Professional Documents
Culture Documents
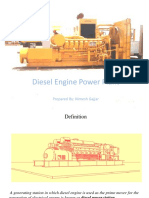
Diesel Engine Power Plant
Uploaded by
Dheer Singh MeenaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diesel Engine Power Plant
Uploaded by
Dheer Singh MeenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Diesel Engine power plant
Used where coal and water is not available in sufficient quantity Where power is generated in small quantities Where standby sets are required like in hospitals, radio stations and cinemas. Range 2 to 50 MW
Advantages: Design and installation simple Easily respond to variation in load Standby losses are less Occupy less space Start time is less Require less quantity of water for cooling purpose Overall capital cost is less Less manpower required Can be located very near to the load centers No problem of ash handling Lubrication system is more economical than the steam power plant
Disadvantages High operating cost Capacity is limited Noise is a serious problem Life of this plant is small (2 to 5 years) The diesel power plant not economical when diesel is imported
Applications:
Peak load plants Mobile plants Stand by units Emergency plant Starting stations
Site selection for diesel power plant: Foundation sub-soil condition Access to the site Distance from the load center Availability of water Fuel transportation
Components of diesel engine: Engine Air intake system o o o Air intake manifold Scavenging pump inlet in case of two stroke Super charger in case of supercharger four stroke
Exhaust system o o A pipe taking exhaust gas to out of the building. There should be minimum number of bends
Fuel system o Fuel injection system Functions of fuel injection system Filter the fuel Meter the correct quantity of fuel
Time the fuel injection Control the rate of fuel injection Break up the fuel to fine particles
Types of fuel injection system Common rail injection system Individual pump system Distributor
Cooling system o o Air cooling Liquid cooling Thermosyphon Forced or pump Thermostat cooling Pressurized water cooling Evaporative cooling
Lubrication system o o o o o Wet sump lubrication Semi pressure system Full pressure system Dry sump lubrication Mist lubrication system
Engine starting system o o o Auxiliary engine By using an electric motor By compressed air system
Advantages of GT Warm up time Less weight and size Fuel flexibility Floor space Start up and shut down time High efficiency (37%) Combined cycle mode (55%) Cooling water Ash disposal Transmission loss Cost of installation Scope of cogeneration Low capital cost
Optimal effi. Con. Optimal work Effect of regeneration Effect of intercooling Effect of reheating
You might also like
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- DieselPower PlantDocument12 pagesDieselPower PlantJC ElarmoNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant PDFDocument12 pagesDiesel Power Plant PDFZaul tatingNo ratings yet
- Bts GeneratorsDocument53 pagesBts Generatorsmohsinaliqureshi02No ratings yet
- IC Engine Notes Petrol Injection SystemDocument38 pagesIC Engine Notes Petrol Injection SystemNithinvpNo ratings yet
- Uice001-Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit-IV Module-IIIDocument28 pagesUice001-Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit-IV Module-IIIBoovendra VarmanNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine IntroductionDocument57 pagesGas Turbine IntroductionMohsin Murtaza100% (3)
- Diesel PPDocument58 pagesDiesel PPManvendra Pratap Singh Bisht100% (1)
- Gas TurbineDocument25 pagesGas Turbineapi-238832008No ratings yet
- Combustion PDFDocument79 pagesCombustion PDFKranthi ReddyNo ratings yet
- DIESEL PPDocument62 pagesDIESEL PPjaz squaredNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant PresentationDocument13 pagesDiesel Power Plant PresentationAljomar Bas JularbalNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Basic Information of Engine (CATERPILLAR)Document50 pagesPresentation On Basic Information of Engine (CATERPILLAR)SAVANT PANWARNo ratings yet
- ChillersDocument36 pagesChillersSilverblack Man100% (3)
- Diesel Engine Power PlantsDocument58 pagesDiesel Engine Power PlantsVadiraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument60 pagesLecture 1 - Diesel Engine Power PlantbarryNo ratings yet
- Diesel Powerpoint PDFDocument19 pagesDiesel Powerpoint PDFfranzNo ratings yet
- WebastoDocument1 pageWebastovale_andraNo ratings yet
- 2 Stroke EnginesDocument28 pages2 Stroke EnginesAnsysAnanthNo ratings yet
- Diesel Pwer Plant by Kalpit RautDocument21 pagesDiesel Pwer Plant by Kalpit RautKalpit RautNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power PlantDocument17 pagesDiesel Power PlantMuhammed ThaslimNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power PlantDocument34 pagesDiesel Power PlantAnonymous HyOfbJ6100% (1)
- UNIT 2 Diesel Power PlantDocument27 pagesUNIT 2 Diesel Power Plantkavinraj vNo ratings yet
- Seminar On "Diesel Power Plant": BY Gautam DangiDocument14 pagesSeminar On "Diesel Power Plant": BY Gautam DangiGautam DangiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 09 - Gas Turbines IDocument25 pagesLesson 09 - Gas Turbines ISohaib Arshad100% (3)
- Diesel EngineDocument33 pagesDiesel EngineCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument33 pagesDiesel Engine Power PlantVance NavalesNo ratings yet
- 4-2 Stroke DieselDocument36 pages4-2 Stroke DieselatulsemiloNo ratings yet
- Oil Systems 2Document23 pagesOil Systems 2Ravi SankarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Gas Turbines IIDocument34 pagesLesson 10 - Gas Turbines IIROBANGANo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Theory MJHDocument29 pagesGas Turbine Theory MJHDee ⎝⏠⏝⏠ DeeNo ratings yet
- Simple Steam: Power PlantDocument49 pagesSimple Steam: Power PlantMacky GutierrezNo ratings yet
- F5118 FP382Document2 pagesF5118 FP382José Emilio D' LeónNo ratings yet
- Cylinder DeactivationDocument20 pagesCylinder DeactivationgbpecditNo ratings yet
- Engine SystemsDocument87 pagesEngine SystemsprabhjotbhangalNo ratings yet
- Different Types of IC Engine: - Rated by Their Maximum Horsepower - Three TypesDocument14 pagesDifferent Types of IC Engine: - Rated by Their Maximum Horsepower - Three TypesmharitmsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 09 - Gas Turbines IDocument25 pagesLesson 09 - Gas Turbines ISandi NurmalikNo ratings yet
- DA PresentationDocument32 pagesDA PresentationRuwinda BandaraNo ratings yet
- DMW PatialaDocument31 pagesDMW PatialaHarsimran Singh100% (1)
- Automobile EngineeringDocument160 pagesAutomobile EngineeringDin Ash100% (4)
- Chapter 5 TheoryDocument57 pagesChapter 5 TheorySigit Penuh IdeNo ratings yet
- Diesel Fa19Document35 pagesDiesel Fa19Muhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Negative Pressure SuperchargingDocument38 pagesNegative Pressure SuperchargingPrakash Chandrasekaran100% (1)
- Gas Turbine 1Document41 pagesGas Turbine 1Mohamed ElgendyNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument18 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesSameerAhsanNo ratings yet
- VPCL Essar PowerDocument49 pagesVPCL Essar Powerbhavya_nmimsNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine and ConstructionDocument25 pagesGas Turbine and ConstructionRamanujam SankarNo ratings yet
- Marine Piping SystemDocument75 pagesMarine Piping SystemNguyễn Hoàng Thành100% (1)
- Diesel Power Plant Operation and Efficiency: Submitted To:-Submitted By: - Mahesh Chandra JoshiDocument14 pagesDiesel Power Plant Operation and Efficiency: Submitted To:-Submitted By: - Mahesh Chandra JoshiMahesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Gas TurbineDocument31 pagesPresentation On Gas TurbineDhruvKandwalNo ratings yet
- Bosch K Jetronic Filter Diesel PDFDocument14 pagesBosch K Jetronic Filter Diesel PDFPuneeth obliNo ratings yet
- Developments in IC EnginesDocument41 pagesDevelopments in IC EnginesRohit K Murthy67% (3)
- Unit 3 Power Plant EngineeringDocument49 pagesUnit 3 Power Plant EngineeringNaren NathanNo ratings yet
- 05 Cooling SystemDocument45 pages05 Cooling Systemramalingeswarao annamdevulaNo ratings yet
- Overiew of Comb Cycle Rev 6.0 - Part 1Document73 pagesOveriew of Comb Cycle Rev 6.0 - Part 1SamNo ratings yet
- Larkin MOHAVEDocument36 pagesLarkin MOHAVEscribdwasNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell Electric VehiclesDocument31 pagesFuel Cell Electric VehiclesKhalil RazaNo ratings yet
- Materials Management On Indian Railways PDFDocument110 pagesMaterials Management On Indian Railways PDFDheer Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Orbit and Rotation: NamingDocument4 pagesOrbit and Rotation: NamingDheer Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- ReliabilityDocument30 pagesReliabilityDheer Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- RPT Time Table StudentDocument1 pageRPT Time Table StudentDheer Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Magneto Hydro Dynamics MHD SystemDocument20 pagesMagneto Hydro Dynamics MHD SystemDheer Singh Meena100% (1)
- Beginning of World War IIDocument23 pagesBeginning of World War IIDheer Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- 03-Classification of EnginesDocument36 pages03-Classification of EnginesDheer Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet-5Document2 pagesPractice Sheet-5Dheer Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Emission Control Analysis On BS-VI Diesel Engine in Heavy VehicleDocument11 pagesEmission Control Analysis On BS-VI Diesel Engine in Heavy VehicleajayNo ratings yet
- Maintenance: 1.2 General Maintenance Chart For Hitachi S12A2 EngineDocument36 pagesMaintenance: 1.2 General Maintenance Chart For Hitachi S12A2 EngineKolo BenduNo ratings yet
- BMW M47D20 Engine Specifications & ProblemsDocument4 pagesBMW M47D20 Engine Specifications & ProblemsCallum Smith60% (5)
- m57 Common RailDocument13 pagesm57 Common RailMartin Hani100% (4)
- Mahindra Scorpio MHawk 2.2 TD 2007-2013 Service ManualDocument762 pagesMahindra Scorpio MHawk 2.2 TD 2007-2013 Service ManualYader Chamorro83% (6)
- Mitsubishi Pajero Parts Catalog PDFDocument2 pagesMitsubishi Pajero Parts Catalog PDFEghie RahardiNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual Lga 280 OhcDocument100 pagesWorkshop Manual Lga 280 Ohcptheo2088No ratings yet
- RX8 - Complete-Engine-TeardownDocument46 pagesRX8 - Complete-Engine-Teardowngo0n100% (8)
- Chapter 4Document21 pagesChapter 4ゞ『HaiDerツ98〆No ratings yet
- 4.10T Parts Catalog (Ok)Document79 pages4.10T Parts Catalog (Ok)Noor Sa'adahNo ratings yet
- Paccar MX11 MX13 Engine Brochure 2019Document7 pagesPaccar MX11 MX13 Engine Brochure 2019ddi11100% (1)
- Kohler Command 16HP Vertical Shaft Engine Service ManualDocument148 pagesKohler Command 16HP Vertical Shaft Engine Service Manualbobbilow100% (5)
- SNECMA Safran Aero Diesel Engine 230 HPDocument2 pagesSNECMA Safran Aero Diesel Engine 230 HPSilvije Filipović100% (1)
- Buick Rendezvous 2005 3.4LDocument538 pagesBuick Rendezvous 2005 3.4LjuventinocoronapNo ratings yet
- TP30Document9 pagesTP30abelmonte_geotecniaNo ratings yet
- Engine Control System: Click The Volvo-Logo in The Lower Right Corner To Return To This Menu Main MenuDocument23 pagesEngine Control System: Click The Volvo-Logo in The Lower Right Corner To Return To This Menu Main MenuNaing Min Htun100% (12)
- Data For Tightening Torque: LubricantDocument5 pagesData For Tightening Torque: LubricantAtanasio PerezNo ratings yet
- Product BrochureDocument8 pagesProduct BrochureMagaly PeraltaNo ratings yet
- ENGENIRINGDocument7 pagesENGENIRINGMostafa Mohamed Adel0% (1)
- Deutz Change From Tier II To Tier III TCD 2013 l06 2vDocument18 pagesDeutz Change From Tier II To Tier III TCD 2013 l06 2vduongpndngNo ratings yet
- PDF Modul 9 Bahan Belajar Sekolah Dasar Mata Kuliah Perspektif Pendidikan SD Pdgk4104Document93 pagesPDF Modul 9 Bahan Belajar Sekolah Dasar Mata Kuliah Perspektif Pendidikan SD Pdgk4104Miftakhul NikmahNo ratings yet
- Qute 2019Document99 pagesQute 2019Aroldo RuizNo ratings yet
- SP526 7Document3 pagesSP526 7Vitor FreitasNo ratings yet
- Stihl 038 IPLDocument36 pagesStihl 038 IPLKia Anne BaconNo ratings yet
- Vértice Tipo Estructura Coordenadas Reales Real Este Norte #Estructura Kilometraje (M)Document3 pagesVértice Tipo Estructura Coordenadas Reales Real Este Norte #Estructura Kilometraje (M)CarlosChavezPonceNo ratings yet
- 3D72-2B Parts CatalogueDocument40 pages3D72-2B Parts CatalogueMichael AkhramovichNo ratings yet
- Technical Datasheet TCG2020V20 @2000kW - 220222 - 182253Document1 pageTechnical Datasheet TCG2020V20 @2000kW - 220222 - 182253Jack ElhaqNo ratings yet
- Cilindru Hamm DV 6Document3 pagesCilindru Hamm DV 6Adrian DumescuNo ratings yet
- Training Manual 85-21Document177 pagesTraining Manual 85-21Rasoul gholinia kivi0% (1)
- Rio 2005 1.6LDocument151 pagesRio 2005 1.6LJavikoo Javier Chicaiza MezaNo ratings yet