Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Endometriosis
Uploaded by
Afizah MuhammadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Endometriosis
Uploaded by
Afizah MuhammadCopyright:
Available Formats
What is endometriosis?
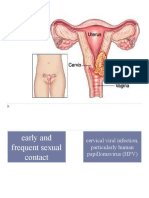
Endometriosis is the abnormal growth of cells (endometrial cells) similar to those that form the inside of the uterus, but in a location outside of the uterus. Endometrial cells are cells that are shed each month during menstruation. The cells of endometriosis attach themselves to tissue outside the uterus and are called endometriosis implants. These implants are most commonly found on the ovaries, the Fallopian tubes, outer surfaces of the uterus or intestines, and on the surface lining of the pelvic cavity. They can also be found in the vagina, cervix, and bladder, although less commonly than other locations in the pelvis. Rarely, endometriosis implants can occur outside the pelvis, on the liver, in old surgery scars, and even in or around the lung or brain. Endometrial implants, while they can cause problems, are benign (not cancerous).
Who is affected by endometriosis?
Endometriosis affects women in their reproductive years. The exact prevalence of endometriosis is not known, since many women may have the condition and have no symptoms. Endometriosis is estimated to affect over one million women (estimates range from 3% to 18% of women) in the United States. It is one of the leading causes of pelvic pain and reasons forlaparoscopic surgery and hysterectomy in this country. Estimates suggest that between 20% to 50% of women being treated for infertility have endometriosis, and up to 80% of women with chronic pelvic pain may be affected. While most cases of endometriosis are diagnosed in women aged around 25-35 years, endometriosis has been reported in girls as young as 11 years of age. Endometriosis is rare in postmenopausal women. Endometriosis is more commonly found in white women as compared with African American and Asian women. Studies further suggest that endometriosis is most common in taller, thin women with a low body mass index (BMI). Delaying pregnancy until an older age is also believed to increase the risk of developing endometriosis.
Endometriosis Symptoms
Common Endometriosis Symptoms Most women who have endometriosis, in fact, do not have symptoms. Of those who do experience symptoms, the common symptoms are pain (usually pelvic) and infertility. Pelvic pain usually occurs during or just before menstruation and lessens after menstruation. Some women experience painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia) or cramping during intercourse, and or/pain during bowel movements and/or urination. Even pelvic examination by a doctor can be painful. The pain intensity can change from month to month, and vary greatly among women. Some women experience progressive worsening of symptoms, while others can have resolution of pain without treatment. Other symptoms related to endometriosis include:
lower abdominal pain, diarrhea and/or constipation, low back pain, irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding, or blood in the urine.
Rare symptoms of endometriosis include chest pain or coughing blood due to endometriosis in the lungs and headache and/or seizures due to endometriosis in the brain.
You might also like
- Pic Xzam KVKVDocument1 pagePic Xzam KVKVAfizah MuhammadNo ratings yet
- RPT SC PpkiDocument4 pagesRPT SC PpkiAfizah MuhammadNo ratings yet
- B. Inggeris EditDocument5 pagesB. Inggeris EditAfizah MuhammadNo ratings yet
- What Is EndometriosisDocument2 pagesWhat Is EndometriosisAfizah MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Economics Assignement Week 4Document2 pagesEconomics Assignement Week 4Grace FranzNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument49 pagesHeart Failureأبوأحمد الحكيمNo ratings yet
- UNODCDocument128 pagesUNODCMohammed Mohammed Shoukry Naiem100% (1)
- Wing Chun Dit Da JowDocument7 pagesWing Chun Dit Da Jowkosen58No ratings yet
- Original Article Efficacy of TCA CROSS For Acne ScarsDocument6 pagesOriginal Article Efficacy of TCA CROSS For Acne ScarsVinod JogurNo ratings yet
- Emdr SchemaDocument8 pagesEmdr SchemayodoidNo ratings yet
- INTRAUTERINE DEATH WidyaDocument11 pagesINTRAUTERINE DEATH WidyaNabilaNo ratings yet
- Madness in Buenos AiresDocument340 pagesMadness in Buenos AiresLaura VanadiaNo ratings yet
- Cervical CADocument28 pagesCervical CABeb Raquel GamiaoNo ratings yet
- Gina Danford Fertility Treatment LetterDocument4 pagesGina Danford Fertility Treatment LetterPBS NewsHourNo ratings yet
- Katz Adl Lawton IadlDocument4 pagesKatz Adl Lawton IadlAmbaejo96No ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Complementary ManualDocument10 pagesThe Effectiveness of Complementary ManualAli DptNo ratings yet
- How To Mix InsulinDocument2 pagesHow To Mix InsulinchareneadamsNo ratings yet
- General ObjectivesDocument13 pagesGeneral ObjectiveskevinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Impaired Bowel EliminationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Impaired Bowel EliminationMara Jon Ocden CasibenNo ratings yet
- Eurowater Pressure No Address)Document8 pagesEurowater Pressure No Address)shalabyahmedNo ratings yet
- Eye Conditions: DiplopiaDocument10 pagesEye Conditions: DiplopiaAngel Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Risk for Temperature Regulation IssuesDocument12 pagesRisk for Temperature Regulation IssuesCamelia NuraNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Infant Formula FeedingDocument20 pagesChapter4 Infant Formula FeedingMuhammad AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- B.Pharmacy-6 Semester (New PCI Syllabus) : Toxicology and ChronopharmacologyDocument4 pagesB.Pharmacy-6 Semester (New PCI Syllabus) : Toxicology and ChronopharmacologySaurabh Kumar RawatNo ratings yet
- Types of Dosage Forms and Their DefinitionsDocument11 pagesTypes of Dosage Forms and Their DefinitionsNashia FaridNo ratings yet
- Cannabis Use and Disorder - Epidemiology, Comorbidity, Health Consequences, and Medico-Legal Status - UpToDateDocument34 pagesCannabis Use and Disorder - Epidemiology, Comorbidity, Health Consequences, and Medico-Legal Status - UpToDateAnonymous kvI7zBNNo ratings yet
- Medical Tourism: A Study of Kerala: Project SynopsisDocument2 pagesMedical Tourism: A Study of Kerala: Project SynopsisbhatiaharryjassiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Tooth PreparationDocument46 pagesPrinciples of Tooth PreparationSukhjeet Kaur88% (8)
- Organizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsDocument24 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Stephen P. Robbinskria1167% (3)
- Uremia NEJMDocument10 pagesUremia NEJMnathalieNo ratings yet
- Case 7 - Newborn With Respiratory DistressDocument10 pagesCase 7 - Newborn With Respiratory DistressSue HuangNo ratings yet
- Health Traingle Assessment Worksheet 14 15 PDFDocument3 pagesHealth Traingle Assessment Worksheet 14 15 PDFPraveen Reddy AlikipalliNo ratings yet
- Trauma and Recovery PrimerDocument15 pagesTrauma and Recovery Primershperka100% (1)
- Jac Brown Specific Techniques vs. Common Factors 2015Document17 pagesJac Brown Specific Techniques vs. Common Factors 2015Mayra HernandezNo ratings yet