Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 06
Uploaded by
Suhail AkraamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 06
Uploaded by
Suhail AkraamCopyright:
Available Formats
Hand-out
Tutorial 6
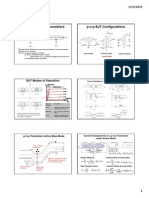
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): Having two junctions and hence called bipolar junction transistor. The charge is carried by both majority and minority carriers, often called transistor. Widely used in analog electronics, whereas FETs/unipolar devices are more widely used in digital electronics. Types: npn a p-type semiconductor doping in an n-type wafer pnp a n-type semiconductor doping in an p-type wafer Operation: pnp structure produces two pn-junctions connected back to back as shown in previous figure. If a voltage is applied across collector and the emitter and the base is open circuited, one of these junctions will be reversed biased and very little current will flow. Normal circuit configuration for npn transistor is to make the collector more positive than the emitter. VCE might be a few volts. ICEO is the leakage current flowing from the collector to the emitter with open circuited base.
A Simple amplifier: FETs are voltage controlled devices; transistors could be voltage controlled or current controlled. When no input, its called quiescent state and the quiescent base current, quiescent output voltage is determined. RB and RC are chosen for correct operating point.
Small signal equivalent circuits:
In the suffix, the first letter indicates nature of the parameters and the second, type of connection, i.e, for hie,i-input resistance and e- common emitter connection. hoe is output Admittance
Elektronik - F2 - 1TT044 - HT06 - Tutorial 6
(figures taken from N. Storeys book)
Page 1 of 2
BJT characteristics: eV I I s (exp 1) I s exp(40V ) , kT
I E = I C + I B = (1 + hFE ) I B hFE I B = I C Emitter resistance re =
also hie
Is is the reverse saturation current. I represents IB and V represents the junction voltage VBE. The slope indicates the small signal input resistance of the arrangement.
1 1 1 [], g m 40 I C 40 I E
1 h fe re , 40 I B gm is the transconductance I c Slope = = g m [-1] VBE
h-parameter model:
hfe, hie, re indicates small signal quantities
hfe is forward current gain (AC current gain) I Slope = C = h fe I B
hoe is output admittance I C = hoe [-1] Slope = VCE
hie is input resistance 1 V Slope-1 = BE = hie = [] 40 I B I B
Small signal voltage gain
v0 RC 1 = g m ( // RC ) = g m g m RC 40 I C RC 40 VRC vi hoe hoe RC + 1
Usage of feedback: BJT amplifiers suffer from problems related with the variability of the gain. A negative feedback improves the constancy of the output current by increasing the output resistance and will increase the input resistance, leading to a better voltage amplifier.
Elektronik - F2 - 1TT044 - HT06 - Tutorial 6
(figures taken from N. Storeys book)
Page 2 of 2
Problems
Tutorial 6
hFE = 100.
You might also like
- SemiconductorsDocument4 pagesSemiconductorsGiezel RevisNo ratings yet
- Transistors and AmplifiersDocument9 pagesTransistors and AmplifiersBharat SolankiNo ratings yet
- EE 306 ManualDocument55 pagesEE 306 Manualzain khuramNo ratings yet
- AEC LabManualDocument30 pagesAEC LabManualPrateek PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of A Typical Electronic Amplifier System: Eg. BatteryDocument44 pagesBlock Diagram of A Typical Electronic Amplifier System: Eg. BatteryPiyush DubeyNo ratings yet
- BJT Lecture 2Document67 pagesBJT Lecture 2rktiwary256034No ratings yet
- EDC II Lab ManualDocument46 pagesEDC II Lab Manualshreeyak841No ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge RectifierDocument8 pagesElectronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge RectifierEng. Ahmad ELsamakNo ratings yet
- Edc Lab Manuals Third SemesterDocument56 pagesEdc Lab Manuals Third SemesterSprout GigsNo ratings yet
- Transistors Amplifiers: Out inDocument6 pagesTransistors Amplifiers: Out inabguitarNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : DR Derek Molloy, DCUDocument17 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : DR Derek Molloy, DCUraja_ramalingam07No ratings yet
- Iv - Semester, Ece List of ExperimentsDocument117 pagesIv - Semester, Ece List of ExperimentsvibinmanualNo ratings yet
- Electronics Module 3Document18 pagesElectronics Module 3tirsollantada100% (1)
- Operational Amplifier As Differentiator: o Ip Op IpDocument5 pagesOperational Amplifier As Differentiator: o Ip Op IpEdward Raja KumarNo ratings yet
- Transistors and AmplifiersDocument285 pagesTransistors and AmplifiersCris Diane G. DatingginooNo ratings yet
- EECS 245 Lab 5 Bipolar Transistor Characteristics and Amplification ObjectiveDocument4 pagesEECS 245 Lab 5 Bipolar Transistor Characteristics and Amplification ObjectiveSarahNo ratings yet
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFDocument21 pagesADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuNo ratings yet
- Bel CH5Document6 pagesBel CH5PravinNo ratings yet
- (L3) - Semiconductors - 22th DecDocument52 pages(L3) - Semiconductors - 22th DecShreshth GuptaNo ratings yet
- BJT PresentationDocument128 pagesBJT PresentationMarcus FNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Understanding Op-AmpsDocument11 pagesChapter 1: Understanding Op-Ampsrockrockyrocker123No ratings yet
- 9 CE AmplifierDocument5 pages9 CE AmplifierAnsh PratapNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) P-N-P BJT ConfigurationsDocument3 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) P-N-P BJT Configurationsminhduy223No ratings yet
- Refresher Course in Transistor CombinedDocument149 pagesRefresher Course in Transistor CombinedZyxmn Daley JesNo ratings yet
- EE 306 - Electrical Engineering LaboratoryDocument7 pagesEE 306 - Electrical Engineering LaboratoryMohammed KhouliNo ratings yet
- Op-Amps: I. Practical Op-AmpDocument7 pagesOp-Amps: I. Practical Op-AmpSteven Nelson100% (1)
- EE 200 - Electronic Circuits Implementation Lab #4Document8 pagesEE 200 - Electronic Circuits Implementation Lab #4Poyraz EmelNo ratings yet
- EE 200 - Electronic Circuits Implementation Lab #4Document8 pagesEE 200 - Electronic Circuits Implementation Lab #4Poyraz EmelNo ratings yet
- Transistor Low Frequency Analysis: Types, Models and ApplicationsDocument22 pagesTransistor Low Frequency Analysis: Types, Models and Applicationscinthu chizhian22100% (1)
- AC PPTDocument28 pagesAC PPTPrajwal BirwadkarNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment N 2, Diode Applications RectifiersDocument18 pagesLab Experiment N 2, Diode Applications RectifiersSeif-El-Islam BayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document34 pagesChapter 8Abhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- RC Coupled Transistor AmplifierDocument7 pagesRC Coupled Transistor AmplifierIshratNo ratings yet
- Devices and Circuits Ii: I-V Characteristics of Bipolar TransistorDocument4 pagesDevices and Circuits Ii: I-V Characteristics of Bipolar TransistorMạnh Cường TrầnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transistors: Presented: October 23, 2001 Chris Green Carl Hanna Ancil Marshall Kwame OforiDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Transistors: Presented: October 23, 2001 Chris Green Carl Hanna Ancil Marshall Kwame OforiJobz Van- GNo ratings yet
- MH 02N 2Document36 pagesMH 02N 2ganeshNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier:, or Op Amp, Is A Dual-Input, Single-Output Linear Amplifier That ExhibitsDocument3 pagesOperational Amplifier:, or Op Amp, Is A Dual-Input, Single-Output Linear Amplifier That ExhibitsSUNILKHUNTIA1988No ratings yet
- BJTsDocument43 pagesBJTs_DarkseidNo ratings yet
- BJT AMPLIFIER GAIN & FREQUENCY RESPONSEDocument5 pagesBJT AMPLIFIER GAIN & FREQUENCY RESPONSEkostia1100% (1)
- Divya Soni Exp 9Document6 pagesDivya Soni Exp 9Vish ThakurNo ratings yet
- Eca UNIT IIDocument49 pagesEca UNIT IIchitravel7010No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Code and Transistor HistoryDocument44 pagesBasic Electronics Code and Transistor HistoryNidhi PatelNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Electronics I Laboratory - EXPERIMENT 10 Common Emitter AmplifierDocument6 pagesObjectives:: Electronics I Laboratory - EXPERIMENT 10 Common Emitter AmplifierRabindraMaharanaNo ratings yet
- De La Salle University - Dasmariñas College of Engineering, Architecture, and Technology Engineering ProgramDocument8 pagesDe La Salle University - Dasmariñas College of Engineering, Architecture, and Technology Engineering ProgramJm RezanoNo ratings yet
- First Order RC High Pass Filter: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesFirst Order RC High Pass Filter: ObjectivesismailNo ratings yet
- IC and ECAD LabDocument88 pagesIC and ECAD LabVeerayya JavvajiNo ratings yet
- Metallization Process Is Used in Interconn DesiredDocument52 pagesMetallization Process Is Used in Interconn DesiredSanjay KashiNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors - Transistor: An Essential Semiconductor DeviceDocument66 pagesSemiconductors - Transistor: An Essential Semiconductor DeviceAshfaq khanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector AmplifierDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector Amplifier5611 M.Mubeen M.yaseenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Ayesha TahirNo ratings yet
- Ecd Manuals 1-7Document46 pagesEcd Manuals 1-7Muhammad Hozaifa100% (1)
- True FalseDocument5 pagesTrue FalseShuvodip Das50% (2)
- Diodes and Applications FinalDocument117 pagesDiodes and Applications FinalCris Diane G. DatingginooNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- Physical VerificationDocument18 pagesPhysical VerificationSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- SOLID STATE DEVICES CLASSIFICATIONDocument42 pagesSOLID STATE DEVICES CLASSIFICATIONPadanam MaathramNo ratings yet
- TwoDimensional Electronics and OptoelectronicsDocument154 pagesTwoDimensional Electronics and OptoelectronicsAriana Mestanza50% (2)
- Aon 7702Document6 pagesAon 7702Agung HaryantoNo ratings yet
- EC-8001 Unit 1 PDFDocument60 pagesEC-8001 Unit 1 PDFrupeshNo ratings yet
- 2 N 1711Document8 pages2 N 1711cataclg24No ratings yet
- SM4833NSK PDFDocument10 pagesSM4833NSK PDFsike1977100% (1)
- Lecture 080 - Latchup and Esd: CMOS Analog Circuit Design, 2Document16 pagesLecture 080 - Latchup and Esd: CMOS Analog Circuit Design, 2Milan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Physics: Understanding Semiconductors and DopingDocument47 pagesSemiconductor Physics: Understanding Semiconductors and DopingMahendra Singh83% (6)
- Critical raw materials QA flowDocument6 pagesCritical raw materials QA flow2malaysiaNo ratings yet
- 7mbi100sa 060BDocument8 pages7mbi100sa 060BPaulo Henrique ValérioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 2022Document59 pagesLecture 2 2022Dana GhoulNo ratings yet
- Vishay Bare Copper Lead Frame Plating Line Manufacturing Improvement PCN DD 005 2013 PDFDocument8 pagesVishay Bare Copper Lead Frame Plating Line Manufacturing Improvement PCN DD 005 2013 PDFPablo AllosiaNo ratings yet
- 10N60C PDFDocument10 pages10N60C PDFhectorsevillaNo ratings yet
- 1991 - Calatog Microelectronica - Dispozitive Optoelectronice - Color - 300dpi PDFDocument60 pages1991 - Calatog Microelectronica - Dispozitive Optoelectronice - Color - 300dpi PDFTeodor SerbanNo ratings yet
- Buv48a PDFDocument7 pagesBuv48a PDFFelicia MarceanNo ratings yet
- Physics For Information Science Course ContentDocument2 pagesPhysics For Information Science Course ContentB KARUPPASAMYNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Electronic Devices 9th Edition by Floyd Pp1aDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Electronic Devices 9th Edition by Floyd Pp1aAmr AbdelnaserNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Solar Cell Technology and Industry TrendsDocument62 pagesAn Overview of Solar Cell Technology and Industry TrendsMr. K.S. Raghul Asst Prof MECHNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Digital Logic and Microcomputer DesignDocument1 pageFundamentals Digital Logic and Microcomputer Designty3919883665No ratings yet
- hcpl0730 PDFDocument13 pageshcpl0730 PDFgoogle manNo ratings yet
- RFP12N10LDocument6 pagesRFP12N10LSasi Kiran SNo ratings yet
- Exercises V1 Part2Document8 pagesExercises V1 Part2Ahmed AlgadriNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1bahmanNo ratings yet
- IXYS Igbt - Rectifiermodules PDFDocument32 pagesIXYS Igbt - Rectifiermodules PDFchidambaram kasiNo ratings yet
- BD135 BD139: NPN Silicon TransistorsDocument4 pagesBD135 BD139: NPN Silicon TransistorsEduardo CostaNo ratings yet
- Flexible OLED Displays: Seminar OnDocument20 pagesFlexible OLED Displays: Seminar OnShwetaNo ratings yet
- Abrupt PN Junctions Analytical SolutionsDocument9 pagesAbrupt PN Junctions Analytical Solutionsombraga1896No ratings yet
- CNTFET-Based Ternary Logic Gates: Design and Analysis ApproachDocument22 pagesCNTFET-Based Ternary Logic Gates: Design and Analysis ApproachHemant SaraswatNo ratings yet