Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iind Sem Me (Cad) Rcet - Bhilai
Uploaded by
Mohammed Abu SufianOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iind Sem Me (Cad) Rcet - Bhilai
Uploaded by
Mohammed Abu SufianCopyright:
Available Formats
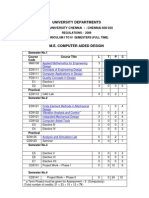
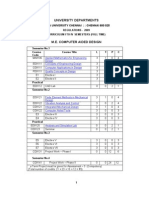
RCET, BHILAI
CHHATTISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Scheme of Teaching & Examination M. E. in CAD II Semester
Periods per Week Scheme of Examination
Theory / Practical
S. Board of Study No.
Subject Code
Subject
Credit L+(T+P)/2
L 1 2 3
T 1 1 1 1 1 5
P 3 3 6
ESE 100 100 100 100 100 75 75 650
CT 20 20 20 20 20 -
TA 20 20 20 20 20 75 75
Total 140 140 140 140 140 150 150 4 4 4 4 4 2 2 24
Mech. Engg Mech. Engg Mech. Engg
563211(37)
Modeling and Analysis
3 3 3 3 3 15
558212(37) Optimization Techniques 563213(37)
Computer Added design of Machine Elements Finite element 4 Mech. Engg 558214(37) Analysis 5 Refer Table - II Elective II
6 7
Mech. Engg Mech. Engg
563221(37) 563222(37) Total
FEM Lab. CAD of Machine Elements Lab
100 250 1000
L- Lecture
T- Tutorial
P- Practical ,ESE- End Semester Exam
CT- Class Test
TA- Teacher's Assessment
Table-II
ELECTIVE II S.No. Board of Study Subject Code Subject
1 2 3
th
Mech. Engg Mech. Engg Mech. Engg
558231 (37) 563233 (37) 558232 (37)
Mechatronics Industrial Automation Computer aided Process Planning
Note (1) 1/4 of total strength of students subject to offer an elective in the college in a Particular academic session. Note (2) Choice of elective course once made for an examination cannot be changed in future examinations.
CHHATTISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Semester: M. E. II Subject:: Modeling and Analysis Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100 Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Code: 563211 (37) Total Tutorial Periods: 12
UNIT-I CAD Overview: Introduction to use of computer in Product Life Cycle. Software for mechanical engineeringCAD/CAM/CAE. UNIT-II Geometric Modeling: Parametric sketching, constrained model dimensioning, material addition and removal for extruded, revolved, swept and blended features. References and construction features of points, axis, curves, planes, surfaces and customized analysis features. Feature and sequence of feature editing. Cosmetic features, chamfers, rounds, standard holes. File formats for data transfer. Feature patterns, duplication, grouping, suppression. UNIT-III Assembly modeling: Assembly analysis tools. Top-down vs. bottom-up design. Parametric relations and design optimization parameters creation. Mass property analysis. Automatic production drawing creation and detailing. UNIT-IV Software automation and customization tools: Colors and rendering. Advanced features for non parallel blend, helical sweep, swept blend, variable section sweep, draft, ribs, sketched holes. Mechanism design and assembly. Customized design & CAD automation using user defined features UDF. UNIT-V Mechanical Design Analysis and Optimization: Design analysis for mass properties, stress, thermal stress, fatigue, fluid flow, etc using CAD/CAE packages. Optimum design of machine components using multivariable non linear optimization techniques using iterative CAD/CAE software tools. TEXT BOOKS 1. Mathematical Elements for computer graphics Roger D.F.& Adams A. 2. Geometric modeling Mortenson M.E. 3. Surface modeling for CAD CAM Choi B.K. RFERENCE BOOKS 1. Principles of interactive computer graphics Newman 2. Computational geometry for design & manufacture Faux & Pratt
CHHATTISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Semester: M. E. II Subject:: Optimization Techniques Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100 Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Code: 558212(37) Total Tutorial Periods: 12
UNIT 1 Integer and parametric programming: cutting plane method, Branch & Bound method, Sensitivity analysis Changes in bi, changes in cj, changes in aij. Parametric Programming Parametric variation in cj, bi & aij, simultaneous parametric variations.Goal Programming. UNIT 2 Non- linear Programming: langragian function, saddle point, Kuhn- tucker conditions, primal & dual problem, Quadratic programming, separable programming. Geometric programming Generalization high Kuhn- Tucker theory. UNIT 3 Dynamic Programming: Serial multistage model, backward & forward recursion, system with more than one constraints, Application of Dynamic Programming in continuous system. Direct search & Gradient methods- one dimensional & n- dimensional search. UNIT 4 Taguchi Technique: Introduction to DOE, ANOVA, F-Test, Response surface Methodology. Markov chain. UNIT 5 Introduction to modern Optimization Techniques: ANN, Fuzzy logic, Genetic Algorithms. Memetic Algorithms, Antz colony Algorithm, Tabu Search. TEXT BOOKS 1. Optimization methods in Operation Research & System Analysis- K.V. Mithal & C. Mohan.- New Age International Publishers. 2. Neural Networks & Fuzzy System- Bart Kosko- PHI publications. 3. Quality Engineering using Robust Design- M.S. Phadke, PHI publication. 4. Introduction to Operation Research by Frederick S. Hillier Gerald J. Lieberman RFERENCE BOOKS 1. Operation Research Principles and Practice- Ravindran, Phillips, solbers Wiley Publication. 2. Established Quality Control- Engene L.Grant, Richard. S. Leaven Worth- TMH 3. Neural Engineering Computation, Representation and Dynamics in Neurobiological systems.- Chris Eliasmith and Charles H. Anderson.- EEE 4. Quantitative Technique in Management N.D. Vohra, - TMH Publication. 5. Neural Network in Computer intelligence Li Min Fu - TMH.
CHHATTISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Semester: M. E. II Subject:: CAD of Machine Elements Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100 Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Code: 563213 (37) Total Tutorial Periods: 12
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION: The design process and roll of CAD types and application of design models- Computer representation of drawing, three dimensional modeling schemes, wire frames and surface representation schemes, solid modeling UNIT 2 INTRODUCTION TO CAD SOFTWARES: Writing interactive programs to solve design problems and production of drawing/ solid model using language like auto LISP/ C++, system customization and design automation, features of various solid modeling packages UNIT 3 COMPUTER ADDED DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS- Development of programs for design, drawing & plotting of Machine Elements shafts, gears, pulleys, flywheel, connecting rods etc., Interfacing with packages. UNIT 4 ENTITY MANIPULATION AND DATA STORAGE : Manipulation of the model, Model storage, Data structures, Data base considerations, Objects oriented representations, organizing data for CIM applications, Design information system. UNIT 5 EXPANDING THE CAPABILITY OF CAD: Parametric and variation modeling, Design by features, Assembly and Tolerance modeling, Tolerance representation, specification, analysis and synthesis, Rapid prototyping, Al in Design. TEXT BOOK 1. Donald Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, Computer Graphics, Prentice Hall Inc., 1992. 2. Mikell, P. Grooves and Emory W.Zimmers Jr., CAD/CAM Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing, Prentice Hall Inc., 1995. 3. William M Neumann and Robert F.Sproul, Principles of Computer Graphics, McGraw Hill Book Co., 1989. REFERENCE 1. Ibrahim Zeid, CAD/CAM Theory and Practice, McGraw Hill, International Edition, 1998. 2. Sandor G.N. and Erdman A.G., Advanced Mechanism Design Analysis and Synthesis, Prentice Hall, 1984. 3. Kenneth J, Waldron, Gary L. Kinzel, Kinematics, Dynamics and Design of Machinery, John Wiley-sons, 1999.
CHHATISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Semester: M. E. II Subject: Finite Element Analysis Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100 Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Code: 558214 (37) Total Tutorial Periods: 12
UNIT 1 Introduction to FEM: basic concepts, historical back ground, application of FEM, general description, comparison of FEM with other methods. UNIT 2 Variational approach, Galerkin Methods. Co-ordinates, basic element shapes, interpolation function. Virtual energy principle, Rayleigh - Ritz method, properties of stiffness matrix, treatment of boundary conditions, solution of system of equations, shape functions and characteristics, Basic equations of elasticity, strain displacement relations UNIT 3 1-D structural problems axial bar element stiffness matrix, load vector, temperature effects, Quadratic shape function. Analysis of Trusses Plane Truss and Space Truss elements. UNIT 4 Analysis of beams Hermite shape functions stiffness matrix Load Vector Problems 2-D problems Constant Strain Triangles, force terms, Stiffness matrix and load vector, boundary conditions. UNIT 5 Application of FEM to elasticity, structural, fluid flow and lubrication problems. Scalar field problems - 1-D Heat conduction 1-D fin element 2-D heat conduction problems Introduction to Torsional problems. Dynamic considerations, Dynamic equations consistent mass matrix Eigen Values, Eigen Vector, natural frequencies mode shapes modal analysis. TEXT BOOKS 1. The Finite Element Method -- O C Zienkiewicz, R L Taylor 2. An Introduction to the Finite Element Method J. N. Reddy, TMH Publication RFERENCE BOOKS 1. Finite Element Analysis P. Seshu, PHI Publication 2. Introduction to Finite Element Method C.S. Desai and J. F. Abel 3. Introduction to Finite Elements in Engineering T. R. Chandrupatla & A. D Belegundu, PHI Publication. 4. Applied Finite Element Analysis L. J. Segerland , John Wiley Publications
CHHATISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Semester: M. E. II Subject: Mechatronics Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100 Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Code: 558231 (37) Total Tutorial Periods: 12
UNIT 1 Introduction: Mechatronics, Measurement Systems, Basic Electrical Elements, Kerchoeffs Law, Voltage And Current Sources and Meters, Thevenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits, Alternating Current Circuit Analysis, Power in Electrical Circuits, Transformer, Impendence Matching, Grounding and Electrical Interference. UNIT 2 Semiconductor Electronics: Introduction, Semiconductor Physics as the Basis for Understanding Electronic Devices, Junction Diode, Bipolar Junction Transistor, and Field Effect Transistors UNIT 3 Microcontroller Programming and Interfacing: Microprocessor and Microcomputers, Microcontrollers, The PIC16F84 Microcontroller, Programming a PIC, Pic Basic Pro, Using Interrupts, Interfacing Common PIC Peripherals, Interfacing to the PIC. Data Acquisition: Introduction, Quantizing Theory, Analog-to-Digital Conversion, Digital-toAnalog (D/A) Conversion, UNIT 4 Sensors: Introduction, Position and Speed Measurement, Stress and Strain Measurement, Temperature Measurement Vibration and Acceleration Measurement, Pressure and Flow Measurement, Semiconductor sensors and Microelectromechanical Devices. UNIT 5 Actuators: Introduction, Electromagnetic Principles, Solenoids and Relays, Electric Motors, Motors, Stepper Motors, Selecting a Motor, Hydraulics, Pneumatics, TEXT BOOKS 1. Introduction to Mechatronics and Measurement Systems David G. Alciatore, Michael B.Histand, TMH Publication. 2. Mechatronics Principles, Concepts and Applications Dan Necsulescu, Published by Pearson Education (Singapore) RFERENCE BOOKS 1. Mechanical Measurments Thomas G. Beckwith, Roy D. Marangoni, John H. Lienhard V, Pearson Education. 2. Mechatronics -Principles, Concepts and Applications Nitaigour Premchand Mahalik, Tata McGraw-Hill Publication.
CHHATTISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Semester: M. E. I Subject: Industrial Automation Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100 Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Code: 563233 (37) Total Tutorial Periods: 12
UNIT-1 Introduction to Factory Automation and Integration: Basic Concepts, types of automation, automation strategies. Introduction to Hydraulics/Pneumatics controls and devices: Simple systems for obtaining motions in combination or in sequence by the use of hydraulic, pneumatic automation devices and controls. UNIT-2 Fluid Power Control: Fluid Power Control elements and standard graphical symbols for them, Construction and performance of fluid power generators, Hydraulic & pneumatic cylinders construction, design and mounting, Hydraulic & pneumatic valves for pressure, flow & direction control; Servo valves and simple servo systems with mechanical feedback, Simple hydraulic and pneumatic circuits. UNIT-3 Pneumatic Logic Circuits: Boolean Algebra, Truth tables, Un-complementation algorithm and Karnaugh Maps, Design of pneumatic logic circuits for a given time displacement diagram or sequence of operation. Pneumatic safety and remote control circuits and their applications to clamping, traversing and releasing operations. Program logic controllers. Modern developments. UNIT- 4 Automatic Transfer Systems: Introduction to automatic transfer, feeding and orientation devices. Automatic feeding using - vibratory and mechanical feeders, feed tracks, Escapements, Partplacement Mechanisms and Robots; Orienting devices, Designing Parts for feeding, manual and automatic assembly and Robotic Assembly. UNIT-5 Automatic loading: types of loading facilities and their purpose, Magazines, bunker loading acilities, Work flow lines and automatic transfer machines; classification; design and applications. Analysis of automated flow-lines: Reliability and efficiencies of automatic transfer machines. Assembly automation: Types of assembly systems, assembly line balancing, performance and economics of assembly systems. TEXT BOOK 1. Industrial Automation
by A.K. Gupta and S.K. Arora
REFERENCE BOOKS 1. Handbook of industrial automation By Ernest L. Hall 2. Fluid Power Control by Shearer P. ,John Wiley 3. Robotics and Flexible Automation by SR Deb
CHHATISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Semester: M. E. II Subject: Computer Aided Process Planning Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100 Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Code: 558232 (37) Total Tutorial Periods: 12
UNIT 1 Introduction to CAPP: Information requirement for process planning system, Role of process planning, advantages of conventional process planning over CAPP, Structure of Automated process plannning system, feature recognition, methods. UNIT 2 Generative CAPP system: Importance, principle of Generative CAPP system, automation of logical decisions, Knowledge based systems, Inference Engine, implementation, benefits. Retrieval CAPP system: Significance, group technology, structure, relative advantages, implementation, and applications. UNIT 3 Selection of manufacturing sequence: Significance, alternative-manufacturing processes, reduction of total set-up cost for a particular sequence, quantitative methods for optimal selection, examples. UNIT 4 Determination of machining parameters: reasons for optimal selection of machining parameters, effect of parameters on production rate, cost and surface quality, different approaches, advantages of mathematical approach over conventional approach, solving optimization models of machining processes. UNIT 5 Generation of tool path: Simulation of machining processes, NC tool path generation, graphical implementation, determination of optimal index positions for executing fixed sequence, quantitative methods. TEXT BOOKS 1. Automation , Production systems and Computer Integrated Manufacturing System Mikell P.Groover, PHI Publication. 2. Computer Aided Engineering David Bedworth, TMH Publishers RFERENCE BOOKS 1. Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing Dr.Sadhu Singh, Khanna Publisher
CHHATTISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Semester: M. E. II Subject: FEM Lab Total Practical Periods: 40 Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 75 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Code: 563221 (37)
Analysis of Mechanical Components Use of FEA Packages, like ANSYS NASTRON etc., Excesses shell include FEA analysis of i) ii) iii) iv) v) Machine elements under static loads Heat transfer in mechanical systems Determination of natural frequency Axi-Symmetric Non-linear systems
Use of kinematics and dynamics simulation software like ADAMS software. Analysis of velocity and acceleration for mechanical linkages of different mechanisms.
CHHATTISGARH SWAMI VIVEKANAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, BHILAI (C.G.)
Semester: M. E. II Subject: CAD of Machine Elements Lab Total Practical Periods: 40 Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 75 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Code: 563222 (37)
Development of programs for design, drawing & plotting of Machine Elements using language like auto LISP/ C++.
You might also like
- Cad - CamDocument27 pagesCad - CamBhuvanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Elective - IDocument33 pagesElective - IMohit RanaNo ratings yet
- Chhatisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical UniversityDocument6 pagesChhatisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical UniversityDr Abhijeet GangulyNo ratings yet
- M.E. Computer Aided Design SyllabusDocument50 pagesM.E. Computer Aided Design SyllabusJoswa CaxtonNo ratings yet
- ME CAD SyllabusDocument50 pagesME CAD Syllabussubha_aeroNo ratings yet
- Saurashtra University: Me Mech (Cad/Cam) 1Document19 pagesSaurashtra University: Me Mech (Cad/Cam) 1Raj K PatelNo ratings yet
- M.E. Engineering DesignDocument47 pagesM.E. Engineering DesignSms RajaNo ratings yet
- VTU SyllabusDocument39 pagesVTU SyllabusAnilNo ratings yet
- Scheme & Syllabi: (Total Credits 70)Document38 pagesScheme & Syllabi: (Total Credits 70)BalvinderNo ratings yet
- Engineering DesignDocument34 pagesEngineering DesignEmmanuel NicholasNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3jpbhimaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Sem Mtech Cad Cam MpccetDocument5 pages3 Sem Mtech Cad Cam MpccetEL-Sayed HamedNo ratings yet
- Anna University EDDocument48 pagesAnna University EDSivaji SivaNo ratings yet
- Karanataka State Open University: M Tech in Mechanical (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)Document35 pagesKaranataka State Open University: M Tech in Mechanical (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)nav1278No ratings yet
- 4-1 Syllabus PDFDocument8 pages4-1 Syllabus PDFJohn CenaNo ratings yet
- Anna University, Chennai: Affiliated InstitutionsDocument36 pagesAnna University, Chennai: Affiliated InstitutionsAnonymous RCbfTbNo ratings yet
- Course Outline PDFDocument5 pagesCourse Outline PDFbukhariNo ratings yet
- Pgdi (Cad Cam Cae) Semester IDocument7 pagesPgdi (Cad Cam Cae) Semester IPRADEEP NNo ratings yet
- M.E Design 2008 SyllabusDocument35 pagesM.E Design 2008 SyllabusmeindyaNo ratings yet
- Me Manufacturing Curriculum-2Document11 pagesMe Manufacturing Curriculum-2Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- 2nd Semester SyllabusDocument6 pages2nd Semester SyllabusNitin RathoreNo ratings yet
- MTech Machine Design PDFDocument41 pagesMTech Machine Design PDFswapnilNo ratings yet
- M Tech. Design Mnnit2010Document6 pagesM Tech. Design Mnnit2010ambujsharma08No ratings yet
- Computer Aided DesignDocument2 pagesComputer Aided DesignKeyur TNo ratings yet
- ME Engineering Design-2013 Syllabus Anna UnivDocument28 pagesME Engineering Design-2013 Syllabus Anna Univshibumankulath4727No ratings yet
- Final BTech MechanicalDocument31 pagesFinal BTech MechanicalAniket GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Mahmaya Techanical University, Noida (U. P) : M. Tech (Regular Programme)Document31 pagesMahmaya Techanical University, Noida (U. P) : M. Tech (Regular Programme)durgeshrsharmaNo ratings yet
- Fem CoDocument5 pagesFem Comuralict2009No ratings yet
- Shri G. S. Institute of Technology and ScienceDocument32 pagesShri G. S. Institute of Technology and Scienceabhaymvyas1144No ratings yet
- 3 0 3 3 0 3 3 0 3 3 0 3 Elective - I 3 0 3Document13 pages3 0 3 3 0 3 3 0 3 3 0 3 Elective - I 3 0 3Swaroop KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Science EngineeringDocument16 pagesComputer Science EngineeringChinmay MokhareNo ratings yet
- BEBI2 CurriculumDocument14 pagesBEBI2 CurriculumRagnar RagnarsonNo ratings yet
- Panjab University, Chandigarh: Syllabi of First Year Courses in B.E. (Computer Science and Engineering)Document32 pagesPanjab University, Chandigarh: Syllabi of First Year Courses in B.E. (Computer Science and Engineering)Anonymous t97R3yqNo ratings yet
- Nirma University Institute of Technology School of EngineeringDocument30 pagesNirma University Institute of Technology School of EngineeringKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusAnonymous 4h9p1EIQYSNo ratings yet
- Cad SyllabusDocument5 pagesCad SyllabusSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- PDD Syllabus Anna UniversityDocument41 pagesPDD Syllabus Anna UniversityVenkatakrishnan NatchiappanNo ratings yet
- M.Tech - CAD - CAM - Syllabus UpdatedDocument47 pagesM.Tech - CAD - CAM - Syllabus Updatedgaurav tripathiNo ratings yet
- Mahamaya Technical University Noida: SyllabusDocument14 pagesMahamaya Technical University Noida: SyllabussmsmbaNo ratings yet
- University of Kerala: Syllabus For Vii SemesterDocument43 pagesUniversity of Kerala: Syllabus For Vii SemesterSreekanthKottavilayilNo ratings yet
- E-4 Me Sem-1 SyllabusDocument14 pagesE-4 Me Sem-1 SyllabusraviNo ratings yet
- Me Manufacturing CurriculumDocument37 pagesMe Manufacturing CurriculumJeyaram kumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Engineering 2Document16 pagesComputer Science Engineering 2Chandrashekhar Goswami100% (1)
- CAD CAM Final 1Document15 pagesCAD CAM Final 1ram00345No ratings yet
- M.E. MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING AU SyllabusDocument35 pagesM.E. MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING AU SyllabusJoswa CaxtonNo ratings yet
- Core Courses: Med611 Stress AnalysisDocument10 pagesCore Courses: Med611 Stress AnalysisPiyush SankhalaNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesCad Cam Syllabus PDFBrijesh Kumar ChaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- Advanced ManufacturingDocument13 pagesAdvanced ManufacturingnagNo ratings yet
- The System Designer's Guide to VHDL-AMS: Analog, Mixed-Signal, and Mixed-Technology ModelingFrom EverandThe System Designer's Guide to VHDL-AMS: Analog, Mixed-Signal, and Mixed-Technology ModelingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Up and Running with AutoCAD 2012: 2D Drawing and ModelingFrom EverandUp and Running with AutoCAD 2012: 2D Drawing and ModelingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Machine Intelligence and Pattern RecognitionFrom EverandMachine Intelligence and Pattern RecognitionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Finite Element Analysis for Design Engineers, Second EditionFrom EverandFinite Element Analysis for Design Engineers, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- In Solid State Contaminants AreDocument1 pageIn Solid State Contaminants AreMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- UsgepDocument1 pageUsgepMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- CBDHHSDocument1 pageCBDHHSMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function Tests: Blood TestDocument2 pagesKidney Function Tests: Blood TestMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Hot Rolling: Plate MillsDocument4 pagesHot Rolling: Plate MillsMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- JdkksDocument1 pageJdkksMohammed Abu Sufian0% (1)
- Ms. MenushaDocument11 pagesMs. MenushaMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Jamal Sir CVDocument4 pagesJamal Sir CVMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Prof. RubayetDocument13 pagesProf. RubayetMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Abstract (Times New Roman, 11 Point-Bold, 200 %, Center)Document1 pageAbstract (Times New Roman, 11 Point-Bold, 200 %, Center)Mohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- 35 Bcs Exam RulesDocument5 pages35 Bcs Exam RulesMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Decoupling: Decoupling Get The Facts: Pipeline SafetyDocument6 pagesDecoupling: Decoupling Get The Facts: Pipeline SafetyMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Paper-I Marks-100Document1 pageMechanical Engineering Paper-I Marks-100Mohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Dr. Md. Shofiqul Islam: Shofiqul@eee - Buet.ac - BDDocument8 pagesDr. Md. Shofiqul Islam: Shofiqul@eee - Buet.ac - BDMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- BCS - Exam DetailsDocument4 pagesBCS - Exam DetailsMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- PRL!LL!LF / - T/ - 8b - (/5f '"T - ) / o /) J - O8 - o 8: 11 Gilr Gi TSDocument5 pagesPRL!LL!LF / - T/ - 8b - (/5f '"T - ) / o /) J - O8 - o 8: 11 Gilr Gi TSMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electricity/Electronics: Description Get It FromDocument12 pagesBasics of Electricity/Electronics: Description Get It FromMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument5 pagesBiotechnology and Pharmaceutical IndustryNaveenraj SNo ratings yet
- 3827-E10-062 - Two Position Valve - DDocument4 pages3827-E10-062 - Two Position Valve - DMohamed Elsaid El ShallNo ratings yet
- Tronair CatalogDocument122 pagesTronair CatalogPhilMadezNo ratings yet
- Project Ideas PDDocument56 pagesProject Ideas PDrobiromasNo ratings yet
- Fcde 0110uk PDFDocument580 pagesFcde 0110uk PDFbtsgr parkerNo ratings yet
- Cdi t2 12 Adv SampleDocument6 pagesCdi t2 12 Adv SampleTroy ParkerNo ratings yet
- Electro Pneumatic TrainerDocument2 pagesElectro Pneumatic TrainerAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- Accesorios DyniscoDocument3 pagesAccesorios DyniscomigueldemacrolabNo ratings yet
- Damper Technology BrochureDocument8 pagesDamper Technology Brochurejoy100% (1)
- Course Content HPCDocument4 pagesCourse Content HPCjaya1945No ratings yet
- อุปกรณ์นิวเมติกส์ BurkertDocument26 pagesอุปกรณ์นิวเมติกส์ BurkertParinpa KetarNo ratings yet
- 7787G Longslit1013P .EDocument151 pages7787G Longslit1013P .EAhmed Moemen Ali Elrouby MoemenNo ratings yet
- PNEUMATİCDocument13 pagesPNEUMATİCAyşenur ÇetinNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manualual Vacuum Blasting - 178941Document170 pagesInstruction Manualual Vacuum Blasting - 178941sajsigalomaNo ratings yet
- OEM Compact Pressure Switch Socket Wrench Mounting Model PSM01Document3 pagesOEM Compact Pressure Switch Socket Wrench Mounting Model PSM01Cornel BordeiNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling System Operetaion and Maintenance InstructionDocument162 pagesAsh Handling System Operetaion and Maintenance InstructionHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- 0 Basic Principle of Pneumatic CircuitsDocument76 pages0 Basic Principle of Pneumatic CircuitsBayu RafliNo ratings yet
- Rail Brochure PDFDocument11 pagesRail Brochure PDF1thirdNo ratings yet
- Alarm Trip Setting List 8Document20 pagesAlarm Trip Setting List 8Vraja KisoriNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Pneumatic Sheet Metal CuDocument3 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Pneumatic Sheet Metal CuMohammed Abdul KaleemNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Auto Feed Sheet Cutting MachineDocument5 pagesPneumatic Auto Feed Sheet Cutting MachineVigneshwaran Srinivasan100% (1)
- Papcel: Coach Agitators CA Main Parts AuxiliariesDocument65 pagesPapcel: Coach Agitators CA Main Parts AuxiliariesmiguelamenozaNo ratings yet
- C Part4 Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument12 pagesC Part4 Hydraulics and PneumaticszsmithNo ratings yet
- Service Totalgas 8060Document59 pagesService Totalgas 8060William Oswaldo0% (1)
- HAZARDS Pneumatic TestDocument4 pagesHAZARDS Pneumatic TesthazopmanNo ratings yet
- Arrow Neumatic Filtering SystemsDocument135 pagesArrow Neumatic Filtering SystemsDavidRiveraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PneumaticDocument19 pagesIntroduction To PneumaticKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Simbolos NeumaticosDocument7 pagesSimbolos NeumaticosSergio Martínez LópezNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Pneumatic Punching MachineDocument3 pagesDesign and Development of Pneumatic Punching MachineUjjwal UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Robot GeometryDocument50 pagesRobot Geometrymk_chandruNo ratings yet