Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Fasteners
Uploaded by
Krm LeoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Fasteners
Uploaded by
Krm LeoCopyright:
Available Formats
UNINVERSITY OF KHARTOUM FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICAL DESIGN I ME411 TUTORIALS January 2013
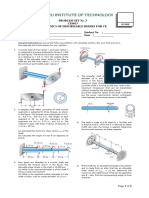
1. For a standard bolt and nut made of steel, determine the relation between the thickness of the nut and the outside diameter of the thread for equal strengths of the bolt in tension and the threads in shear. Assume that the root diameter of threads is 0.85xthe outside diameter and the allowable stress in shear equals 0.55xthe allowable stress in tension. 2. A pulley bracket is supported by four bolts, two at A and two at B, as shown in fig. The weight of pulley and bracket equals W= 78Kg, and the load on the rope P is 2,700Kg. Assuming that the bracket is held against the wall and prevented from tipping about O by the two bolts at A (i.e., neglecting the bolts at B), and using an allowable stress in the bolts as 35N/mm2, determine the size of the NC bolts required.
3. A bolt is subjected to axial shock loading so that the maximum applied load equals 1000Kg. (a) Assuming an allowable stress 51N/mm2, determine the size of bolt required, using NC threads. Neglect stress concentration. (b) It is desired to increase the shock absorbing capacity of the above bolt. Determine the diameter of the hole required to reduce the cross-sectional area of the shank to that at the root of the threads. (c) Determine the percentage of improvement in shockabsorbing capacity by using the drilled bolt (bolt with a hole drilled along its axis in the center). 4. Assuming that the load on a bolt due to tightening is equal to 16,000 times the nominal bolt diameter d, derive an equation for the stress due to tightening. The result should be in terms of d. Assume the root diameter is 0.8xthe nominal diameter. What should be the minimum size of the bolts used on the basis of the above? 5. For a sliding hub connected to a shaft by means of feather keys, show that the friction of sliding when two keys are used is one-half the friction when one key is used.
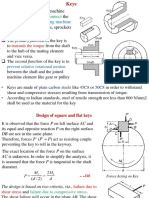
6. Draw a neat sketch of a shaft with a key, and derive equations for (a) the bearing pressure on the key and (b) the shearing stress in the key. The results should be in terms of the transmitted torque T, the shaft diameter D, length L of key, width w of key, and depth h. (c) assuming that the key is equally strong in bearing and shear and that the yield in compression is twice the yield point in shear, determine the proper proportions of the cross section of the key. (d) assuming that there is a square key whose sides are one-quarter the shaft diameter and that the shaft, key and hub are made from the same material, determine the length of key in terms of shaft diameter so that the key will be as strong as the solid shaft. 7. Make a neat sketch showing two views of a cotter joint with key and write equations showing the strength of the joint for the most probable modes of failure. 8. The torque capacity of a spline fitting s based on the allowable pressure on the active surfaces of the splines. Assuming a value of the pressure as 64.00N/mm2, determine for the spline in the fig. the following: (a) Length of spline required for a torque capacity of 670Nm; (b) the force required to slide the member axially under load, assuming the coefficient of friction as 0.1.
You might also like
- DME 1 Question BankDocument5 pagesDME 1 Question BankRahul YedduNo ratings yet
- Dme Question BankDocument4 pagesDme Question BankRavi Patil100% (1)
- Question Bank - DMEDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank - DMEBdhdhshNo ratings yet
- Dme Home Assignment 2019-20Document4 pagesDme Home Assignment 2019-20VenkateshNo ratings yet
- No of Pages Course Code:: Fig.1 Fig 2Document4 pagesNo of Pages Course Code:: Fig.1 Fig 2CRAZY PIANO PLAYERNo ratings yet
- QB Unit-3,4,5Document7 pagesQB Unit-3,4,5Agranshu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Machine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01Document10 pagesMachine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01The AIRS CreationsNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Machine Design A: Numerical Problems: Problems On Pin, Cotter and Knuckle JointsDocument25 pagesQuestion Bank Machine Design A: Numerical Problems: Problems On Pin, Cotter and Knuckle Jointsamol pogakeNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 3Document2 pagesProblem Set No. 3marcusluismacusiNo ratings yet
- DME Chapter 2Document5 pagesDME Chapter 2dhananjayvermaNo ratings yet
- Time Allowed: 1.5 Hours Full Marks: 70: 604 (S) August 2021Document3 pagesTime Allowed: 1.5 Hours Full Marks: 70: 604 (S) August 2021Sourav BhowmikNo ratings yet
- MD Tut PDFDocument6 pagesMD Tut PDFNelsan PatelNo ratings yet
- Me331-Design of Machine Elements Unit Iii Design of Fasteners and JointsDocument21 pagesMe331-Design of Machine Elements Unit Iii Design of Fasteners and JointsMuthuvel MNo ratings yet
- ME6503-Design of Machine Elements PDFDocument15 pagesME6503-Design of Machine Elements PDFkarthikNo ratings yet
- DME Question Bank - 3171917Document4 pagesDME Question Bank - 3171917fgyjnsv786No ratings yet
- Mech-nd-2020-Me 8593-Design of Machine Elements-334300796-X10703 (Me8593) Design of Machine ElementsDocument5 pagesMech-nd-2020-Me 8593-Design of Machine Elements-334300796-X10703 (Me8593) Design of Machine ElementsARIGARAN SNo ratings yet
- 12me52 MQP-1Document3 pages12me52 MQP-1SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- 3-1 DMM1 (Nov 2009 Regular)Document9 pages3-1 DMM1 (Nov 2009 Regular)micmechNo ratings yet
- MDDocument5 pagesMDYogesh DanekarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1sonawanepmsNo ratings yet
- Me 6503 Design of Machine Elements QBDocument3 pagesMe 6503 Design of Machine Elements QBDeepak SNo ratings yet
- Me1302 Dme 2Document4 pagesMe1302 Dme 2sumikannu100% (1)
- Assignment 02 - Machine DesignDocument2 pagesAssignment 02 - Machine DesignRatan Sadanandan O MNo ratings yet
- Dme Assignment 2Document21 pagesDme Assignment 2helloapple1211No ratings yet
- Snist Dom Previous PaperDocument9 pagesSnist Dom Previous PaperKapil Siddhant DevulapalliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - LoadStressAnalysisDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 - LoadStressAnalysisSanthosh AmaraNo ratings yet
- Cat 2 Ear 306Document4 pagesCat 2 Ear 306Mercy MerryNo ratings yet
- GTU BE Semester IV Machine Design & Industrial Drafting ExamDocument3 pagesGTU BE Semester IV Machine Design & Industrial Drafting ExamhukNo ratings yet
- Akshat DmeDocument38 pagesAkshat DmekartikeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 3 &4 B.Tech Mechanical Engineering Third YearDocument4 pagesAssignment No. 3 &4 B.Tech Mechanical Engineering Third Yearharish_kumar201301No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document6 pagesTutorial 4Ysgn MysgnNo ratings yet
- Arm301 QBDocument6 pagesArm301 QBKunal KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- TE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFDocument4 pagesTE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFonkar nikamNo ratings yet
- End Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021Document3 pagesEnd Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021FelishiaNo ratings yet
- dmm1 PDFDocument9 pagesdmm1 PDFmohan_rapaka6095No ratings yet
- 08 r05310305 Design of Machine Members IDocument9 pages08 r05310305 Design of Machine Members IKrupanandareddyYarragudiNo ratings yet
- Assignment No1MDDocument4 pagesAssignment No1MDPradeep MirajgaveNo ratings yet
- Machine Members Design AssignmentDocument13 pagesMachine Members Design AssignmentHafiz Mahar28No ratings yet
- Common Subject Code: Shivaji University, KolhapurDocument10 pagesCommon Subject Code: Shivaji University, Kolhapursatyamchgl2010No ratings yet
- First Project ExamplesDocument49 pagesFirst Project ExamplesMeleti Meleti MeletiouNo ratings yet
- Me 2303 Imp QnsDocument3 pagesMe 2303 Imp QnsAJAY63No ratings yet
- PMD ModelDocument8 pagesPMD ModelDamodara SatyaDeva MadhukarNo ratings yet
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDocument11 pagesDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNo ratings yet
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDocument11 pagesDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiMilton CobaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 02Document2 pagesAssignment 02adhnan_rasheed0% (1)
- TUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and CouplingDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and Couplingrip111176100% (1)
- Screws, Fasteners, and Nonpermanent Joint DesignDocument5 pagesScrews, Fasteners, and Nonpermanent Joint DesignMohamed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionDocument15 pagesAssignment QuestionPratik WalimbeNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Term WorkDocument1 pageMachine Design Term WorkChirag PatilNo ratings yet
- Me8593 Iq R17Document4 pagesMe8593 Iq R17Vaideesh LJNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityBhavesh PatelNo ratings yet
- MODEL QUESTION PAPER Mechanical VibrationsDocument3 pagesMODEL QUESTION PAPER Mechanical VibrationsDarani PriyaNo ratings yet
- Me1302 DmeDocument4 pagesMe1302 DmesumikannuNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Unit 1,2Document7 pagesImportant Questions Unit 1,2rajeswariNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityBhavesh PatelNo ratings yet
- DME - Assignment - IDocument3 pagesDME - Assignment - ISathis KumarNo ratings yet
- Fig. P3.129, P3.130Document4 pagesFig. P3.129, P3.130Alen RustemovicNo ratings yet
- 1411294910.3123impact of A Water Jet - ExperimentDocument3 pages1411294910.3123impact of A Water Jet - ExperimentKrm LeoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Jet PDFDocument4 pagesImpact of Jet PDFKrm LeoNo ratings yet
- Sun TurckerDocument1 pageSun TurckerKrm LeoNo ratings yet
- CFD Lect 6Document29 pagesCFD Lect 6Krm LeoNo ratings yet
- Wind Tunnel ExperimentDocument46 pagesWind Tunnel ExperimentAbhilash Mathew50% (2)
- QB Series Housed BLDC Servo Motor R4Document12 pagesQB Series Housed BLDC Servo Motor R4Nguyen Thanh LuanNo ratings yet
- ReserchDocument26 pagesReserchKrm LeoNo ratings yet
- Purwanchal Vidyamandir Session: 2020 - 2021 Class: IX Subject: Geography Study Material - 3 Chapter - 8 EarthquakesDocument4 pagesPurwanchal Vidyamandir Session: 2020 - 2021 Class: IX Subject: Geography Study Material - 3 Chapter - 8 EarthquakesKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9ANo ratings yet
- The (N, G) Cross Section of 135 - Cs.Document25 pagesThe (N, G) Cross Section of 135 - Cs.Saed DababnehNo ratings yet
- KTT111 Sem1 2010 2011 PDFDocument11 pagesKTT111 Sem1 2010 2011 PDFBilah BilahNo ratings yet
- GALATIANSDocument2 pagesGALATIANSFuckyouuNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification References: I! OI C UDocument30 pagesTechnical Specification References: I! OI C Uabubakar aliNo ratings yet
- Mock Che1Document5 pagesMock Che1nassorussi9No ratings yet
- Forces and scalars vectorsDocument5 pagesForces and scalars vectorsHadirah Dunglah0% (1)
- Thermal Relief Therm - VTDocument6 pagesThermal Relief Therm - VTRafael ReyesNo ratings yet
- Effective-Stress Analysis of Berm-Supported Retaining WallsDocument10 pagesEffective-Stress Analysis of Berm-Supported Retaining WallsDerek WongNo ratings yet
- HW 2 - ChemDocument14 pagesHW 2 - ChemStephanieNo ratings yet
- Types of pumps explainedDocument1 pageTypes of pumps explainedI AM NOT CHINESENo ratings yet
- Tos Notes 1,2,3Document13 pagesTos Notes 1,2,3Star Youtuber Prashant100% (1)
- Tsunami Simulations Using Dashboard and Delft3DDocument17 pagesTsunami Simulations Using Dashboard and Delft3DbukanastutikNo ratings yet
- Manual N0360BBMMLL0217 X X en 4309777 20160301Document12 pagesManual N0360BBMMLL0217 X X en 4309777 20160301Amal WahidNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Operations GuideDocument4 pagesManufacturing Operations GuidetarasasankaNo ratings yet
- List of Courses PHY 2022-2023-I New-06-04-23Document1 pageList of Courses PHY 2022-2023-I New-06-04-23Sushi KeerNo ratings yet
- Sheet: 4: 1) Two Plates of 7 MM Thick Are Connected by A Triple Riveted Lap Joint of ZigDocument1 pageSheet: 4: 1) Two Plates of 7 MM Thick Are Connected by A Triple Riveted Lap Joint of ZigBen AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab Course on Bauschinger EffectDocument9 pagesLab Course on Bauschinger EffectTuladhar R AmreetNo ratings yet
- General Brochure - Johnson ControlsDocument4 pagesGeneral Brochure - Johnson Controlst_i_f_anoNo ratings yet
- Astm E1220Document6 pagesAstm E1220Gerardo Mediavilla100% (1)
- Hasyim Muhammad Agiel-Cv3Document3 pagesHasyim Muhammad Agiel-Cv3Satria GinanjarNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document31 pagesChap 5Kali DasNo ratings yet
- Pages From EPRI EL-6800Document6 pagesPages From EPRI EL-6800981002No ratings yet
- Distillation Process CalculationDocument11 pagesDistillation Process CalculationjaffliangNo ratings yet
- Stress TransformationDocument22 pagesStress TransformationTran Manh HuyNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual: Air Cooled Water Chillers With Helical FansDocument36 pagesTechnical Manual: Air Cooled Water Chillers With Helical FansAndreeaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Analysis For Piled Raft FoundationDocument5 pagesDynamic Soil Structure Interaction Analysis For Piled Raft FoundationjaswantNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - Introduction (Pressure, Reference Levels) PDFDocument8 pages3.1 - Introduction (Pressure, Reference Levels) PDFJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Contracted Rectangular WeirDocument9 pagesCalibration of Contracted Rectangular WeirDianne Ilao LondobNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 BLT AE19B102Document34 pagesAssignment 2 BLT AE19B102Anuj NigamNo ratings yet