Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Engine General
Uploaded by
Chabou RafikCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Engine General
Uploaded by
Chabou RafikCopyright:
Available Formats
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Engine Specifications Objectives
2-E ngine Ge neral
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to: Identify the location of the identification data plate Identify the identification data plate and engine specifications Identify the purpose of the identification data plate and engine specifications
Overview The engine specifications for the CF6-80E1 engine consist of
the following information:
Application Ratings Dimensions Engine safety hazards Ground transportation requirements
Each engine has an engine identification data plate that indicates the ratings and other information for that engine. In this lesson, you will learn about the identification and purpose of different engine specifications. You will also learn about the identification, location, and purpose of the engine identification data plate.
Purpose The engine specifications show the dimensions of the engine. The
applications identify the aircraft that are powered by the CF6-80E1 engine. The ratings indicate the thrust developed by the engine. The engine safety hazards show the areas that should be avoided when working close to an operating engine. Information about the ground transportation requirements helps to avoid damage to the engine and injury to the personnel during transportation.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Application
The CF6-80E1 engine is available in the following variants:
CF6-80E1A1 CF6-80E1A2 CF6-80E1A3 CF6-80E1A4
These variants are installed on the following types of aircraft:
CF6-80E1A1 - Airbus A330-300 CF6-80E1A2 - Airbus A330-300 CF6-80E1A3 - Airbus A330-200 CF6-80E1A4 - Airbus A330-200
Ratings
Identification Data Plate
Location: The identification data plate is on the lower left-hand side of the aft fan case at the 8:30 position. Identification: The identification data plate is a metal plate with a redcolored background and with text boxes for recording engine-related information. Purpose: The identification data plate serves as a single source of important engine information. This engine information includes the following data:
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Type certificate no. Production certificate number Model number Serial number Configuration type Take-off thrust rating Maximum continuous thrust rating Service bulletin numbers Date of manufacturing Status of EPA compliance
Specifications
Engine Safety Hazards
Location: The engine safety hazards are areas that are specified on the inlet and exhaust sides of an installed engine. Identification: These hazard areas are designated as follows:
Inlet suction danger area Exhaust wake danger area
However, personnel can approach an operating engine at minimum ground idle thrust using a specified
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
area called the Entry Corridor Safety zone. For more information on these areas and the precautions that need to be taken when working close to a running engine, refer to the Aircraft Maintenance Manual. Purpose: The engine safety hazard areas help to prevent injury to personnel and damage to the engine and the aircraft.
Ground Transportation Requirements
Identification: The CF6-80E1 engine can be transported as a complete engine assembly or as separate subassemblies or as individual modules by ground, air, or sea transportation. Note: GE Aircraft Engines does not recommend shipment of the engine by rail. When transporting the engine, great care must be taken about the following:
The shipping stand must meet GEAE specification M50TF1338. Proper tie-down techniques must be used. Minimum clearances between the engine, stand and the trailer bed must be maintained. When transporting by ground, vehicles with shock and vibration absorbing systems should be used.
Purpose: The ground transportation requirements help to prevent damage to the engine and injury to personnel during transportation.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Engine Modules Objectives
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to: Identify the location of the engine modules Identify the engine modules Identify the purpose of the engine modules
Overview
The CF6-80E1 engine is divided into the following modules: Fan module Core module High pressure turbine (HPT) module Low pressure turbine (LPT) module Accessory drive module In this lesson, you will learn about the identification, and purpose of these modules.
location,
Fan Module Location Left Side View Identification
The fan module is installed at the front of the engine, adjacent to the core module. The fan module consists of the following components: Fan blades assembly Low pressure compressor rotor Low pressure compressor stator Fan frame
Purpose
Supplies approximately 80 % of the engine thrust due to the acceleration of the fan bypass airflow Boosts the primary airflow before it enters the high pressure compressor, Houses the A-sump containing nos. 1, 2, and 3 bearings
Core Module Location Left Side View
The core module is installed aft of the fan module, adjacent to the high
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
pressure turbine (HPT) module.
Identification
The core module consists of the following components: Compressor rotor Compressor stator Compressor rear frame (CRF) Combustor Stage 1 HPT nozzle
Purpose
The core module supplies approximately 20 % of the engine thrust through the combustion and subsequent acceleration of the core airflow. The core module also provides drive to the accessory gearbox (AGB).
HPT Module Location Left Side View Identification
The HPT module is installed aft of the core module, adjacent to the low pressure turbine (LPT) module. The HPT module consists of the following components: HPT rotor HPT stator
Purpose
The HPT module extracts energy from the hot combustion gases leaving the combustor. This energy is used by the HPT module to drive the HPC.
LPT Module Location Left Side View Identification
The LPT module is installed immediately aft of the HPT module. The LPT module consists of the following components: LPT rotor LPT stator
Purpose
Extracts energy from the exhaust gases leaving the HPT module. This energy is used by the LPT module to drive the fan assembly. Houses the D-sump and contains the No. 6 bearing.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Accessory Drive Module Location Left Side View
The accessory drive module consists of components that are installed below the core module and inside the fan module.
Identification
The accessory drive module consists of the following components: Inlet gearbox Transfer gearbox Accessory gearbox
Purpose
The accessory drive module receives the driving torque from the compressor and drives the various accessories that are mounted on its forward and rear sides.
Fan Module Objectives
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify the location of the components of the fan module Identify the components of the fan module Identify the purpose of the components of the fan module Identify the purpose of the fan module
Overview
The fan module is divided into the following components:
Fan blades assembly Low pressure compressor rotor Low pressure compressor stator Fan frame
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components of the fan module
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Location Left Side View
The fan module is at the front of the engine. The fan module consists of a number of components that are listed below. The fan blades assembly is installed at the front of the fan module. The LPC rotor is installed aft of the fan blades assembly inside the forward and aft fan cases. The LPC stator is inside the forward and aft fan cases and surrounds the LPC rotor. The fan frame is installed between the LPC and the HPC assemblies.
Purpose
Supplies approximately 80 % of the engine thrust by accelerating the fan bypass airflow Boosts the primary airflow before it enters the high pressure compressor Houses the A-sump containing nos. 1, 2, and 3 bearings
Fan Blades Assembly
Location: The fan blades assembly is installed at the front of the fan module. Identification: The fan blades assembly consists of the following components:
Stage 1 fan disk 34 fan blades
The fan blades are installed on the stage 1 fan disk. Purpose: The fan blades assembly brings in air and accelerates it through the fan duct to produce approximately 80 % of the rated thrust.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Low Pressure Compressor Rotor
Location: The LPC rotor is installed aft of the fan blades assembly inside the forward and aft fan cases. Identification: The LPC rotor consists of the following components:
Stages 2 to 5 booster spools Stages 2 to 5 blades
Both the spools and the blades are made of titanium. Purpose: The primary function of the LPC rotor is to boost the flow of the fan inlet air into the HPC.
Low Pressure Compressor Stator
Location: The LPC stator is located inside the forward and aft fan cases and surrounds the LPC. Identification: The LPC stator consists of the stages 2 to 5 stator vanes. Purpose: The different stages of the LPC stator make sure that air is sent to the various stages of the LPC rotor at the correct angle.
Fan Frame
Location: The fan frame is installed between the LPC and the HPC assemblies. Identification: The fan frame is a cast titanium unit with a central hub and 12 radial struts.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The fan frame provides the main structural support for the subassemblies of the fan module, core module, accessory drive module, and the forward engine thrust mount. The fan frame also contains air extraction ports and passages for sump
pressurization, core compartment cooling, and active clearance control. A variable bleed valve (VBV) is installed in the fan frame to control the airflow from the LPC rotor to the HPC rotor.
Core Module Objectives
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify the location of the components of the core module Identify the components of the core module Identify the purpose of the components of the core module Identify the purpose of the core module
Overview
The core module is divided into the following components:
Compressor rotor Compressor stator Compressor rear frame (CRF) Combustor Stage 1 HPT Nozzle
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components of the core module.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Location Left Side View
The core module is aft of the fan module. The core module consists of a number of components that are listed below. The compressor rotor is aft of the fan assembly and is surrounded by the compressor stator. The front of the rotor is held in the aft end of the A-sump. In the rear, the rotor is held in the B and C sumps. The compressor stator is aft of the fan module and surrounds the compressor rotor. The combustor is installed aft of the HPC. The compressor rear frame (CRF) is installed between the HPC and the HPT. The stage 1 HPT nozzle is installed immediately aft of the combustor.
Purpose
Compresses the inlet air and allows combustion to take place, thus providing the engine with approximately 20 % of the thrust Provides driving torque to the AGB Provides structural support to several engine components
Compressor Rotor
Location: The compressor rotor is aft of the fan assembly and is surrounded by the compressor stator. The front of the rotor is held in the aft end of the A-sump. In the rear, the compressor rotor is held in the B and C sumps. Identification: The compressor rotor
consists of 14 high-pressure compressor stages. Each stage contains a set of blades. The front of the rotor is supported by the No. 3 roller bearing. The aft of the the rotor
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
is supported by the No. 4 roller bearing and the No. 4 ball bearing. Purpose: The compressor rotor compresses the air coming from the LPC before the air enters the combustor for combustion.
Compressor Stator
Location: The compressor stator is at the aft of the fan assembly and surrounds the compressor rotor. Identification: The compressor stator consists of two casing halves. The two halves contain one stage of inlet guide vanes (IGV), five stages of variable stator vanes, and eight stages of fixed stator vanes. Purpose: The compressor stator makes sure that air compressed by each compressor rotor stage is passed to the next compressor rotor stage at the correct angle. The stator also provides the main structural support to the central portion of the engine.
Compressor Rear Frame (CRF)
Location: The compressor rear frame (CRF) is between the HPC and the HPT. Identification: The CRF is a casting that consists of the following components:
Annular combustor Fuel nozzles Fuel manifold Igniter plugs 10 struts Stage 1 HPT nozzle
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose:
Provides main structural support to the engine Provides space for the B-C sump and the accompanying bearings
Provides a flowpath between the HPC and the HPT. Transmits axial and radial loads from the HPT rotor to the static structure
Combustor
Location: The combustor is installed aft of the HPC. Identification: The combustor consists of the following components:
Inner and outer cowl assemblies Dome assembly Inner and outer liner assemblies
Purpose: The combustor provides space for proper mixing and subsequent combustion of the mixture of fuel and air.
Stage 1 HPT Nozzle
Location: The stage 1 HPT nozzle is installed immediately aft of the combustor. Identification: The stage 1 HPT nozzle consists of 23, two-vane nozzle segments. The nozzle is mounted on the stationary seal support. Purpose: The stage one HPT nozzle directs hot, high-velocity, high-pressure gases onto the stage 1 HPT rotor blades, thus causing them to rotate.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
HPT Module Objectives
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify the location of the components of the HPT module Identify the components of the HPT module Identify the purpose of the components of the HPT module Identify the purpose of the HPT module
Overview
The high pressure turbine (HPT) module of the CF6-80E1 engine consists of the following components:
HPT rotor HPT stator
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and
purpose of the components of the HPT module.
Location Left Side View
The HPT module is installed aft of the core module. The components of the module are listed below.
The HPT rotor is installed aft of the stage 1 HPT nozzle. The HPT stator surrounds the HPT rotor and is installed aft of the
Purpose
stage 1 HPT nozzle.
The HPT module extracts energy from the hot combustion gases leaving the combustor. This energy is used by the HPT module to drive the HPC rotor.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
HPT Rotor
Location: The HPT rotor is installed aft of the stage 1 HPT nozzle. Identification: The HPT rotor is a two-stage turbine that is splined to the HPC rotor in the core module. Purpose: The purpose of the HPT rotor is to extract energy from the hot, high-pressure combustion gases leaving the combustor. This energy is used by the HPT rotor to drive the HPC rotor in the core module.
HPT Stator
Location: The HPT stator surrounds the HPT rotor and is installed aft of the stage 1 HPT nozzle. Identification: The HPT stator consists of the following components:
Stage 2 HPT nozzle assembly Stages 1 and 2 shrouds Stator case Active clearance control manifold
Purpose:
Provides a sealed flowpath for gases flowing out from the HPT rotor Forms part of the active and passive clearance control system that is used to maintain close clearances between the shrouds and the HPT rotor blades
LPT Module Objectives
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify the location of the components of the LPT module Identify the components of the LPT module
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Identify the purpose of the components of the LPT module Identify the purpose of the LPT module
Overview
The low pressure turbine (LPT) module of the CF6-80E1 engine consists of the following components:
LPT rotor LPT stator Turbine rear frame (TRF)
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components of the LPT module.
Location Left Side View
The LPT module is aft of the HPT module. The components of the module are listed below. The LPT rotor is installed aft of the HPT module and is enclosed within the LPT stator. The LPT stator is aft of the HPT module and encloses the LPT rotor. The turbine rear frame (TRF) is installed between the LPT stator and the exhaust nozzle.
Purpose
The LPT module drives the fan blades assembly and the LPC rotor in the fan module. The LPT module also provides support and space for components at the rear of the engine.
LPT Rotor
Location: The LPT rotor is installed aft of the HPT module and is enclosed within the LPT stator.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Identification: The LPT rotor is a five-stage turbine that is driven by the combustion gases leaving the HPT. The LPT rotor is supported by the No. 6 roller bearing housed in the D-sump. Purpose: The LPT rotor drives the fan blades assembly and the LPC rotor in the fan module.
LPT Stator
Location: The LPT stator is aft of the HPT module and encloses the LPT rotor. Identification: The LPT stator consists of a one-piece, tapered casing. The inside of the casing contains five stages of stator vanes. Purpose: Each stage of the LPT stator makes sure that the exhaust gases exiting from the previous LPT rotor stage are directed to the next stage at the correct angle. The LPT stator provides support to the rear of the engine. The outer portion of the LPT stator casing provides space for different pipes and manifolds.
Turbine Rear Frame (TRF)
Location: The turbine rear frame (TRF) is installed between the LPT stator and the exhaust nozzle.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Identification: The TRF consists of an inner and an outer flange that are held together by 12 radial struts. The outer flange contains two bolt circles, rear engine mounts, and radial ports. The inner flange houses the D-sump. Purpose:
Supports the rear of the engine and the LPT rotor and stator assemblies Houses the D-sump Straightens the airflow into the exhaust nozzle for improved engine performance Provides space for rear engine mounts Provides ports for insertion of the T5 sensor and for borescope inspection
Accessory Drive Module Objectives
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify Identify Identify Identify
the the the the
location of the components of the accessory drive module components of the accessory drive module purpose of the components of the accessory drive module purpose of the accessory drive module
Overview
The accessory drive module of the CF6-80E1 engine consists of the following components:
Inlet gearbox (IGB) Transfer gearbox (TGB) Accessory gearbox (AGB)
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components of the accessory drive module.
Location Left Side View
The accessory drive module is installed below the core module. The module is mounted on the lower surface of the compressor casing. The components of the module are listed below.
The inlet gearbox (IGB) is attached to the forward side of the
fan frame. The transfer gear box (TGB) is installed aft of the fan frame at the 6 oclock position The accessory gearbox (AGB) is mounted on the lower portion of the engine core at the 6 o'clock position.
Purpose
The accessory drive module transfers torque from the HPC rotor to the AGB to drive the various engine and aircraft accessories.
Inlet Gearbox Assembly
Location: The inlet gearbox (IGB) assembly is attached to the forward side of the fan frame. Identification: The IGB consists of a titanium housing containing an adapter, bevel gears, bearings, and oil jets. Purpose: The IGB transfers torque from the HPC rotor to the transfer gearbox (TGB) through the radial drive shaft.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Transfer Gearbox
Location: The transfer gearbox (TGB) is installed on the lower, rear side of the fan module between the inlet gearbox (IGB) and the accessory gearbox (AGB). Identification: The TGB is made up of an aluminum housing, adapters, bevel gears, bearings, and oil jets. Purpose: The TGB transfers the torque to the AGB through the horizontal drive shaft.
Accessory Gearbox
Location: The accessory gearbox (AGB) is mounted on the lower portion of the engine core at the 6 o'clock position. Identification: The AGB is made up of a one-piece aluminum alloy housing containing drive pad
adapters, spur gears, bearings, and seals. Purpose: The AGB provides torque to a number of engine and aircraft accessories such as the IDG, the hydraulic pump, and the fuel pump.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Airflow Paths Objectives
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify the location of the components of the airflow paths Identify the components of the airflow paths Identify the purpose of the components of the airflow paths
Overview
The airflow paths of the CF6-80E1 engine can be divided into the following components:
Fan bypass airflow Core/combustor airflow Parasitic airflow Sump pressurization
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components of the airflow paths.
Location
The various airflow paths of the CF6-80E1 engine are listed below: The fan bypass airflow or the secondary airflow is the fan air that bypasses the engine core and exits through the fan nozzle. The core/combustor airflow or the primary airflow consists of air that flows through various sections of the engine core. This air then exits into the atmosphere through the engine exhaust nozzle. Parasitic airflow is the air that is bled from the core/combustor airflow and the fan bypass airflow. Sump pressurization consists of parasitic airflow that is used to pressurize the engine sumps.
Fan Bypass Airflow
Location: The fan bypass airflow or the secondary airflow is the fan air that bypasses the engine core and exits through the fan nozzle.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The fan bypass airflow provides approximately 80 %of the thrust to the engine. The fan bypass airflow also
provides a portion of the air for parasitic airflow.
Core/Combustor Airflow
Location: The core/combustor airflow or the primary airflow consists of air that flows through various sections of the engine core. This air then exits into the atmosphere through the engine exhaust nozzle. Purpose: The core/combustor airflow provides
approximately 20 % of the thrust to the engine. The core/combustor airflow also provides a majority of the air for parasitic airflow.
Parasitic Airflow
Location: Parasitic airflow is the air that is bled from the core/combustor airflow and the fan bypass airflow. Purpose: The parasitic airflow is used for various external and internal engine functions such as:
Sump pressurization, internal cooling, and thrust reverser operation. HPT and LPT active clearance control. Engine anti-icing, aircraft ventilation, and cabin air-conditioning.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Sump Pressurization
Location: Sump pressurization consists of parasitic airflow that is used to pressurize the engine sumps.
Purpose: Sump pressurization is used to
provide pressurized air to the areas around the sumps. This minimizes leakage of oil across the sump seals during engine operation, especially at high power settings.
You might also like
- 1 - Cowling&EBU (CF6-80E1)Document9 pages1 - Cowling&EBU (CF6-80E1)Chabou_r1627100% (3)
- Pages From 70 Power Plant Iae v2500Document2 pagesPages From 70 Power Plant Iae v2500AldoNo ratings yet
- Ata 75 CFM56-3Document17 pagesAta 75 CFM56-3ccoyure100% (1)
- CFM56 C PDFDocument1 pageCFM56 C PDFhamidrezachamaniNo ratings yet
- Clean, Efficient Power For Ultra-Long-Range Business Jets: Title AreaDocument4 pagesClean, Efficient Power For Ultra-Long-Range Business Jets: Title AreaGabo Alba Garcia0% (1)
- CFM 56-7B Basic EngineDocument183 pagesCFM 56-7B Basic EngineAnupam Vettukuzhiyil100% (1)
- Cf34-8e 72-A0221Document8 pagesCf34-8e 72-A0221Stephen Hyde100% (1)
- Data Sheet - 1 (CFM56-5 Series) PDFDocument8 pagesData Sheet - 1 (CFM56-5 Series) PDFhNo ratings yet
- CFM56-7B26 Engine Mini-PackDocument2 pagesCFM56-7B26 Engine Mini-PackAHAMEDNo ratings yet
- GEnx Development Emphasizes Composites, Combustor TechnologyDocument3 pagesGEnx Development Emphasizes Composites, Combustor TechnologySiva KumarNo ratings yet
- I. Models CF34-10E5 CF34-10E5A1 CF34-10E6 CF34-10E6A1: Maximum ContinuousDocument6 pagesI. Models CF34-10E5 CF34-10E5A1 CF34-10E6 CF34-10E6A1: Maximum ContinuousEstevam Gomes de AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Line and Base: Pw1100G-JMDocument16 pagesLine and Base: Pw1100G-JMGenaro Rodriguez100% (1)
- B Trent41368ATDocument81 pagesB Trent41368ATArabyAbdel Hamed SadekNo ratings yet
- Leap-1A Program Status Program Status: June 2015 June 2015Document11 pagesLeap-1A Program Status Program Status: June 2015 June 2015bnmmauricioNo ratings yet
- cfm56 3Document126 pagescfm56 3mohamad TomcatNo ratings yet
- CFM Doc Leap 1B Co Fda 3 V2Document51 pagesCFM Doc Leap 1B Co Fda 3 V2Paulo SanzNo ratings yet
- Sensitivity of Engine Performance To Component Degradation of A Turbofan Aircraft EngineDocument111 pagesSensitivity of Engine Performance To Component Degradation of A Turbofan Aircraft EngineAdeyemi Oluwaseun EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- ATA 49 06.08.2008 - B2 Ready To PrintDocument130 pagesATA 49 06.08.2008 - B2 Ready To PrintDmitryNo ratings yet
- LBM Day8Document9 pagesLBM Day8Genaro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ATA 77 EngineDocument16 pagesATA 77 EnginebrandonNo ratings yet
- CF34-3 Engine Notes Chapter 72 Course NotesDocument30 pagesCF34-3 Engine Notes Chapter 72 Course NotesinternetsurfingNo ratings yet
- Trent 700 - L & B Maintenance TrainingDocument1 pageTrent 700 - L & B Maintenance TrainingIrfan05No ratings yet
- 747-200F Flight HandbookDocument18 pages747-200F Flight HandbookexpairtiseNo ratings yet
- Cfm56 5b C SeriesDocument10 pagesCfm56 5b C SeriesRobertNo ratings yet
- RB211 Trent 500 Series TCDS Issue 02Document9 pagesRB211 Trent 500 Series TCDS Issue 02makumba1972No ratings yet
- Defueling Procedure Erj 190Document4 pagesDefueling Procedure Erj 190jucamallaNo ratings yet
- ATA 06decoded PDFDocument52 pagesATA 06decoded PDFraiday840% (1)
- Progress in Aeroengine Technology (1939-2003) : University of Dayton, Dayton, Ohio 45469-0102Document8 pagesProgress in Aeroengine Technology (1939-2003) : University of Dayton, Dayton, Ohio 45469-0102ArashNo ratings yet
- Airbus Commercial Aircraft AC A350 900 1000Document411 pagesAirbus Commercial Aircraft AC A350 900 1000librada diazNo ratings yet
- V2500. The Engine of Choice.: Product FactsDocument1 pageV2500. The Engine of Choice.: Product FactsMahmoud KrayemNo ratings yet
- CFM56 5B SB Rev 72-1094 TSN.00 N 20201216Document42 pagesCFM56 5B SB Rev 72-1094 TSN.00 N 20201216Irfan05100% (1)
- EASA TCDS E.007 (IM) General Electric CF6 80E1 Series Engines 02 25102011Document9 pagesEASA TCDS E.007 (IM) General Electric CF6 80E1 Series Engines 02 25102011Graham WaterfieldNo ratings yet
- Cf680c2 Engine HistoryDocument5 pagesCf680c2 Engine HistoryJingliang ZhouNo ratings yet
- Done By:: Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology ThiruvananthapuramDocument48 pagesDone By:: Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology Thiruvananthapuramsrijani pal100% (1)
- CFM International CFM56: HistoryDocument24 pagesCFM International CFM56: HistoryĐoàn Hồng NgọcNo ratings yet
- 767 - 49 ApuDocument22 pages767 - 49 ApuAndres Aldunate QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Fan Lub CFM56-7 - HandbookDocument44 pagesFan Lub CFM56-7 - HandbookANDRANo ratings yet
- Trent 1000 Borescope Inspection CourseDocument1 pageTrent 1000 Borescope Inspection CourseMohamed AbdelSalamNo ratings yet
- 18 - WTT - CFM56-3 Shop Visit AnalysisDocument29 pages18 - WTT - CFM56-3 Shop Visit AnalysisOrlando PérezNo ratings yet
- CFM56Document5 pagesCFM56Anonymous wkL8YVBENo ratings yet
- CFM56 3book2t Shoot PDFDocument10 pagesCFM56 3book2t Shoot PDFDiniswari Alrino100% (1)
- PW 1500G Final ReportDocument35 pagesPW 1500G Final ReportAhsan100% (1)
- Brochure CFM56 Fiches 2017 PDFDocument9 pagesBrochure CFM56 Fiches 2017 PDFpbonnetNo ratings yet
- COMMERCIAL AIRCRAFT ENGINES POWERING A318-A321Document2 pagesCOMMERCIAL AIRCRAFT ENGINES POWERING A318-A321syahirazaihadNo ratings yet
- CFM56 5B SB Rev 72-1092 TSN.00 N 20201210Document20 pagesCFM56 5B SB Rev 72-1092 TSN.00 N 20201210Irfan05No ratings yet
- Manage Engine Maintenance for Leased AssetsDocument31 pagesManage Engine Maintenance for Leased AssetsPrimadi Fajriansyah NawawiNo ratings yet
- New CFM Leap1 TestDocument2 pagesNew CFM Leap1 TestLahu KureNo ratings yet
- Aircraft DesignDocument76 pagesAircraft Designmilanmitic3No ratings yet
- ATA 36 PneumaticsDocument58 pagesATA 36 PneumaticsBao HuynhNo ratings yet
- Lgciu Ts GuideDocument34 pagesLgciu Ts GuidePankaj KhondgeNo ratings yet
- 737MAX OIL SERVICING Best PracticesDocument5 pages737MAX OIL SERVICING Best PracticesrakeshNo ratings yet
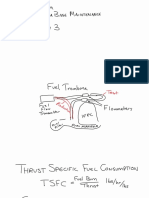
- TSFCDocument5 pagesTSFCRohit RaviNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On FadecDocument17 pagesSeminar Report On FadecMithil Pandey100% (2)
- Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 ExplainedDocument4 pagesRolls-Royce Trent 1000 ExplainedaliNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Engine MRO Marketing PlanDocument7 pagesAircraft Engine MRO Marketing PlanDonManuelNo ratings yet
- Stabilization and Dynamic of Premixed Swirling Flames: Prevaporized, Stratified, Partially, and Fully Premixed RegimesFrom EverandStabilization and Dynamic of Premixed Swirling Flames: Prevaporized, Stratified, Partially, and Fully Premixed RegimesNo ratings yet
- Jet Shop Training PresentationDocument28 pagesJet Shop Training PresentationGAURAV SINGHNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual PDFDocument28 pagesOperation Manual PDFPanagiotis PanagosNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - NavigationDocument62 pagesVolare Questions - NavigationChabou Rafik100% (1)
- Volare Answers - Mass and BalanceDocument2 pagesVolare Answers - Mass and Balancehusseinih100% (1)
- 3 Engine SystemDocument69 pages3 Engine SystemChabou Rafik100% (1)
- Volare Answers - Human FactorDocument6 pagesVolare Answers - Human FactorpontooNo ratings yet
- 062 - Radionavegacion - . - Radio NavigationDocument3 pages062 - Radionavegacion - . - Radio NavigationViorel CroitoruNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - InstrumentationDocument46 pagesVolare Questions - Instrumentationpontoo33% (3)
- Volare Questions - MeteorologyDocument86 pagesVolare Questions - Meteorologypontoo100% (5)
- Volare Questions - Mass and BalanceDocument33 pagesVolare Questions - Mass and Balancepontoo50% (2)
- 032 - Performance - . - PerformancesDocument3 pages032 - Performance - . - PerformancesViorel CroitoruNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - Airplane SystemsDocument68 pagesVolare Questions - Airplane Systemspontoo100% (2)
- Volare Answers - Airplane SystemsDocument5 pagesVolare Answers - Airplane SystemsChabou Rafik0% (2)
- Volare Questions - Human FactorDocument85 pagesVolare Questions - Human Factorpontoo100% (2)
- Volare Questions - AerodynamicsDocument45 pagesVolare Questions - Aerodynamicspontoo67% (3)
- Volare Answers - Ops ProceduresDocument3 pagesVolare Answers - Ops ProcedurespontooNo ratings yet
- Volare Answers - MeteorologyDocument6 pagesVolare Answers - Meteorologymomanbh0% (1)
- Jaa - NL IntroductionDocument6 pagesJaa - NL IntroductionChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- ATPL-Air Law Professione Volare-AnswersDocument4 pagesATPL-Air Law Professione Volare-AnswerspatrouilledeafranceNo ratings yet
- JAA ECAC Member StatesDocument1 pageJAA ECAC Member StatesChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- RVSMDocument40 pagesRVSMs gNo ratings yet
- Volare Answers - InstrumentationDocument3 pagesVolare Answers - InstrumentationBalaji DurairajNo ratings yet
- Volare ATPL Question BankDocument3 pagesVolare ATPL Question Bankmomanbh0% (3)
- Cap 768Document194 pagesCap 768Chabou RafikNo ratings yet
- Annex 1Document1 pageAnnex 1Chabou RafikNo ratings yet
- AGMTGL010Document2 pagesAGMTGL010Chabou RafikNo ratings yet
- Aa - NL Publications Jar AmdtsDocument4 pagesAa - NL Publications Jar AmdtsChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- 145 ORGSbyCompanyNameDocument253 pages145 ORGSbyCompanyNameChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- TGL ListDocument3 pagesTGL ListChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- Jar-Std 4A: Basic Instrument Training Devices: Oint Viation UthoritiesDocument12 pagesJar-Std 4A: Basic Instrument Training Devices: Oint Viation UthoritiesChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- DWTS, WDWTS: Improving MRI Image Reconstruction with Directional Wavelet ThresholdingDocument1 pageDWTS, WDWTS: Improving MRI Image Reconstruction with Directional Wavelet ThresholdingSumit ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- SHINI Hopper-Loader - SAL-400 SERIES MANUALDocument38 pagesSHINI Hopper-Loader - SAL-400 SERIES MANUALRick ChenNo ratings yet
- Fontaine Quinta RuedaDocument2 pagesFontaine Quinta RuedaHamilton MirandaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Xstrata VOD Implementation - BartschDocument35 pages2010 Xstrata VOD Implementation - BartschFlávia GomesNo ratings yet
- ATS1801 - Interface PC - ImpDocument8 pagesATS1801 - Interface PC - ImpluismantonioNo ratings yet
- EPMA Introduction To Powder MetallurgyDocument36 pagesEPMA Introduction To Powder MetallurgyPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- Properties of LPGDocument33 pagesProperties of LPGmukund madhav100% (2)
- Ball MillsDocument8 pagesBall MillsBoy Alfredo PangaribuanNo ratings yet
- Price Quotation: Quote/Project Description Ref. Details: Project DetailDocument3 pagesPrice Quotation: Quote/Project Description Ref. Details: Project DetailAhmad AyyoubNo ratings yet
- Emergency CallDocument6 pagesEmergency CallNugrohoNo ratings yet
- Sant Gadge Baba Amravati University: Backlog From Session Winter-2019Document2 pagesSant Gadge Baba Amravati University: Backlog From Session Winter-2019Prashant pandeNo ratings yet
- Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11i Upgrade To R12.1Document60 pagesOracle E-Business Suite Release 11i Upgrade To R12.1Vladimir PacotaipeNo ratings yet
- Sensotronic Brake ControlDocument20 pagesSensotronic Brake ControlShubhankar Banerjee100% (1)
- Plant Cost EstimationDocument49 pagesPlant Cost EstimationAlpianto100% (1)
- Shiela S. Portillo Ang Specification 09112021Document9 pagesShiela S. Portillo Ang Specification 09112021JR De LeonNo ratings yet
- Address Book in JAVADocument18 pagesAddress Book in JAVAmelyfony100% (1)
- Pump HydraulicsDocument5 pagesPump HydraulicsSiddharth Kharat100% (1)
- IPE 401-Drive SystemDocument16 pagesIPE 401-Drive SystemElmerNo ratings yet
- Universal CNC Turning Center Maxxturn 65 G2Document13 pagesUniversal CNC Turning Center Maxxturn 65 G2Vũ LêNo ratings yet
- Grouting in Rock TunnellingDocument161 pagesGrouting in Rock TunnellingOanaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Structures: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesEngineering Structures: SciencedirectFeleki AttilaNo ratings yet
- Advanced clutter options for radio propagation modelingDocument40 pagesAdvanced clutter options for radio propagation modelingLaura VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Formulation - Beton - Dreux - Gorisse Good - Fr.enDocument9 pagesFormulation - Beton - Dreux - Gorisse Good - Fr.enRabnawaz ImamNo ratings yet
- OSHA Standard For Fixed Ladders SummaryDocument12 pagesOSHA Standard For Fixed Ladders SummarysesabcdNo ratings yet
- Yasnac Mx-3 Fault Finding GuideDocument70 pagesYasnac Mx-3 Fault Finding Guidechidambaram kasi100% (1)
- Ahmed Mohammed EL Desouky 2007Document8 pagesAhmed Mohammed EL Desouky 2007Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TestingDocument55 pagesUltrasonic Testingdhasdj100% (1)
- Earth Gravity and Satellite Orbits CalculationsDocument9 pagesEarth Gravity and Satellite Orbits CalculationsYoobsan Asaffaa FufaaNo ratings yet
- RTJ Dimension ASME B16.5/B16.47Document1 pageRTJ Dimension ASME B16.5/B16.47parayilomer0% (1)
- Tu 1-5Document8 pagesTu 1-5Made easy classes0% (2)