Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sensation and Perception - Docx Michael Pintoy
Uploaded by
Jovenil BacatanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sensation and Perception - Docx Michael Pintoy
Uploaded by
Jovenil BacatanCopyright:
Available Formats
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION To represent the world in our hand, we must detect physical energy from the environment
and encode its as neural signals through a process known as sensation. We select, organize, and interpret our sensation through a process known as perception. After losing a temporal lobe, essential to recognizing faces, patient E.H. suffers from a condition called prosopagnosia.
A. CONDITION FOR SENSORY AWARENESS 1. The stimulation of a sensory receptor to have sensory experience. 2. The presents of receptor cells that are found in each sense organ. 3. The stimulation is then converted into electrochemical impulses thought known as transduction. B. THRESHOLDS Threshold divides the line between what energy can be detected or not. Absolute Threshold is the minimal amount energy that can produce a sensation. Difference Threshold tells about minimum difference in the magnitude of two stimuli present.
C. SIIGNAL-DETECTION THEORY
The signal detection theory cited several factors that determine whether people will perceive sensory stimuli or a difference between two signals.
D. SENSORY ADAPTATION Is the process of becoming more sensitive to stimulation is called sensitization. This process of becoming less sensitive to stimulation is referred to as desensitization.
E. THE SENSORY SYSTEMfrom 1. The vision- The eye and its Basic Structure The eye is the receptor organ of vision which is sensitive to light waves. Influences Three Physical Characteristics of light help determined our sensory experiences: a. Wavelength is the distances from one wave push to the next that determines its hue. b. Intensity is the amount of energy in the waves in which influences brightness. c. The extent, to which light contains only one wavelength, rather than many, determines our experiences of saturation. Light rays first pass through a transparent protective structure called Cornea and then enter the eye through the pupil, a round opening in which size varies with lighting conditions; the less light present, the wider in the pupil opening. There adjustments are executed by iris, the colored part of the eye, which is the circular muscle that contracts or expands to let the varying amount of light. After entering through the pupil, light rays pass through the lens, a clear structure in which shape adjust to permit us to focus objects at varying distances and are projected on retina at the back of eyeball. Visual Problems Problems in Visual Acuity 1. Visual acuity- is sharpness of vision or ability to discriminate usual details, which can be measured through a Snellen chart.
Nearsightedness or myopia- is a condition where a person is capable of seeing nearby objects with greater activity than objects. Farsightedness or Hyperopia Is condition where a person can see distant object with greater activity than nearby objects. 2. Presbyopia- is a condition characterized by bittleness of the lens which usually begins at about the age of 38 to 46. 3. Strabismus- is visual disorder in which both eyes cannot focus the same point at the same time. 4. Astigmatisim- is visual disorder caused by abnormal curvature of the lens. 5. Color Blindness- is a condition in which person suffering from this are monochromats and sensitive to light- dark only. Partial color blindness is more common than total color blind and it is a sex-link trait that strikes mostly males.
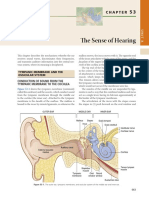
THEORIES OF COLOR VISION 1. Trichromatic Theory holds that color vision is made possible by three types of cones, some of which respond to red light, some to green, and others to blue. 2. Opponent-processes Theory- also holds that there are three types of color receptors, but they are not theorized to be red, green. The hearins- The ear and Its basic Structure The humans ear good for lots of things- catching dust, combining your hair around , hanging jewelry from and nibbling. Is shaped to funnel sound waves to the eardrum, a thin membrane that vibrates in response to sound waves and thereby, transmits them to the middle Outer Ear and inner ears. Middle Ear- it functions as an amplifier- it increases the magnitude of the air pressure. Stirrup- is attached to another vibrating membrane, the oval window.
Inner Ear- the oval window transmits vibrations into the inner ear, bony tube called the cochlea. Organ of Corti- known as the command post of hearing is attached to the basilar membrane. PSYCHOLOGICAL DIMENSION OF SOUND
1. Pitch is determined by its frequency, or the number of cycles per second as expressed in the unit 2. Loudness is determined by the height or amplitude of sound waves. 3. The combination of pleasant tones is called Consonant sound while unpleasant combination will result to the discount sound.
AUDITORY PROBLEMS 1. Conduction deafness occurs because of damage to the structure of the middle ear to the eardrum or to the three bones that conduct and imply sound from the outer and inner ear. 2. Sensory neural deafness usually stems from damage to the structure to the inner, most often the loss of hair cells, which will regenerate. 3. Stimulation Deafness stems from exposure to very loud sounds. SMELL AND TASTE; THE CHEMICAL SENSES
Although smell and taste are separate senses, we will consider them together for two reasons. First, both respond to substances in solution- that is substances that have been dissolved in a fluid or gas usually water or air. Second, in everyday life, smell and taste are intimately related.
THE SKIN SENSES The skin which is the largest organ in our body discriminate five kinds of sensation: touch, pressure, warmth, cold, and pain.
TOUCH AND PRESSURE
Sensory receptors located around the roots of hair cells appear in response to touching the surface of the skin.
TEMPERATURE The receptors for temperature are neurons just beneath the skin. Sensations of temperature are relative.
PAIN Pain is a signal that something is wrong in the body. Pain is adaptive in the sense that motivates us to something about.
KINESTHESIA, VISUAL AND ORGANIC SENSATION
Kenesthesia is the sense that gives us information about the location of our body parts and allows us to perform from a simple touching of nose to more complex movements such as dancing, driving, and gymnastics. Vestibular Sense gives us information about position, movement acceleration. and
Organic Sensation is found the visceral organs such as stomach, intestine, internal sex organs, lungs, throat, and heart.
IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS IN PSYCHOLOGY 1
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
SUBMITTED BY: ELMOR MAGONCIA Student SUBMITTED TO: AILLEN M. VERAS Professor
OCTOBER 2, 2012
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Practical Guide To TATDocument14 pagesPractical Guide To TATwyhiso33% (12)
- Vocab PhillipsDocument632 pagesVocab PhillipsJorge LorenzoNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Physiologic Response To Noise and VibrationDocument86 pagesPhysiologic Response To Noise and VibrationEly-Carla Marshall100% (1)
- Theories On Language Learning - Vygotsky, Piaget, & Habit FormationDocument30 pagesTheories On Language Learning - Vygotsky, Piaget, & Habit FormationShofia NafisahNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Audiometry Procedures Manual: January 2011Document121 pagesAudiometry Procedures Manual: January 2011Ioana Alexandra IliseiNo ratings yet
- Liam's 4 effective ways to silence your tinnitusDocument19 pagesLiam's 4 effective ways to silence your tinnituswakine55No ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument8 pagesSense OrgansKeelah BennNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Review For FPGEE PDFDocument23 pagesAnatomy Review For FPGEE PDFGo Go Art100% (1)
- Human Factors Part-66 Student Notes PDFDocument112 pagesHuman Factors Part-66 Student Notes PDFdavidNo ratings yet
- Juan C. Dela Cruz: With HighesthonorsDocument5 pagesJuan C. Dela Cruz: With HighesthonorsMarieAntonietteYumiNidua100% (1)
- Chemistry - Exam Drill IDocument6 pagesChemistry - Exam Drill IJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- 500 Real English PhrasesDocument38 pages500 Real English PhrasesIon Sava100% (2)
- Grade 4 Mtap Reviewer With Answer KeyDocument3 pagesGrade 4 Mtap Reviewer With Answer KeyJovenil Bacatan92% (53)
- Harvard Style: Citing & ReferencingDocument28 pagesHarvard Style: Citing & ReferencinganyesNo ratings yet
- Paired TestDocument2 pagesPaired TestJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Mtap Reviewer With Answer KeyDocument2 pagesGrade 5 Mtap Reviewer With Answer KeyJovenil Bacatan90% (39)
- National Achievement Test (Nat) : GRADE/ YEARDocument2 pagesNational Achievement Test (Nat) : GRADE/ YEARJovenil Bacatan100% (3)
- What Does A Piano Tuner Do When He Goes Deaf PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Does A Piano Tuner Do When He Goes Deaf PDFSpencer GrahamNo ratings yet
- BPPV CaseDocument24 pagesBPPV CaseAnonymous ZbVovJEFuNo ratings yet
- Formal Models For Predicting Behavioral IntentionsDocument33 pagesFormal Models For Predicting Behavioral IntentionsJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- When Do We Use Chi Square?Document10 pagesWhen Do We Use Chi Square?Cristhian JAGQNo ratings yet
- DepEd Region 3 Monthly Class Observation ReportDocument1 pageDepEd Region 3 Monthly Class Observation ReportJovenil Bacatan100% (1)
- Sum Cells Based On Background ColorDocument10 pagesSum Cells Based On Background ColorJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- 50 50 A Powerpoint QuizDocument9 pages50 50 A Powerpoint QuizJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Nat 6 Msa Reviewer - Part 1Document70 pagesNat 6 Msa Reviewer - Part 1Jovenil Bacatan73% (11)
- Test Item Analysis CalculatorDocument3 pagesTest Item Analysis CalculatorJovenil Bacatan100% (1)
- Projective Drawings 1Document39 pagesProjective Drawings 1Jovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofDocument24 pagesZumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofDocument11 pagesZumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofDocument33 pagesZumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofDocument24 pagesZumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofDocument7 pagesZumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofDocument9 pagesZumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Chap 03Document24 pagesChap 03Jovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofDocument33 pagesZumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagents - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument5 pagesLimiting Reagents - Chemistry LibreTextsJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofDocument4 pagesZumdahl Zumdahl Decoste: World ofJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument18 pagesEducationLary BagsNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-AP Psych-Sensation and PerceptionDocument122 pagesUnit 3-AP Psych-Sensation and Perceptiondarthsamuel42No ratings yet
- Vibrations, Waves and Sound ExplainedDocument98 pagesVibrations, Waves and Sound ExplainedLegdor EdralaNo ratings yet
- ENT Care For CHO & SN - Introduction & Understanding The Structure of ENTDocument18 pagesENT Care For CHO & SN - Introduction & Understanding The Structure of ENTsanmukh chawlaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of the Ear DevelopmentDocument3 pagesEmbryology of the Ear DevelopmentJem MontañaNo ratings yet
- Noise Study ReportDocument4 pagesNoise Study ReportLiew Shu YanNo ratings yet
- Speech PerceptionDocument92 pagesSpeech PerceptionestrellaNo ratings yet
- Hearning Impairment DocumentdocxDocument51 pagesHearning Impairment DocumentdocxHabtamu DebasuNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Pathway: Visual, Auditory & VestibularDocument56 pagesSpecial Senses Pathway: Visual, Auditory & Vestibularmyka brilliant cristobalNo ratings yet
- Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Hou-Yong KangDocument12 pagesSudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Hou-Yong KangsuciNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear TMN NewDocument26 pagesAnatomy of The Ear TMN NewMerriNo ratings yet
- Auditory PathwayDocument33 pagesAuditory PathwayAnusha Varanasi100% (1)
- Ent 1Document170 pagesEnt 1Dicle GÜLNo ratings yet
- Bio Ass I QPDocument7 pagesBio Ass I QPSwayam GosaviNo ratings yet
- The Sense of HearingDocument11 pagesThe Sense of HearingAfdalia AmandaNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Module Explains Vision, Hearing & EquilibriumDocument13 pagesSpecial Senses Module Explains Vision, Hearing & EquilibriumMark Owen QuilatanNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology - Myers Module 17-22 VocabularyDocument7 pagesAP Psychology - Myers Module 17-22 VocabularyJaakkiiee YungNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The EarVirya WijayatiNo ratings yet
- NCERT solutions for class 11 biology chapter 21 neural control and coordinationDocument35 pagesNCERT solutions for class 11 biology chapter 21 neural control and coordinationGajiniNo ratings yet
- A Prospective Observational Study of Temporalis Fascia With Tragal Perichondrium As Graft Material in Type I TympanoplastyDocument23 pagesA Prospective Observational Study of Temporalis Fascia With Tragal Perichondrium As Graft Material in Type I TympanoplastyIjsrnet EditorialNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Of The Ear In 40 CharactersDocument46 pagesAnatomy Of The Ear In 40 Charactersadel madanyNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 1 Stimuli and ResponseDocument21 pagesF3 Chapter 1 Stimuli and ResponseJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - SensesDocument20 pagesChapter 9 - SenseslNo ratings yet