Professional Documents
Culture Documents
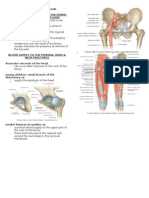
Anatomy Tables-Muscles of The Head and Neck
Uploaded by
Tracie YWOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy Tables-Muscles of The Head and Neck
Uploaded by
Tracie YWCopyright:
Available Formats
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
Muscles of the Head and Neck - Listed Alphabetically
Muscle anterior scalene Origin Insertion Action elevates the first rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck Innervation brachial plexus, C5-C7 Artery ascending cervical a., a branch of the thyrocervical trunk Notes a muscle of inspiration; an important landmark of the neck; it is located between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery; the roots of the brachial plexus pass posterior to it; the phrenic nerve crosses its anterior surface the mucosa is raised by the underlying aryepiglottic m. to form the aryepiglottic fold the oblique arytenoid m. lies posterior to the transverse arytenoid m.; the arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse fibers the transverse arytenoid m.lies anterior to the oblique arytenoid m.; the anterior tubercles of scalene tubercle of the transverse the first rib processes of vertebrae C3-C6
aryepiglottic
apex (superior part) of the arytenoid cartilage
epiglottis
draws the epiglottis posteriorly and downward during swallowing draws arytenoid cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds
inferior laryngeal laryngeal br. of the nerve, from superior thyroid a. recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the of vagus (X) inferior laryngeal laryngeal br. of the nerve, from superior thyroid a. recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the of vagus (X)
arytenoid, oblique
muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage
posterior surface of the contralateral arytenoid cartilage, near its apex
arytenoid, transverse
posterior surface of the arytenoid cartilage
posterior surface of the contralateral arytenoid cartilage
draws arytenoid cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds
inferior laryngeal laryngeal br. of the nerve, from superior thyroid a. recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
the vagus nerve (X)
arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse parts the auricular muscles are derived from the mesenchyme of the second pharyngeal arch, as are the muscles of facial expression although the buccinator is important in mastication, it is innervated by the buccal branch of the facial nerve and NOT by the buccal nerve from V3 (a sensory nerve) chondroglossus is often considered to be part of the hyoglossus muscle relaxation of the suspensory ligament allows the lens to thicken for accommodation (near vision) the most external of
auricular
anterior: galea aponeurotica anterior to ear; superior: galea aponeurotica superior to ear; posterior: mastoid process pterygomandibular raphe, mandible, and the maxilla lateral to the molar teeth
auricle anteriorly, superiorly and posteriorly
wiggle the ears
anterior & superficial temporal superior: temporal a., posterior branches of facial auricular a. nerve (VII); posterior: posterior auricular branch of facial nerve (VII) buccal branches of facial a. the facial nerve (VII)
buccinator
angle of mouth and the lateral portion of the upper and lower lips
pulls the corner of mouth laterally; presses the cheek against the teeth
chondroglossus
medial side of the lesser horn and body of the hyoid bone meridional fibers: scleral spur; circular fibers: encircle the ciliary process
ascends to blend with the intrinsic tongue musculature meridional fibers: ciliary process; circular fibers: encircle the ciliary process midline pharyngeal
pulls the sides of the tongue down
hypoglossal nerve (XII)
lingual a.
ciliary
relaxes the suspensory ligament of the lens
parasympathetic fibers in the oculomotor nerve (III), synapsing in the ciliary ganglion vagus (X), via the
ophthalmic a.
constrictor, inferior
oblique line of the
constricts pharyngeal
ascending
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
pharyngeal
thyroid cartilage, lateral surface of cricoid cartilage
raphe
cavity
pharyngeal plexus, pharyngeal a., with aid from the superior thyroid a., superior laryngeal inferior thyroid a. and recurrent laryngeal nerves vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus ascending pharyngeal a.
the three pharyngeal constructor mm.
constrictor, middle pharyngeal
lesser and greater horns of the hyoid bone and the inferior part of the stylohyoid ligament
midline pharyngeal raphe
constricts the pharyngeal cavity
of the three pharyngeal constrictors, this one is intermediate in both superior/inferior position and depth the most internal of the three pharyngeal constructor mm.
constrictor, superior medial pterygoid pharyngeal plate, pterygoid hamulus, pterygomandibular raphe, mylohyoid line of mandible corrugator medial part of the supercillary arch arch of the cricoid cartilage
pharyngeal tubercle and midline pharyngeal raphe
constricts the pharyngeal cavity
vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus
ascending pharyngeal a.
skin of the medial half of the eyebrow muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage
pulls eyebrows together medially draws the muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage anteriorly, which pivots the arytenoid cartilage and adducts the vocal folds
temporal branch of supratrochlear a. the facial nerve (VII) inferior laryngeal nerve, from the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X) superior laryngeal a., cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a.
this muscle causes the furrowed brow of the worried look an antagonist of the posterior cricoarytenoid m.; the arteries that supply the larynx anastomose within the larynx to supply the mucous membranes and muscles the posterior cricoarytenoid is the only ABductor of the vocal folds; the arteries
cricoarytenoid, lateral
cricoarytenoid, posterior
posterior surface of the lamina of the cricoid cartilage
muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage
draws the muscular process posteriorly, which pivots the arytenoid cartilage
inferior laryngeal nerve, from the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of
superior laryngeal a., cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a.
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
and abducts the vocal the vagus nerve folds (X)
that supply the larynx anastomose within the larynx to supply the mucous membranes and muscles cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a., ascending pharyngeal a. cricopharyngeus represents the lowest fibers of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor; it is continuous with the esophagus below and marks the beginning of it this is the only intrinsic muscle of the larynx that is not supplied by the recurrent laryngeal n.; ALL other laryngeal muscles are innervated by recurrent laryngeal nerve, via its inferior laryngeal branch
cricopharyngeus
lateral surface of the midline pharyngeal cricoid cartilage raphe
constricts the pharyngeal cavity and the entrance to the esophagus
recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X)
cricothyroid
arch of the cricoid cartilage
inferior border of the draws the thyroid thyroid cartilage cartilage forward, lengthening the vocal ligaments
external branch of superior laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X)
cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a.
depressor anguli oris
oblique line of the mandible
angle of the mouth
pulls the corner of the marginal inferior labial branch a "frown" muscle mouth downward mandibular & of the facial a., buccal branches of mental a. the facial nerve (VII) depresses the lower lip marginal inferior labial branch this muscle is used to mandibular branch of the facial a., bare the lower incisor of the facial nerve mental a. teeth (VII)
depressor labii inferioris
anterior surface of the mandible
skin of the lower lip
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
depressor septi
maxilla near the midline above the incisor teeth anterior belly: digastric fossa of the mandible; posterior belly: mastoid notch of the temporal bone
nasal septum
depresses the nasal septum; involved in flaring the nostrils elevates the hyoid bone; depresses the mandible
buccal branch of facial nerve (VII) anterior belly: mylohyoid nerve, from the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V); posterior belly: facial nerve (VII) sympathetic fibers via short ciliary nerves, synapsing in superior cervical sympathetic ganglion
superior labial branch of the facial a. anterior belly: submental a.; posterior belly: occipital a.
depressor septi is considered a part of the nasalis m. the digastric m. forms two sides of the submandibular triangle; it is formed from mesenchyme derived from the first two pharyngeal arches, hence its dual innervation none
digastric
body of the hyoid via a fibrous loop over an intermediate tendon
dilator pupillae
outer margin of iris
inner margin of iris
dilates the pupil
ophthalmic a.
epicranius
frontalis: galea aponeurotica; occipitalis: superior nuchal line
frontalis: skin of the eyebrows; occipitalis: galea aponeurotica
elevates the eyebrows frontalis: temporal and wrinkles the branches of the forehead facial nerve (VII); occipitalis: posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve (VII) elevates the eyebrows temporal branches and wrinkles the of the facial nerve forehead (VII) hypoglossal nerve (XII)
frontalis: supraorbital and supratrochlear aa.; occipitalis: occipital a.
the frontalis and occipitalis muscles are two bellies of the epicranius muscle; also known as: occipitofrontalis m. frontalis is the anterior belly of the epicranius muscle an extrinsic muscle of the tongue; XII innervates all tongue
frontalis
galea aponeurotica
skin of the eyebrow
supraorbital and supratrochlear aa. lingual a.
genioglossus
mental spine on the inner aspect of the mental symphysis
fans out to insert into protrudes the tongue the tongue from the (inferior fibers); tip to the base depresses tongue
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
(middle fibers)
muscles except palatoglossus [innervated by vagus (X), as are most of the palate and pharynx muscles]; genioglossus is used to test the function of cranial nerve XII ventral primary lingual a., submental ramus of spinal a. nerve C1 via fibers carried by the hypoglossal nerve thyrohyoid and geniohyoid receive ansa cervicalis fibers that travel with the hypoglossal nerve distal to the superior limb of the ansa cervicalis an extrinsic muscle of the tongue
geniohyoid
mental spines of the body of the hyoid mandible bone
elevates the hyoid bone; depresses the mandible
hyoglossus
upper border of the greater horn of the hyoid and body of the hyoid bone floor of the orbit lateral to the lacrimal groove
spreads out into the intrinsic muscles of the tongue
depresses the sides of hypoglossal nerve the tongue; retracts (XII) the tongue
lingual a.
inferior oblique
sclera on the inferior elevates and abducts oculomotor nerve surface of the the corneal part of the (III), inferior eyeball eye; rotates the division superior pole of the iris laterally; when the eye is adducted, this muscle elevates the cornea midline pharyngeal raphe constricts pharyngeal cavity
ophthalmic a.
clinicians examining the eye will ask the patient to look toward the bridge of the nose to test the function of this muscle
inferior pharyngeal constrictor
oblique line of the thyroid cartilage, lateral surface of
vagus (X), via the ascending pharyngeal plexus, pharyngeal a., with aid from the superior thyroid a.,
the most external of the three pharyngeal constructor mm.
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
cricoid cartilage
superior laryngeal and recurrent laryngeal nerves sclera on the inferior depresses and adducts oculomotor nerve surface of the the corneal part of the (III), inferior eyeball eyeball; rotates the division superior pole of the iris laterally muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage draws the muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage anteriorly, which pivots the arytenoid cartilage and adducts the vocal folds inferior laryngeal nerve, from the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X)
inferior thyroid a.
inferior rectus
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit
ophthalmic a.
because this muscle approaches the eyeball from a medial direction, it has a rotational action on the iris an antagonist of the posterior cricoarytenoid m.; the arteries that supply the larynx anastomose within the larynx to supply the mucous membranes and muscles the only one of the muscles of mastication that opens the mouth; the superior head of lateral pterygoid is sometimes called sphenomeniscus due to its insertion into the disc of the temporomandibular joint loss of function of the abducens nerve will cause the eye to be
lateral cricoarytenoid
arch of the cricoid cartilage
superior laryngeal a., cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a.
lateral pterygoid
superior head: greater wing of the sphenoid bone; inferior head: lateral surface of the lateral pterygoid plate
superior head: capsule and & articular disk of the temporomandibular joint; inferior head: neck of the mandible
protracts the mandible; opens the mouth; active in grinding actions of chewing
lateral pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V)
pterygoid branch of the maxillary a.
lateral rectus
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit
sclera on the lateral surface of the eyeball
abducts the corneal part of the eyeball
abducens nerve (VI)
ophthalmic a.
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
abducted levator anguli oris canine fossa of the maxilla angle (corner) of the mouth elevates the angle of the mouth buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) oculomotor nerve (III) and sympathetics (to the superior tarsal portion) infraorbital a., superior labial branch of the facial a. infraorbital a., superior labial branch of the facial a. infraorbital a., superior labial branch of the facial a. ophthalmic a. a "smile" muscle
levator labii superioris
inferior margin of the orbit
skin of the upper lip
elevates the upper lip
levator labii superioris is used to bare the upper incisor teeth, as in a sneer none
levator labii superioris alaque nasi levator palpebrae superioris
frontal process of the maxilla
ala of the nose and skin of the upper lip
elevates the upper lip and flares the nostril
apex of the orbit above the optic canal
skin and fascia of upper eyelid and the superior tarsal plate
elevates the upper eyelid
fibers inserting into the superior tarsal plate are called superior tarsal muscle and are smooth muscle; lesion of the sympathetic supply causes slight ptosis (drooping of the eyelid) named for its action
levator scapulae
transverse processes medial border of the of C1-4 vertebrae scapula from the superior angle to the spine
elevates scapula
dorsal scapular nerve (C5); the upper part of the muscle receives branches of C3 & C4 spinal nerves vagus nerve (X) via the pharyngeal plexus
dorsal scapular a.
levator veli palatini
apex of the petrous muscles and fascia part of the temporal of the soft palate; bone and the medial palatine aponeurosis
elevates the soft palate
ascending pharyngeal a.
a derivative of the fourth pharyngeal arch
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
surface of the auditory tube cartilage linguae, longitudinalis within tongue within tongue near the apex shapes the tongue for speech and mastication hypoglossal nerve (XII) lingual a. an intrinsic muscle of the tongue; longitudinalis has superior and inferior subdivisions that span the length of the tongue an intrinsic muscle of the tongue whose fibers run transversely an intrinsic muscle of the tongue whose fibers run superoinferiorly none
linguae, transversus within tongue
within tongue
compresses the sides of the tongue; shapes the tongue for speech and mastication shapes the tongue for speech and mastication
hypoglossal nerve (XII)
lingual a.
linguae, verticalis
within tongue
within tongue
hypoglossal nerve (XII)
lingual a.
longus capitis
anterior tubercles of basilar portion of the flex the head and vertebrae C3-6 occipital bone neck
cervical plexus, ventral primary rami of spinal nerves C1-4 cervical and brachial plexus, C2-7
deep cervical a.
longus colli
anterior tubercles and anterior surfaces of the bodies of vertebrae C3-T3 zygomatic arch and zygomatic bone
anterior arch of atlas, flex neck, rotate and anterior tubercles of laterally bend neck C5-6, anterior surfaces of bodies of vertebrae C2-4 lateral surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible
deep cervical a.
none
masseter
elevates the mandible nerve to the masseter, from the mandibular division of the
masseteric branch of a powerful chewing the maxillary a. muscle
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
trigeminal nerve (V) medial pterygoid medial surface of medial surface of the elevates and protracts the lateral pterygoid ramus and angle of the mandible plate, pyramidal the mandible process of the palatine bone, tuberosity of the maxilla common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit sclera on the medial surface of the eyeball adducts the corneal part of the eyeball elevates the lower lip and skin of chin medial pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V) oculomotor nerve (III) (inferior division) pterygoid branch of the maxillary a. this muscle mirrors the masseter m. in position and action with the ramus of the mandible between the two mm.
medial rectus
ophthalmic a.
this muscle directly opposes the action of the lateral rectus m.
mentalis
anterior surface of skin of the chin the mandible near the mental symphysis (midline) lesser and greater horns of the hyoid bone and the inferior part of the stylohyoid ligament posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C2-C7 midline pharyngeal raphe
marginal mental a., inferior mandibular branch labial branch of the of the facial nerve facial a. (VII) vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus ascending pharyngeal a. of the three pharyngeal constrictors, this one is intermediate in both superior/inferior position and depth
middle pharyngeal constrictor
constricts the pharyngeal cavity
middle scalene
upper surface of the first rib behind the subclavian artery
elevates the first rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck
brachial plexus, C3-C8
ascending cervical a. a muscle of respiration (inspiratory); also called scalenus medius; penetrated by the dorsal scapular n. and long thoracic n. lesser palatine a. the soft palate and uvula resist the upward pressure of the tongue during swallowing
musculus uvulae
posterior nasal spine mucosa of the uvula
shortens the uvula
vagus nerve (X) via pharyngeal plexus
10
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
mylohyoid
mylohyoid line of mandible
midline raphe and body of the hyoid bone
elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue; depresses the mandible
mylohyoid nerve from the inferior alveolar nerve, a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V)
mylohyoid branch of the nerve to mylohyoid the inferior alveolar also innervates the a. anterior belly of digastric m.; both muscles are derivatives of the second pharygneal arch superior labial branch of the facial a. superior labial branch of the facial a. superior labial branch of the facial a. nasalis has two subsidiary parts: nasalis pars alaris and pars transversa a subdivision of the nasalis m. a subdivision of the nasalis m. the oblique arytenoid m. lies posterior to the transverse arytenoid m.; the arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse fibers clinicians examining the eye will ask the patient to look toward the bridge of the nose to test the function of this muscle
nasalis
maxilla above the ala of the nose and incisor teeth and the midline aponeurosis canine teeth maxilla above the canine teeth maxilla above the incisor teeth muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage ala of the nose
flattens the nose, flare buccal branch of the nostrils the facial nerve (VII) flares the nostrils buccal branch of facial nerve (VII) buccal branch of facial nerve (VII)
nasalis pars alaris
nasalis pars transversa oblique arytenoid
midline aponeurosis
flattens the nose
posterior surface of the contralateral arytenoid cartilage, near its apex
draws arytenoid cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds
inferior laryngeal laryngeal br. of the nerve, from superior thyroid a. recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the of vagus (X)
oblique, inferior
floor of the orbit lateral to the lacrimal groove
sclera on the inferior elevates and abducts oculomotor nerve surface of the the corneal part of the (III), inferior eyeball eye; rotates the division superior pole of the iris laterally; when the eye is adducted,
ophthalmic a.
11
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
this muscle elevates the cornea oblique, superior apex of the orbit above the optic canal sclera on the posterior superior surface of the eyeball depresses and abducts trochlear nerve the eyeball; rotates (IV) the superior pole of the iris medially ophthalmic a. passes through a fibrocartilagenous pulley known as the trochlea; when the eye is adducted, this muscle moves the cornea inferiorly occipitalis is the posterior belly of the epicranius muscle the frontalis and occipitalis muscles are two bellies of the occipitofrontalis muscle; also known as: epicranius m.
occipitalis
superior nuchal line
galea aponeurotica
pulls the scalp posteriorly; elevates the eyebrows
posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve (VII)
occipital a.
occipitofrontalis
frontalis: galea aponeurotica; occipitalis: superior nuchal line
frontalis: skin of the eyebrows; occipitalis: galea aponeurotica
elevates the eyebrows frontalis: temporal and wrinkles the branches of the forehead facial nerve (VII); occipitalis: posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve (VII) ansa cervicalis
frontalis: supraorbital and supratrochlear aa.; occipitalis: occipital a.
omohyoid
inferior belly: upper border of the scapula medial to the scapular notch; superior belly: intermediate tendon orbital part: medial orbital margin and the medial palpebral ligament; palpebral part: medial palpebral ligament
inferior belly: depresses/stabilizes intermediate tendon; the hyoid bone superior belly: lower border of the hyoid bone lateral to the sternohyoid insertion orbital part: skin of the lateral cheek; palpebral part: lateral palpebral raphe closes the eyelids
transverse cervical a. the intermediate tendon of omohyoid is tethered to the clavicle by a fascial sling
orbicularis oculi
temporal & zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (VII)
supraorbital a., supratrochlear a., infraorbital a., angular branch of the facial a.
activated involuntarily in the blink reflex; the palpebral part is active in normal blinking and the orbital part is used to forcefully close the eye
12
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
orbicularis oris
skin and fascia of lips and the area surrounding the lips
skin and fascia of the purses the lips lips
buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) vagus nerve (X) via the pharyngeal plexus
superior and inferior the "kissing" muscle labial branches of the facial a., mental a., infraorbital a. tonsilar branch of the facial a., ascending pharyngeal a. although palatoglossus sounds like a tongue muscle (and would therefore be innervated by XII), it is a palatal muscle innervated by X palatopharyngeus is part of the inner longitudinal muscle layer of the pharynx platysma is derived from the mesenchyme of the second pharyngeal arch the posterior cricoarytenoid is the only ABductor of the vocal folds; the arteries that supply the larynx anastomose within the larynx to supply the mucous membranes and muscles
palatoglossus
palatine aponeurosis side of the tongue, entering it from above
elevates and retracts the tongue
palatopharyngeus
posterior margin of the bony palate and the palatine aponeurosis
posterior wall of the pharynx and the posterior margin of the thyroid cartilage
elevates the larynx
vagus nerve (X) via pharyngeal plexus cervical branch of the facial nerve (VII) inferior laryngeal nerve, from the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X)
ascending pharyngeal a.
platysma
fascia overlying the inferior border of the draws the corners of pectoralis major and mandible and skin of the mouth down; it deltoid muscles lower face aids in depression of the mandible posterior surface of the lamina of the cricoid cartilage muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage draws the muscular process posteriorly, which pivots the arytenoid cartilage and abducts the vocal folds
facial a.
posterior cricoarytenoid
superior laryngeal a., cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a.
posterior scalene
posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C5-C7
lateral surface of the second rib
elevates the second rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck
brachial plexus, C7-C8
ascending cervical a. a muscle of respiration (inspiratory); it is the longest of the scalene muscles
13
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
procerus
nasal bone
skin between the eyebrows superior head: capsule and & articular disk of the temporomandibular joint; inferior head: neck of the mandible
depresses the medial corners of the eyebrows protracts the mandible; opens the mouth; active in grinding actions of chewing
temporal branch of supratrochlear a. the facial nerve (VII) lateral pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V) pterygoid branch of the maxillary a.
none
pterygoid, lateral
superior head: greater wing of the sphenoid bone; inferior head: lateral surface of the lateral pterygoid plate
the only one of the muscles of mastication that opens the mouth; the superior head of lateral pterygoid is sometimes called sphenomeniscus due to its insertion into the disc of the temporomandibular joint this muscle mirrors the masseter m. in position and action with the ramus of the mandible between the two mm.
pterygoid, medial
medial surface of medial surface of the elevates and protracts the lateral pterygoid ramus and angle of the mandible plate, pyramidal the mandible process of the palatine bone, tuberosity of the maxilla outer margin of iris inner margin of iris dilates the pupil
medial pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V) sympathetic fibers via short ciliary nerves, synapsing in superior cervical sympathetic ganglion parasympathetic fibers of oculomotor nerve (III), synapsing in
pterygoid branch of the maxillary a.
pupillae, dilator
ophthalmic a.
none
pupillae, sphincter
encircles iris
encircles iris
constricts the pupil
ophthalmic a.
none
14
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
ciliary ganglion rectus capitis anterior rectus capitis lateralis rectus, inferior lateral mass of atlas basilar portion of occipital bone occipital bone anterolateral to foramen magnum flexes the head ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve C1 ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve C1 deep cervical a. none
transverse process of atlas common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit
laterally bends the head
deep cervical a.
none
sclera on the inferior depresses and adducts oculomotor nerve surface of the the corneal part of the (III), inferior eyeball eyeball; rotates the division superior pole of the iris laterally sclera on the lateral surface of the eyeball sclera on the medial surface of the eyeball sclera on the superior surface of the eyeball abducts the corneal part of the eyeball abducens nerve (VI)
ophthalmic a.
because this muscle approaches the eyeball from a medial direction, it has a rotational action on the iris loss of function of the abducens nerve will cause the eye to be abducted this muscle directly opposes the action of the lateral rectus m. because this muscle approaches the eye from a medial position, it causes the iris to rotate medially risorius is active in expressions of mirth like other muscles of the pharyngeal wall,
rectus, lateral
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit
ophthalmic a.
rectus, medial
adducts the corneal part of the eyeball elevates and adducts the eyeball; rotates the superior pole of the iris medially draws the corner of the mouth laterally elevates the larynx
oculomotor nerve (III) (inferior division) oculomotor nerve (III), superior division
ophthalmic a.
rectus, superior
ophthalmic a.
risorius
fascia of the lateral cheek
skin of the angle (corner) of the mouth pharyngeal wall and superior border of
buccal branches of transverse facial a., the facial nerve facial a. (VII) vagus nerve (X) via the pharyngeal ascending pharyngeal a.
salpingopharyngeus inferior surface of the anteromedial
15
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
end of the auditory tube cartilage scalene, anterior
the thyroid cartilage along with the palatopharyngeus m. elevates the first rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck
plexus
salpingopharyngeus is derived from the fourth pharyngeal arch ascending cervical a., a branch of the thyrocervical trunk a muscle of inspiration; an important landmark of the neck; it is located between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery; the roots of the brachial plexus pass posterior to it; the phrenic nerve crosses its anterior surface
anterior tubercles of scalene tubercle of the transverse the first rib processes of vertebrae C3-C6
brachial plexus, C5-C7
scalene, middle
posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C2-C7
upper surface of the first rib behind the subclavian artery
elevates the first rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck
brachial plexus, C3-C8
ascending cervical a. a muscle of respiration (inspiratory); also called scalenus medius; penetrated by the dorsal scapular n. and long thoracic n. ascending cervical a. a muscle of respiration (inspiratory); it is the longest of the scalene muscles pterygoid branch of the maxillary a. sphenomeniscus is another name for the superior belly of the lateral pterygoid m.
scalene, posterior
posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C5-C7 greater wing of the sphenoid
lateral surface of the second rib
elevates the second rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck pulls the articular disk forward in opening of the mouth
brachial plexus, C7-C8
sphenomeniscus
capsule and articular disk of the temporomandibular joint
lateral pterygoid branch of mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (V) parasympathetic
sphincter pupillae
encircles iris
encircles iris
constricts the pupil
ophthalmic a.
none
16
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
fibers of oculomotor nerve (III), synapsing in ciliary ganglion splenius ligamentum nuchae and spines C7-T6 capitis: mastoid process & superior nuchal line laterally; cervicis: posterior tubercles of C1-3 extends and laterally bends neck and head; rotates head to same side dampens vibration of the stapes dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C2-6 supplied segmentally by: deep cervical a., posterior intercostal aa. anterior tympanic a. splenius means bandage; it gets its name from its broad, flat shape entirely enclosed in bone, except for its tendon; a derivative of the second pharyngeal arch carotid sheath structures lie deep to it
stapedius
walls of the neck of the stapes pyramidal eminence
facial nerve (VII)
sternocleidomastoid sternal head: anterior surface of the manubrium; clavicular head: medial 1/3rd of the clavicle
mastoid process and lateral 1/2 of the superior nuchal line
draws the mastoid process down toward the same side which causes the chin to turn up toward the opposite side; acting together, the muscles of the two sides flex the neck depresses/stabilizes the hyoid bone
spinal accessory sternocleidomastoid nerve (XI), with branch of the sensory supply occipital a. from C2 & C3 (for proprioception)
sternohyoid
posterior surfaces of both the manubrium and sternal end of the clavicle posterior surface of the manubrium below the origin of the sternohyoid m.
lower border of the hyoid bone, medial to the omohyoid m. insertion oblique line of the thyroid cartilage
ansa cervicalis
superior thyroid a.
sternohyoid overlies the sternothyroid and thyrohyoid mm. sternothyroid lies deep to the sternohyoid m.
sternothyroid
depresses/stabilizes the hyoid bone
ansa cervicalis
superior thyroid a.
17
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
styloglossus
anterior side of the styloid process
posterolateral side of retracts and elevates the tongue the tongue
hypoglossal nerve (XII)
ascending pharyngeal a., ascending palatine branch of the facial a. ascending pharyngeal a.
an extrinsic muscle of the tongue
stylohyoid
posterior side of the styloid process
splits around the elevates and retracts intermediate tendon the hyoid bone of the digastric m. to insert on the body of the hyoid bone
facial nerve (VII)
facial nerve innervates both the stylohyoid m. and the posterior belly of the digastric m. shortly after exiting from the stylomastoid foramen stylopharyngeus, the only muscle innervated by IX, is the only muscle of the pharyngeal wall NOT innervated by the vagus (X) nerve; it is a derivative of the third pharyngeal arch passes through a fibrocartilagenous pulley known as the trochlea; when the eye is adducted, this muscle moves the cornea inferiorly the most internal of the three pharyngeal constructor mm.
stylopharyngeus
medial side of the styloid process
superior border of the thyroid cartilage and also into the pharyngeal wall
elevates the larynx
glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
ascending pharyngeal a.
superior oblique
apex of the orbit above the optic canal
sclera on the posterior superior surface of the eyeball
depresses and abducts trochlear nerve the eyeball; rotates (IV) the superior pole of the iris medially
ophthalmic a.
superior pharyngeal medial pterygoid constrictor plate, pterygoid hamulus, pterygomandibular
pharyngeal tubercle and midline pharyngeal raphe
constricts the pharyngeal cavity
vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus
ascending pharyngeal a.
18
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
raphe, mylohyoid line of mandible superior rectus common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit sclera on the superior surface of the eyeball elevates and adducts the eyeball; rotates the superior pole of the iris medially elevates the mandible; retracts the mandible (posterior fibers) oculomotor nerve (III), superior division ophthalmic a. because this muscle approaches the eye from a medial position, it causes the iris to rotate medially a powerful chewing muscle; a derivative of the first pharyngeal arch
temporalis
temporal fossa and the temporal fascia
coronoid process of the mandible and the anterior surface of the ramus of the mandible
anterior and posterior deep temporal nerves from the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V) medial pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V) mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V)
anterior and posterior deep temporal aa.
tensor tympani
cartilagenous auditory tube and the greater wing of the sphenoid bone which lies adjacent to it scaphoid fossa, lateral wall of the auditory tube cartilage
manubrium of the malleus
dampens vibrations of the tympanic membrane
superior tympanic V3 innervates both branch of the middle tensor muscles of the meningeal a. head (tympani and veli palatini) which are derivatives of the first pharyngeal arch ascending pharyngeal a. remember: V3 innervates both tensor muscles (tympani and veli palatini); ALL other palatal muscles are innervated by vagus its subsidiary parts are the thyroepiglottic m. and the vocalis m.; the medial most fibers of
tensor veli palatini
palatine aponeurosis
opens the auditory tube; tenses the soft palate
thyroarytenoid
inner surface of the thyroid cartilage anteriorly
lateral border of the arytenoid cartilage
draws the arytenoid cartilage forward, relaxing and adducting the vocal
inferior laryngeal laryngeal branch of nerve, from the superior thyroid recurrent laryngeal a. nerve, a branch of
19
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
folds
the vagus nerve (X)
thyroarytenoid that insert along the vocal ligament are called the vocalis muscle represents the superior fibers of thyroarytenoid muscle which fan out to the quadrangular membrane and epiglottis thyrohyoid lies deep to the sternohyoid
thyroepiglottic
inner surface of the thyroid cartilage near the laryngeal prominence
lateral surface of the epiglottic cartilage
draws the epiglottic cartilage downward
inferior laryngeal laryngeal branch of nerve, from the superior thyroid recurrent laryngeal a. nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X) ansa cervicalis (via superior thyroid a. fibers running with the hypoglossal nerve that leave XII distal to the superior limb of ansa) preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from the vagus (X) nerve inferior thyroid a., bronchial aa.
thyrohyoid
oblique line of the thyroid cartilage
lower border of the hyoid bone
elevates the larynx; depresses/stabilizes the hyoid bone
trachealis
posterior edge of the posterior edge of the tracheal cartilage tracheal cartilage of other side (joins tracheal rings posteriorly) posterior surface of the contralateral arytenoid cartilage
constricts the bronchi and trachea
smooth muscle, found in the submucosal layer
transverse arytenoid posterior surface of the arytenoid cartilage
draws arytenoid cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds
inferior laryngeal laryngeal br. of the nerve, from superior thyroid a. recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X)
the transverse arytenoid m.lies anterior to the oblique arytenoid m.; the arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse parts the transverse
transverse arytenoid posterior surface of
posterior surface of
draws arytenoid
inferior laryngeal
laryngeal br. of the
20
ANATOMY TABLES | MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
Med.bramjnet.com
the arytenoid cartilage
the contralateral arytenoid cartilage
cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds
nerve, from superior thyroid a. recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X)
arytenoid m.lies anterior to the oblique arytenoid m.; the arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse parts represents the innermost fibers of the thyroarytenoid muscle; the cricothyroid m. grossly tenses the vocal ligaments, while the vocalis muscle provides the mechanism for fine tuning the vibrations of the vocal folds a "smile" muscle
vocalis
surface of the thyroid cartilage, vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage
vocal ligament
relaxes segments of the vocal ligament, thereby adjusting pitch
inferior laryngeal laryngeal br. of the nerve, from the superior thyroid a. recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X)
zygomaticus major
upper lateral surface skin of the angle of of the zygomatic the mouth bone lower surface of the zygomatic bone lateral part of the upper lip
elevates and draws the corner of the mouth laterally elevates the upper lip
zygomatic and transverse facial a., buccal branches of facial a. the facial nerve (VII) buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) transverse facial a., facial a.
zygomaticus minor
a "smile" muscle
21
You might also like
- Anatomy Mnemonics PDFDocument31 pagesAnatomy Mnemonics PDFNonoy JoyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeadDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The HeadAbdul Nasifh Bn Hamsa100% (1)
- Clinical Notes of Lower LimbDocument5 pagesClinical Notes of Lower Limbbeia21100% (1)
- Mnemonic SDocument8 pagesMnemonic Smueen hashmiNo ratings yet
- List BonesDocument38 pagesList Bonesshahera rosdiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Final ReviewDocument35 pagesAnatomy Final ReviewMarie100% (1)
- Flower Crochet Ebook - 294885.PDF (Pdfdrive)Document125 pagesFlower Crochet Ebook - 294885.PDF (Pdfdrive)Lhen Pranciliso100% (1)
- 6.nerves of Head and NeckDocument36 pages6.nerves of Head and NeckDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics Head NeckDocument8 pagesMnemonics Head NeckMartin Susanto, MD100% (2)
- Cranial Nerves DiagramDocument12 pagesCranial Nerves Diagramsahana2791100% (2)
- The Lower LimbDocument89 pagesThe Lower LimbSantiFaridKalukuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Head and Neck Table of NervesDocument11 pagesAnatomy - Head and Neck Table of NervesIke Ononiwu100% (3)
- MnemonicsDocument34 pagesMnemonicsAleena Stephen100% (2)
- Gluteal RegionDocument34 pagesGluteal Regionlion2chNo ratings yet
- Manual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THDocument6 pagesManual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THAljon S. TemploNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument544 pagesCranial NerveszenabNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2 MnemonicsDocument17 pagesAnatomy 2 MnemonicsRosalie Catalan EslabraNo ratings yet
- Unisystem PiratesDocument8 pagesUnisystem PiratesAnime300100% (1)
- Anatomy of PharynxDocument27 pagesAnatomy of PharynxmichelleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Mnemonics Collections For Medical Students2Document99 pagesAnatomy Mnemonics Collections For Medical Students2kuku93No ratings yet
- Anterior Triangle of The Neck JDVDocument5 pagesAnterior Triangle of The Neck JDVNica Lopez Fernandez100% (3)
- Neuroanatomy Revision Notes PDFDocument7 pagesNeuroanatomy Revision Notes PDFTanya Tanu100% (1)
- Embryology of The Head and NeckDocument18 pagesEmbryology of The Head and NeckDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity For Grade 6Document49 pagesBiodiversity For Grade 6Jennifer Silva-PabillareNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument46 pagesAnatomy MnemonicsMini ManraiNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia: Presented byDocument68 pagesCerebellum and Basal Ganglia: Presented byDivya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck AnatomyDocument115 pagesHead and Neck AnatomyMobarobber100% (11)
- Head and Neck QuestionsDocument8 pagesHead and Neck QuestionsANDRE MA100% (2)
- Arterial Supply of Head and NeckDocument41 pagesArterial Supply of Head and NeckKhadija VasiNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument11 pagesHead and NeckHisham ChomanyNo ratings yet
- MBR 2019 - Anatomy Handouts - CompleteDocument88 pagesMBR 2019 - Anatomy Handouts - CompleteNica Lopez Fernandez100% (4)
- ForearmDocument58 pagesForearmRamon Jovi Lumayag100% (1)
- Anatomy of PharynxDocument31 pagesAnatomy of PharynxMuhammad KamilNo ratings yet
- HSB - Neck: Anterior TriangleDocument8 pagesHSB - Neck: Anterior TriangleRaki Iligan100% (1)
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument15 pagesAnatomy Mnemonicsamarch517No ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Notes 2010Document33 pagesNeuroanatomy Notes 2010Jennifer David InauenNo ratings yet
- Lapbook About CanadaDocument45 pagesLapbook About CanadaTanyaHrabovaNo ratings yet
- MeningesDocument43 pagesMeningesRehab NaeemNo ratings yet
- Posterior and Anterior MediastinumDocument6 pagesPosterior and Anterior MediastinumYheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument11 pagesHead and NeckdrsamnNo ratings yet
- GRSANA - Lec5 Temporal Fossa, Infratemporal Fossa, and TMJ - WongDocument9 pagesGRSANA - Lec5 Temporal Fossa, Infratemporal Fossa, and TMJ - WongRainier Raul Echipare100% (1)
- Brainstem (Pons, Medulla, Midbrain) : Dr. MariaDocument23 pagesBrainstem (Pons, Medulla, Midbrain) : Dr. MariaMuhammad Mustaqeem100% (1)
- Tips For Studying MusclesDocument2 pagesTips For Studying Musclesapi-19510625100% (11)
- Head and Neck Cheat Sheets PDFDocument8 pagesHead and Neck Cheat Sheets PDFJM LiensNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of LarynxDocument63 pagesAnatomy of Larynxdrsaurabhvijay100% (1)
- Anatomy Tables-Veins of The Head and NeckDocument8 pagesAnatomy Tables-Veins of The Head and NeckTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb ReviewDocument24 pagesLower Limb ReviewRyan SilberNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckDocument20 pagesAnatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of LarynxDocument49 pagesAnatomy of LarynxenoNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITDocument5 pagesPharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITdrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Neck Axilla BackDocument24 pagesNeck Axilla BackmoregutsNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin, Insertion and Action TableDocument12 pagesMuscle Origin, Insertion and Action TableCort07186% (14)
- Triangles of The NeckDocument65 pagesTriangles of The NeckPaulo Duata100% (3)
- Univ of Michigan - Gross Anatomy - Muscles TablesDocument41 pagesUniv of Michigan - Gross Anatomy - Muscles TablesDarren Lim100% (1)
- Head and Neck AnswersDocument15 pagesHead and Neck AnswersANDRE MANo ratings yet
- Anatomy Tables-Nerves of The Head and NeckDocument36 pagesAnatomy Tables-Nerves of The Head and NeckTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Enamel Etching and Dentine ConditionerDocument1 pageEnamel Etching and Dentine ConditionerTracie YW100% (4)
- Animal Sacrifice in The Ancient Greek Wo PDFDocument11 pagesAnimal Sacrifice in The Ancient Greek Wo PDFANY1NEXT100% (1)
- Petersen's Bowhunting 2019-01Document68 pagesPetersen's Bowhunting 2019-01Michael CuaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Dentine StructureDocument5 pagesNotes On Dentine StructureTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Sinelnikov Vol IIDocument436 pagesSinelnikov Vol IIOana Musteaţǎ95% (59)
- Reinforcement and Extension 2Document12 pagesReinforcement and Extension 2Patri Pardellas BlunierNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocument72 pagesAnatomy - Upper LimbAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- Muscles of MasticationDocument23 pagesMuscles of Masticationبراءة أحمد السلامات100% (1)
- Anatomy Mnemonics (Upper Limbs) - Mnemonics - MosaicedDocument4 pagesAnatomy Mnemonics (Upper Limbs) - Mnemonics - MosaicedMDreamer50% (2)
- Nerve and Blood Supply of Lower ExtremitiesDocument22 pagesNerve and Blood Supply of Lower ExtremitiesBenjamin Prabhu100% (3)
- Upper LimbDocument20 pagesUpper LimbsamzailNo ratings yet
- NeckDocument68 pagesNeckKannan GovindanNo ratings yet
- Bones and Cartilages of The Head and NeckDocument27 pagesBones and Cartilages of The Head and Neckyachiru121100% (1)
- Toothache On The Left SideDocument3 pagesToothache On The Left SideTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency VirusDocument9 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency VirusTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerotic PlaqueDocument12 pagesAtherosclerotic PlaqueTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Fissure SealantsfinalDocument1 pageFissure SealantsfinalTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Caries Risk and SusceptibilityDocument6 pagesCaries Risk and SusceptibilityTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Tregs in The Control of Immune PathologyDocument7 pagesTregs in The Control of Immune PathologyTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Notes On Biological Considerations of Restorative DentistryDocument5 pagesNotes On Biological Considerations of Restorative DentistryTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases That Cause Prolonged Bleeding (Poster)Document1 pageInfectious Diseases That Cause Prolonged Bleeding (Poster)Tracie YWNo ratings yet
- Flav I VirusesDocument1 pageFlav I VirusesTracie YWNo ratings yet
- D. L. Bliss State Park HandbookDocument4 pagesD. L. Bliss State Park HandbookCalifornia State ParksNo ratings yet
- Raggedyannstories PDFDocument83 pagesRaggedyannstories PDFMilena MarquesNo ratings yet
- Brain Training Dogs (Develops Your Dog's "Hidden Intelligence")Document16 pagesBrain Training Dogs (Develops Your Dog's "Hidden Intelligence")JohnNo ratings yet
- OSCE - Chest PainDocument2 pagesOSCE - Chest PaincgalongNo ratings yet
- WWW Healingqigong Org 8 Section BrocadeDocument8 pagesWWW Healingqigong Org 8 Section BrocadeqpidoneuroNo ratings yet
- Sentence Corrections PracticeDocument112 pagesSentence Corrections Practicebook_reader_regularNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5. Gas Exchange: Cellular Respiration, Oxidative Processes Within External Respiration, Exchange of O2 and CO2Document24 pagesLecture 5. Gas Exchange: Cellular Respiration, Oxidative Processes Within External Respiration, Exchange of O2 and CO2Jay JayNo ratings yet
- FOM STUDY GUIDE 3rd Block 1Document3 pagesFOM STUDY GUIDE 3rd Block 1Bernadine Cruz Par100% (1)
- DR Mushtaq Amna Ashraf Aqsa Bashir Ayesha Bibi Hira Nisar Iqra HabibDocument5 pagesDR Mushtaq Amna Ashraf Aqsa Bashir Ayesha Bibi Hira Nisar Iqra HabibtaibiNo ratings yet
- Lion and Tiger Hybrid: Liger: Presented By: Harsh Salunkhe Xi ScienceDocument14 pagesLion and Tiger Hybrid: Liger: Presented By: Harsh Salunkhe Xi ScienceHarsh SalunkheNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ 48Document7 pagesĐỀ 48bichngocvonagiNo ratings yet
- Wild Life PDFDocument27 pagesWild Life PDFSaagar SenniNo ratings yet
- Medical Form For NimDocument1 pageMedical Form For NimvishalNo ratings yet
- Ensayo StreptococoDocument3 pagesEnsayo StreptococoEfraín Carrera FigueroaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-19-20 XI Zoo Study-Package-1 Level-1 Chapter-1 PDFDocument20 pagesCLS Aipmt-19-20 XI Zoo Study-Package-1 Level-1 Chapter-1 PDFJainil PatelNo ratings yet
- WALIKI Mens Knits 2010Document17 pagesWALIKI Mens Knits 2010Waliki Design TeamNo ratings yet
- Passion and Deceit Part VI PDFDocument20 pagesPassion and Deceit Part VI PDFno2meNo ratings yet
- Daily Reading Book 1 PDFDocument11 pagesDaily Reading Book 1 PDFSanjeevan SivapaleswararajahNo ratings yet
- I. EmbryologyDocument6 pagesI. EmbryologyEzra GenerosoNo ratings yet
- Support For WSU Researcher Dr. RobbinsDocument12 pagesSupport For WSU Researcher Dr. RobbinsKaitlin RiordanNo ratings yet
- Vem007 Sas01Document8 pagesVem007 Sas01wgyk54ypkmNo ratings yet
- Livestock LineDocument44 pagesLivestock LinePoultry LivestockNo ratings yet