Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharynyx and Larynx
Uploaded by
kep1313Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharynyx and Larynx
Uploaded by
kep1313Copyright:
Available Formats
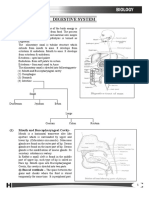
Pharynx and larynx Nasal cavity: from anterior nares to posterior nasal aperture Oral cavity: from mouth
to oropharyngeal isthmus between palatoglossal folds Pharynx: first part of foregut Attached above to skull and continuous below the esophagus Subdivided into 3 regions o Nasopharynx behind nasal cavity and above the soft pale o Oropharynx 0 behind the oral cavity and below the soft palate o Laryngopharynx - behind the pharynx (extends from tip of epiglottis to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage Posterior apertures of the nasal cavities open into the nasopharynx (behind the nasal cavity and above the soft palate Posterior opening of oral cavity - the oropharyngeal isthmus opens into the oropharynx Superior aperture of the larynx, the laryngeal inlet opens into the laryngopharynx Esophagus- beings at lower edge of cricoid cartilage Larynx - upper part of the lower respiratory path - control air outflow and inflow Trachea - begins at lower edge of the cricoid cartilage Muscles Constrictor muscles: Posteriorly muscles from each side join together at pharyngeal raphe Muscles overlap each other from above downward All innervated by pharyngeal branch of vagus Muscles narrow pharyngeal cavity Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Superior Pharyngeal Pterygomandibular raphe and Vagus constrictor raphe adjacent bone on the mandible nerve and pterygoid hamulus Middle Upper margin of greater horn constrictor and lesser horn of hyoid bone and stylohyoid ligament Inferior Cricoid cartilage, oblique line of constrictor thyroid cartilage Longitudinal muscles All descend from originates to attach to pharyngeal wall Muscles elevate the pharyngeal wall Muscle Origin Insertion Stylopharyngeus Medial side of styloid process Salpingopharyngeus Pharyngeal end of pharyngotympanic tube Palatopharyngeus Upper surface of palatine aponeurosis (soft palate) Pharyngeal wall
Function Constriction of pharynx
Innervatio n CN 9 CN 10
Function Elevation of pharynx
Elevation of pharynx, closure of oropharyngeal isthmus
Fascia Layers: Buccopharyngeal fascia - thin layer that coats outside of muscular wall Pharyngobasilar fascia - thick layers that lines inner surface Nasopharynx Borders o Posterior: chonae of nasal cavity o Anterior: back edge of soft palate, pharyngeal recess o Lateral wall: opening of the auditory canal o Superior: pharyngeal tonsil in roof Pharyngeal tonsil - collection of lymphoid tissue in the mucosa on roof of nasopharynx Prominent features on the lateral walls o Opining of pharyngotympanic tube o Pharyngeal recess: posterior and superior to the elevation caused by the entrance of the pharyngotympanic tube o Salpingopharyngeus folds Oropharynx Borders o Posterior: oral cavity o Anterior: oropharyngeal isthmus o Inferior to soft palate o Superior to upper edge of epiglottis o Palatoglossal folds mark the boundary between the oral cavity and oropharynx Prominent features o Lingual tonsils: collection of lymphoid tissue on pharyngeal part of the tongue o Palatopharyngeal folds: vertical folds covering palatopharyngeus muscles o Palatine tonsils: ovoid collections of lymphoid tissue between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds Laryngopharynx Borders o Extends from tip of epiglottis to lower border of the esophagus o Laryngeal inlet opens into the laryngopharynx Prominent features o Valleculae - mucosal pouches on each side btwn base of tongue and epiglottis o Piriform recess: between central part of the larynx and lateral lamina of the thyroid cartilage o Posterior lamina o the cricoid cartilage: forms the lower anterior wall of the space Tonsils: collections of lymphatic tissue in the mucosa of the pharynx Pharyngeal tonsils: known as adenoids when enlarged o Located in midline, on roof of the nasopharynx Palatine tonsils: o Located on each side of the oropharynx between palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches Lingual tonsils: located on posterior third of the tongue Arteries: Ascending pharyngeal artery branches from ECA Ascending palatine and Tonsillar arteries branch from facial
Nemours branches from maxillary and lingual arteries Pharyngeal branches from inferior thyroid arteries Veins and Lymphatics Veins of pharynx form a plexus o Pharyngeal plexus drains superiorly into pterygoid plexus of veins o Pharyngeal plexus drains inferiorly into facial veins and IJV Lymphatic vessels from pharynx drain to deep cervical nodes (retropharyngeal, pretracheal, infrahyoid_ Lymphatic vessels from palatine tonsils drain into the jugulodigastric node on each side Innervation Motor and most sensory innervation is by the pharyngeal plexus Pharyngeal plexus: formed by the pharyngeal branch from vagus nerve and the pharyngeal branches from the glossopharyngeal nerve All muscles innervated by the vagus nerve thought the pharyngeal plexus except for the stylopharyngeus which is innervated by CN 9 Sensory innervation Nasopharynx: pharyngeal branch of V2 Oropharynx: glossopharyngeal nerve by way of pharyngeal plexus Laryngopharynx: vagus nerve by way of the pharyngeal plexus Larynx Laryngeal cartilages Cricoid cartilage o Most inferior o Completely encircles the airway o Broad lamina of cricoid cartilage lies posterior to airway o Narrower arch of cricoid cartilage circles anteriorly o Shaped like a signet ring with posterior shield (lamina) and narrow anterior arch o Articulates superiorly with inferior horns of thyroid cartilage at cricothyroid joints o Articulates with arytenoid cartilages at the cricoarytenoid joints o Base of larynx o Cricothyroid membrane between thyroid cartilage and cricoid o Cricothyroid ligament: extends fro arch of cricoid cartilages superiorly Upper free margin attached to thyroid cartilage and posteriorly to vocal process of arytenoid cartilages Free margin btwn 2 points thickens to form the vocal ligament under the foval fold (true vocal cord) Thickens anteriorly in midline to form median cricothyroid ligament Thyroid cartilage o Largest o Consist of right and left lamina joined anteriorly but widely separated posteriorly o Most superior point of union projects as the laryngeal prominence o Posterior margin of each lamina o Superior horn of the laryngeal cartilage is attached to greater horn f hyoid bone o Inferior horn articulates with cricoid cartilage o Thyrohyoid membrane - between the thyroid and the hyoid bone
Superior laryngeal vessels and internal laryngeal nerve pierces membrane to provide vascular supply and sensory information to the mucosa superiorly to vocal folds Posterior borders thicken to form lateral thyrohyoid ligament Thickened anteriorly in the midline to form the medial thyrohyoid ligament Arytenoid cartilage - shaped like a pyramid o On upper edge of posterior side of cricoid cartilage o Base of each articulates with cricoid cartilage o Apex of each articulates it the corniculate cartilage o Vocal process - anterior angle of base is elongated (attachment of vocal ligament) o Muscular process - lateral angle of base elongated (attachment of posterior and lateral cricoarytenoid muscles) Epiglottis - leaf shaped carriage posterior to the root of tongue and anterior to laryngeal aditus o Lower end attached to deep surface of the thyroid cartilage o When air flowing through larynx, inlet of the larynx is open wide with free edge of the epiglottis projecting superiorly and anteriorly o During swallowing, the larynx is pulled superiorly and the epiglottis tips posteriorly to cover the laryngeal inlet Corniculate and cuneiform cartilages o Corniculate - 2 small conical cartilages whose base articulate with arytenoid cartilages o Cuneiform - 2 club shaped cartilages suspended anteriorly to the corniculate cartilages
Membranes Thyrohyoid membrane - connects superior border of thyroid cartilage to inferior border of hyoid Cricothyroid membrane (conus elasticus) o Extends from cricoid cartilage upward deep to thyroid cartilage Vocal ligament o Thickened free margin of conus elasticus forming core of vocal fold o Attached to thyroid cartilage and vocal process of arytenoid cartilage Quadrangular membrane o Connects arytenoid and epiglottic cartilages in lateral wall of vestibule with superior and inferior free margins forming cores of aryepiglottic and vestibular folds o Only posterior cricoarytenoid muscles can abduct the vocal cords to open airway o Extends between lateral margin of epiglottis and the anterolateral surface of arytenoid cartilage on the same side o Free lower margin thickens to form the vestibular ligament under the vestibular fold (false vocal cord) o Vestibular ligament attached posteriorly to arytenoid cartilage and anteriorly to the thyroid cartilage just superior to vocal ligament Muscles Muscle Cricothyroid muscle (extrinsic muscle of pharynx) Origin Anterolateral aspect of arch of cricoid cartilage Insertion Inferior margin of thyroid cartilage Innervation External branch of superior laryngeal nerve from vagus Function Forward and downward rotation of thyroid cartilage -Primary tensor of the vocal cords -> vocal cords elongate
Posterior cricoarytenoid Lateral cricoarytenoid muscles Vocalis Thyroarytenoid muscles
Posterior surface of lamina of cricoid cartilage Arch of cricoid cartilage Lateral surface of vocal process Thyroid angle
Muscular process of arytenoid cartilage Anterior surface of muscular process of arytenoid cartilage Vocal ligament and thyroid angle Anterolateral surface of arytenoid cartilage
Recurrent laryngeal nerve of the vagus nerve Recurrent laryngeal branch Recurrent laryngeal branch Recurrent laryngeal branch
External rotation and abduction of vocal cords Adduct vocal cords by medial rotation of arytenoid cartilage Adjusts tension and thickness of vocal ligaments Sphincter of the vestibule and laryngeal inlet
Superior laryngeal nerves: inferior vagal ganglia Descend medial to the ICA and divide into internal and external branches o External branch descends along lateral wall of pharynx to supply innervation to he cricothyroid muscle o Internal branch penetrates the thyrohyoid ligament and provides sensory innervation above the vocal cords Recurrent laryngeal nerves: Supplies sensory information to the laryngeal cavity below level of vocal cords Motor information of all intrinsic muscles of larynx except cricothyroid Sensory innervation from the mucosa inferior the vocal folds Left recurrent laryngeal nerve originates in thorax Right recurrent laryngeal nerve originates in root of neck Both ascend in a groove between esophagus and trachea Enter larynx deep to margin of the inferior constrictor
Oral cavity: Hard palate: bony plate separating oral cavity for nasal cavity Anterior - palatine processes of the maxillary bone Posterior - horizontal plates of the palatine bone Posteriorly continuous with soft palate Incisive canal is in the anterior midline: o Nasopalatine and greater palatine nerves - branches of maxillary nerve o Sphenopalatine and greater palatine arteries - branches of maxillary artery originating from the infratemporal fossa Soft palate: soft, posterior segment of the palate Valve that can close the oropharyngeal isthmus and separate nasopharynx from oropharynx Uvula: muscular projection from the midline Continuous with palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Function Tensor veli Sphenoid bone, Palatine Mandibular nerve Tense anterior palatine pharyngotympanic aponeurosis by way of the part of soft palate tube, spine of branch to the
sphenoid Levator veli palatine Petrous part of Superior surface of temporal bone the palatine anterior to aponeurosis opening for carotid canal
medial pterygoid muscle Vagus nerve by way of pharyngeal branch to pharyngeal plexus
Elevate soft palate
Vasculature: Greater palatine branches from axillary Lesser palatine artery is branch of greater palatine Ascending palatine artery branches from fascial artery Palatine branch of ascending artery Veins run with arteries and drain to the pterygoid plexus of veins or veins associated with the palatine tonsil Lymphatics drain to n deep cervical nodes Innervation Sensory innervation - V2 Special afferents for tastes supplied by facial nerve Parasympathetic from facial nerve run through the pterygopalatine ganglion Sympathetics from T1 pass though sympathetic trunk, superior cervical ganglion and deep petrosal nerve Tongue: Oral part is anterior 2/3 Pharyngeal part is posterior 3 Divided by v shaped sulcus of the tongue Papillae - located on superior surface of oral part Pharyngeal surface has small nodules of lymphoid tissue - lingual fossa Muscles: Intrinsic: Stay within substance of the tongue Alter shape of tongue Superior and inferior longitudinal muscles, transverse and vertical muscles Innervated by hypoglossal nerve Extrinsic- originates from outside the tongue and insert into the tongue Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Genioglossus Superior mental Hyoid, entire Hypoglossal nerve tubercles length of tongue Hyoglossus Greater horn and Lateral tongue body of hyoid bone Styloglossus Styloid process Lateral surface of tongue
Function Protrude tongue Depress tongue Elevate and retract tongue
Lingual artery - courses between hyoglossus and genioglossus CN 12/CN v3 course from infratemporal fossa to the tongue along the external surface of the hyoglossus Vasculature:
Lingual artery from ECA is main artery o Courses between hyoglossus and genioglossus Dorsal lingual and deep lingual veins join the internal jugular vein Lymphatics Pharyngeal part of tongue drains to the jugulodigastric node (deep cervical) Oral part of tongue drains deep into deep cervical nodes and indirectly through the submental and submandibular noes to the deep cervical nodes Innervation CN V3 (lingual nerve) - anterior 2/3 of tongue receive general sensory innervation from the lingual branch of CN v-3. Cell bodies located in trigeminal ganglion. Submandibular duct ascends from the submandibular gland, lingual nerve courses inferior to submandibular gland CN VII: anterior 2/3 of tongue receive its special sensory from the chorda tympanic nerve CN IX - posterior 1/3 of tongue receives its general sensor and taste innervation from CN IX CN XIII - all of tongue muscles receive their somatic motor innervation via CN XII Glands: bilateral opening of ducts of the salivary glands Submandibular gland o Hooks around posterior margin of mylohyoid muscle o Superficial part lies inferior to mylohyoid muscle and against submandibular fossa on the medial surface of the mandible o Smaller portion, the deep art lies within floor of oral cavity o Duct course medial to the lingual gland and opens into area adjacent to lingual frenulum o Submandibular duct emerges from medial side of the deep par and moves forward to pen near the frenulum of the tongue Sublingual gland - smallest of the 3 glands o Located lateral to submandibular duct o Lies against medial surface of mandible in sublingual fossa o Superior margin of gland raises a fold of mucosa on floro of ral cavity o Duct opens at the base of tongue Paroid gland o Outside boudnaries of oral cacity o Duct opens opposite the second maxillary motor Innervation of glnds: parasympathietic provides visceral motor innervation ot the salivary galnds via the following cranial enrves Submandibular and sublingual glands: CN VII via the submandibular ganglion o Facial nerve (VII) to the chorda tympani (VII) to the lingual nerve (branch of V3) to the submandibular ganglion to the glands Parotid gland: CN IX, via the otic ganglion o CN IX to the tympanic branch to the tympanic pelxu to the lesser petrosal nerve to otic ganglion to auricuotemporal nerve (branch of V3) to parotid gland
You might also like
- Case Studies 6Document8 pagesCase Studies 6kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 10Document5 pagesCase Studies 10kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 7Document6 pagesCase Studies 7kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 9Document7 pagesCase Studies 9kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 5Document4 pagesCase Studies 5kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 8Document7 pagesCase Studies 8kep1313No ratings yet
- Virology 1 3Document5 pagesVirology 1 3kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 3Document4 pagesCase Studies 3kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 4Document4 pagesCase Studies 4kep1313No ratings yet
- SeizuresDocument3 pagesSeizureskep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 1Document11 pagesCase Studies 1kep1313No ratings yet
- Case 1: Cystic FibrosisDocument5 pagesCase 1: Cystic Fibrosiskep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 2Document4 pagesCase Studies 2kep1313No ratings yet
- Neurology Notes For Clerkship ReviewDocument22 pagesNeurology Notes For Clerkship Reviewkep1313No ratings yet
- Psychiatry - BSDocument15 pagesPsychiatry - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- Case 1: Cystic FibrosisDocument5 pagesCase 1: Cystic Fibrosiskep1313No ratings yet
- Week 4 Learning ObjectivesDocument24 pagesWeek 4 Learning Objectiveskep1313No ratings yet
- Week 3 Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesWeek 3 Learning Objectiveskep1313100% (1)
- Week 5 Learning ObjectivesDocument34 pagesWeek 5 Learning Objectiveskep1313No ratings yet
- Preventative Medicine PM - BSDocument22 pagesPreventative Medicine PM - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Physiology - BSDocument14 pagesPhysiology - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- MicroanatomyDocument59 pagesMicroanatomykep1313No ratings yet
- Week 2 Learning ObjectivesDocument21 pagesWeek 2 Learning Objectiveskep1313No ratings yet
- Genetics - MMDocument25 pagesGenetics - MMkep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- Physiology - BSDocument14 pagesPhysiology - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- 2-5-10 Introduction To Acute LeukemiaDocument3 pages2-5-10 Introduction To Acute Leukemiakep1313No ratings yet
- Biogenic AminesDocument5 pagesBiogenic Amineskep1313No ratings yet
- 2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune DisordersDocument2 pages2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune Disorderskep1313No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Oral Cancer Diagnosis and TherapyDocument427 pagesOral Cancer Diagnosis and TherapyJacky Junaedi100% (2)
- Guia Anatomia TerminadaDocument120 pagesGuia Anatomia TerminadaAlex ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Endotracheal IntubationDocument14 pagesEndotracheal IntubationajayvarvalaNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment TemplateDocument9 pagesPhysical Assessment TemplateArky VessaliuzNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Oral Pathology-Anil G. Ghom, S. Mhaske (2013)Document1,050 pagesTextbook of Oral Pathology-Anil G. Ghom, S. Mhaske (2013)Khánh Vũ100% (2)
- In Intervention For Speech Sound Disorders - Lateralize SDocument5 pagesIn Intervention For Speech Sound Disorders - Lateralize SSaraOliveiraNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Urogenital Lecture ComparativeDocument136 pagesSkeletal Urogenital Lecture ComparativeLei Jenevive UmbayNo ratings yet
- The Atlas of The Human Embryo - A Scanning Electron Microscopic AtlasDocument308 pagesThe Atlas of The Human Embryo - A Scanning Electron Microscopic AtlasHakan AY100% (2)
- Major and Minor ConnectorsDocument32 pagesMajor and Minor ConnectorsJustDen09100% (1)
- Daftar Penyakit Telinga Hidung Tenggorok-Kepala Leher Menurut Icd 10Document10 pagesDaftar Penyakit Telinga Hidung Tenggorok-Kepala Leher Menurut Icd 10Poliklinik RSPHNo ratings yet
- Mammalian System-01 (Digestive System)Document35 pagesMammalian System-01 (Digestive System)Saumya99No ratings yet
- Histo Compre ReviewerDocument49 pagesHisto Compre ReviewerPi NgNo ratings yet
- Diagnosa Icd 10Document424 pagesDiagnosa Icd 10Sinta FiraniNo ratings yet
- Retention Support Stability CDDocument53 pagesRetention Support Stability CDAshraf GebreelNo ratings yet
- 15SPECIALSENSESDocument5 pages15SPECIALSENSESDaniellaRuth Cajurao CanalesNo ratings yet
- Homeopathy - Remedy 191013Document30 pagesHomeopathy - Remedy 191013ira nurrasyidahNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Upper GITDocument43 pagesHistology of The Upper GITBenedict OkotNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption: Digestive System of HumanDocument4 pagesDigestion and Absorption: Digestive System of HumanrajaijahNo ratings yet
- Danilo Domingues Millen, Mario de Beni Arrigoni, Rodrigo Dias Lauritano Pacheco (Eds.) - Rumenology-Springer International Publishing (2016)Document326 pagesDanilo Domingues Millen, Mario de Beni Arrigoni, Rodrigo Dias Lauritano Pacheco (Eds.) - Rumenology-Springer International Publishing (2016)Merve EFİLNo ratings yet
- Comparative Morphological Histological Analysis Buffalo Goat Tongues Comparison Human TongueDocument8 pagesComparative Morphological Histological Analysis Buffalo Goat Tongues Comparison Human TongueSSR-IIJLS JournalNo ratings yet
- Class 7 MouthDocument2 pagesClass 7 Mouthapi-245312762No ratings yet
- Study Guide - Treatment of Edentulous PatientsDocument107 pagesStudy Guide - Treatment of Edentulous PatientsTosca Mavourneen100% (1)
- Oral Mucous MembraneDocument71 pagesOral Mucous MembraneHarleen GrewalNo ratings yet
- Bahan Local FlapDocument72 pagesBahan Local FlapChandrawati PramanaNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument13 pagesPhysical AssessmentRuhvie Ann PielagoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 16 LAB EXERCISE - Special SensesDocument10 pagesWEEK 16 LAB EXERCISE - Special SensesLance KennethNo ratings yet
- Digestive and Respiratory Organs DefinitionDocument4 pagesDigestive and Respiratory Organs DefinitionSidne E. AgorNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument277 pagesHandoutKhus RahoNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Vowels and ConsonantsDocument8 pagesDifferences Between Vowels and Consonantsschiatti3071No ratings yet
- Aramentarium For Minor Oral Surgical Procedure: Deepthi P.R. Intern Dept. of Oral SurgeryDocument80 pagesAramentarium For Minor Oral Surgical Procedure: Deepthi P.R. Intern Dept. of Oral Surgerymehak malhotraNo ratings yet