Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conf Vlan
Uploaded by
tazer11Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conf Vlan
Uploaded by
tazer11Copyright:
Available Formats
Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)
Document ID: 98154
Contents
Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Understand VTP VTP Configuration Guidelines VTP Configuration on Catalyst Switches Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Cisco IOS Software/Catalyst 4500/4000 Cisco IOS Software (Supervisor Engine III/Supervisor Engine IV), Catalyst 2950, 3550, and 3750 Series Switches Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, or 6500/6000 Series CatOS Catalyst 2900XL, 3500XL, 2950, and 3550 Catalyst Express 500 Series Switches Practical Examples Troubleshoot VTP Related Information
Introduction
This document provides information on how to configure VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP). VTP reduces administration in a switched network. When you configure a new VLAN on one VTP server, the VLAN is distributed through all switches in the domain. This reduces the need to configure the same VLAN everywhere. VTP is a Ciscoproprietary protocol that is available on most of the Cisco Catalyst series products.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Understand VTP
Refer to Understanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) for more information on VTP.
VTP Configuration Guidelines
This section provides some guidelines for the configuration of VTP in the network. All switches have the same the VTP domain name, unless the network design insists for different VTP domains. Note: Trunk negotiation does not work across VTP domains. Refer to the Data Traffic Blocked between VTP Domains section of Troubleshooting VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) for more information. All switches in a VTP domain must run the same VTP version. All switches in a VTP domain has the same VTP password, if there is any. All VTP Server switch(es) should have the same configuration revision number and it should also be the highest in the domain. When you move a VTP mode of a switch from Transparent to Server, VLANs configured on the VTP Transparent switch should exist on the Server switch.
VTP Configuration on Catalyst Switches
This section provides some basic commands in order to configure VTP on the most commonly used Catalyst switches. Note: The Catalyst 2948GL3 and Catalyst 4908GL3 Layer 3 (L3) switches do not support several Layer 2 (L2)oriented protocols that are found on other Catalyst switches. Such protocols include VTP, DTP, and Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP).
Catalyst 6500/6000 Series Cisco IOS Software/Catalyst 4500/4000 Cisco IOS Software (Supervisor Engine III/Supervisor Engine IV), Catalyst 2950, 3550, and 3750 Series Switches
There are two methods that you can use in order to configure VTP, as this section shows. Method 2 (the global configuration mode method) is not available in earlier software on Catalyst 6500 series switches that run Cisco IOS Software. 1. In VLAN database mode: In Cisco IOS Software, you can configure the VTP domain name, the VTP mode, and the VLANs in VLAN configuration mode. a. In EXEC mode, issue this command in order to enter VLAN configuration mode:
Router#vlan database ! Issue this command in privileged EXEC mode, ! not in global configuration mode. Router(vlan)# ! This is VLAN configuration mode.
b. Issue this command in order to set the VTP domain name:
Router(vlan)#vtp domain domainname
c. Issue this command in order to set the VTP mode:
Router(vlan)#vtp {client | server | transparent}
d. Issue the exit command in order to exit VLAN configuration mode. Note: The end and the CtrlZ commands do not work in this mode.
Router(vlan)#end Router(vlan)#^Z % Invalid input detected at '^' marker. Router(vlan)# Router(vlan)#exit APPLY completed. Exiting.... Router#
2. In global configuration mode: In Cisco IOS Software global configuration mode, you can configure all VTP parameters with Cisco IOS Software commands. This is the command format:
Router(config)#vtp ? domain file interface mode password pruning version Set the name of the VTP administrative domain. Configure IFS filesystem file where VTP configuration is stored. Configure interface as the preferred source for the VTP IP updater address. Configure VTP device mode Set the password for the VTP administrative domain Set the administrative domain to permit pruning Set the administrative domain to VTP version
3. Issue these commands in order to monitor VTP operation and status:
Router#show vtp status Router#show vtp counters
Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, or 6500/6000 Series CatOS
Complete these steps: 1. Issue this command in order to set the domain name:
set vtp domain name
Note: When you configure a new switch, the VTP domain name should be configured before you create any nondefault VLANs. 2. Issue this command in order to set the mode:
set vtp mode [server | client | transparent]
3. Issue these commands in order to monitor the VTP operation and status:
show vtp domain show vtp statistics
Catalyst 2900XL, 3500XL, 2950, and 3550
Complete these steps: 1. Issue these commands from the VLAN database mode: Note: This is similar to the method for Cisco 6500 series switches that run Cisco IOS Software.
vtp [client | server | transparent] vtp domain name
2. From enable mode, issue these commands in order to monitor VTP operation:
show vtp counters show vtp status
Note: The Catalyst 2900XL series switches with Cisco IOS Software Release 11.2(8)SA4 and later support VTP protocol. The Cisco IOS Software Release 11.2(8)SA3 and earlier code do not support VTP protocol on Catalyst 2900XL series switches.
Catalyst Express 500 Series Switches
Catalyst Express 500 series switches support only VTP transparent mode. There is currently no support for VTP client or VTP server mode. The user must manually configure all VLANs that are used on the switch. Open the Switch Management, choose Configure > VLAN > Create, and fill out the available fields in order to configure a VLAN on a Catalyst Express 500 series switch. Refer to the Create, Modify, and Delete VLANs section of Customization for more information.
Practical Examples
Example 1: This example involves two Catalyst 4000 switches that are connected by a Fast Ethernet link: 1. Bing is a new switch that has no VTP domain name and no VLAN. Clic is a switch that currently exists and runs with 12 VLANs in the VTP domain test. 2. In this sample output from the show vtp domain command, you can see that the VTP version is set at 2. This means that the switch is VTP V2capable. However, the switch does not run VTP V2 in this case. The switch only runs VTP V2 if the V2 mode is enabled with the set vtp v2 enable command:
bing (enable) show vtp domain Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode Password 1 2 server Vlancount Maxvlanstorage Config Revision Notifications 5 1023 0 disabled Last Updater V2 Mode Pruning PruneEligible on Vlans 0.0.0.0 disabled disabled 21000 bing (enable)
bing (enable) show vlan VLAN Name Status IfIndex Mod/Ports, Vlans 1 default active 67 2/12,2/448 3/16 1002 fddidefault active 68 1003 tokenringdefault active 71 1004 fddinetdefault active 69 1005 trnetdefault active 70 clic (enable) show vtp domain
Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode Password test 1 2 server Vlancount Maxvlanstorage Config Revision Notifications 12 1023 11 disabled Last Updater V2 Mode Pruning PruneEligible on Vlans 0.0.0.0 disabled disabled 21000 clic (enable) show vlan VLAN 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 10 1002 1003 1004 1005 Name default VLAN0002 VLAN0003 VLAN0004 VLAN0005 VLAN0006 VLAN0007 VLAN0010 fddidefault tokenringdefault fddinetdefault trnetdefault Status active active active active active active active active active active active active IfIndex 65 77 78 79 73 74 76 80 66 69 67 68 Mod/Ports, Vlans 2/12,2/450 2/3
68
3. At this stage, a trunk is created between the two switches. Notice how they synchronize and watch the VTP packet exchange:
MAC 005014BB63FD is clic MAC 003019798CFD is bing
4. Clic sends a summary advertisement to bing. Bing learns the VTP domain name from this packet, in FRAME 1 in this sample output:
! On bing: received vtp packet: mNo = 2 pNo = 1 VTP: i summary, domain = test, rev = 11, followers = 0 ! This indicates that bing has received its ! first summary advertisement. domain change notification sent VTP: transitioning from null to test domain ! This is where bing gets the VTP domain name. VTP: summary packet rev 11 greater than domain test rev 0
VTP: domain test currently not in updating state VTP: summary packet with followers field zero
FRAME 1 DLC: DLC Header DLC: DLC: Frame 1988 arrived at 15:01:00.1223; frame size is 99 (0063 hex) bytes. DLC: Destination = Multicast 01000CCCCCCC DLC: Source = Station 005014BB63FD DLC: 802.3 length = 85 DLC: LLC: LLC Header LLC: LLC: DSAP Address = AA, DSAP IG Bit = 00 (Individual Address) LLC: SSAP Address = AA, SSAP CR Bit = 00 (Command) LLC: Unnumbered frame: UI LLC: SNAP: SNAP Header SNAP: SNAP: Vendor ID = Cisco1 SNAP: Type = 2003 (VTP) SNAP: VTP: Cisco Virtual Trunk Protocol (VTP) Packet VTP: VTP: Version = 1 VTP: Message type = 0x01 (SummaryAdvert) VTP: Number of SubsetAdvert messages = 0 VTP: Length of management domain name = 4 VTP: Management domain name = "test" VTP: Number of Padding bytes = 28 VTP: Configuration revision number = 0x0000000b VTP: Updater Identity IP address = 0.0.0.0 VTP: Update Timestamp = "930525053753" VTP: MD5 Digest value = 0x857610862F3015F0 VTP: 0x220A52427247A7A0
5. With the trace command set, bing receives a summary advertisement with no followers. Therefore, bing updates its domain name and sends advertisement requests to obtain the VLAN information, in FRAME 2 in this sample output:
! On bing: VTP: tx vtp request, domain test, start value 0 ! This is where the advertisement request is sent.
FRAME 2 DLC: DLC Header DLC: DLC: Frame 1683 arrived at 17:38:55.9383; frame size is 60 (003C hex) bytes. DLC: Destination = Multicast 01000CCCCCCC DLC: Source = Station 003019798CFD DLC: 802.3 length = 46 DLC: LLC: LLC Header LLC: LLC: DSAP Address = AA, DSAP IG Bit = 00 (Individual Address) LLC: SSAP Address = AA, SSAP CR Bit = 00 (Command) LLC: Unnumbered frame: UI LLC: SNAP: SNAP Header SNAP: SNAP: Vendor ID = Cisco1 SNAP: Type = 2003 (VTP)
SNAP: VTP: Cisco Virtual Trunk Protocol (VTP) Packet VTP: VTP: Version = 1 VTP: Message type = 0x03 (AdvertRequest) VTP: Reserved VTP: Length of management domain name = 4 VTP: Management domain name = "test" VTP: Padding bytes = 28 VTP: Start value = 0 (all VLANs)
6. Clic sends another summary advertisement with field followers to VLAN 1. The subset advertisement that contains all VLANs, in FRAME 3 in this output, follows this packet. Then, bing configures all the VLANs:
! On bing: received vtp packet: mNo = 2 pNo = 1 VTP: i summary, domain = test, rev = 11, followers = 1 ! Bing has received its second summary advertisement. VTP: domain test, current rev = 0 found for summary pkt VTP: summary packet rev 11 greater than domain test rev 0 ! This configuration revision is higher than that on bing. VTP: domain test currently not in updating state received vtp packet: mNo = 2 pNo = 1 VTP: i subset, domain = test, rev = 11, seq = 1, length = 344 ! Bing has received its subset advertisement. VTP: domain test, current rev = 0 found for subset pkt domain change notification sent vlan 1 unknown tlv change notification sent vlan 2 unknown tlv change notification sent vtp_vlan_change_notification: vlan = 2, mode = 1 (ADD,ACTIVE), mNo = 2 pNo = 1 vlan = 2 vlan 3 unknown tlv change notification sent vtp_vlan_change_notification: vlan = 3, mode = 1 (ADD,ACTIVE), mNo = 2 pNo = 1 vlan = 3 vlan 4 unknown tlv change notification sent vtp_vlan_change_notification: vlan = 4, mode = 1 (ADD,ACTIVE), mNo = 2 pNo = 1 vlan = 4 vlan 5 unknown tlv change notification sent vtp_vlan_change_notification: vlan = 5, mode = 1 (ADD,ACTIVE), mNo = 2 pNo = 1 vlan = 5 vlan 6 unknown tlv change notification sent vtp_vlan_change_notification: vlan = 6, mode = 1 (ADD,ACTIVE), mNo = 2 pNo = 1 vlan = 6 vlan 7 unknown tlv change notification sent vtp_vlan_change_notification: vlan = 7, mode = 1 (ADD,ACTIVE), mNo = 2 pNo = 1 vlan = 7
FRAME 3 DLC: DLC Header DLC: DLC: Frame 2008 arrived at 15:01:03.9661; frame size is 99 (0063 hex) bytes. DLC: Destination = Multicast 01000CCCCCCC DLC: Source = Station 003019798CFD DLC: 802.3 length = 85 DLC: LLC: LLC Header
LLC: LLC: DSAP Address = AA, DSAP IG Bit = 00 (Individual Address) LLC: SSAP Address = AA, SSAP CR Bit = 00 (Command) LLC: Unnumbered frame: UI LLC: SNAP: SNAP Header SNAP: SNAP: Vendor ID = Cisco1 SNAP: Type = 2003 (VTP) SNAP: VTP: Cisco Virtual Trunk Protocol (VTP) Packet VTP: VTP: Version = 1 VTP: Message type = 0x01 (SummaryAdvert) VTP: Number of SubsetAdvert messages = 1 ! Here are the numbers. VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: DLC: Length of management domain name Management domain name Number of Padding bytes Configuration revision number Updater Identity IP address Update Timestamp MD5 Digest value = = = = = = = 4 "test" 28 0x0000000b 0.0.0.0 "930525053753" 0x857610862F3015F0 0x220A52427247A7A0
DLC Header DLC: DLC: Frame 2009 arrived at 15:01:03.9664; frame size is 366 (016E hex) bytes DLC: Destination = Multicast 01000CCCCCCC DLC: Source = Station 003019798CFD DLC: 802.3 length = 352 DLC: LLC: LLC Header LLC: LLC: DSAP Address = AA, DSAP IG Bit = 00 (Individual Address) LLC: SSAP Address = AA, SSAP CR Bit = 00 (Command) LLC: Unnumbered frame: UI LLC: SNAP: SNAP Header SNAP: SNAP: Vendor ID = Cisco1 SNAP: Type = 2003 (VTP) SNAP: VTP: Cisco Virtual Trunk Protocol (VTP) Packet VTP: VTP: Version = 1 VTP: Message type = 0x02 (SubsetAdvert) VTP: Sequence number = 1 VTP: Management Domain Name length = 4 VTP: Management Domain Name = "test" VTP: Number of Padding bytes = 28 VTP: Configuration revision number = 0x0000000b VTP: VTP: VLAN Information Field # 1: VTP: VLAN information field length = 20 VTP: VLAN Status = 00 (Operational) VTP: VLAN type = 1 (Ethernet) VTP: Length of VLAN name = 7 VTP: ISL VLANid = 1 VTP: MTU size = 1500 VTP: 802.10 SAID field = 100001 VTP: VLAN Name = "default" VTP: # padding bytes in VLAN Name = 1 VTP:
VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP: VTP:
VLAN Information Field # 2: VLAN information field length VLAN Status VLAN type Length of VLAN name ISL VLANid MTU size 802.10 SAID field VLAN Name # padding bytes in VLAN Name VLAN Information Field # 3: VLAN information field length VLAN Status VLAN type Length of VLAN name ISL VLANid MTU size 802.10 SAID field VLAN Name # padding bytes in VLAN Name VLAN Information Field # 4: VLAN information field length VLAN Status VLAN type Length of VLAN name ISL VLANid MTU size 802.10 SAID field VLAN Name # padding bytes in VLAN Name VLAN Information Field # 5: VLAN information field length VLAN Status VLAN type Length of VLAN name ISL VLANid MTU size 802.10 SAID field VLAN Name # padding bytes in VLAN Name VLAN Information Field # 6: VLAN information field length VLAN Status VLAN type Length of VLAN name ISL VLANid MTU size 802.10 SAID field VLAN Name # padding bytes in VLAN Name VLAN Information Field # 7: VLAN information field length VLAN Status VLAN type Length of VLAN name ISL VLANid MTU size 802.10 SAID field VLAN Name # padding bytes in VLAN Name
= = = = = = = = =
20 00 (Operational) 1 (Ethernet) 8 2 1500 100002 "VLAN0002" 0
= = = = = = = = =
20 00 (Operational) 1 (Ethernet) 8 3 1500 100003 "VLAN0003" 0
= = = = = = = = =
20 00 (Operational) 1 (Ethernet) 8 4 1500 100004 "VLAN0004" 0
= = = = = = = = =
20 00 (Operational) 1 (Ethernet) 8 5 1500 100005 "VLAN0005" 0
= = = = = = = = =
20 00 (Operational) 1 (Ethernet) 8 6 1500 100006 "VLAN0006" 0
= = = = = = = = =
20 00 (Operational) 1 (Ethernet) 8 7 1500 100007 "VLAN0007" 0
VTP: VLAN Information Field # 8: VTP: VLAN information field length = 20 VTP: VLAN Status = 00 (Operational) VTP: VLAN type = 1 (Ethernet) VTP: Length of VLAN name = 8 VTP: ISL VLANid = 10 VTP: MTU size = 1500 VTP: 802.10 SAID field = 100010 VTP: VLAN Name = "VLAN0010" VTP: # padding bytes in VLAN Name = 0 VTP: VTP: VLAN Information Field # 9: VTP: VLAN information field length = 32 VTP: VLAN Status = 00 (Operational) VTP: VLAN type = 2 (FDDI) VTP: Length of VLAN name = 12 VTP: ISL VLANid = 1002 VTP: MTU size = 1500 VTP: 802.10 SAID field = 101002 VTP: VLAN Name = "fddidefault" VTP: # padding bytes in VLAN Name = 0 VTP: Reserved 8 bytes VTP: VTP: VLAN Information Field # 10: VTP: VLAN information field length = 40 VTP: VLAN Status = 00 (Operational) VTP: VLAN type = 3 (TokenRing) VTP: Length of VLAN name = 18 VTP: ISL VLANid = 1003 VTP: MTU size = 1500 VTP: 802.10 SAID field = 101003 VTP: VLAN Name = "tokenringdefault" VTP: # padding bytes in VLAN Name = 2 VTP: Reserved 8 bytes VTP: VTP: VLAN Information Field # 11: VTP: VLAN information field length = 36 VTP: VLAN Status = 00 (Operational) VTP: VLAN type = 4 (FDDINet) VTP: Length of VLAN name = 15 VTP: ISL VLANid = 1004 VTP: MTU size = 1500 VTP: 802.10 SAID field = 101004 VTP: VLAN Name = "fddinetdefault" VTP: # padding bytes in VLAN Name = 1 VTP: Reserved 8 bytes VTP: VTP: VLAN Information Field # 12: VTP: VLAN information field length = 36 VTP: VLAN Status = 00 (Operational) VTP: VLAN type = 5 (TRNet) VTP: Length of VLAN name = 13 VTP: ISL VLANid = 1005 VTP: MTU size = 1500 VTP: 802.10 SAID field = 101005 VTP: VLAN Name = "trnetdefault" VTP: # padding bytes in VLAN Name = 3 VTP: Reserved 8 bytes
7. At this point, both switches are synchronized:
bing (enable) show vtp domain Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode Password test 1 2 server
Vlancount Maxvlanstorage Config Revision Notifications 12 1023 11 disabled Last Updater V2 Mode Pruning PruneEligible on Vlans 0.0.0.0 disabled disabled 21000 bing (enable) show vlan VLAN Name Status IfIndex Mod/Ports, Vlans 1 default active 127 2/248 3/16 2 VLAN0002 active 132 3 VLAN0003 active 133 4 VLAN0004 active 134 5 VLAN0005 active 135 6 VLAN0006 active 136 7 VLAN0007 active 137 10 VLAN0010 active 138 1002 fddidefault active 128 1003 tokenringdefault active 131 1004 fddinetdefault active 129 1005 trnetdefault active 130
Example 2: This example shows how to verify the VTP configuration on a Catalyst 6000 that runs Cisco IOS Software:
Router#show vtp status VTP Version: 2 Configuration Revision: 247 Maximum VLANs supported locally: 1005 Number of existing VLANs: 33 VTP Operating Mode: Client VTP Domain Name: Lab_Network VTP Pruning Mode: Enabled VTP V2 Mode: Disabled VTP Traps Generation: Disabled MD5 digest: 0x45 0x52 0xB6 0xFD 0x63 0xC8 0x49 0x80 Configuration last modified by 0.0.0.0 at 81299 15:04:49 Router#
Example 3: This example shows how to display VTP statistics on a Catalyst 6000 that runs Cisco IOS Software:
Router#show vtp counters VTP statistics: Summary advertisements received: 7 Subset advertisements received: 5 Request advertisements received: 0 Summary advertisements transmitted: 997 Subset advertisements transmitted: 13 Request advertisements transmitted: 3 Number of config revision errors: 0 Number of config digest errors: 0 Number of V1 summary errors: 0 VTP pruning statistics:
Trunk
Summary advts received from onpruningcapable device Fa5/8 43071 42766 5
Join Transmitted Join Received
Troubleshoot VTP
Refer to Troubleshooting VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) for information to troubleshoot VTP.
Related Information
LAN Product Support LAN Switching Technology Support Technical Support & Documentation Cisco Systems
Contacts & Feedback | Help | Site Map 2011 2012 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms & Conditions | Privacy Statement | Cookie Policy | Trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.
Updated: Nov 29, 2011
Document ID: 98154
You might also like
- Lab Worksheet 4: VTP ConfigurationDocument7 pagesLab Worksheet 4: VTP ConfigurationCj LlemosNo ratings yet
- Creating VLANsDocument31 pagesCreating VLANsjt2496No ratings yet
- Configuring VTP, Vlans, Vlan Trunks, and VmpsDocument50 pagesConfiguring VTP, Vlans, Vlan Trunks, and VmpsapNo ratings yet
- VLAN and VTPDocument13 pagesVLAN and VTPرفال الجهنيNo ratings yet
- 2creating Ethernet VLANs On Catalyst Switches - CiscoDocument39 pages2creating Ethernet VLANs On Catalyst Switches - Ciscomoises benjumeNo ratings yet
- VTP MigrationDocument12 pagesVTP MigrationSteven TrungNo ratings yet
- VTP PDFDocument37 pagesVTP PDFmonique0077620No ratings yet
- 4.2.1 Default VTP ConfigurationsDocument9 pages4.2.1 Default VTP ConfigurationsmmasliniaNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)Document36 pagesUnderstanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)Raj100% (1)
- Catalyst Switch How To Make VlansDocument6 pagesCatalyst Switch How To Make VlansAileen CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) : Document ID: 10558Document36 pagesUnderstanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) : Document ID: 10558John PeterNo ratings yet
- PT Activity 4.3.3: Configure VTP: Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesPT Activity 4.3.3: Configure VTP: Topology DiagramWayne E. BollmanNo ratings yet
- 0.2 VTPv2 and v3Document4 pages0.2 VTPv2 and v3Kv142 KvNo ratings yet
- Ccnav3.3 308Document32 pagesCcnav3.3 308Tung HoangNo ratings yet
- Configuring Virtual Lans: Configure Vlan Trunk ProtocolDocument10 pagesConfiguring Virtual Lans: Configure Vlan Trunk Protocolitaliani2009100% (2)
- Lab # 06 Object: in This Lab, You Will Learn About VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and Its ImplementationDocument5 pagesLab # 06 Object: in This Lab, You Will Learn About VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and Its ImplementationarshamahNo ratings yet
- Cisco Catalyst 2960 Series Switches VlansDocument31 pagesCisco Catalyst 2960 Series Switches VlansEzequiel AraujoNo ratings yet
- VLANDocument31 pagesVLANPrashant MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Ccna3 CommandsDocument54 pagesCcna3 CommandsDiatomspinalcordNo ratings yet
- Configure VTP Server and Client in SwitchDocument4 pagesConfigure VTP Server and Client in SwitchPerbz JayNo ratings yet
- Configuring VTP: Understanding How VTP WorksDocument12 pagesConfiguring VTP: Understanding How VTP WorksIamSajid JatoiNo ratings yet
- Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN TrunkingDocument16 pagesLab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN TrunkingMoh diakNo ratings yet
- CCNP3 Lab 2 1 enDocument17 pagesCCNP3 Lab 2 1 enCarlos LopezNo ratings yet
- Cisco VLAN Trunking ProtocolDocument3 pagesCisco VLAN Trunking ProtocolHe RoNo ratings yet
- Lab4.1 - VLAN - VTP - DTPDocument3 pagesLab4.1 - VLAN - VTP - DTPshadowdragon112kNo ratings yet
- Understanding VTPDocument22 pagesUnderstanding VTPBurhan RabbaniNo ratings yet
- 4 VTPDocument45 pages4 VTPvisurattNo ratings yet
- Ccnpv7 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-VtpDocument20 pagesCcnpv7 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-VtpKevin KimNo ratings yet
- Virtual Trunking Protocol: Compiled By: Miss Kiran AyubDocument13 pagesVirtual Trunking Protocol: Compiled By: Miss Kiran AyubMuhammad WaqasNo ratings yet
- VTPDocument14 pagesVTPMuhammad AZibNo ratings yet
- Configuring VTPDocument16 pagesConfiguring VTPcatalinolopezNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration 3, Chapter 4. "VTP" WorksheetDocument12 pagesCCNA Exploration 3, Chapter 4. "VTP" WorksheetThomas StineNo ratings yet
- VTPDocument14 pagesVTPAmro GoneimNo ratings yet
- Basic VTP Configuration Lab Instructions 2Document8 pagesBasic VTP Configuration Lab Instructions 2Matchgirl42100% (1)
- CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab3-1 VLAN-TRUNK-VTP STUDENT PDFDocument36 pagesCCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab3-1 VLAN-TRUNK-VTP STUDENT PDFHollman JimenezNo ratings yet
- Newps401 Switching: LU5: Perform VTP ConfigurationsDocument37 pagesNewps401 Switching: LU5: Perform VTP ConfigurationsIhirwe Shidy MegnyNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 2 - Labs: Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering - Ho Chi Minh City University of TechnologyDocument14 pagesComputer Networks 2 - Labs: Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering - Ho Chi Minh City University of Technologyquocdung89No ratings yet
- Lab 4Document6 pagesLab 4Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exp3 - Chapter04 - VTPDocument60 pagesCCNA Exp3 - Chapter04 - VTPhttp://heiserz.com/No ratings yet
- VLAN NetlabDocument25 pagesVLAN Netlabphuc1231991100% (1)
- VTP SlidesDocument72 pagesVTP SlidesSuman GhimireNo ratings yet
- VLAN Trunking Protocol1Document2 pagesVLAN Trunking Protocol1Dara IsmailNo ratings yet
- Week13 Data Communication and NetworkingDocument16 pagesWeek13 Data Communication and NetworkingMark Dhel VillaramaNo ratings yet
- Tutoria2 Configuring VLANs, VTP (VLAN Trunking ProtocolDocument9 pagesTutoria2 Configuring VLANs, VTP (VLAN Trunking ProtocolbuntyNo ratings yet
- PT Activity 4.4.1: Basic VTP Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument8 pagesPT Activity 4.4.1: Basic VTP Configuration: Topology Diagramangel_of_love31290No ratings yet
- SWVTPDocument18 pagesSWVTPAjith PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Understanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) : Document ID: 10558 This Document Contains Flash AnimationDocument8 pagesUnderstanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) : Document ID: 10558 This Document Contains Flash AnimationCesar A. Romero CarranzaNo ratings yet
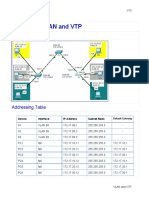
- Packet Tracer Lab 3: VLAN and VTP: Network DiagramDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer Lab 3: VLAN and VTP: Network DiagramjohnNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Scaling VLANs PDFDocument37 pagesWeek 2 - Scaling VLANs PDFJacob Satorious ExcaliburNo ratings yet
- UnderStand VTP ModesDocument9 pagesUnderStand VTP Modesgjump0103No ratings yet
- TN 323: Lan Switching: Lecture 07: Implementing VTPDocument14 pagesTN 323: Lan Switching: Lecture 07: Implementing VTPAlango Jr TzNo ratings yet
- Comnet Lab 8 Manual Pamantasan NG CabuyaoDocument4 pagesComnet Lab 8 Manual Pamantasan NG CabuyaoRicardo ZapantaNo ratings yet
- 2.1.4.4 Packet Tracer - Configure VLANs, VTP, and DTPDocument7 pages2.1.4.4 Packet Tracer - Configure VLANs, VTP, and DTPJessica GregoryNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2 Lab - Implement VTP - ILMDocument26 pages5.1.2 Lab - Implement VTP - ILMAndrei Petru PârvNo ratings yet
- Configuring Intervlan Routing Using An Internal Router (Layer 3 Card) On Catalyst 5500/5000 and 6500/6000 Switches That Run Catos System SoftwareDocument14 pagesConfiguring Intervlan Routing Using An Internal Router (Layer 3 Card) On Catalyst 5500/5000 and 6500/6000 Switches That Run Catos System Softwarevijay6996No ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet