valid cmdlet structure? a. b. c. d. Get-PublicFolder Enable-MailboxDatabase Email-Send Update-Content
Cmdlets are always verb-noun commands. 9.Which of the following allows Exchange Server 2007 to scale from small to large organizations? (Choose all that apply.) a. b. c. d. 64-bit architecture separation of roles unlimited database size support for new business requirements such as UM and MRM
All of these features allow for scalability in Exchange Server 2007. 10. What must be configured if your organization uses the Edge role? a. b. ActiveSync EdgeSync
3-5
Lesson 1 c. d. X.400 MAPI
Edge role servers use the EdgeSync protocol to function.
True/False
Circle T if the statement is true or F if the statement is false. TF 1. TF 2. TF 3. TF 4. TF 5. 1.False 2.False 3.True 4.False 5.True Server that contain the Edge role access their configuration information from the Active Directory database. Email systems typically adhere to the X.400 directory service standard. Exchange servers store mailboxes in a database. The Exchange Management Shell (EMS) can only perform a subset of the functions available in the Exchange Management Console (EMC). IMAP4 was designed as a more robust replacement for POP3.
Matching
Match the term in Column 1 to its description in Column 2. a.PBX b.MTA c.ActiveSync d.Edge e.Thunderbird ___d____ ___c ____ 1. A server role that provides smart host capabilities in Exchange Server 2007. 2. A common Mail User Agent (MUA).
___ e ____ 3. A software program that relays mail across computer networks such as the Internet. ___ a ____ 4. Sends fax and voice mail to the Unified Messaging (UM) role. ___ b ____ 5. An email protocol used by smart phones.
Review Questions
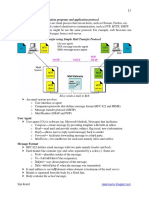
1.Outline the process and protocols used to relay email on the Internet. Although answers will vary, email is typically relayed across the Internet using the SMTP or ESMTP protocols as well as their encrypted variants (SMTPS, ESMTPS). The
3-6
Lesson 1 source email server first resolves the MX records of the target email domain name using DNS and selects the first email server listed with the highest priority. The A record of this email server is then resolved using DNS and the email is sent to the target email server using the SMTP/ESMTP/SMTPS/ESMTPS protocol depending on the configuration of the email servers involved. 2.Describe the protocols that email client can use to obtains email from an email server as well as send email to an email server. Although answers will vary, email protocols configured on the client computer must match the email protocols configured on the email server. Protocols such as Activesync, HTTP/HTTPS, RPC(MAPI), and RPC over HTTP (Outlook Anywhere) may be used to send and receive email. Alternatively, POP3/POP3S and IMAP4/IMAP4S are designed to download email only and must be configured alongside SMTP/ESMTP/SMTPS/ESMTPS in order for clients to send email.
Case Scenarios Scenario 1-1: Creating a Proposal You are the network administrator for a medium sized organization. Currently, your organization has been using Windows 2000 servers running Exchange Server 2000 to provide email services. Your manager has asked you whether the organization should consider replacing their current Exchange servers with new servers that run Exchange Server 2007. Prepare a short proposal outlining the key benefits and costs associated with replacing the current Exchange server with several servers running Exchange Server 2007. Answers will vary, but will include many of the new features in Exchange Server 2007 such as role-based deployment, as well as features that were introduced since Exchange Server 2000 such as ActiveSync, RSGs and spam filtering. The main cost associated with upgrading is the purchase of 64-bit servers, Windows Server 2003/2008 licenses, Exchange Server 2007 licenses, as well as the possible purchase of additional servers to support the Edge and UM roles.
Scenario 1-2: Designing Server Roles Your company has opened a new division that will employ 200 people and work under its own Internet identity. This new division will need a secure email system that allows internal Outlook clients to check their emails, fax and voice mail. In addition, mobile clients require the ability to check their email from a telephone or smart phone. In a short memo, diagram the necessary server roles and email protocols that will need to be implemented in this new environment using Exchange Sever 2007.
3-7
Lesson 1
Answers will vary, but will include at least two servers: one server will hold the Edge role, and the other server can hold the UM, Hub, Mailbox, and CAS roles. The MAPI RPC protocol will be used by the Outlook clients, ActiveSync will be used by the smart phone clients, VOIP will be used between the PBX and the UM role, and SMTP will be used to route Internet email between the Hub and Edge roles as well as between the Edge role and Internet email servers.
3-8
You might also like
- Exchange 2010 PosterDocument1 pageExchange 2010 PosterGautam SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is Exchange ServerDocument16 pagesWhat Is Exchange Serverkmrs_888No ratings yet
- Exchange Server 2007 Learning GuideDocument75 pagesExchange Server 2007 Learning GuiderahamathullahkamalmNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 - Sizing, Designing and Configuration: A Practical LookFrom EverandMicrosoft Exchange Server 2013 - Sizing, Designing and Configuration: A Practical LookNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Providing E-Mail Services: at A GlanceDocument9 pagesChapter 8 - Providing E-Mail Services: at A Glanceghar_dashNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- Exchange Server Interview QuestionsDocument59 pagesExchange Server Interview QuestionsKddoor0% (1)
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - The TechnologyDocument14 pagesChapter2 - The TechnologyRaven Laurdain PasiaNo ratings yet
- Exchange 2013 Summary Eng Mohamed ElemamDocument30 pagesExchange 2013 Summary Eng Mohamed ElemamMayyaR Al-shiekhNo ratings yet
- Distinguish Between Application Programs and Application ProtocolDocument13 pagesDistinguish Between Application Programs and Application ProtocolvgNo ratings yet
- BSC IT 63 Advanced Computer NetworksDocument24 pagesBSC IT 63 Advanced Computer NetworksAshutosh SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Exchange Interview QuestionsDocument187 pagesExchange Interview QuestionsVipul KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 03 Rev Final PDFDocument9 pagesLesson 03 Rev Final PDFThilan NawagamuwaNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Report - Java Based Email Server SystemDocument6 pagesMini Project Report - Java Based Email Server SystemGokulsuriNo ratings yet
- Exchange 2007 Overview and SP1 AdditionsDocument44 pagesExchange 2007 Overview and SP1 AdditionsSoumya GangulyNo ratings yet
- 2013 RegulationDocument29 pages2013 RegulationfencyNo ratings yet
- E-Mail ServerDocument32 pagesE-Mail ServerMehari TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Exchange Server 2013 Question and AnswersDocument12 pagesExchange Server 2013 Question and AnswersAnonymous PZW11xWeOo100% (1)
- EXCH 2010 Server RolesDocument5 pagesEXCH 2010 Server RolesVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT V - Application LayerDocument46 pagesUNIT V - Application LayerSenthilkumar SNo ratings yet
- Lab Exchange 2010Document9 pagesLab Exchange 2010THAVIN LAYNo ratings yet
- 70-236, Lesson 1 Exchange Server 2007 Basics Practice Quiz: Fill in The BlankDocument2 pages70-236, Lesson 1 Exchange Server 2007 Basics Practice Quiz: Fill in The BlankJyoti PatelNo ratings yet
- Cs8591 Computer Networks 1103969345 CN NotesDocument240 pagesCs8591 Computer Networks 1103969345 CN Notesfirstandlastname1100No ratings yet
- 70-236 Lesson03 IG 030609Document7 pages70-236 Lesson03 IG 030609Nolan HiltonNo ratings yet
- Configuration of Postfix Mail Server Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusFrom EverandConfiguration of Postfix Mail Server Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusNo ratings yet
- Home Microsoft Exchange 2003 Exchange 2003 Interview Questions and Answers - Part 2Document17 pagesHome Microsoft Exchange 2003 Exchange 2003 Interview Questions and Answers - Part 2chainsawrNo ratings yet
- O365 Interview Questiones & AnswersDocument7 pagesO365 Interview Questiones & AnswersShaik AmanullahNo ratings yet
- UNIT - II - Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesUNIT - II - Computer Networkssankalpsamant2001No ratings yet
- Autodiscover MobDocument5 pagesAutodiscover MobHg HgNo ratings yet
- Edge Transport Role: Figure 1: Exchange 2007 RolesDocument4 pagesEdge Transport Role: Figure 1: Exchange 2007 RolesdarlingdarlingNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: System and Network Admin IssuesDocument25 pagesChapter Six: System and Network Admin IssuesPro NebyuNo ratings yet
- Protecting Exchange 2010 WhitepaperDocument5 pagesProtecting Exchange 2010 WhitepaperjjosssNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument40 pagesUnit VsathiyaNo ratings yet
- Starting Guide for Postfix Mail Server Configuration Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusFrom EverandStarting Guide for Postfix Mail Server Configuration Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusNo ratings yet
- Exchange 2003Document28 pagesExchange 2003Shankar JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Application LayerDocument10 pagesChapter 6: Application LayerRoshan BasnetNo ratings yet
- Debre Tabor University: Network and System AdministrationDocument28 pagesDebre Tabor University: Network and System AdministrationBethelhem YetwaleNo ratings yet
- What Is Exchange 2003 Forestprep?Document33 pagesWhat Is Exchange 2003 Forestprep?ganesan1979No ratings yet
- Exchange 2010 UnderstandDocument493 pagesExchange 2010 UnderstandSeKoFieNo ratings yet
- Email Web Servers Isps: What Are The Types of Mail Servers?Document4 pagesEmail Web Servers Isps: What Are The Types of Mail Servers?Divya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mail Server ReportDocument39 pagesMail Server ReportWan Yusri0% (1)
- Mini Project Report Java Based Email Server System PDFDocument6 pagesMini Project Report Java Based Email Server System PDFakshayNo ratings yet
- Unit V Application Layer Traditional ApplicationsDocument29 pagesUnit V Application Layer Traditional ApplicationsakashNo ratings yet
- Linux Tcp-Ip PROJECT 2013Document42 pagesLinux Tcp-Ip PROJECT 2013OmPrakashKumarNo ratings yet
- Administration Débian Serveur Installation Mail Serveur Bernier FrancoisDocument38 pagesAdministration Débian Serveur Installation Mail Serveur Bernier Francoisgakou05No ratings yet
- Building Full Linux Mail Server Solution with Virtual Domains and UsersFrom EverandBuilding Full Linux Mail Server Solution with Virtual Domains and UsersNo ratings yet
- Mail Enable Standard GuideDocument71 pagesMail Enable Standard Guidepersonal8276No ratings yet
- It Unit4Document13 pagesIt Unit4rogithaNo ratings yet
- Exchange Server 2010 Interview Questions and Answers PDFDocument11 pagesExchange Server 2010 Interview Questions and Answers PDFtripathi.shivani702550% (2)
- Computer Networks - Chapter 2 - Application LayerDocument9 pagesComputer Networks - Chapter 2 - Application LayerNirzor LiveNo ratings yet
- Creation of Postfix Mail Server Based on Virtual Users and DomainsFrom EverandCreation of Postfix Mail Server Based on Virtual Users and DomainsNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 with SP1: Tony Redmond's Guide to Successful ImplementationFrom EverandMicrosoft Exchange Server 2007 with SP1: Tony Redmond's Guide to Successful ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Small Business Server 2008: Installation, Migration, and ConfigurationFrom EverandSmall Business Server 2008: Installation, Migration, and ConfigurationNo ratings yet
- 70-236 Lesson03 IG 030609Document7 pages70-236 Lesson03 IG 030609Nolan HiltonNo ratings yet
- 70-236 Lesson02 IG 030609Document8 pages70-236 Lesson02 IG 030609Nolan HiltonNo ratings yet
- 70-236 Lesson01 IG 030609Document8 pages70-236 Lesson01 IG 030609Nolan HiltonNo ratings yet
- Price Cost Capstone ProjectDocument1 pagePrice Cost Capstone ProjectNolan HiltonNo ratings yet
- Deploying Office 365 in Production - Part 1Document62 pagesDeploying Office 365 in Production - Part 1Riki RinaldoNo ratings yet
- FortiMail Install Guide V 3Document108 pagesFortiMail Install Guide V 3Fredy Gualdron VargasNo ratings yet
- AdministrationDocument682 pagesAdministrationTanmoy Sen100% (1)
- Understanding How DNS WorksDocument8 pagesUnderstanding How DNS WorksEduardo Andrés Loaiza MataNo ratings yet
- rc182 010d DNS PDFDocument7 pagesrc182 010d DNS PDFmiromarkoNo ratings yet
- Linux Interview Questions AnswersDocument80 pagesLinux Interview Questions AnswersMishraa_jiNo ratings yet
- Planning and Provisioning Office 365Document9 pagesPlanning and Provisioning Office 365DIPANJALINo ratings yet
- Build Your Own Email Server On Ubuntu: Basic Postfix SetupDocument19 pagesBuild Your Own Email Server On Ubuntu: Basic Postfix SetupBasuraNo ratings yet
- M3GuideTransforms PDFDocument97 pagesM3GuideTransforms PDFRicardo GermanoNo ratings yet
- Configuring Linux Mail Servers: - Objectives - ContentsDocument30 pagesConfiguring Linux Mail Servers: - Objectives - ContentsAmine BesrourNo ratings yet
- Configuration Report DemonDocument11 pagesConfiguration Report DemonYus JayaNo ratings yet
- Network Administration Guide For Scanning Functions: Multifunctional Digital SystemsDocument46 pagesNetwork Administration Guide For Scanning Functions: Multifunctional Digital SystemsCatalin ComiNo ratings yet
- Lotus Note Questions ForL1 - L2 LevelDocument52 pagesLotus Note Questions ForL1 - L2 LevelShilpi Guleria0% (2)
- Configuring Office 365 (Microsoft) With Cisco Cloud Email Security (CES)Document13 pagesConfiguring Office 365 (Microsoft) With Cisco Cloud Email Security (CES)mhakeem.elsaeedNo ratings yet
- How To Configure The DNS Server: Step 1. Enable Authoritative DNSDocument4 pagesHow To Configure The DNS Server: Step 1. Enable Authoritative DNSDavid JacksonNo ratings yet
- Office365 AdminDocument480 pagesOffice365 AdminDoccon PT Synergy100% (3)
- AaaDocument29 pagesAaaapi-453983900No ratings yet
- ESVADocument30 pagesESVAluperoseNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up The Integrated DNS Server For Inbound Load BalancingDocument7 pagesHow To Set Up The Integrated DNS Server For Inbound Load BalancingThy LyNo ratings yet
- Linux Interview QuestionsDocument52 pagesLinux Interview Questionsvinnuthegreat100% (1)
- Lion Server - Advanced AdministrationDocument474 pagesLion Server - Advanced Administrationpaillet01No ratings yet
- Managing Forcepoint Email Security CloudDocument6 pagesManaging Forcepoint Email Security Cloudajay chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Deploying The BIG-IP System With SMTP Servers: Deployment GuideDocument28 pagesDeploying The BIG-IP System With SMTP Servers: Deployment GuideCamson HuynhNo ratings yet
- FortiMail Lab Guide-OnlineDocument154 pagesFortiMail Lab Guide-OnlineCharles Assy100% (1)
- Step-By-Step Guide To Office 365 Hybrid DeploymentDocument153 pagesStep-By-Step Guide To Office 365 Hybrid DeploymentduongtangsgNo ratings yet
- Linux Interview QuestionsDocument51 pagesLinux Interview Questionsseenu933No ratings yet
- Fortimail Admin 620Document686 pagesFortimail Admin 620Miguel Angel Callupe MejiaNo ratings yet
- Symantec Messaging Gateway 9.5.3 Installation GuideDocument111 pagesSymantec Messaging Gateway 9.5.3 Installation Guidefspoitoru123No ratings yet
- MX Record DNS Explained Example ConfiguratiDocument24 pagesMX Record DNS Explained Example ConfiguratiAleksandar Antic100% (1)
- How To Configure Sendmail To Forward Mails To A Relay Host Aka Smarthost (Doc ID 2018587.1)Document2 pagesHow To Configure Sendmail To Forward Mails To A Relay Host Aka Smarthost (Doc ID 2018587.1)JuanNo ratings yet