Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study - Psychiatric NSG
Uploaded by
Camille PinedaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study - Psychiatric NSG
Uploaded by
Camille PinedaCopyright:
Available Formats
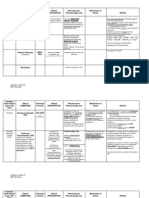
Patients name: Amy Rose B.
Reyes Age: 30y/o Gender: Female Status: Single Address: Palanas, Masbate City Date of Admission: 11-20-1983 Chief complaint: According to mother: nantatapon ng gamit, irritable, ayaw uminom ng gamot According to patient: ok lang ako Diagnosis: Undifferentiated Schizophrenia Dr. In-charge: Dr. Afroilan Medications: Clozapine 50mg bid Biperiden hydrochloride 2mg x EPS DRUG STUDY
Generic Name : Clozapine Brand Name: Clozaril, FazaClo, Gen-Clozapine (CAN) Classification: Antipsychotic, Dopaminergic blocker Pregnancy Category B Dosage & Route Adults
Initial therapy: 12.5 mg PO once or twice daily. If using orally disintegrating tablets, begin with 1/2 (12.5 mg) of a 25-mg tablet and destroy the remaining half. Continue to 25 mg PO daily or bid; then gradually increase with daily increments of 2550 mg/day, if tolerated, to a dose of 300450 mg/day by the end of second week. Adjust later dosage no more often than twice weekly in increments < 100 mg. Do not exceed 900 mg/day. Maintenance: Maintain at the lowest effective dose for remission of symptoms. Discontinuation of therapy: Gradual reduction over a 2-wk period is preferred. If abrupt discontinuation is required, carefully monitor patient for signs of acute psychotic symptoms. Reinitiation of treatment: Follow initial dosage guidelines, use extreme care; increased risk of severe adverse effects with re-exposure.
Pediatric Patients
Safety and efficacy in patients < 16 yr not established.
Therapeutic actions
Clozapine has relatively weak dopamine receptor-blocking activity at D1, D2, D3 and D5 receptors but has high affinity for the D4 receptor. It has also blocking effects on serotonin, -adrenergic histamine H1 and cholinergic receptors.
Indications
Management of severely ill schizophrenics who are unresponsive to standard antipsychotic drugs Reduction of the risk of recurrent suicidal behavior in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder (not orally disintegrating tablet)
Adverse effects
Drowsiness, dizziness, headache; nausea, vomiting, constipation; anxiety, confusion, fatigue, transient fever. Rarely, dysphagia, acute pancreatitis, cholestatic jaundice; orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia; seizures; hypersalivation. Potentially Fatal: Rarely, thromboembolism. Reversible neutropenia which may progress to a potentially fatal agranulocytosis. Fatal myocarditis.
Contraindications
History of bone marrow disorders including agranulocytosis, circulatory collapse, alcoholic or toxic psychosis, drug intoxication, uncontrolled epilepsy, severe renal, hepatic or cardiac disease; paralytic ileus. Pregnancy and lactation.
Nursing considerations Assessment
History: Allergy to clozapine, myeloproliferative disorders, history of clozapine-induced agranulocytosis or severe granulocytopenia, severe CNS depression, comatose states, history of seizure disorders, CV disease, narrow-angle glaucoma, lactation, pregnancy Physical: T, weight; reflexes, orientation, IOP, ophthalmologic examination; P, BP, orthostatic BP, ECG; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output, liver evaluation; prostate palpation, normal urine output; CBC, urinalysis, LFTs, renal function tests, EEG
Interventions
BLACK BOX WARNING: Use only when unresponsive to conventional antipsychotic drugs; risk of serious CV and respiratory effects. Obtain clozapine through the Clozaril Patient Assistance Program. For more information, call 1-800-448-5938.
Dispense only 1 wk supply at a time. Monitor WBC carefully prior to first dose. BLACK BOX WARNING: Weekly monitoring of WBC during treatment and for 4 wk thereafter. Dosage may be adjusted based on WBC count. Potentially fatal agranulocytosis has been reported. Monitor T. If fever occurs, rule out underlying infection, and consult physician for comfort measures. BLACK BOX WARNING: Monitor for seizures; with history of seizures, risk increases as dose increases. Monitor elderly patients for dehydration. Institute remedial measures promptly; sedation and decreased thirst related to CNS effects can lead to dehydration. Monitor patient regularly for signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus. Encourage voiding before taking drug to decrease anticholinergic effects of urinary retention. Follow guidelines for discontinuation or reinstitution of the drug. Educate patient on seriousness of potential agranulocytosis.
Teaching points
Weekly blood tests will be taken to determine safe dosage; dosage will be increased gradually to achieve most effective dose. Only 1 week of medication can be dispensed at a time and will depend on your white blood cell count. Do not take more than your prescribed dosage. Do not make up missed doses, instead contact your health care provider. Do not stop taking this drug suddenly; gradual reduction of dosage is needed to prevent side effects. If you think you are pregnant or wish to become pregnant, contact your health care provider. You may experience these side effects: Drowsiness, dizziness, sedation, seizures (avoid driving or performing tasks that require concentration); dizziness, faintness on arising (change positions slowly); increased salivation (reversible); constipation (consult your health care provider for correctives); fast heart rate (rest, take your time). Report lethargy, weakness, fever, sore throat, malaise, mouth ulcers, and flulike symptoms.
Generic Name : biperiden hydrochloride(oral) biperiden lactate (injection) Brand Name: Akineton Classification: Antiparkinson Agents Pregnancy Category C Dosage & Route Adults Parkinsonism: 2 mg PO tidqid; individualize dosage with a maximum dose of 16 mg/day. Drug-induced extrapyramidal disorders
Oral: 2 mg PO daily to tid. Parenteral: 2 mg IM or IV; repeat q 30 min until symptoms are resolved, do not give more than 4 consecutive doses per 24 hr. Pediatric patients Safety and efficacy not established. Geriatric patients Strict dosage regulation may be necessary; patients > 60 yr often develop increased sensitivity to the CNS effects of anticholinergic drugs.
Therapeutic actions Anticholinergic activity in the CNS that is believed to help normalize the hypothesized imbalance of cholinergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission in the basal ganglia in the brain of a parkinsonism patient. Reduces severity of rigidity, and to a lesser extent akinesia and tremor characterizing parkinsonism; less effective overall than levodopa; peripheral anticholinergic effects suppress secondary symptoms of parkinsonism, such as drooling.
Indications Adjunct in the therapy of parkinsonism (post-encephalitic, arteriosclerotic, and idiopathic types) Relief of symptoms of extrapyramidal disorders that accompany phenothiazine therapy Adverse effects CNS: Some are characteristic of centrally acting anticholinergic drugs: disorientation, confusion, memory loss, hallucinations, psychoses, agitation, nervousness, delusions, delirium, paranoia, euphoria, excitement, light-headedness, dizziness, depression, drowsiness, weakness, giddiness, paresthesia, heaviness of the limbs Peripheral anticholinergic effects CV: Tachycardia, palpitations, hypotension, orthostatic hypotension Dermatologic: Rash, urticaria, other dermatoses EENT: Blurred vision, mydriasis, diplopia, increased intraocular tension, angle-closure glaucoma GI: Dry mouth, constipation, dilation of the colon, paralytic ileus, acute suppurative parotitis, nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress GU: Urinary retention, urinary hesitancy, dysuria, difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection Other: Flushing, decreased sweating, elevated temperature, muscular weakness, muscular cramping
Contraindications and Cautions Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to benztropine; glaucoma, especially angle-closure glaucoma; pyloric or duodenal obstruction, stenosing peptic ulcers, achalasia (megaesophagus); prostatic hypertrophy or bladder neck obstructions; myasthenia gravis. Use cautiously with tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension, hypotension, hepatic or renal dysfunction, alcoholism, chronic illness, people who work in hot environment; hot weather; lactation.
Nursing considerations Assessment History: Hypersensitivity to benztropine; glaucoma; pyloric or duodenal obstruction, stenosing peptic ulcers, achalasia; prostatic hypertrophy or bladder neck obstructions; myasthenia gravis; cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension, hypotension; hepatic or renal dysfunction; alcoholism, chronic illness, work in hot environment; lactation Physical: Body weight; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes, bilateral grip strength, visual exam, including tonometry; P, BP, orthostatic BP; adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output, liver evaluation; normal urinary output, voiding pattern, prostate palpation; liver and kidney function tests Interventions . Decrease dosage or discontinue temporarily if dry mouth makes swallowing or speaking difficult. Give with caution, and reduce dosage in hot weather. Drug interferes with sweating and ability of body to maintain heat equilibrium; anhidrosis and fatal hyperthermia have occurred. Give with meals if GI upset occurs; give before meals to patients with dry mouth; give after meals if drooling or nausea occurs. Ensure that patient voids just before receiving each dose of drug if urinary retention is a problem. Teaching points Take this drug exactly as prescribed. Avoid the use of alcohol, sedative, and OTC drugs (can cause dangerous effects). These side effects may occur: drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, blurred vision (avoid driving or engaging in activities that require alertness and visual acuity); nausea (try frequent small meals); dry mouth (suck sugarless lozenges or ice chips); painful or difficult urination (empty the bladder immediately before each dose); constipation (maintain adequate fluid intake and exercise regularly); use caution in hot weather (you are susceptible to heat prostration). Report difficult or painful urination; constipation; rapid or pounding heartbeat; confusion, eye pain, or rash. SUBMITTED BY: Camille M. Pineda
Student Nurse
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Neurology: Timothy E. Welty, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPSDocument68 pagesNeurology: Timothy E. Welty, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPSAlmaha AlfakhriNo ratings yet
- English Annual Report 2021-22Document172 pagesEnglish Annual Report 2021-22Ashish SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Social Media Powerpoint PresentationDocument36 pagesThe Impact of Social Media Powerpoint PresentationCamille Pineda60% (5)
- Administering An Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering An Intramuscular Injectionapi-26570979100% (4)
- HoxseyDocument7 pagesHoxseyuncoveringconsciousNo ratings yet
- Role of Salvestrols in The Treatment of CancerDocument10 pagesRole of Salvestrols in The Treatment of CancerRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Antihistamine Bilastine A Novel Antihistamine 2018Document4 pagesAntihistamine Bilastine A Novel Antihistamine 2018SRINIVASNo ratings yet
- Health and Emergency Medical Services - MSRDocument37 pagesHealth and Emergency Medical Services - MSRCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment. - TyphoidDocument4 pagesPhysical Assessment. - TyphoidCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- His T SpiritualityDocument83 pagesHis T SpiritualityCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Stahlmann-2002-Clinical Toxicological Aspects of FQ-Toxicology LettersDocument9 pagesStahlmann-2002-Clinical Toxicological Aspects of FQ-Toxicology LettersAndy KumarNo ratings yet
- CRS Requisition List...........Document4 pagesCRS Requisition List...........M N Sharif MintuNo ratings yet
- Neostigmine IV Test PDFDocument7 pagesNeostigmine IV Test PDFnaveen851986No ratings yet
- Giverny CapitalDocument18 pagesGiverny CapitalAnonymous Ht0MIJNo ratings yet
- Group3 ElementsDocument7 pagesGroup3 ElementsPeter JimenezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacogenetics Case StudyDocument9 pagesPharmacogenetics Case Studyapi-256755409No ratings yet
- Protein Binding of Drug: Page - 1 CMR College of Pharmacy, 2013Document18 pagesProtein Binding of Drug: Page - 1 CMR College of Pharmacy, 2013REDDYGAARI ABBAYINo ratings yet
- BC-ZEMY, A Digital Therapeutic Developed by Roche Pharma France in Partnership With VoluntisDocument2 pagesBC-ZEMY, A Digital Therapeutic Developed by Roche Pharma France in Partnership With VoluntisVishal YadavNo ratings yet
- Determining The Effects of Stachytarpheta JamaicenDocument2 pagesDetermining The Effects of Stachytarpheta JamaicenFritzel Pallon SusbillaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Pharmacognosy On Chinese PharmacopoeiaDocument11 pagesPresentation of Pharmacognosy On Chinese PharmacopoeiaAnant kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Graylands Hospital Drug Bulletin: Medications and Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument9 pagesGraylands Hospital Drug Bulletin: Medications and Electroconvulsive TherapyRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmacy PracticeDocument63 pagesAdvanced Pharmacy PracticeRawan AmerNo ratings yet
- FIP Webinar BOVA Jones July 2023Document13 pagesFIP Webinar BOVA Jones July 2023Phuong Anh BuiNo ratings yet
- Ethnopharmacology Final)Document62 pagesEthnopharmacology Final)api-3728522100% (2)
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Madhya Pradesh Name of Institutions Courses SeatsDocument3 pagesList of Pharmacy Colleges in Madhya Pradesh Name of Institutions Courses Seats3neetinNo ratings yet
- Bromelain, The Enzyme Complex of PineappleDocument13 pagesBromelain, The Enzyme Complex of PineappleEllisaTanNo ratings yet
- Opioid AnalgesicsDocument38 pagesOpioid AnalgesicslinggarNo ratings yet
- Solubility CalculationDocument14 pagesSolubility Calculationapi-253216442No ratings yet
- Pharma Art of PricingDocument52 pagesPharma Art of PricingmaheshtimsrNo ratings yet
- The Entourage Effect of The PhytocannabinoidsDocument1 pageThe Entourage Effect of The PhytocannabinoidsCarlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- A Review On Ethnopharmacolgy, Phytochemistry and Bioactivity of LeonotisDocument4 pagesA Review On Ethnopharmacolgy, Phytochemistry and Bioactivity of LeonotisAnonymous HBRjaTX5YFNo ratings yet
- The King of Blotter Art: Mark McCloud Speaks...Document8 pagesThe King of Blotter Art: Mark McCloud Speaks...Jon_R_HannaNo ratings yet
- Acute Wheeze Flowchart PDFDocument2 pagesAcute Wheeze Flowchart PDFgeonMMNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of RP-HPLC Method For The Assay of Pregabalin CapsuleDocument9 pagesDevelopment and Validation of RP-HPLC Method For The Assay of Pregabalin CapsuleRubinaNo ratings yet