Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mrsa 2
Uploaded by
Henra HalimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mrsa 2
Uploaded by
Henra HalimCopyright:
Available Formats
What is MRSA?
Staphylococcus aureus, also called staph, is a type of germ known as bacteria. Many healthy people have this germ on their skin and in their Nose.
How is MRSA spread?
Anyone can get a staph infection, but people are at higher risk if they have:
Skin-to-skin contact with someone who has a staph infection.
Contact with items and surfaces that have the staph germ on them.
Cuts or scrapes on their skin. Crowded living conditions, such as schools. A lot of physical contact such as sports teams. Poor hygiene.
Testing for MRSA
See a doctor if you has a skin wound that is not healing or if there are signs of an infection, such as fever, pain, redness, swelling or drainage from skin wounds.
The doctor may collect a sample of drainage or tissue from the area and send it to a lab to test for MRSA. A blood sample may also be taken to check for MRSA in the blood. The lab test can also tell which antibiotic will be best to treat MRSA.
Babies or children placed in Intensive Care Units (ICUs) are often tested for MRSA.
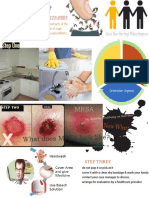
Clinical Manifestations of MRSA
Boils or draining pimples Spider Bites or bug bites Sores that wont heal Red areas of skin that may feel warm to the touch Abscesses Systemic infections (e.g. pneumonia, blood infections) much less common
How is MRSA treated?
Most staph infections, including MRSA, can be treated with certain antibiotics. If the doctor prescribes an antibiotic, it is very important to take all the medicine as ordered. If an ointment is prescribed, apply it to all skin lesions even the tiny ones If there is a skin infection, the doctor may make an incision to drain the infection.
Note:
Do dressing change on the wound Do not take part in contact sports until the infection has healed. Call the doctor if the infection does not get better with treatment.
How do I prevent the spread of MRSA?
To prevent the spread of MRSA and other bacteria:
Wash with soap and water or use alcohol hand especially after touching a skin lesion.
Keep any cuts or lesions clean. Keep them covered with clean, dry bandages until healed.
Do not touch other peoples cuts or bandages. Do not share personal items like towels, razors, clothing or equipment. Clean surfaces where bare skin rubs such as exercise equipment. Take a shower with soap after working out or playing sports
But the vast majority of MRSA infections occur in hospital.
There are a number of reasons for this:
People who are ill or weakened as a result of surgery or medical treatment are more vulnerable to infection.
In hospital, there are usually plenty of opportunities for MRSA to enter the body, e.g. via wounds, surgical scars or through the use of equipment such as catheters or intravenous drips. MRSA may develop in open wounds and is easily spread from one wound to another. Hospital wards are often fairly crowded and unless staff and patients take adequate precautions, MRSA can be transferred from one patient to the next.
And now, lets look at what MRSA really looks like
MRSA Infection Threatens Us
You might also like
- MrsaDocument2 pagesMrsauli_siahaanNo ratings yet
- Drug Resistance and Antibiotic PoliciesDocument13 pagesDrug Resistance and Antibiotic PoliciesChinky GalNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Nursing Skills & Concepts P1of5Document5 pagesLearning Objectives: Nursing Skills & Concepts P1of5rizza_servandoNo ratings yet
- Infective Endocarditis 4TH (Compatibility Mode)Document14 pagesInfective Endocarditis 4TH (Compatibility Mode)Mohammed Al-KebsiNo ratings yet
- SalmonellaDocument23 pagesSalmonellaahmedtwanaahmedNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Awareness PreventionDocument13 pagesAnesthesia Awareness PreventionsanaNo ratings yet
- Report Topic:: National Botanical Garden of Bangladesh and Bangladesh National ZooDocument7 pagesReport Topic:: National Botanical Garden of Bangladesh and Bangladesh National ZooBishal SahaNo ratings yet
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAEDocument23 pagesENTEROBACTERIACEAEapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Biosafety Level 3 Procedures and RequirementsDocument9 pagesBiosafety Level 3 Procedures and RequirementsZain HadiNo ratings yet
- Suprapubic Cateterization Andrie Rev 2Document37 pagesSuprapubic Cateterization Andrie Rev 2Dwiyanti OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Brucellosis: A Highly Contagious Zoonotic DiseaseDocument55 pagesBrucellosis: A Highly Contagious Zoonotic Diseasesana shakeelNo ratings yet
- RLE FAMILY REVIEWDocument22 pagesRLE FAMILY REVIEWEniamrahs DnalonNo ratings yet
- Im BasketballDocument56 pagesIm BasketballCj SernaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Microbiology: CampylobacterDocument25 pagesDiagnostic Microbiology: Campylobacteranon_914901469No ratings yet
- The Ehealth LandscapeDocument7 pagesThe Ehealth LandscapeJasper CayangaNo ratings yet
- Removing Philippine History in The Age oDocument6 pagesRemoving Philippine History in The Age oDinamak KalatNo ratings yet
- CWTS Group 5 - Learning Exercises 1 & 2Document4 pagesCWTS Group 5 - Learning Exercises 1 & 2Marjie VistaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Chlamydiae InfectionsDocument32 pagesUnderstanding Chlamydiae InfectionsNaing Lin SoeNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan for a Diabetic ClientDocument12 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan for a Diabetic ClientChristi MilanNo ratings yet
- MrsaDocument1 pageMrsaapi-314460549No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agents (Ug/ml) Zone of Inhibition (MM) : Escherichia Coli Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Staphylococcus AureusDocument4 pagesAntimicrobial Agents (Ug/ml) Zone of Inhibition (MM) : Escherichia Coli Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Staphylococcus AureuseatpryNo ratings yet
- DR Julian-MYOCARDITISDocument83 pagesDR Julian-MYOCARDITISArmando Esteban Coa SandovalNo ratings yet
- Skills Check ListDocument4 pagesSkills Check Listapi-301335830No ratings yet
- Movie AwakeDocument7 pagesMovie AwakemefacostaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology For Nursing LectureDocument13 pagesParasitology For Nursing LectureebenezermanzanormtNo ratings yet
- Culture and IdentificationDocument4 pagesCulture and IdentificationDewa Denis100% (1)
- Deepshikha Chhetri Msc. FSNDocument50 pagesDeepshikha Chhetri Msc. FSNDaiane SantanaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Elctrolyte Balance.... Power PointDocument40 pagesFluid and Elctrolyte Balance.... Power PointMarwan M.100% (1)
- Koh PrepDocument4 pagesKoh PrepIndhumathiNo ratings yet
- Bordetella Pertussis and Whooping CoughDocument22 pagesBordetella Pertussis and Whooping CoughDian TikaNo ratings yet
- Lab Diagnosis of Wound InfectionDocument3 pagesLab Diagnosis of Wound InfectionsaketNo ratings yet
- StreptococciDocument40 pagesStreptococciGjfyigyivNo ratings yet
- Intestinal NematodesDocument96 pagesIntestinal NematodesYeyeh Santos100% (1)
- Nurs Pocket CardsDocument10 pagesNurs Pocket CardsKiara SalvageNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument10 pagesGenetic Engineeringfrancisco_sanchez_truebaNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument5 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- DiphteriaDocument64 pagesDiphteriaOmarNo ratings yet
- Morpholofy of MoDocument44 pagesMorpholofy of MoPathumavathy RamanathanNo ratings yet
- BSL Level 1-2 Lab SafetyDocument30 pagesBSL Level 1-2 Lab SafetyEriani WulandariNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic FungiDocument61 pagesOpportunistic Fungisarguss14No ratings yet
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument9 pagesMicrobiology and ParasitologyDefensor Pison Gringgo0% (1)
- STIs: Learn About Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, HPV, Hepatitis B, Herpes, HIV and Syphilis (35 charactersDocument25 pagesSTIs: Learn About Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, HPV, Hepatitis B, Herpes, HIV and Syphilis (35 charactersMohamoud MohamedNo ratings yet
- MicroparasitologyDocument28 pagesMicroparasitologyMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic MycosesDocument36 pagesOpportunistic MycosesTrinain ChakravartiNo ratings yet
- Immunology For AiimsDocument21 pagesImmunology For AiimssureshNo ratings yet
- Exotoxic Model Corynebacterium DiphteriaeDocument37 pagesExotoxic Model Corynebacterium Diphteriaekohinoor815256100% (1)
- Trichomoniasis: T. Vaginalis Is A Parasitic Protozoan, and The Taxonomic Position Is Based On The ClassificationDocument15 pagesTrichomoniasis: T. Vaginalis Is A Parasitic Protozoan, and The Taxonomic Position Is Based On The Classificationrave robNo ratings yet
- Types of Mycoses According To SiteDocument8 pagesTypes of Mycoses According To SiteAlyanna ManguerraNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument23 pagesTetanusRiska PriyaniNo ratings yet
- Lec5 MP Bacteria and DiseaseDocument51 pagesLec5 MP Bacteria and DiseasePriya ManobalNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell StructureDocument6 pagesBacterial Cell StructureCasey StuartNo ratings yet
- Rash Fever DDXDocument7 pagesRash Fever DDXirsaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Gel ElectrophoresisDocument47 pagesA Guide To Gel ElectrophoresisJakapan RodsupNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sadeli Masria, DR., SPMK., Ms. DMMDocument64 pagesDr. Sadeli Masria, DR., SPMK., Ms. DMMPraluki HerliawanNo ratings yet
- Dientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesDocument4 pagesDientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- ImmunoDocument18 pagesImmunoirish o-oNo ratings yet
- Novel Drugs Disarm MRSA BacteriaDocument32 pagesNovel Drugs Disarm MRSA BacteriaJenita Magdalena100% (1)
- General Information About MRSADocument4 pagesGeneral Information About MRSATati MaryatiNo ratings yet
- MRSA InfectionDocument5 pagesMRSA InfectionHoàng Kiều OanhNo ratings yet
- Ch6 LightingDocument138 pagesCh6 LightingHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Dead Loads PDFDocument3 pagesDead Loads PDFHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Architectural and Structural Development of Tall BuildingsDocument15 pagesArchitectural and Structural Development of Tall BuildingsHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- A Study On Behavior of Structural Systems For Tall Buildings Subjected To Lateral LoadsDocument6 pagesA Study On Behavior of Structural Systems For Tall Buildings Subjected To Lateral LoadsHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Laporan Studi Better Air Quality (BAQ) Conference Hongkong Trip 2 - 8 December 2012 - OptDocument26 pagesLaporan Studi Better Air Quality (BAQ) Conference Hongkong Trip 2 - 8 December 2012 - OptHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Lean Supply ChainDocument45 pagesLean Supply ChainHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Design of Slab Wall SystemDocument10 pagesDesign of Slab Wall Systemkushaljp8989No ratings yet
- Evaluasi Hasil BelajarDocument2 pagesEvaluasi Hasil BelajarWahyuddin MahmudNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Policy Options For Sustainable Urban Transportation Development in ChinaDocument16 pagesChallenges and Policy Options For Sustainable Urban Transportation Development in ChinaHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- BeltTruss Virtual OutriggersDocument7 pagesBeltTruss Virtual OutriggersBilly TseNo ratings yet
- High Rise BuildingDocument5 pagesHigh Rise Buildingmadina1386No ratings yet
- Analisis Perbandingan Simpangan Lateralbangunan Tinggi Dengan Variasi Bentuk Dan Posisi Dinding GeserDocument10 pagesAnalisis Perbandingan Simpangan Lateralbangunan Tinggi Dengan Variasi Bentuk Dan Posisi Dinding GeserHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Ch.6 Cast in Drilled Hole Piles - CaltransDocument18 pagesCh.6 Cast in Drilled Hole Piles - CaltransHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Home Design Architectural Series 3000Document337 pagesHome Design Architectural Series 3000api-3698190100% (5)
- FRP Repair of Corrosion-Damaged Concrete BeamsDocument13 pagesFRP Repair of Corrosion-Damaged Concrete BeamsahmadlieNo ratings yet
- In The HW Sheet You Will Find The Examples in The Power Point Slides We Made in The Class Good Luck:)Document4 pagesIn The HW Sheet You Will Find The Examples in The Power Point Slides We Made in The Class Good Luck:)Henra HalimNo ratings yet
- Faktor Ekspor TembakauDocument106 pagesFaktor Ekspor TembakauHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Timber ManualDocument145 pagesTimber Manualspiderlance100% (1)
- 5 Qunik WiqoyahDocument10 pages5 Qunik Wiqoyahwilly_tobing9454No ratings yet
- Egypt Transformation ParametersDocument5 pagesEgypt Transformation ParametersHenra Halim100% (3)
- EM 1110-2-2504 - Design of Sheet Pile Walls 1Document75 pagesEM 1110-2-2504 - Design of Sheet Pile Walls 1PDHLibrary100% (2)
- E-Commerce Dan E-Bisnis 2Document44 pagesE-Commerce Dan E-Bisnis 2Henra HalimNo ratings yet
- CH5 Bearing Design PDFDocument42 pagesCH5 Bearing Design PDFHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Drift Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Columns Subjected To Displacement Reversals (PHD Thesis)Document77 pagesDrift Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Columns Subjected To Displacement Reversals (PHD Thesis)Henra HalimNo ratings yet
- Granular Back Fill Retaining Wall Stability AnalysisDocument3 pagesGranular Back Fill Retaining Wall Stability AnalysisHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- ACI E702 Buried Concrete Basement Wall DesignDocument9 pagesACI E702 Buried Concrete Basement Wall DesignleodegarioporralNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Driven Pile FoundationDocument59 pagesDesign and Construction of Driven Pile Foundationadnan88% (8)
- Chapter 16 - Joints For Reinforced ConcreteDocument8 pagesChapter 16 - Joints For Reinforced Concretemike_ole02No ratings yet
- Bending and Punching Shear Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Glass Concrete SlabsDocument22 pagesBending and Punching Shear Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Glass Concrete SlabsHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Probabilistic Damage Detection of A Reinforced-Concrete Bridge ColumnDocument23 pagesBayesian Probabilistic Damage Detection of A Reinforced-Concrete Bridge ColumnHenra HalimNo ratings yet
- Malaysia - Kontrak - Pusat - Ubat-Ubatan - KKM - 20.03.12Document21 pagesMalaysia - Kontrak - Pusat - Ubat-Ubatan - KKM - 20.03.12Anuj Mairh0% (1)
- Mortality Review - ppt2Document27 pagesMortality Review - ppt2mohamad ashmuniNo ratings yet
- Insuficienta Venoasa CronicaDocument15 pagesInsuficienta Venoasa CronicaSimona IonitaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Equality ToolkitDocument64 pagesBenefits of Equality ToolkitBasic Rights OregonNo ratings yet
- The Abc of Handover: E.D. Registrar A: Areas AllocationDocument1 pageThe Abc of Handover: E.D. Registrar A: Areas AllocationDiahNiatiNo ratings yet
- Yorkville Advisors Completes $7.5M Equity Facility With EntreMed, Inc.Document2 pagesYorkville Advisors Completes $7.5M Equity Facility With EntreMed, Inc.YorkvilleAdvisorsNo ratings yet
- IM Shelf - AmbossDocument61 pagesIM Shelf - AmbossHaadi AliNo ratings yet
- AYR Patient Experience PresentationDocument29 pagesAYR Patient Experience Presentationaustin_tx6No ratings yet
- CelecoxibDocument2 pagesCelecoxibLaromac RolandNo ratings yet
- Autologous Transfusion Strategies to Reduce Allogeneic Blood UseDocument31 pagesAutologous Transfusion Strategies to Reduce Allogeneic Blood Usethalida24100% (1)
- Morning Report (Cardiology) : On Duty: Nadya Julaifa, Nadya Julaifa Supervisor: Dr. Yusra Pintaningrum, Sp. JP (K) FIHADocument16 pagesMorning Report (Cardiology) : On Duty: Nadya Julaifa, Nadya Julaifa Supervisor: Dr. Yusra Pintaningrum, Sp. JP (K) FIHAAdisti NurutamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter33Walker2015 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter33Walker2015 PDFMai AngelNo ratings yet
- 1583 - Intermediate Grammar Test 22Document4 pages1583 - Intermediate Grammar Test 22SabinaNo ratings yet
- Niyog-Niyogan - Quisqualis Indica Herbal Medicine-Health Benefits-Side Effects PDFDocument4 pagesNiyog-Niyogan - Quisqualis Indica Herbal Medicine-Health Benefits-Side Effects PDFJikka RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pembimbing: Dr. Dr. Maria Regina Rachmawati, Pa (K), SPKFR Presentan: DR Ratna EkawatiDocument27 pagesPembimbing: Dr. Dr. Maria Regina Rachmawati, Pa (K), SPKFR Presentan: DR Ratna EkawatiratnaekawatiNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade (Level F) Spelling ListsDocument36 pages6th Grade (Level F) Spelling ListsArmaan100% (1)
- An Intergenerational Approach to Family TherapyDocument31 pagesAn Intergenerational Approach to Family TherapyBeatriz Eugenia Guerra100% (5)
- Gait Analysis PresentationDocument41 pagesGait Analysis PresentationKýñg ButlerNo ratings yet
- Chester V Afshar (2005) 1 A.C. 134Document33 pagesChester V Afshar (2005) 1 A.C. 134V100% (1)
- What Is Down SyndromeDocument4 pagesWhat Is Down SyndromeJanica GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Fatal Airway Obstruction Due To Ludwig'sDocument6 pagesFatal Airway Obstruction Due To Ludwig'sRegina MugopalNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous MycosesDocument23 pagesSubcutaneous Mycosessarguss14100% (1)
- Medication - ALT-Template - Docusate SodiumDocument1 pageMedication - ALT-Template - Docusate SodiumNancyAmissahNo ratings yet
- Gas Transport 2Document29 pagesGas Transport 2Charmaine LucNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DengueDocument3 pagesDrug Study DengueiamELHIZANo ratings yet
- FCPS Ii Major Tentative Schedule 2a Feb 2024Document1 pageFCPS Ii Major Tentative Schedule 2a Feb 2024haseeb ur rehmanNo ratings yet
- Joint Disorders - Ay NewDocument46 pagesJoint Disorders - Ay NewPraisingson SyiemliehNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument54 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeKristine CaringalNo ratings yet
- List of Empanelled Hospitals/Diagnostic Centres, and Cghs RatesDocument53 pagesList of Empanelled Hospitals/Diagnostic Centres, and Cghs RatesArputNo ratings yet
- 0nvkwxysn505jodxuxkr5z3v PDFDocument2 pages0nvkwxysn505jodxuxkr5z3v PDFAnjali Thomas50% (2)