Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CCNA Access List and DHCP Questions
Uploaded by
Vladimir CortezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CCNA Access List and DHCP Questions
Uploaded by
Vladimir CortezCopyright:
Available Formats
CCNA Access List Questions
May 1st, 2011Go to comments
Here you will find answers to CCNA Access list questions Note: If you are not sure about how to use Access list, please read my Access list tutorial Question 1 Your boss is learning a CCNA training course, refer to the exhibit. The access list has been configured on the S0/0 interface of router RTB in the outbound direction. Which two packets, if routed to the interface, will be denied? (Choose two)
access-list 101 deny tcp 192.168.15.32 0.0.0.15 any eq telnet access-list 101 permit ip any any A. source ip address: 192.168.15.5; destination port: 21 B. source ip address: 192.168.15.37 destination port: 21 C. source ip address: 192.168.15.41 destination port: 21 D. source ip address: 192.168.15.36 destination port: 23 E. source ip address: 192.168.15.46; destination port: 23 F. source ip address: 192.168.15.49 destination port: 23
Answer: D E Explanation First we notice that telnet uses port 23 so only D, E & F can satisfy this requirement. The purpose of this access-list is to deny traffic from network 192.168.15.32 255.255.255.240 (to find out the subnet mask just convert all bit 0 to 1 and all bit 1 to 0 of the wildcard mask) to telnet to any device. So we need to figure out the range of this network to learn which ip address will be denied. Increment: 16 Network address: 192.168.15.32 Broadcast address: 192.168.15.47 -> Only 192.168.15.36 (Answer D) & 192.168.15.46 (Answer E) belong to this range so they are the correct answer.
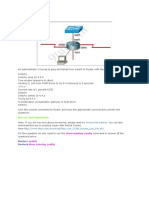
Question 2 Refer to the graphic. It has been decided that PC1 should be denied access to Server. Which of the following commands are required to prevent only PC1 from accessing Server1 while allowing all other traffic to flow normally? (Choose two)
A Router(config)# interface fa0/0 Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 out B Router(config)# interface fa0/0 Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in C Router(config)# access-list 101 deny ip host 172.16.161.150 host 172.16.162.163 Router(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any any D Router(config)# access-list 101 deny ip 172.16.161.150 0.0.0.255 172.16.162.163 0.0.0.0 Router(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any any
Answer: B C
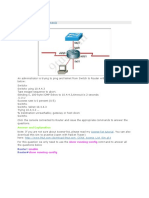
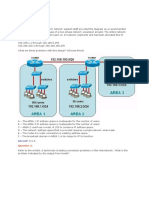
Question 3 Refer to the exhibit. Why would the network administrator configure RA in this manner?
A. to give students access to the Internet B. to prevent students from accessing the command prompt of RA C. to prevent administrators from accessing the console of RA D. to give administrators access to the Internet E. to prevent students from accessing the Internet F. to prevent students from accessing the Admin network
Answer: B Explanation Although the access-list is used to permit network 10.1.1.0/24 but the best answer here is to prevent students from accessing the command prompt of RA. From the picture above, we know that 10.1.1.0/24 is the Admin network. This access list is applied to line vty 0 4 so it will permit only Telnet traffic from Admin to RA while drop all other traffic (because of the implicit deny all command at the end of the access list). Therefore we can deduce that it will prevent students from accessing the command prompt of RA. This access list only filters Telnet traffic (because it is applied to vty line) so it will not prevent or allow anyone to access the Internet -> A, D, E are not correct. C is not correct as this access list allows administrators to access the console of RA. F is not correct as this access list does not proceed TCP, UDP or IP traffic so the students still access the Admin network. (Notice that the command prompt here implies telnet as telnet is the only way to remotely access RA) Question 4 An access list was written with the four statements shown in the graphic. Which single access list statement will combine all four of these statements into a single statement that will have exactly the same effect?
A. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.0.255 B. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.1.255 C. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.3.255 D. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.15.255 E. access-list 10 permit 172.29.0.0 0.0.255.255
Answer: C Explanation Four statements above allow 4 networks (from 172.29.16.0/24 to 172.29.19.0/24) to go through so we can summary them as network 172.29.16.0/22. /22 = 255.255.252.0 so it equals 0.0.3.255 when converting into wildcard mask -> C is correct. A, B, D are not correct as their wildcard masks are false. For example: Answer A allows from 172.29.16.0 to 172.29.16.255 Answer B allows from 172.29.16.0 to 172.29.17.255 Answer D allows from 172.29.16.0 to 172.29.31.255 Both the network address and wildcard mask of answer E are false as it allows the whole major network 172.29.0.0/16 to go through. Question 5
A network administrator wants to add a line to an access list that will block only Telnet access by the hosts on subnet 192.168.1.128/28 to the server at 192.168.1.5. What command should be issued to accomplish this task? A access-list 101 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 192.168.1.5 0.0.0.0 eq 23 access-list 101 permit ip any any B access-list 101 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.240 192.168.1.5 0.0.0.0 eq 23 access-list 101 permit ip any any C access-list 1 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.5 0.0.0.0 eq 21 access-list 1 permit ip any any D access-list 1 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 host 192.168.1.5 eq 23 access-list 1 permit ip any any
Answer: A Explanation: First the question asks to block only Telnet access so the port we have to use is 23 -> C is not correct. Next we need to block traffic from hosts on the subnet 192.168.1.128/28, which is 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 if we convert to wildcard mask (just invert all bits of the subnet mask,from 0 to 1 and from 1 to 0 we will get the equivalent wildcard mask of that subnet mask) -> so B is incorrect In this case, we have to use extended access list because we need to specify which type of traffic (TCP) and which port (23) we want to block -> so D is incorrect because it uses standard access list. Question 6 As a network administrator, you have been instructed to prevent all traffic originating on the LAN from entering the R2 router. Which the following command would implement the access list on the interface of the R2 router?
A access-list 101 in B access-list 101 out C ip access-group 101 in D ip access-group 101 out
Answer: C Question 7 The following access list below was applied outbound on the E0 interface connected to the 192.169.1.8/29 LAN:
access-list 135 deny tcp 192.169.1.8 0.0.0.7 eq 20 any access-list 135 deny tcp 192.169.1.8 0.0.0.7 eq 21 any How will the above access lists affect traffic? A FTP traffic from 192.169.1.22 will be denied B No traffic, except for FTP traffic will be allowed to exit E0 C FTP traffic from 192.169.1.9 to any host will be denied D All traffic exiting E0 will be denied E All FTP traffic to network 192.169.1.9/29 will be denied
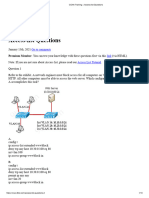
Answer: D Explanation: There is always an implicit deny all command at the end of every access list, so if an access list doesnt have any permit command, it will block all the traffic. If we use the command access-list 135 permit ip any any at the end of this access list then the answer should be C FTP traffic from 192.169.1.9 to any host will be denied. Question 8 The access control list shown in the graphic has been applied to the Ethernet interface of router R1 using the ip access-group 101 in command. Which of the following Telnet sessions will be blocked by this ACL? (Choose two)
A from host PC1 to host 5.1.1.10 B from host PC1 to host 5.1.3.10 C from host PC2 to host 5.1.2.10 D from host PC2 to host 5.1.3.8
Answer: B D Explanation Below is the simple syntax of an extended access list: access-list access-list-number {deny | permit} {ip|tcp|udp|icmp} source [source-mask] dest [dest-mask] [eq dest-port]
Notice that this access list is applied to the Ethernet interface of R1 in the in direction so in this case, it will filter all the packets originated from E1 network (host PC1 and PC2) with these parameters: Source network: 5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3 which means 5.1.1.8/252 (just invert all the wildcard bits to get the equivalent subnet mask) -> Packets from 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11 will be filtered. Destination network: 5.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 which means 5.1.3.0/24-> Packets to 5.1.3.0/24 will be filtered Therefore packets originated from 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11 and have the destination to the host 5.1.3.x (via Telnet) will be denied. Question 9 The following configuration line was added to router R1 Access-list 101 permit ip 10.25.30.0 0.0.0.255 any What is the effect of this access list configuration? A permit all packets matching the first three octets of the source address to all destinations B permit all packet matching the last octet of the destination address and accept all source addresses C permit all packet matching the host bits in the source address to all destinations D permit all packet from the third subnet of the network address to all destinations
Answer: A
CCNA DHCP Questions
March 2nd, 2011Go to comments
Here you will find answers to DHCP Questions Question 1 Refer to the exhibit. Which rule does the DHCP server use when there is an IP address conflict?
A. The address is removed from the pool until the conflict is resolved. B. The address remains in the pool until the conflict is resolved. C. Only the IP detected by Gratuitous ARP is removed from the pool. D. Only the IP detected by Ping is removed from the pool. E. The IP will be shown, even after the conflict is resolved.
Answer: A Question 2 How dose a DHCP server dynamically assign IP address to host?
A. Addresses are allocated after a negotiation between the server and the host to determine the length of the agreement. B. Addresses are assigned for a fixed period of time. At the end of period, a new quest for an address must be made, and another address is then assigned. C. Addresses are leased to host. A host will usually keep the same address by periodically contacting the DHCP sever to renew the lease. D. Addresses are permanently assigned so that the host uses the same address at all times.
Answer: C Question 3 Which two tasks does the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol perform? (Choose two) A. Set the IP gateway to be used by the network. B. Perform host discovery used DHCPDISCOVER message. C. Configure IP address parameters from DHCP server to a host. D. Provide an easy management of layer 3 devices. E. Monitor IP performance using the DHCP server. F. Assign and renew IP address from the default pool.
Answer: C F Question 4 Which statement is correct regarding the operation of DHCP? A. A DHCP client uses a ping to detect address conflicts. B. A DHCP server uses a gratuitous ARP to detect DHCP clients. C. A DHCP client uses a gratuitous ARP to detect a DHCP server. D. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool and an administrator must resolve the conflict. E. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool for an amount of time configurable by the administrator. F. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool and will not be reused until the server is rebooted.
Answer: D Explanation An address conflict occurs when two hosts use the same IP address. During address assignment, DHCP checks for conflicts using ping and gratuitous ARP. If a conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool. The address will not be assigned until the administrator resolves the conflict.
You might also like
- CCNA - Access List QuestionsDocument8 pagesCCNA - Access List Questionsmakhija7ish77No ratings yet
- CCNA Access List QuestionsDocument6 pagesCCNA Access List QuestionsKelvin RoaNo ratings yet
- ACLDocument12 pagesACLBui Minh SinhNo ratings yet
- CCNA Access List Sim: (Updated From Real CCNA Exam On Jan-09-2010)Document6 pagesCCNA Access List Sim: (Updated From Real CCNA Exam On Jan-09-2010)whiteroseeNo ratings yet
- Access Lists QUESTIONDocument7 pagesAccess Lists QUESTIONĐinhĐạiĐồngNo ratings yet
- Exam Code: 640-802 Cisco Certified Network Associate: Demo VersionDocument7 pagesExam Code: 640-802 Cisco Certified Network Associate: Demo VersionMasterImranNo ratings yet
- Domande ACLDocument9 pagesDomande ACLferranti.mNo ratings yet
- CCNA Access List Sim: Go To CommentsDocument5 pagesCCNA Access List Sim: Go To CommentsFarhan BukhariNo ratings yet
- Resolve ping and telnet issues between Switch and RouterDocument6 pagesResolve ping and telnet issues between Switch and RouterCovered AngelNo ratings yet
- 4 9tut - Com CCNA Access List SimDocument6 pages4 9tut - Com CCNA Access List SimHumberth PadillaNo ratings yet
- 1Document12 pages1Nguyễn Ngọc ViệtNo ratings yet
- Go To Comments: CCNA Access List SimDocument6 pagesGo To Comments: CCNA Access List SimArslan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Port Security Questions: AnswerDocument28 pagesPort Security Questions: AnswerHoai Duc HoangNo ratings yet
- Troubleshoot Ping and Telnet Issues Between Switch and RouterDocument6 pagesTroubleshoot Ping and Telnet Issues Between Switch and RouterNguyen Anh TuanNo ratings yet
- ALL in OneDocument74 pagesALL in Oneazimcuetcse01100% (19)
- Latest Version - CCNP Route - 300-101 - Version 2018 - 91q - Prince-V1 PDFDocument33 pagesLatest Version - CCNP Route - 300-101 - Version 2018 - 91q - Prince-V1 PDFtho anhNo ratings yet
- Jazzy Dumps V3 PDFDocument81 pagesJazzy Dumps V3 PDFAquadigNo ratings yet
- Access-list Questions Quiz for Network EngineersDocument6 pagesAccess-list Questions Quiz for Network EngineersJowel RanaNo ratings yet
- OSPF, RIP, PPP, and IPv6 routing protocol questionsDocument20 pagesOSPF, RIP, PPP, and IPv6 routing protocol questionsAla AntabliNo ratings yet
- CCNA Training Access-List QuestionsDocument10 pagesCCNA Training Access-List QuestionsNgô cao cườngNo ratings yet
- Pass4: 100% Real IT Exam Q&As. Easily Pass With A High ScoreDocument93 pagesPass4: 100% Real IT Exam Q&As. Easily Pass With A High ScoreThomaz Stepheson de Souza GomesNo ratings yet
- CCNA Boot Camp Post Test 13 QuestionsDocument4 pagesCCNA Boot Camp Post Test 13 QuestionsEric ResuelloNo ratings yet
- CCNA Training CCNA - Access List Questions 2Document12 pagesCCNA Training CCNA - Access List Questions 2dauzayl3529100% (1)
- Huawei.H12-211.v2020-01-04.q86: Leave A ReplyDocument26 pagesHuawei.H12-211.v2020-01-04.q86: Leave A Replywilson sottiNo ratings yet
- CCNAv3 – New Questions ReviewDocument238 pagesCCNAv3 – New Questions ReviewSunda100% (1)
- CCNAv3 – New Questions ReviewDocument276 pagesCCNAv3 – New Questions Reviewdufreine100% (1)
- OperationsDocument4 pagesOperationsMadhawhan NairNo ratings yet
- CCNA - Access List Questions: Premium Member: You Can Test Your Knowledge With These Questions First Via ThisDocument4 pagesCCNA - Access List Questions: Premium Member: You Can Test Your Knowledge With These Questions First Via Thiskrishna kumarNo ratings yet
- Examcollection 200-120 VCEDocument8 pagesExamcollection 200-120 VCEAdamNo ratings yet
- CCNA Simulator QuestionsDocument54 pagesCCNA Simulator Questionscreature1990No ratings yet
- Ccna Drag and Drop QuestionsDocument11 pagesCcna Drag and Drop QuestionsaddislibroNo ratings yet
- 300-101 Updated Questions 2 14 PDFDocument19 pages300-101 Updated Questions 2 14 PDFPadam Dhami100% (2)
- HCIA, HCNA-R&S Latest Dumps PDFDocument56 pagesHCIA, HCNA-R&S Latest Dumps PDFIhtram Hafeez71% (24)
- 100 105Document159 pages100 105Roger Rodriguez CNo ratings yet
- Final Exam BDocument12 pagesFinal Exam BJemila BekeleNo ratings yet
- 07 Final Exam - B - 1610961584815Document11 pages07 Final Exam - B - 1610961584815Paksi Alam100% (1)
- SecurityDocument3 pagesSecurityGlennNo ratings yet
- CCNA 200-301 Exam (Demo QuestionsDocument19 pagesCCNA 200-301 Exam (Demo QuestionsJoffre Ramiro Pesantez VerdezotoNo ratings yet
- CCNP Ccie 300 410 Enarsi DigitalTUT New-Q PDFDocument14 pagesCCNP Ccie 300 410 Enarsi DigitalTUT New-Q PDFCristihan RenteriaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Actualtests 100-101 v2014-09-20 by CODY 122qDocument44 pagesCisco Actualtests 100-101 v2014-09-20 by CODY 122qManuel Tito MiguelNo ratings yet
- Cisco IP ACL Practice Questions and ExplanationsDocument3 pagesCisco IP ACL Practice Questions and ExplanationsBaaska214No ratings yet
- Cisco IP Phones, EIGRP Differences, IPv6 Prefixes, Troubleshooting ProblemsDocument19 pagesCisco IP Phones, EIGRP Differences, IPv6 Prefixes, Troubleshooting Problemsnguyen hong sonNo ratings yet
- Ccna HCL Exam QuestionsDocument25 pagesCcna HCL Exam Questionsshyam80No ratings yet
- Huawei.H12 811 ENU.v2022 06 08.q166Document47 pagesHuawei.H12 811 ENU.v2022 06 08.q166Anas H AlNaieratNo ratings yet
- Enarsi Nov 2021Document142 pagesEnarsi Nov 2021Crypto AlchemistNo ratings yet
- CCNP 300 410 ENARSI NetworkTUT 26 5 2021Document104 pagesCCNP 300 410 ENARSI NetworkTUT 26 5 2021Olga BradyNo ratings yet
- CCNA Simulator QuestionsDocument54 pagesCCNA Simulator Questionsdemon332No ratings yet
- CCNP 300-410 October 2020Document51 pagesCCNP 300-410 October 2020Sang Nguyen NgocNo ratings yet
- MikroTik MTCNA v2020-05-02 q116Document28 pagesMikroTik MTCNA v2020-05-02 q116DIMAS SURYANSYAHNo ratings yet
- Tshoot CH 4Document10 pagesTshoot CH 4Daniel Corfu82% (11)
- CCNA sample questions to help prepare for Cisco certification examDocument23 pagesCCNA sample questions to help prepare for Cisco certification examMangesh KakadeNo ratings yet
- DUMP1Document102 pagesDUMP1Moulaye KoureichNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Networktut V2Document67 pagesMCQ - Networktut V2dee_g666No ratings yet
- ENARSI Sep 2020Document55 pagesENARSI Sep 2020Giàng A TrungNo ratings yet
- 640 822Document161 pages640 822Simina StrengarescuNo ratings yet
- Final Thang1.Document21 pagesFinal Thang1.Hùng QuáchNo ratings yet
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- 3001 98.21I SRM Manual E 06 2007Document328 pages3001 98.21I SRM Manual E 06 2007Vladimir CortezNo ratings yet
- Map Info Professional User GuideDocument525 pagesMap Info Professional User GuideL'Homme De GammeNo ratings yet
- Raisecom Role MasterDocument1 pageRaisecom Role MasterVladimir CortezNo ratings yet
- Pn-3-4935.07 v033 Ims Charg Arch Post BallotDocument14 pagesPn-3-4935.07 v033 Ims Charg Arch Post BallotVladimir CortezNo ratings yet
- LTE GSM Handovers meeting agendaDocument16 pagesLTE GSM Handovers meeting agendaOlivier RenimelNo ratings yet
- Contactless Linear Position TransducerDocument5 pagesContactless Linear Position TransducerRONALDECCONANo ratings yet
- Hardware WorksheetDocument4 pagesHardware WorksheetNikita KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 SFCDocument48 pagesChapter 14 SFCSiswo Ponco RahardjoNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Boost Converter: A Project Report SubmittedDocument7 pagesDC-DC Boost Converter: A Project Report SubmittedSantosh PadhiNo ratings yet
- Script (English)Document7 pagesScript (English)Jona Mae CamachoNo ratings yet
- أسئلة دورات تجميعDocument131 pagesأسئلة دورات تجميعRashed Abu AlsondosNo ratings yet
- Water Specialist WS2H and WS3 Control Valve ManualDocument40 pagesWater Specialist WS2H and WS3 Control Valve ManualjnpaisNo ratings yet
- The Integration of Social Media Technologies For Teaching and Learning in Kenyan SchoolsDocument7 pagesThe Integration of Social Media Technologies For Teaching and Learning in Kenyan SchoolsIJRIT JournalNo ratings yet
- Teams HandbookDocument18 pagesTeams HandbookLudi D. LunarNo ratings yet
- DS-160 Fault CodesDocument9 pagesDS-160 Fault CodesKrum KashavarovNo ratings yet
- FSP150-50LE Is An Industrial Level of Switching Power Supply - SpecificationDocument1 pageFSP150-50LE Is An Industrial Level of Switching Power Supply - SpecificationJohn HallowsNo ratings yet
- End of Chapter 8 (p.606) Questions 1,2,4,8,14.: Short AnswerDocument4 pagesEnd of Chapter 8 (p.606) Questions 1,2,4,8,14.: Short AnswerTung VanNo ratings yet
- ZJ 5780s Instruction BookDocument102 pagesZJ 5780s Instruction BookRATSITOHARA EricNo ratings yet
- Cell Barring (RAN15.0 02)Document51 pagesCell Barring (RAN15.0 02)hekriNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection Centre: RSC Vacancy Bulletin No. 1/2013 Public Service Staff PostsDocument48 pagesRecruitment and Selection Centre: RSC Vacancy Bulletin No. 1/2013 Public Service Staff PostsRich bitchNo ratings yet
- (ED) .DC Amp Design With FETs Zero-TCDocument5 pages(ED) .DC Amp Design With FETs Zero-TCf826401No ratings yet
- LoRaWan BookDocument132 pagesLoRaWan BookHợpですNo ratings yet
- REB670 2.1 PPT 4CAE000113 RevDocument13 pagesREB670 2.1 PPT 4CAE000113 RevDinesh govindNo ratings yet
- 5-V Low-Drop Voltage Regulator TLE 4263: FeaturesDocument17 pages5-V Low-Drop Voltage Regulator TLE 4263: FeaturesWelleyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledmoch bagas setya rahmanNo ratings yet
- Ghid Automatizari SchneiderDocument372 pagesGhid Automatizari SchneidervalicanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Excel Formulas and FunctionsDocument80 pagesAdvanced Excel Formulas and FunctionsSanjay MoreNo ratings yet
- International Technology Roadmap For Semiconductors: 2008 Itrs OrtcDocument23 pagesInternational Technology Roadmap For Semiconductors: 2008 Itrs Ortcvishal garadNo ratings yet
- ABB ROBOT Training IRC5 Hardware PDFDocument97 pagesABB ROBOT Training IRC5 Hardware PDFTensaigaNo ratings yet
- Fidelityfx Cas: Lou Kramer, Developer Technology Engineer, AmdDocument92 pagesFidelityfx Cas: Lou Kramer, Developer Technology Engineer, AmdJohn K SmithNo ratings yet
- Satyendra Kumar Mishra1 - CVDocument3 pagesSatyendra Kumar Mishra1 - CVsatyendra_mishra08No ratings yet
- AQA Physics A-Level Electricity Questions (Pack 3)Document90 pagesAQA Physics A-Level Electricity Questions (Pack 3)BDNo ratings yet
- To Call A Function From BI PublisherDocument6 pagesTo Call A Function From BI PublisherbalasukNo ratings yet
- Review of Industrial Deployment of Multi-Agent SystemsDocument24 pagesReview of Industrial Deployment of Multi-Agent SystemsVasant RaghavNo ratings yet