Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01 - M012 - 4228 New
Uploaded by
Sathish KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01 - M012 - 4228 New
Uploaded by
Sathish KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
RA1IV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES, BANGALORE,
KARNATAKA.
ANNEXURE II
PROFORMA FOR REGISTRATION OF SUB1ECT FOR DISSERTATION
1. NAME OF THE CANDIDATE AND
ADDRESS
DR. VIDYA 1ANAKI. R.
PG IN ENT,
KARNATAKA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL
SCIENCES,
HUBLI - 580 022.
2. NAME OF THE INSTITUTION KARNATAKA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL
SCIENCES, HUBLI-22.
3. COURSE OF THE STUDY AND
SUB1ECT
M.S. IN ENT.
4. DATE OF ADMISSION TO THE
COURSE
10-06-2008.
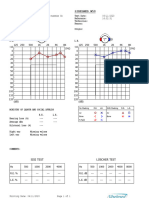
5. TITLE OF THE TOPIC CORRELATION OF SITE AND
SIZE OF TYMPANIC MEMBRANE
PERFORATION WITH PURE TONE
AUDIOGRAM.
6. BRIEF RESUME OF INTENDED WORK:
6.1 NEED FOR THE STUDY:
Chronic suppurative otitis media(CSOM) is a wide spread disease oI the
developing countries like India especially in the rural areas. It is one oI the
commonest causes oI hearing loss that mainly results due to a tympanic membrane
perIoration.
The large eIIective surIace area oI an intact and normally vibrating
tympanic membrane plays a major role in the middle ear transIormer mechanism.
PerIoration oI the tympanic membrane is a common cause Ior hearing loss due to loss
oI eIIective area oI vibration. PerIorations can result Irom various reasons including
middle ear disease, trauma.
It has been generally believed that the degree oI hearing loss increases with
the size oI the perIoration. Many prior clinical studies have shown that hearing loss
associated with perIoration was more at low Irequencies than at high Irequencies and
it increases with the size oI perIoration.
Correlation oI the site oI perIoration to hearing loss is not very clearly
established though a Iew studies have shown no signiIicance oI site oI perIoration.
Another showed postero inIerior perIoration caused more hearing loss than others.
Accurate assessment oI the TM PerIoration and its relationship with hearing
loss is important as it enables the clinician to optimally assess the condition and oIIer
an appropriate solution. Hence the need Ior the study.
6.2 REVIEW OF LITERATURE:
1. In 1979, Ahmad.S.W and Ramani G. V studied 70 patients with dry central
perIorations to assess the hearing loss and concluded that hearing loss was greater
at the lower Irequencies and increases with the size oI the perIoration. They
also Iound that posteroinIerior quadrant perIorations caused more hearing loss
than antero inIerior ones, the diIIerence being greater at lower than at higher
Irequencies.
1
2. In 2006, Ritvik P Mehta, Rosowski J John et al conducted a study on 56 patients
with isolated TM PerIorations and showed that hearing loss is Irequency dependant
and the greatest loss occurred at the lowest Irequencies, hearing loss increased with
increase in size oI perIoration, varied inversely with middle ear volume and does
not vary substantially with location oI the perIoration.
2
3. In 2003, Bhusal C L et al studied IiIty patients with CSOM Tubo tympanic
type undergoing myringoplasty and showed that hearing loss was more at lower
Irequencies and less as Irequencies increase and hearing loss increased with the size
oI perIoration.
3
4. In 2001 ,Voss S E, Rosowski JJ et al measured acoustic transmission beIore and
aIter making controlled perIorations in cadaver ears and showed that perIorations
caused Irequency dependent loss that was largest at low Irequencies ,increased as
the size oI perIoration increased and did not depend on perIoration location.
4
5. In 1972, Walter P et al studied the eIIects oI both size and location oI tympanic
membrane perIorations on hearing loss in 103 patients who had undergone
myringoplasty and concluded that eIIectiveness oI the TM decreased with loss oI
total area.
5
6.3 AIMS OF THE STUDY:
1. To record the site and size oI tympanic membrane perIorations.
2. To correlate the site and size oI the perIoration with pure tone audiogram in such
patients who IulIilled the study criteria..
7. MATERIALS AND METHODS:
7.1 SOURCE OF DATA:
Patients attending ENT OPD in KIMS, Hubli in the study period Irom January 2009 to
December 2009 who have a tympanic membrane perIoration.
7.2 METHODS OF COLLECTION OF DATA:
A cross sectional, correlative study is planned.
Every consecutive eligible patient will be recruited into the study and divided into two
to three groups depending on the size oI the perIoration. The site oI perIoration will
also be recorded and a pure tone audiogram will be perIormed on the patient. The data
obtained will be analyzed using an appropriate statistical test.
INCLUSION CRITERIA:
1. Subject should have central TM perIoration due to trauma or CSOM.
2. All subjects should have dry ears ( duration 3 months )
3. Patients with intact ossicular chain- conIirmed by patch test.
4. Age between 10 to 60 years.
EXCLUSION CRITERIA:
1. Patients with Attico- antral disease- presence oI cholesteatoma or granulation
tissue.
2. Active CSOM.
3. Patients with ossicular chain pathology.
4. Patients who cannot give a valid and consistent PTA response.
5. Patients with sensorineural hearing loss.
7.3 DOES THE STUDY REQUIRE ANY INVESTIGATIONS OR
INTERVENTIONS
TO BE CONDUCTED ON PATIENTS OR OTHER HUMANS OR
ANIMALS? IF
SO, PLEASE DESCRIBE BRIEFLY.
~Yes
Pure tone audiometry and patch test.
7.4 HAS ETHICAL CLEARANCE BEEN OBTAINED FROM YOUR
INSTITUTION
IN CASE OF 7.3?
Yes, Ethical clearance has been obtained Irom ethical committee oI KIMS, Hubli.
8. LIST OF REFERENCES:
1. Ahmad S W and Ramani G V 'Hearing loss in perIorations oI the tympanic
membrane. The Journal oI Laryngology and Otology 1979;93;1091-1098.
2. Ritvik P Mehta et al 'Determinants oI hearing loss in perIorations oI the tympanic
membrane. Otology and Neurology 2006;27;136-143.
3. Bhusal et al 'Size oI tympanic membrane perIoration and hearing loss. JNMA J
Nepal Med Assoc. 2006;45(161);167-172.
4. Voss S E et al 'How do tympanic membrane perIorations aIIect human middle ear
sound transmission?Acta otolaryngol. 2001 jan;121(2):169-73.
5. Walter P Anthony et al 'Tympanic membrane perIoration Archives oI
otolaryngology 1972;vol 95 :504-510.
6. Ajith kumar U and Vikram Bhat K. 'Do the site and size oI tympanic membrane
perIoration correlate with audiogram?Asian journal oI Ear,Nose and Throat
2000;4;25-30.
7. Vikram J Jaisinghani et al 'quantitative analysis oI tympanic membrane disease
using video otoscopy The Laryngoscope 2000 oct:110:1726-1730.
8. Ibeweke TS et al 'quantitative analysis oI tympanic membrane perIoration:a
simple and reliable method. The journal oI laryngology and otology 2008 oct 22:1-
4 .
9. Ibeweke TS et al 'assessments oI the size oI tympanic membrane perIorations:a
comparison oI clinical estimations with video otoscopic calculations. Ear Nose and
Throat Journal. 2008 oct:87(10):567-569.
10. Payne M C and Glither F J 1951 archives oI otolaryngology, 54 666-674.
9. SIGNATURE OF THE CANDIDATE
10. REMARKS OF THE GUIDE
11. 11.1 NAME AND DESIGNATION OF
THE GUIDE
DR. VIKRAM K BHAT MS, DNB, Phd.
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF ENT
DEPARTMENT OF ENT,
KIMS, HUBLI.
11.2 SIGNATURE
11.5 HEAD OF THE DEPARTMENT
DR. UMESH S NAGALOTIMATHMS,DNB
PROFESSOR & HEAD,
DEPARTMENT OF ENT,
KIMS, HUBLI.
11.6 SIGNATURE
12 12.1 REMARKS OF THE
CHAIRMAN AND THE
PRINCIPAL
12.2 SIGNATURE
You might also like
- 8889 EntDocument7 pages8889 EntSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- 01 - M027 - 35769 NewDocument8 pages01 - M027 - 35769 NewSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- 02 DO-HNS Regulations Aug 09Document8 pages02 DO-HNS Regulations Aug 09Sathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Mono Immuno InfectDocument8 pagesMono Immuno InfectSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Importance of Sound Design on PerceptionDocument48 pagesThe Importance of Sound Design on PerceptiondoeditNo ratings yet
- Auditory Evoked Potentials - AEPs - Underlying PrinciplesDocument19 pagesAuditory Evoked Potentials - AEPs - Underlying PrinciplesMansi SinghNo ratings yet
- MCQ Oxford Aviation HUMAN FACTORSDocument62 pagesMCQ Oxford Aviation HUMAN FACTORSvidolNo ratings yet
- Basic Listening SkillsDocument21 pagesBasic Listening SkillsAmjad PathanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - SensationDocument59 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Sensationflammy07100% (1)
- Audiometer Sibelmed As5: User ManualDocument42 pagesAudiometer Sibelmed As5: User ManualMihnea CondeescuNo ratings yet
- Noise Induced Hearing Loss and Its Management: by Prerna Sangwan Roll No. 90Document15 pagesNoise Induced Hearing Loss and Its Management: by Prerna Sangwan Roll No. 90Prerna SangwanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Syllabus PDFDocument220 pagesMarketing Syllabus PDFDeepikaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Oxford Fajar 6 SoundDocument5 pagesOxford Fajar 6 SoundAqilah HazwaniNo ratings yet
- Nadlif Muammar KH KhumainiDocument1 pageNadlif Muammar KH KhumainiBoca PetualangNo ratings yet
- NullDocument9 pagesNullapi-26330058No ratings yet
- Theory of The Film Sound BalazsDocument7 pagesTheory of The Film Sound BalazsreaperbunsNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Matching Chart 2007Document1 pageAmplifier Matching Chart 2007bambang2000No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Sound Waves and Their ApplicationsDocument36 pagesCharacteristics of Sound Waves and Their ApplicationsChuahSiewHoonNo ratings yet
- Cases Filed On Electromagnetic Assaults, Gangstalking, Mind Control, V2k and Implaints - by Justice For All Citizens - PeacepinkDocument1 pageCases Filed On Electromagnetic Assaults, Gangstalking, Mind Control, V2k and Implaints - by Justice For All Citizens - PeacepinkGeneration GenerationNo ratings yet
- Calibrate Entomed Audiometers for Accurate Hearing TestsDocument32 pagesCalibrate Entomed Audiometers for Accurate Hearing TestsLuism120100% (1)
- Sense Organs Guide: Classification, Structure & FunctionsDocument26 pagesSense Organs Guide: Classification, Structure & FunctionsArpan AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Auditory-Verbal Techniques and HierarchiesDocument14 pagesAuditory-Verbal Techniques and HierarchiesDEAN MIKO BULLO100% (1)
- High Impulse SoundsDocument58 pagesHigh Impulse SoundsfuckscribNo ratings yet
- Script 2Document4 pagesScript 2Rheanne OseaNo ratings yet
- Understanding-Using - OAE Von KempDocument12 pagesUnderstanding-Using - OAE Von KempWendra SaputraNo ratings yet
- What is sound? Understanding the basicsDocument10 pagesWhat is sound? Understanding the basicsJacqueline Matos BarbosaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE: The Sense of Hearing What Are The Three Main Parts of The Human Ear?Document2 pagesSCIENCE: The Sense of Hearing What Are The Three Main Parts of The Human Ear?Fermina CachoNo ratings yet
- MIXING LIVE STREAM AUDIO AT CHURCHDocument11 pagesMIXING LIVE STREAM AUDIO AT CHURCHJessNo ratings yet
- Using The Tympanometer and AudiometerDocument10 pagesUsing The Tympanometer and AudiometerlaboratorioelectroNo ratings yet
- Listening Test 6 PDFDocument5 pagesListening Test 6 PDFphuong leNo ratings yet
- RM Important Questions at VenkyDocument15 pagesRM Important Questions at VenkyVenkateshYadavCivarlaNo ratings yet
- Optimal Crosstalk Cancellation For Binaural AudioDocument25 pagesOptimal Crosstalk Cancellation For Binaural AudioMartin BakeroNo ratings yet
- Hearing TestDocument11 pagesHearing TestKhaled ToffahaNo ratings yet
- 10-Sense OrgansDocument32 pages10-Sense Organsmesutor100% (2)