Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Comparison Chart
Uploaded by
Jake BryantCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Comparison Chart
Uploaded by
Jake BryantCopyright:
Available Formats
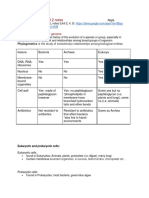
Definition (if applicable)
Nucleus Number of Chromosomes Cell Type Example Telomeres Genetic Recombination Lysosomes and Peroxisomes
Eukaryotic Cell
Present More than one Multicellular Animals & Plants Present (Linear DNA) Mitosis and fusion of gametes Present
Prokaryotic Cell
Absent One Unicellular Bacteria and Archaea Absent (Circular DNA) Unidirectional transfers
Brain of the Cell Compound structure at the end of a chromosome Sexually combining cells to create genetically different species Lysosomes break down materials ingested by the cell and also remove old cellular components and replace with newer ones
Peroxisomes are responsible for the creation of hydrogen peroxide within a cell and are used to break down fats into usable molecules
Absent
Microtubules
Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria
Cytoskeleton
DNA wrapping on proteins Ribosomes
A microscopic tubular structure present in numbers in the cytoplasm of cells, sometimes aggregating to form more complex structures A network of membranous tubules within the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur A microscopic network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm of many living cells, giving them shape and coherence A minute particle consisting of RNA (Ribonucleic acid) and associated proteins, found in large numbers in the cytoplasm of living cells
A small bubble within a cell
Present Present Present Present Yes Larger Present Present
Absent Absent Absent Can be Absent No Smaller Present Absent
Vesicles Golgi apparatus
A complex of vesicles and folded membranes within the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells
Mitosis Chloroplasts Flagella
A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each the same as the parent nucleus A plastid that contains chlorophyll A slender threadlike structure; A microscopic whip like appendage that enables different types of cells to swim A rigid layer of *polysaccharides lying outside the plasma membrane of the cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria A space or vesicle within the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosed by a membrane and typically containing fluid -
Yes Present Microscopic in size (Membrane bound, usually arranged as nine doublets surrounding two singlets) Selective Yes Only in plants Present 10-100um
No Absent (Scattered within cytoplasm) Submicroscopic in size (Composed only of one fibre) Not Present Usually No Chemically Complex Present 1-10um
Permeability of Nuclear Membrane Plasma membrane with steroid Cell wall
Vacuoles
Cell size
* A carbohydrate whose molecules consist of a number of sugar molecules bonded together
You might also like
- Basic Cell StructureDocument50 pagesBasic Cell StructureAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Plant CellDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 2 Plant CellAiman Haikal100% (1)
- Membran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusDocument32 pagesMembran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusAsmaul HusniNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote and Eukaryote CellsDocument22 pagesProkaryote and Eukaryote CellsWeihan ChiewNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 pagesThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESDocument7 pagesProkaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESChristian John Sitjar Dumo100% (1)
- Cells Structure and FunctionDocument56 pagesCells Structure and FunctionAnnisa DiyanabilaNo ratings yet
- lecture_1_-_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanismssdfkgjkDocument12 pageslecture_1_-_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- Training Manual For Medical RepresentativesDocument74 pagesTraining Manual For Medical RepresentativesAman Ghayas50% (4)
- Cell Structure and Function 2012Document69 pagesCell Structure and Function 2012gpranay4100% (1)
- The Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesThe Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsAlix AliNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesThe Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsShakera ReidNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Fundamental Unit of Life (Notes)Document5 pagesClass 9 Fundamental Unit of Life (Notes)Udaya RakavanNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument11 pagesAnimal CellDaryl De LeonNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesdaddysharkNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: PROKARYOTIC & EUKARYOTIC CELLSDocument10 pagesMicrobiology: PROKARYOTIC & EUKARYOTIC CELLSEmily RaeNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Abejay, Vanessa D. Balsomo, Princess Bangalan, JhayDocument64 pagesCell Structure: Abejay, Vanessa D. Balsomo, Princess Bangalan, JhayVanessaDulayAbejayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesDocument35 pagesChapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesFairview PenangNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathNo ratings yet
- Cells and Microorganisms SM 2021Document4 pagesCells and Microorganisms SM 2021Sami Ali 123No ratings yet
- H2 Biology - Notes On Cell Structure - Cell OrganellesDocument5 pagesH2 Biology - Notes On Cell Structure - Cell OrganellesSefLRho100% (1)
- Cell (Biology)Document4 pagesCell (Biology)Marella SatorreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Micropara (Outline)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Micropara (Outline)Jezrylle BalaongNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument41 pagesAnimal and Plant CellSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- The Significance of Biosciences in Understanding Cell Structure and FunctionDocument21 pagesThe Significance of Biosciences in Understanding Cell Structure and FunctionMaryum JavedNo ratings yet
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- For Ntse CellDocument73 pagesFor Ntse CellPrakhar RajNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument24 pagesCellsapi-95529788No ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) - WikipediaDocument29 pagesCell (Biology) - WikipediaMokariya SanjayNo ratings yet
- Biology Igcse SummaryDocument86 pagesBiology Igcse SummaryTarun PatelNo ratings yet
- Bioloy Notes From NCERT (Mahendra Coaching NotesDocument385 pagesBioloy Notes From NCERT (Mahendra Coaching NotesBabu VermaNo ratings yet
- Biology Key TermsDocument3 pagesBiology Key TermsTia TiaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledlgNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class IxDocument56 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Class IxIftikhar Hussain RizviNo ratings yet
- Plant and animal cell comparisonDocument22 pagesPlant and animal cell comparisonadilsiddiqueNo ratings yet
- SMA 11-1 CellsDocument111 pagesSMA 11-1 Cellsnur aulia100% (1)
- Robert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byDocument11 pagesRobert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byKamlesh RatnamNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology GuideDocument37 pagesCell Biology GuideManuelNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class IxDocument57 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Class IxAthar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Prokaryotic EukaryoticDocument28 pagesThe Cell: Prokaryotic EukaryoticMastersBestHackersNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Cell Bacteria Basic Organizational Principles BiologyDocument3 pagesThe Cell: Cell Bacteria Basic Organizational Principles BiologyRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- AS Biology NotesDocument20 pagesAS Biology NotesAlaska DavisNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document5 pagesBiology 1Zeynep AkıNo ratings yet
- Biology Syllabus NotesDocument92 pagesBiology Syllabus NotesClive Remix BoatengNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Structure FunctionDocument124 pages1 Cell Structure FunctionIntoy, Stephanie Mae100% (1)
- Science Class 9th Lesson 5 NOTESDocument6 pagesScience Class 9th Lesson 5 NOTESChaitanya SeriouskalhapureNo ratings yet
- 1.cell StructureDocument77 pages1.cell StructureSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- Notes Science CellsDocument12 pagesNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and Taxonomyporkypig100% (11)
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- Bio ASDocument189 pagesBio ASNgu War KhinNo ratings yet
- biology bacterium yeast animals atoms mycoplasmas μmDocument4 pagesbiology bacterium yeast animals atoms mycoplasmas μmLeenie A.A.ANo ratings yet
- BTN-345 L1 Cell StructureDocument30 pagesBTN-345 L1 Cell StructureAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- The Making of CRP Home ShoppingDocument69 pagesThe Making of CRP Home ShoppingJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Mission StatementDocument1 pageMission StatementJake BryantNo ratings yet
- C.R.P Minor Project Making of (WIP)Document46 pagesC.R.P Minor Project Making of (WIP)Jake BryantNo ratings yet
- Schindler GraphicsDocument11 pagesSchindler GraphicsJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Interim PresentationDocument11 pagesInterim PresentationJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Touchstone Submission - Work Collection So FarDocument33 pagesTouchstone Submission - Work Collection So FarJake BryantNo ratings yet
- The Making of Logen NinefingersDocument22 pagesThe Making of Logen NinefingersJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Journey To Shadow Peak - Character DesignDocument18 pagesJourney To Shadow Peak - Character DesignJake BryantNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle - Script V1Document3 pagesThe Cell Cycle - Script V1Jake BryantNo ratings yet
- Narrative Interim PitchDocument19 pagesNarrative Interim PitchJake BryantNo ratings yet
- The Career of Oskar SchindlerDocument4 pagesThe Career of Oskar SchindlerJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Lifedrawing ArchiveDocument31 pagesLifedrawing ArchiveJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Extended Research - The VikingsDocument7 pagesExtended Research - The VikingsJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Django Unchained - The Hero's JourneyDocument4 pagesDjango Unchained - The Hero's JourneyJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Initial Research - The VikingsDocument11 pagesInitial Research - The VikingsJake BryantNo ratings yet
- The ColosseumDocument13 pagesThe ColosseumJake BryantNo ratings yet
- The Art of The Fantastic VoyageDocument43 pagesThe Art of The Fantastic VoyageJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Essay PresentationDocument4 pagesEssay PresentationJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Rope Film ReviewDocument5 pagesRope Film ReviewJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Commission TimetableDocument11 pagesCommission TimetableJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Dogs (1999) - Dir. Quentin TarantinoDocument5 pagesReservoir Dogs (1999) - Dir. Quentin TarantinoJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Script Draft 3Document5 pagesScript Draft 3Jake BryantNo ratings yet
- The Birds (1963) - Alfred Hitchcock - Film ReviewDocument5 pagesThe Birds (1963) - Alfred Hitchcock - Film ReviewJake BryantNo ratings yet
- The Art of The Interstellar ComplexDocument35 pagesThe Art of The Interstellar ComplexJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Jaws (1975) Film ReviewDocument5 pagesJaws (1975) Film ReviewJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Online Greenlight Review - Part 2Document19 pagesOnline Greenlight Review - Part 2Jake BryantNo ratings yet
- Psycho (1960) Film ReviewDocument4 pagesPsycho (1960) Film ReviewJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Character Profiles - Draft 2Document3 pagesCharacter Profiles - Draft 2Jake BryantNo ratings yet
- La Jetée Film ReviewDocument4 pagesLa Jetée Film ReviewJake BryantNo ratings yet
- Classic Beer Style Series #02 - Continental PilsnerDocument106 pagesClassic Beer Style Series #02 - Continental PilsnerFred smith100% (1)
- 10.3 Gene Pools and SpeciationDocument26 pages10.3 Gene Pools and Speciationmike bevnNo ratings yet
- advtJRF DIPAS212023Document4 pagesadvtJRF DIPAS212023Rathod Chandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Singlet Oxygeno PDFDocument489 pagesSinglet Oxygeno PDFSergio Ramirez BarrosoNo ratings yet
- Elle Canada 2010-03Document203 pagesElle Canada 2010-03PontesDebora100% (1)
- Heredity Determines PersonalityDocument1 pageHeredity Determines Personalityjyotigosain0% (1)
- Support System and MovementDocument38 pagesSupport System and MovementNinamay FajardoNo ratings yet
- Sharma M Et - Al. (1) - 1Document12 pagesSharma M Et - Al. (1) - 1P S AmritNo ratings yet
- Scicent AB TE U4 eDocument28 pagesScicent AB TE U4 erayckng2No ratings yet
- 02 The Biology of MindDocument74 pages02 The Biology of MinderhetzNo ratings yet
- Biology Algae A. General Characteristics: Volvox, Etc), Some Are Marine (Sargassum, Laminaria, Etc) and Some AreDocument2 pagesBiology Algae A. General Characteristics: Volvox, Etc), Some Are Marine (Sargassum, Laminaria, Etc) and Some AregespurbaNo ratings yet
- Brandon Keeler Yale University 2012Document2 pagesBrandon Keeler Yale University 2012api-150920413No ratings yet
- Transcript of PBS Frontline-Inside The Teenage BrainDocument28 pagesTranscript of PBS Frontline-Inside The Teenage Brainbrub fishNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph's School, Greater Noida: First Unit Test For 2021 - 22Document1 pageSt. Joseph's School, Greater Noida: First Unit Test For 2021 - 22A PNo ratings yet
- Bach Floral Esoteric Remedies Self Healing WorkbookDocument99 pagesBach Floral Esoteric Remedies Self Healing Workbooksorin100% (9)
- The Spark in The MachineDocument6 pagesThe Spark in The MachineElanghovan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Ecological Succession-2Document7 pages1.5 Ecological Succession-2Patrick batemenNo ratings yet
- Carnivoran Evolution PDFDocument524 pagesCarnivoran Evolution PDFAna Maria PaschoalNo ratings yet
- FILL IN THE BLANKS LISTENING TUTORIALDocument2 pagesFILL IN THE BLANKS LISTENING TUTORIALAvinash SinghNo ratings yet
- UltrarunningDocument55 pagesUltrarunningLynseyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Cardiology Human Cardiovascular SystemDocument46 pagesChapter 14 Cardiology Human Cardiovascular SystemAbegail AcohonNo ratings yet
- Manual of Fisheries Science Part 2Document67 pagesManual of Fisheries Science Part 2daniralNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Picture: 60 Year Female 23321506381Document3 pagesComplete Blood Picture: 60 Year Female 23321506381SilavioNo ratings yet
- Philippine Red Cross Molecular Laboratory: Covid-19 RT-PCR Test Report & CertificationDocument1 pagePhilippine Red Cross Molecular Laboratory: Covid-19 RT-PCR Test Report & CertificationAldrin TevesNo ratings yet
- Tmp1a96 TMPDocument80 pagesTmp1a96 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Characterization and Temperature-Dependent Conductivity of PolyanilineDocument7 pagesCharacterization and Temperature-Dependent Conductivity of PolyanilineBianca Beatrice BaștiureaNo ratings yet
- Humphries Sex DeterminationDocument34 pagesHumphries Sex DeterminationJhonny Huaraquispe HipolitoNo ratings yet
- MEGA: A Biologist-Centric Software For Evolutionary Analysis of DNA and Protein SequencesDocument8 pagesMEGA: A Biologist-Centric Software For Evolutionary Analysis of DNA and Protein SequencesJavier VázquezNo ratings yet
- Plants Can Do MathDocument24 pagesPlants Can Do MathkrltuNo ratings yet
- AA Metatron The Grid and Rebooting Your Reality July 2017Document6 pagesAA Metatron The Grid and Rebooting Your Reality July 2017Meaghan MathewsNo ratings yet