Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprise
Uploaded by
mohammad_shahzad_iiuiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprise
Uploaded by
mohammad_shahzad_iiuiCopyright:
Available Formats
CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
Lab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication
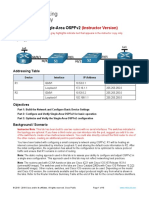
Device Router 1 Router 2 Switch 1 Host 1 Host 2
Host Name R1 R2 S1
Fast Ethernet 0/0 / NIC Address 192.168.0.1/24 192.168.1.1/24 192.168.0.10 192.168.1.10
Serial 0/0/0 Address 192.168.2.1/30 192.168.2.2/30
Serial 0/0/0 Interface Type DCE DTE
Enable Secret Password cisco cisco cisco
Enable, vty, and Console Password class class class
Objectives
Perform basic router configuration. Perform basic single area OSPF configuration. Configure OSPF authentication. Verify OSPF authentication.
Background / Preparation
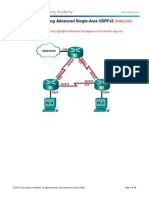
In this lab, you will cable a network similar to the one shown in the diagram. Any router that meets the interface requirements displayed in the addressing table may be used. For example, router series 800, 1600, 1700, 1800, 2500, 2600, or any combination can be used. The information in this lab applies to 1841 routers. Other routers may be used; however, command syntax may vary. Depending on the router model, the interfaces may differ. For example, on some routers Serial 0 may be Serial 0/0 or Serial 0/0/0 and Ethernet 0 may be FastEthernet 0/0. The Cisco Catalyst 2960 switch comes preconfigured and only needs to be assigned basic security information before being connected to a network.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 4
CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
The following resources are required: One Cisco 2960 switch or other comparable switch Two routers. each with a serial connection and an Ethernet interface Two Windows-based PCs, each with a terminal emulation program, and each set up as a host At least one RJ-45-to-DB-9 connector console cable to configure the routers and switch Two straight-through Ethernet cables One crossover Ethernet cable One 2-part (DTE/DCE) serial cable
NOTE: Make sure that the routers and the switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. Instructions for erasing both switch and router are provided in the Lab Manual, located on Academy Connection in the Tools section. NOTE: SDM Enabled Routers If the startup-config is erased in an SDM enabled router, SDM will no longer come up by default when the router is restarted. It will be necessary to build a basic router configuration using IOS commands. The steps provided in this lab use IOS commands and do not require the use of SDM. If you wish to use SDM, refer to the instructions in the Lab Manual, located on the Academy Connection in the Tools section or contact your instructor if necessary.
Step 1: Connect the equipment
a. Connect Router 1 Serial 0/0/0 interface to Router 2 Serial 0/0/0 interface using a serial cable. b. Connect Router 1 Fa0/0 interface to Switch 1 Fa0/1 port using a straight-through cable. c. Connect each PC with a console cable to perform configurations on the router and switches.
d. Connect Host 1 to the Switch 1 Fa0/2 port using a straight-through cable. e. Connect a crossover cable between Host 2 and the Fa0/0 interface of Router 2.
Step 2: Perform basic configuration on the routers
a. Connect a PC to the console port of the routers to perform configurations using a terminal emulation program. b. Configure Router 1 with a hostname, console, Telnet, and privileged passwords according to the table diagram. c. Configure Router 2 with a hostname, console, Telnet, and privileged passwords according to the table diagram.
Step 3: Configure and verify OSPF on the routers
a. Configure single area OSPF on R1 and R2. All interfaces will belong to Area 0. R1(config)#router ospf 1 R1(config-router)#network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R1(config-router)#end R2(config)#router ospf 1 R2(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R2(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R2(config-router)#end
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 2 of 4
CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
b. Verify the OSPF configuration using the show ip route command on both routers. R1#show ip route R2#show ip route Does the 192.168.1.0/24 network appear in the routing table of R1? __________ Does the 192.168.0.0/24 network appear in the routing table of R2? __________
Step 4: Configure and verify OSPF authentication
OSPF allows for both plain text authentication and encrypted authentication. Because plain text authentication is as insecure as having no authentication, Message Digest 5 (MD5) authentication is used. Configuring OSPF authentication is a two-step process. First, it is enabled on a router for an area, and then it is configured on the interfaces in that area. a. Enable MD5 authentication in Area 0 on both routers. R1(config)#router ospf 1 R1(config-router)#area 0 authentication message-digest R2(config)#router ospf 1 R2(config-router)#area 0 authentication message-digest b. Enable OSPF authentication on S0/0/0 of R1. R1(config)#interface s0/0/0 R1(config-if)#ip ospf message-digest-key 10 md5 secretpassword c. Using the show ip ospf neighbor command, view the neighbors known to R1. R1#show ip ospf neighbor Does R1 show any OSPF neighbors? ________________________________________________________________________________ Why or why not? ________________________________________________________________________________ d. Watch the terminal output from R1 for several seconds. What OSPF message was displayed when the MD5 authentication was set on R1 S0/0/0? ________________________________________________________________________________ e. Enable OSPF authentication on S0/0/0 of R2. R2(config)#interface s0/0/0 R2(config-if)#ip ospf message-digest-key 10 md5 secretpassword f. Now, recheck the neighbour status between R1 and R2. R1#show ip ospf neighbor Do R1 and R2 have a neighbor relationship established now? __________ What OSPF console message did you see after the MD5 authentication was set on R2 S0/0? ________________________________________________________________________________ g. Ping from Host 1 to Host 2 to verify connectivity. Can Host 1 ping Host 2? __________
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 3 of 4
CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
Step 5: Reflection
a. Why would OSPF authentication be configured in a network? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ b. Can one OSPF area have different OSPF configuration parameters than another area? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ c. Can a single OSPF router have multiple authentication passwords configured? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- 10 Comm Tractor SafetyDocument30 pages10 Comm Tractor Safetymohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Proxy Bypassing With A SSL VPN: Adri An Puente Z. February 27, 2008Document23 pagesProxy Bypassing With A SSL VPN: Adri An Puente Z. February 27, 2008walaba06No ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Crane Safety & AcciodentsDocument112 pagesCrane Safety & Acciodentsmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Cheat Solaris 11Document19 pagesCheat Solaris 11Mbonk Wae LahNo ratings yet
- Access PROFIBUS Devices via PN IO or S7 RoutingDocument13 pagesAccess PROFIBUS Devices via PN IO or S7 RoutingEdison Olivares DazaNo ratings yet
- AD EHS RI - CoP - 30.0 - Lone Working and or in Remote LocationsDocument14 pagesAD EHS RI - CoP - 30.0 - Lone Working and or in Remote Locationsmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- The National Examination Board inDocument8 pagesThe National Examination Board inmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- 5.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILM PDFDocument14 pages5.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (12)
- Understanding Ergonomics at WorkDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Ergonomics at WorkHealthSafety100% (2)
- Understanding Ergonomics at WorkDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Ergonomics at WorkHealthSafety100% (2)
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsFrom EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Network - ILM PDFDocument13 pages5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Network - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov95% (20)
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDocument54 pages2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDaniel Ergicho100% (1)
- OSPF Configuration Step by Step GuideDocument16 pagesOSPF Configuration Step by Step GuideMark BrownNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: Basic Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesLab 1: Basic Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDat LCNo ratings yet
- FL Dcmds 1.0.1 LGDocument386 pagesFL Dcmds 1.0.1 LGKv142 KvNo ratings yet
- 5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMDocument12 pages5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMرافد البركي75% (12)
- Chapter 11: Business Intelligence and Knowledge Management: Oz (5th Edition)Document20 pagesChapter 11: Business Intelligence and Knowledge Management: Oz (5th Edition)mohammad_shahzad_iiui100% (1)
- Toolbox Talks Confined Space English 0Document1 pageToolbox Talks Confined Space English 0mohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: IntegrantesDocument59 pagesLab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: IntegrantesAlex Fernando GarcesNo ratings yet
- Configuring Basic RIPv2 and RIPngDocument13 pagesConfiguring Basic RIPv2 and RIPngbinj78% (9)
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access (Filled)Document38 pages2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access (Filled)true0soul80% (5)
- Lab 6.3.1 Configuring and Propagating An OSPF Default RouteDocument5 pagesLab 6.3.1 Configuring and Propagating An OSPF Default Routemohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- 2.7.2 Lab - Configure Single Area Ospfv2 EditadoDocument4 pages2.7.2 Lab - Configure Single Area Ospfv2 EditadoMaría ArmijosNo ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesntutaNo ratings yet
- Configuring and Verifying VTY RestrictionsDocument4 pagesConfiguring and Verifying VTY RestrictionsAnatoli ParhinNo ratings yet
- Configure Basic Router Settings with Cisco IOS CLIDocument5 pagesConfigure Basic Router Settings with Cisco IOS CLIPunita VasuNo ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesCesar Lazo DiazNo ratings yet
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument11 pages4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessJesús EnriqueNo ratings yet
- 4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument10 pages4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessHector De Jesus Tapia GorgonioNo ratings yet
- Lab For Extended AclsDocument5 pagesLab For Extended Aclscasilan_90No ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesHani GoytomNo ratings yet
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationDocument7 pages6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationGISTSalehuddinNo ratings yet
- Configure Single-Area OSPFv2Document12 pagesConfigure Single-Area OSPFv2Mohammed AkeelNo ratings yet
- Switching LabDocument17 pagesSwitching LabGabby100% (1)
- Lab5 3 5Document10 pagesLab5 3 5ijot 76No ratings yet
- 6.2.3.8 LabDocument10 pages6.2.3.8 LabAutumn TillmanNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 1 6Document6 pagesLab 4 1 6HamzaSpahijaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktik Lab 2 - Securing The Router For Administrative Access - CompressedDocument57 pagesLaporan Praktik Lab 2 - Securing The Router For Administrative Access - CompressedRizky RismadhantiNo ratings yet
- Configure Admistrative RolesDocument20 pagesConfigure Admistrative RolesestebanNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDocument39 pagesLab 01 - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessespolieeeNo ratings yet
- LabDocument11 pagesLableonora KrasniqiNo ratings yet
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access PDFDocument38 pages2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access PDFAAANo ratings yet
- Lab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route PropagationDocument4 pagesLab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route Propagationmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Configuring Basic Routing and Switching PDFDocument11 pagesLab 2 Configuring Basic Routing and Switching PDFDennis Masuku MacfeeNo ratings yet
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access - UnlockedDocument44 pages2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access - UnlockedAlonso Chi CitukNo ratings yet
- Practica7 - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument9 pagesPractica7 - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesOctavio KuriNo ratings yet
- Routing and Switching Lab - 2019: Anycast TopologyDocument7 pagesRouting and Switching Lab - 2019: Anycast TopologyChinen momoNo ratings yet
- Lab 5.4.1 Implementing EIGRPDocument4 pagesLab 5.4.1 Implementing EIGRPAjith PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Ccnpv7 Route Lab3-2 Multi-Area-ospf StudentDocument19 pagesCcnpv7 Route Lab3-2 Multi-Area-ospf StudentHarrison Hayes0% (1)
- Lab EIGRP 5Document11 pagesLab EIGRP 5Danny Ricce EnriqueNo ratings yet
- 10.1.3.5 Lab Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features PDFDocument8 pages10.1.3.5 Lab Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features PDFбелимNo ratings yet
- CCNA4 Lab 1 2 6Document6 pagesCCNA4 Lab 1 2 6Alexandra AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document8 pagesLab 4pzydf6wjxvNo ratings yet
- 10.1.3.5 Lab Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument7 pages10.1.3.5 Lab Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesjohnathanNo ratings yet
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - ILMDocument18 pages2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - ILMSULTANNo ratings yet
- Basic Router Configuration StepsDocument12 pagesBasic Router Configuration StepsMeme222No ratings yet
- 10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument7 pages10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesdboNo ratings yet
- D 3 Challenge Acl LabDocument5 pagesD 3 Challenge Acl LabAmadouMalickMouamfonMoumbagnaNo ratings yet
- 6.2.3.10 Lab - Troubleshooting Multiarea OSPFv2 and OSPFv3Document11 pages6.2.3.10 Lab - Troubleshooting Multiarea OSPFv2 and OSPFv3SeptimanjaniNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 OSPFv2 - MUHAMMAD IZWAN BIN NAZRI - CS2555ADocument7 pagesExercise 2 OSPFv2 - MUHAMMAD IZWAN BIN NAZRI - CS2555Aezone8553No ratings yet
- 2.7.2 Lab - Configure Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILMDocument16 pages2.7.2 Lab - Configure Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILMMario Alberto Saavedra MeridaNo ratings yet
- A Lab1acceslistDocument5 pagesA Lab1acceslistveracespedesNo ratings yet
- Configuration Cisco Router CCNA Introduction To Networks V7.02Document6 pagesConfiguration Cisco Router CCNA Introduction To Networks V7.02Kim WorldNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- Structural Steel Worker Hazards & Safety TipsDocument4 pagesStructural Steel Worker Hazards & Safety Tips'CHi YucorNo ratings yet
- Wcms 107828Document96 pagesWcms 107828elkaffasNo ratings yet
- Kishwar Khan CV For Foreign LastDocument1 pageKishwar Khan CV For Foreign Lastmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Adec Ehsms Handbook v.01 2011 F eDocument32 pagesAdec Ehsms Handbook v.01 2011 F emohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Road Safety PresentationDocument21 pagesRoad Safety Presentationmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- ErgonomicsDocument7 pagesErgonomicsmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Presentation at DDCDocument20 pagesPresentation at DDCmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Ifc1 Sample MaterialDocument6 pagesIfc1 Sample Materialmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Safety at Work PlaceDocument22 pagesVehicle Safety at Work Placerozan e umeedNo ratings yet
- DrivingDocument10 pagesDrivingmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- AD EHS RI - CoP - 17.0 - Safety Signage and SignalsDocument36 pagesAD EHS RI - CoP - 17.0 - Safety Signage and Signalsmohammad_shahzad_iiui100% (1)
- Machine SafeguardingDocument53 pagesMachine Safeguardingmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Job Site Safety Checklist LongDocument4 pagesJob Site Safety Checklist LongAziz Khan JadoonNo ratings yet
- Ad Ehs Ri - Cop - 37.0 - LaddersDocument16 pagesAd Ehs Ri - Cop - 37.0 - Laddersmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- AD EHS RI - CoP - 31.0 - Working On Over or Adjacent To WaterDocument18 pagesAD EHS RI - CoP - 31.0 - Working On Over or Adjacent To Watermohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Sign Safety Climb Ladder Both HandsDocument1 pageSign Safety Climb Ladder Both Handsmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Course Outline For Igc # 1Document1 pageCourse Outline For Igc # 1mohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- AD EHS RI - CoP - 40.0 - False Work (Formwork)Document15 pagesAD EHS RI - CoP - 40.0 - False Work (Formwork)mohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- AD EHS RI - CoP - 35.0 - Portable Power ToolsDocument16 pagesAD EHS RI - CoP - 35.0 - Portable Power Toolsmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- 06 - HSE Alert Emergency Response - Electrical IncidentDocument2 pages06 - HSE Alert Emergency Response - Electrical Incidentmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Iprating PDFDocument3 pagesIprating PDFMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- ETSDC Training Booking FormDocument1 pageETSDC Training Booking Formmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- HAProxy in Kubernetes - Supercharge Your Ingress RoutingDocument77 pagesHAProxy in Kubernetes - Supercharge Your Ingress Routingadede2009No ratings yet
- Load Balancing Persistent: From Mikrotik WikiDocument5 pagesLoad Balancing Persistent: From Mikrotik Wikiapi-19807007No ratings yet
- Sky X TechnologyDocument24 pagesSky X TechnologychikatisivashankarNo ratings yet
- Sector Base Station RW-5200-2250 Data Sheet: Radwin 5000 - HPMPDocument2 pagesSector Base Station RW-5200-2250 Data Sheet: Radwin 5000 - HPMPJose VazNo ratings yet
- XS AsteriskCLIusefulcommands 290623 2358 1991Document8 pagesXS AsteriskCLIusefulcommands 290623 2358 1991Maximiliano RighettiNo ratings yet
- s9922m Series Lte Router Models User Manual 2019Document76 pagess9922m Series Lte Router Models User Manual 2019Remote AlexNo ratings yet
- KnowledgeNet IP Telephony Express (IPTX) 2.0 Student Guide PDFDocument1,176 pagesKnowledgeNet IP Telephony Express (IPTX) 2.0 Student Guide PDFleonids_hmhNo ratings yet
- 802 1xDocument33 pages802 1xraul7_atmNo ratings yet
- B CBR Basic SW Config Features PDFDocument108 pagesB CBR Basic SW Config Features PDFjunior2223No ratings yet
- 2-Port USB 1-Port Parallel Internet Print ServerDocument64 pages2-Port USB 1-Port Parallel Internet Print ServerdehammoNo ratings yet
- Junos Release Notes 12.1X46Document234 pagesJunos Release Notes 12.1X46Moises Velasquez ClaureNo ratings yet
- 802 Basics of Physical and Logical Networking Concepts.: 802.3 EthernetDocument4 pages802 Basics of Physical and Logical Networking Concepts.: 802.3 EthernetreduxiamNo ratings yet
- VH Thc-Ipv6 AttackDocument58 pagesVH Thc-Ipv6 AttackJudith Cardenas MerchanNo ratings yet
- Baicells ENB Configuration Guide-BaiBLQ - 3.0.X-01Document86 pagesBaicells ENB Configuration Guide-BaiBLQ - 3.0.X-01Rogerio Martins CandidoNo ratings yet
- 140 SP 3100Document25 pages140 SP 3100WaqasMirzaNo ratings yet
- STN 0, Ipinterface Int - S1 Primaryip - Address 10.246.43.37 !siu - Ip Default Gateway - S1 X2!Document16 pagesSTN 0, Ipinterface Int - S1 Primaryip - Address 10.246.43.37 !siu - Ip Default Gateway - S1 X2!fernando_souza385No ratings yet
- Eviction NoticeDocument482 pagesEviction Noticeanon_133720341No ratings yet
- U2 Lmh5401Irmsr: Title: Digvga-SchematicDocument1 pageU2 Lmh5401Irmsr: Title: Digvga-SchematicH SMNo ratings yet
- Intracom Jetspeed - 520 PDFDocument86 pagesIntracom Jetspeed - 520 PDFG FitnessNo ratings yet
- Cisco IP TelephonesDocument8 pagesCisco IP TelephonesAsim Penkar PenkarNo ratings yet
- EasyPath EPON Operation ManualV3Document289 pagesEasyPath EPON Operation ManualV3mileNo ratings yet
- Prod White Paper0900aecd80406232 PDFDocument16 pagesProd White Paper0900aecd80406232 PDFzein wagallahNo ratings yet
- MGate MB3180 QIG v2Document2 pagesMGate MB3180 QIG v2RobertoFuentesNo ratings yet
- Mcse NotesDocument88 pagesMcse NotesraheemNo ratings yet
- Prosoft - Modbus PLX31-MBTCP-MBSDocument3 pagesProsoft - Modbus PLX31-MBTCP-MBSArnezNo ratings yet
- Altai Wireless Network DesignDocument15 pagesAltai Wireless Network DesignMih NdrainibeNo ratings yet