Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory and Diagnostic Examination Results
Uploaded by
Lorina Lynne ApelacioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory and Diagnostic Examination Results
Uploaded by
Lorina Lynne ApelacioCopyright:
Available Formats
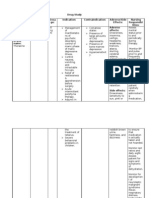
Laboratory and Diagnostic Examination Results Date August 5, 2011 Procedure Sodium Normal 136-148 MEQ/L Results 132
Interpretation Analysis Deviation Hyponatremia is a from normal predictable consequence of decreased intake of sodium. Normal Increased in renal failure, acidosis, cell lysis, tissue breakdown or hemolysis Decreased in GI losses and diuretic administration. Decreased in hypoparathyroidism, diarrhea, celiac disease, vitamin D deficiency, acute pancreatitis, nephrosis and after parathyroidectomy. Increased in Hypercholesterolemia, obstructive jaundice, diabetes, hypothyroidism, nephrotic syndrome. Decreased in malnutrition, chronic anemia, hyperthyroidism, severe infection, terminal states of debilitating disease. Increased in hypertriglyceridemia, liver disease, pancreatitis, nephrotic syndrome and
Potassium
3.5-5.1 mg/dL
3.90 MEQ/L
Calcium
8.40-10.60 mg/dL
6.96
Deviation from normal
Cholesterol
149.81238.38 mg/dL
194.98
Normal
Triglycerides
10.00200.01 mg/dL
115.05
Normal
diabetes. Decreased in malnutrition. HDL > 0.90 mmol/L 1.49 Normal Decreased in patients with increased risk for coronary heart disease. Increased in hyperlipidemia, nephrotic syndrome and liver disease. Decreased in hyperthyroidism, acute stress and chronic anemia.
LDL
1.27-4.47 mmol/L
2.96
Normal
VLDL CHOL/HDL Ratio uric acid
0.05-1.04 mmol/L < 4.40 202.30416.5 umol/L 135.00148.00 mmol/L
0.60 3.39 460.37
Normal Normal Deviation from normal Deviation from normal Increased in gout Decreased in nephritis Hyponatremia is a predictable consequence of decreased intake of sodium. Increased in renal failure, acidosis, cell lysis, tissue breakdown or hemolysis Decreased in GI losses and diuretic administration.
Sodium
131.90
Potassium
3.50-5.30 mmol/L
3.79
Normal
August 6, 2011
Hematology Hematocrit 0.40-0.54 0.35 Deviation from normal Decreased in blood loss, over hydration,
dietary deficiency and anemia. hemoglobin 135-180 g/L 115 Deviation from normal Decreased in blood loss, hemolytic anemia, bone marrow suppression and sickle cell anemia. Decreased in abnormal loss of erythrocytes, abnormal destruction of erythrocytes, lack of needed elements or hormones for erythrocyte production and bone marrow suppression. Decreased in leukopenia and autoimmune disease. Increased in stress and acute infection Decreased in viral diseases, some drugs, and radiation therapy. Increased in viral infection, mononucleosis, tuberculosis, chronic bacterial infection and lymphocytic leukemia. Decreased in adrenal corticosteroids and other immunosuppressant drugs, autoimmune diseases and severe malnutrition. Increased in allergic
RBC count
5.0-6.5 x 10 12 g/L
3.83
Deviation from normal
WBC count
4.5-11.0 x 10 9/L 0.50-0.70
2.6
Deviation from normal Normal
Neutrophils
0.57
Lymphocytes
0.20-0.40
0.40
Normal
Eosinophils
0.00-0.03
0.03
Normal
FBS HbAIc Creatinine
3.85-6.10 mmol/L 4.2-6.07% 53-106 umol/L
5.95 5.61% 160.9
Normal Normal Deviation from normal
reactions and parasitic infestations. Decreased in corticosteroid therapy. For diagnosis of diabetes Increased in muscular dystrophy, fever and carcinoma of liver.
Urinalysis Color Transparency SP gravity Reaction Albumin Glucose Mucous threads Epithelial cells 1.0021.035 yellow slightly hazy 1.010 Acidic ++ trace Few occasional
Normal
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Chronic Pain GuidelinesDocument56 pagesChronic Pain GuidelinesOporadhBiggan100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Behavior Intervention PlanDocument6 pagesBehavior Intervention Planapi-308475283No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- ChartingDocument3 pagesChartingLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- ChartingDocument3 pagesChartingLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Psychiatric NursingDocument11 pagesBasic Concepts in Psychiatric NursingLorina Lynne Apelacio75% (4)
- Health Teaching PlanDocument8 pagesHealth Teaching PlanLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- Louise L HAY AffirmationsDocument10 pagesLouise L HAY AffirmationsEvi Kutasi100% (2)
- Focus ChartingDocument3 pagesFocus ChartingMan GatuankoNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care: Medical and Surgical NursingDocument3 pagesTracheostomy Care: Medical and Surgical NursingLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (1)
- DQ RMGDocument23 pagesDQ RMGDhaval ChaplaNo ratings yet
- Chap-20 - Locomotion & MovementDocument52 pagesChap-20 - Locomotion & MovementMittal SavaniNo ratings yet
- Dave Jay S. Manriquez RN. Acute CholecystitisDocument11 pagesDave Jay S. Manriquez RN. Acute CholecystitisChilleMaeNo ratings yet
- Psych Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- Drug Study of Antidiabetic DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study of Antidiabetic DrugsLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexDocument5 pagesDrug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Sample Nurses Notes CuDocument3 pagesSample Nurses Notes Cuapi-1978086589% (19)
- Lactose IntoleranceDocument20 pagesLactose IntoleranceLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Discover the flavors of Southwestern Luzon and Bicol RegionDocument5 pagesDiscover the flavors of Southwestern Luzon and Bicol RegionGraceCayabyabNiduazaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pain Stimuli and Nerve Fiber TransductionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pain Stimuli and Nerve Fiber TransductionLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (2)
- Drug Study-Grand Case PresDocument8 pagesDrug Study-Grand Case PresLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Types of SuturesDocument6 pagesTypes of SuturesLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Examination Results-SepsisDocument4 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic Examination Results-SepsisLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Psych MSEDocument2 pagesPsych MSELorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Final Case Pres DrugsDocument10 pagesFinal Case Pres DrugsLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Examination Results-SepsisDocument4 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic Examination Results-SepsisLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- LaboratoryDocument10 pagesLaboratoryLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Crohn's Dse DrugsDocument3 pagesCrohn's Dse DrugsLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- PA-P GomezDocument3 pagesPA-P GomezLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Pre-Nightingale Era: Florence Nightingale Edith Cavell ("Mata Hari")Document13 pagesPre-Nightingale Era: Florence Nightingale Edith Cavell ("Mata Hari")Lorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors and Complications of Hypertension and Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesRisk Factors and Complications of Hypertension and Kidney DiseaseLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors and Complications of Hypertension and Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesRisk Factors and Complications of Hypertension and Kidney DiseaseLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors and Complications of Hypertension and Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesRisk Factors and Complications of Hypertension and Kidney DiseaseLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Goal For The Day: Each Sub Group Will Be Able To Present Their Case Study. Time ActivityDocument1 pageGoal For The Day: Each Sub Group Will Be Able To Present Their Case Study. Time ActivityLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Justification of ProblemsDocument4 pagesJustification of ProblemsBoom PastranaNo ratings yet
- Venkateshwara Institute of MedicalDocument10 pagesVenkateshwara Institute of Medicalbolhari070No ratings yet
- GP Series Portable Generator: Owner's ManualDocument48 pagesGP Series Portable Generator: Owner's ManualWilliam Medina CondorNo ratings yet
- FAQ: Product RegistrationDocument5 pagesFAQ: Product RegistrationCalvin WangNo ratings yet
- (Distracted Subjects) CHAPTER 2. Reading The Language of Distraction - Hamlet, Macbeth, King LearDocument23 pages(Distracted Subjects) CHAPTER 2. Reading The Language of Distraction - Hamlet, Macbeth, King LearLCAP ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Sample MCQ Mec201Document10 pagesSample MCQ Mec201UjjalKalitaNo ratings yet
- Atlas Tool Specs SummaryDocument3 pagesAtlas Tool Specs SummaryWaleed Barakat MariaNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Rle NAME: Guerzo, Danniel Dave Y. DATE/TIME: March 9, 2023 Section/Year Level: BSN 3B Group No:10 CIDocument2 pagesNCM 117 Rle NAME: Guerzo, Danniel Dave Y. DATE/TIME: March 9, 2023 Section/Year Level: BSN 3B Group No:10 CISherlyn Miranda GarcesNo ratings yet
- Smartphone Technician Cum App Tester: Trade PracticalDocument218 pagesSmartphone Technician Cum App Tester: Trade PracticalF ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Design Error in The Process IndustriesDocument13 pagesStatistics of Design Error in The Process IndustriesEmmanuel Osorno CaroNo ratings yet
- Breading Guide To All FoodDocument1 pageBreading Guide To All FoodInno EspinaNo ratings yet
- Frontier DL650 Maintenance Guide Ver 1.0Document25 pagesFrontier DL650 Maintenance Guide Ver 1.0philippe raynalNo ratings yet
- En50443 - SC9XC - 11656 - Enq2e (Mod 7 10 10)Document32 pagesEn50443 - SC9XC - 11656 - Enq2e (Mod 7 10 10)Levente CzumbilNo ratings yet
- Three Little PigsDocument9 pagesThree Little PigsrNo ratings yet
- Registration Hike2help 15Document2 pagesRegistration Hike2help 15api-275580337No ratings yet
- Insulation MBMA-NAIMA Acousticical Performance Guide Noise SoundDocument26 pagesInsulation MBMA-NAIMA Acousticical Performance Guide Noise SoundDianna LambertNo ratings yet
- ESP Guidance For All Ships V13.7Document53 pagesESP Guidance For All Ships V13.7Jayasankar GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Feeding ProgramDocument2 pagesSupplementary Feeding ProgramVictor Anthony CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Drama ScriptDocument8 pagesYear 8 Drama ScriptTISMSecondaryNo ratings yet
- A Text Book On Nursing Management AccordDocument790 pagesA Text Book On Nursing Management AccordMohammed AfzalNo ratings yet
- CH 23 PDFDocument42 pagesCH 23 PDFkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Gas Booster Systems Brochure r7Document12 pagesGas Booster Systems Brochure r7ridwansaungnage_5580No ratings yet
- LLL'DSWD: Administrative Order No. Series 2017Document18 pagesLLL'DSWD: Administrative Order No. Series 2017SGTNo ratings yet
- Moot CourtDocument7 pagesMoot CourtsushmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Notesmjamie12345No ratings yet