Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 007
Uploaded by
flowerkmOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap 007
Uploaded by
flowerkmCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
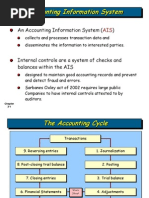
Chapter 7: Accounting Information Systems QUESTIONS 1. 2. GAAP is a set of rules concerning how a company reports its economic activity to stockholders and other external parties. The accounting equation is: assets = liabilities + owners equity. It is important because it must always remain in balance and, therefore, each accounting event must have two effects. An accounting event must (1) be specific to the company for which the accounting records are kept, (2) be measurable in monetary terms, and (3) impact the entitys assets, liabilities, and/or owners equity. A debit means left, as in the left-hand side of an account. A credit means right, as in the right-hand side of an account. Subtraction by opposition means that amounts on the right-hand side of an asset account are subtracted from amounts on the left-hand side of the account. The reverse is true for liabilities and owners equity accounts. For these accounts, amounts on the left-hand side are subtracted from amounts on the right-hand side. To decrease an asset, we credit the account. To decrease a liability, we debit the account. An account is a place where the results of events affecting a particular item are recorded. Accounts are maintained in the ledger in a manual accounting system. The general journal is used to record the impact of an accounting event on the company. The general ledger is used to record the impact of an accounting event on a particular item. Journalizing occurs first and is the process of recording an accounting event in the journal. Posting occurs after journalizing and is the process of recording the appropriate part of a journal entry to the appropriate general ledger account. The accounting cycle is the time period between financial statements. Adjusting entries adjust the accounting records for internal events prior to preparing financial statements. An expense accrual occurs when expenses are incurred but not yet paid for in the current period while a revenue accrual occurs when revenues are earned in the current period but payment is not received until later. A revenue deferral occurs when a company has received assets prior to performing the services for which it was paid, that is, the revenue has been deferred. An expense deferral occurs when a company uses assets previously purchased in an attempt to generate revenue, that is, the expense has been deferred. A contra account is an account whose balance is opposite to its associated account. Therefore a contra-liability would have a debit balance. A trial balance is a listing of all general ledger accounts and their respective balances to ensure that debits equal credits. A trial balance is prepared prior to making adjusting entries. An adjusted trial balance is prepared prior to making closing entries. A post-closing trial balance is prepared prior to starting a new accounting period.
3.
4. 5. 6.
7. 8. 9. 10.
11.
12. 13. 14.
15.
16. 17.
7-1
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
18.
Closing entries zero-out temporary accounts and transfer the balance to owners equity.
EXERCISES E7.1 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. E7.2 a. b. c. d. e. f. E7.3 a. b. c. d. e. f. a. d. a. d. a. d. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Accounting eventassets and liabilities are increased. Not an accounting eventnot measurable. Accounting eventassets are increased and decreased and owners equity is increased and decreased. Not an accounting event (no change in assets, liabilities, and/or owners equity). Not an accounting eventnot measurable. Accounting eventliabilities are increased and owners equity is decreased. Not an accounting eventnot measurable. Assets Liabilities Owners equity I I NA D NA D NA I D D D NA D NA D I/D NA NA Assets Liabilities Owners equity I NA I I I NA I/D NA NA D D NA I I NA I/D I NA 4 b. 3 c. 2 2 e. 1 f. 3 3 b. 1,4 c. 3 3 e. 1 f. 1 1 b. 3 c. 3 1 e. 4 f. 1 Increased by Decreased by Normal balance Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit
E7.4 E7.5 E7.6 E7.7
7-2
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
E7.8
E7.9
a. b. c. d. e. f. a.
b.
c.
E7.10 a.
b.
c.
E7.11 a.
b.
c.
E7.12 a.
b.
c.
E7.13 a. b.
Paid an obligation previously recorded. Paid for rent in advance. Purchased office supplies on open account. Received cash from customers for services to be provided in the future. Sent a bill to a customer for services performed. Received, and paid, the telephone bill. Accounts receivable 8,000 Construction fees earned 8,000 Net income increased. Interest receivable 66.67 Interest earned 66.67 Net income increased. Accounts receivable 1,200 Rental fees earned 1,200 Net income increased. Unearned revenue 4,500 Fees earned 4,500 Net income increased. Unearned subscriptions 2,000 Subscriptions earned 2,000 Net income increased. Unearned fees 5,000 Fees earned 5,000 Net income increased. Telephone expense 210 Utilities payable 210 Net income decreased. Advertising expense 1,400 Advertising payable 1,400 Net income decreased. Interest expense 291.67 Interest payable 291.67 Net income decreased. Insurance expense 500 Prepaid insurance 500 Net income decreased. Supplies expense 1,565 Supplies 1,565 Net income decreased. Depreciation expense 7,500 Accumulated depreciation 7,500 Net income decreased Supplies expense 9,640 Supplies 9,640 Unearned subscriptions 2,800 Subscription fees earned 2,800
7-3
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
E7.14 a. e.
3 4
b. f.
2 3
c. g.
2 2
d. h.
1 3
E7.15 Income Statement Service fee revenue $5,800 Less operating expenses: Supplies expense $ 150 Rent expense 650 Interest expense 25 Depreciation expense 300 Postage expense 125 Telephone expense 50 Utilities expense 100 1,400 Net income $4,400 Statement of Retained Earnings Beginning retained earnings $ 0* Add: net income 4,400 Less: dividends 2,500 Ending retained earnings $ 1,900 * Dividends have already been subtracted from retained earnings in adjusted trial balance. E7.16 Balance Sheet Assets: Cash Supplies Prepaid rent Equipment Accumulated depr. Furniture Accumulated depr. Total assets E7.17 Service fees earned 5,800 Retained earnings 5,800 Retained earnings 1,400 Supplies expense 150 Rent expense 650 Interest expense 25 Depreciation expense 300 Postage expense 125 Telephone expense 50 Utilities expense 100 E7.18 Net income = $4,250 - $2,400 - $485 - $615 - $160 = $590 Ending retained earnings = $3,720 + $590 = $4,310 Liabilities & Owners Equity Accounts payable $ 800 Note payable 3,000 Interest payable 150 Capital stock 6,000 Retained earnings 1,900 Total liab & owners equity $11,850
$ 4,600 400 650 5,600 (1,200) 2,700 (900) $11,850
7-4
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
Event: Prepaid insuranceincrease, $2,400 Cashdecrease, $2,400 Adjustment: Insurance expenseincrease, $300 Prepaid insurancedecrease, $300 b. Event: Cashincrease, $7,200 Unearned feesincrease, $7,200 Adjustment: Unearned feesdecrease, $1,600 Fee revenueincrease, $1,600 c. Event: Cashincrease, $100,000 Note payableincrease, $100,000 Adjustment: Interest expenseincrease, $666.67 Interest payableincrease, $666.67 d. Event: Note receivableincrease, $50,000 Cashdecrease, $50,000 Adjustment: Interest receivableincrease, $1,250 Interest revenueincrease, $1,250 e. Event: Equipmentincrease, $80,000 Cashdecrease, $80,000 Adjustment: Depreciation expenseincrease, $2,500 Accumulated depreciationincrease, $2,500 E7.20 Answers will vary, some examples follow. a. customer contacts by salesperson customer contact information customer credit information customer payment history b. defects by week hours worked by department units produced by hour employee efficiency c. supplier contacts made supplier efficiency returns by supplier returns by item E7.19 a. PROBLEMS P7.1 1. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j.
Assets increase; owners equity increase Assets increase and decrease; liabilities increase Assets increase; liabilities increase Assets increase; owners equity increase (revenue) Assets increase; liabilities increase Assets decrease; liabilities decrease Assets increase; owners equity increase (revenue) Assets decrease; owners equity decrease (expense) Assets decrease; owners equity decrease Liabilities increase; owners equity decrease (expense)
7-5
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
2.
a. b.
Cash
30,000 30,000
3.
4.
5.
Capital stock Land 35,000 Building 165,000 Cash Note payable c. Office equipment 7,500 Accounts payable d. Accounts receivable 5,000 Fees earned e. Cash 800 Unearned fees f. Accounts payable 1,500 Cash g. Cash 2,000 Fees earned h. Utility expense 380 Cash i. Retained earnings 3,000 Cash j. Utility expense 450 Utilities payable Income statement Fees earned Less operating expenses Net income Beginning retained earnings Add: net income Less: dividends Ending retained earnings Statement of cash flows Operating: Cash received from customers Cash paid for expenses Net cash flows from operations Investing: Cash paid for land & building Cash paid for office equipment Net cash flows from investing Financing: Cash received from owners Cash paid to owners Net cash flows from financing Net change in cash Add: beginning balance Ending balance of cash
10,000 190,000 7,500 5,000 800 1,500 2,000 380 3,000 450 $ 7,000 830 $ 6,170 $ -06,170 (3,000) $ 3,170
$ $
2,800 (380) 2,420
$(10,000) (1,500) $(11,500) $ 30,000 (3,000) $ 27,000 $ 17,920 -0$ 17,920
7-6
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
6.
Balance sheet Cash $ 17,920 Accounts receivable 5,000 Office equipment 7,500 Land 35,000 Building 165,000 Total assets $230,420
Accounts payable $ 6,000 Utilities payable 450 Unearned fees 800 Notes payable 190,000 Capital stock 30,000 Retained earnings 3,170 Total liab & own eq. $230,420
P7.2 1.
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i.
Assets increase; liabilities increase Assets increase and decrease; owners equity increase and decrease (revenue and expense) Assets increase; assets decrease Assets increase and decrease; owners equity increase and decrease (revenue and expense) Assets decrease; owners equity decrease (expense) Assets decrease; owners equity decrease (expense) Assets increase; assets decrease Assets decrease; owners equity decrease (expense) Assets decrease; owners equity decrease (expense) Merchandise inventory Accounts payable Accounts receivable Sales Cost of goods sold Merchandise inventory Merchandise inventory Cash Cash Sales Cost of goods sold Merchandise inventory Utility expense Cash Wage expense Cash Cash Accounts receivable Rent expense Cash Depreciation expense Accumulated depreciation 26,000 26,000 89,400 89,400 60,000 60,000 36,000 36,000 85,040 85,040 63,600 63,600 2,150 2,150 8,200 8,200 58,000 58,000 12,000 12,000 6,000 6,000
2.
a. b.
c. d.
e. f. g. h. i.
7-7
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
3.
4.
Income Statement Sales Less cost of goods sold Gross margin Less operating expenses: Utility expense Wage expense Rent expense Depreciation expense Net income Statement of Cash Flows Operating: Cash received from customers Cash paid for inventory Cash paid for operating expenses Net cash from operating
$174,440 (123,600) $ 50,840 $ 2,150 8,200 12,000 6,000
(28,350) $ 22,490
$143,040 (36,000) (22,350) $ 84,690
P7.3 1.
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. a. b. c. d. e. f. g.
2.
h.
Assets increase; owners equity increase Assets increase; liabilities increase Assets increase; assets decrease Assets increase; assets decrease Assets increase; liabilities increase Assets increase; assets decrease Assets increase and decrease; owners equity increase and decrease (revenue and expense) Assets decrease; owners equity decrease (expense) Assets decrease; owners equity decrease Cash 25,000 Capital stock 25,000 Raw materials inventory 50,000 Accounts payable 50,000 Work-in-process inventory 42,000 Raw materials inventory 42,000 Work-in-process inventory 11,500 Cash 11,500 Work-in-process inventory 17,700 Accounts payable 17,700 Finished goods inventory 47,500 Work-in-process inventory 47,500 Cash 50,750 Sales 50,750 Cost of goods sold 36,250 Finished goods inventory 36,250 Selling expenses 7,500 Cash 7,500
7-8
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
i. 3.
4.
Retained earnings Cash Income Statement Sales Less cost of goods sold Gross margin Less selling expenses Net income Statement of Cash Flows Operating: Cash received from customers Cash paid for wages Cash paid for selling expenses Net cash flows from operations Financing: Cash received from owners Cash paid to owners Net cash flows from financing
2,500 2,500 $50,750 (36,250) $14,500 (7,500) $ 7,000
$50,750 (11,500) (7,500) $31,750 $25,000 (2,500) $22,500
P7.4 1.
2.
a. Assets increase by $430,000 and decrease by $43,000; liabilities increase by $387,000. b. Assets increase by $8,000 and decrease by $23,000; liabilities decrease by $15,000. c. Assets increase by $11,000 and decrease by $5,000 ($3,000 accounts receivable and $2,000 inventory); owners equity increases by $8,000 and decreases by $2,000. d. Assets increase by $19,500 and liabilities increase by $19,500. Then assets increase by $34,125 and decrease by $19,500 while owners equity increases by $34,125 and decreases by $19,500. a. Buildings 240,000 Land 190,000 Cash 43,000 Notes payable 387,000 b. Equipment 8,000 Accounts payable 15,000 Cash 23,000 c. Cash 11,000 Cost of goods sold 2,000 Inventory 2,000 Sales 8,000 Accounts receivable 3,000 d. Merchandise inventory 19,500 Accounts payable 19,500 Cash 34,125 Sales 34,125
7-9
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
Cost of goods sold Merchandise inventory P7.5 Income Statement Sales Interest earned Less operating expenses: Wage expense $43,000 Depreciation expense 5,300 Rent expense 24,000 Net income Statement of Cash Flows Operating cash flows: Cash received from customers Cash paid for supplies Cash paid for insurance Net cash flow from operating Financing cash flows: Cash received from owners Cash received from borrowing Net cash flows from financing Net change in cash P7.6 a. d. g. j. a. d. g. j. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i.
19,500 19,500
$85,000 200
72,300 $12,900
$ 65,000 (12,000) (4,800) $ 48,200 $ 80,000 40,000 $120,000 $168,200
P7.7
P7.8
3 b. 3,4 c. 4 1 e. 1 f. 3, 4 2,3 h. 3. i. 3 1 k. 3 l. 3 3 b. 3 c. 2 4 e. 4 f. 2,4 3 h. 3 i. 3 1,2 k. 1 l. 1 Cash is received from a customer on open account. Supplies are purchased for cash. Services are provided to a customer for cash. Inventory is purchased on open account. An amount due to a supplier is paid. Services are provided to a customer on account. A bill is paid upon receipt. A note payable to the bank is paid off. Something is sold to a customer on account and the cost of the item sold is removed from inventory.
P7.9 1.
a.
Supplies expense Supplies
710 710
7-10
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
Rent expense 1,400 Prepaid rent c. Depreciation expense 1,500 Accumulated depreciation --buildings d. Depreciation expense 800 Accumulated depreciation --equipment e. Unearned fees 2,230 Fee revenue f. Salary expense 740 Salaries payable g. Interest expense 240 Interest payable h. Accounts receivable 570 Fees revenue 2. Adjusted trial balance FARLOW CORPORATION Adjusted Trial Balance March 31, 2010 Cash $ 7,280 Accounts receivable 2,270 Supplies 230 Prepaid rent 1,000 Land 52,000 Buildings 94,000 Accumulated depreciationbldgs Equipment 41,500 Accumulated depreciationequip Accounts payable Unearned fees Salaries payable Interest payable Note payable Capital stock Retained earnings Fee revenue Salary expense 10,060 Telephone expense 260 Utilities expense 410 Miscellaneous expense 190 Supplies expense 710 Rent expense 1,400 Depreciation expense 2,300 Interest expense 240 Total $213,850
b.
1,400
1,500
800 2,230 740 240 570
$ 18,100 14,300 3,480 740 740 240 60,000 45,000 39,150 32,100
$213,850
7-11
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
7-12
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
3.
Fees revenue 32,100 Retained earnings Retained earnings 15,570 Salary expense Telephone expense Utilities expense Miscellaneous expense Supplies expense Rent expense Depreciation expense Interest expense 4. Income Statement Fees earned Less operating expenses Net income 5. Post-closing trial balance FARLOW CORPORATION Post-Closing Trial Balance March 31, 2010 Cash $ 7,280 Accounts receivable 2,270 Supplies 230 Prepaid rent 1,000 Land 52,000 Buildings 94,000 Accumulated depreciationbldgs Equipment 41,500 Accumulated depreciationequip Accounts payable Unearned fees Salaries payable Interest payable Note payable Capital stock Retained earnings Total $198,280 P7.10 1. a. b. c.
32,100 10,060 260 410 190 710 1,400 2,300 240 $32,100 (15,570) $16,530
$ 18,100 14,300 3,480 740 740 240 60,000 45,000 55,680 $198,280
Supplies expense Supplies Insurance expense Prepaid insurance Depreciation expense Accumulated depreciation --buildings
560 560 250 250 750 750
7-13
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
Depreciation expense 350 Accumulated depreciation --equipment e. Unearned delivery fees 900 Fees revenue f. Salary expense 280 Salary payable g. Interest expense 500 Interest payable h. Accounts receivable 560 Fees revenue 2. Adjusted trial balance WESAW DELIVERY SERVICE Adjusted Trial Balance June 30, 2010 Cash $ 6,340 Accounts receivable 1,970 Supplies 330 Prepaid insurance 1,650 Land 48,000 Buildings 82,000 Accumulated depreciationbuildings Equipment 53,000 Accumulated depreciationequipment Accounts payable Unearned delivery fees Interest payable Salaries payable Mortgage payable Capital stock Retained earnings Fee revenue Salary expense 9,340 Telephone expense 120 Utilities expense 350 Repairs expense 430 Supplies expense 560 Insurance expense 250 Depreciation expense 1,100 Interest expense 500 Total $205,940
d.
350 900 280 500 560
$ 19,710 17,150 2,550 1,200 500 280 58,000 50,000 21,630 34,920
$205,940
7-14
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
3.
4. 5.
Fees earned 34,920 Retained earnings Retained earnings 12,650 Salary expense Telephone expense Utilities expense Repairs expense Supplies expense Insurance expense Depreciation expense Interest expense Net income = $34,920 - $12,650 = $22,270
34,920 9,340 120 350 430 560 250 1,100 500
Post-closing trial balance WESAW DELIVERY SERVICE Adjusted Trial Balance June 30, 2010 Cash $ 6,340 Accounts receivable 1,970 Supplies 330 Prepaid insurance 1,650 Land 48,000 Buildings 82,000 Accumulated depreciationbuildings Equipment 53,000 Accumulated depreciationequipment Accounts payable Unearned delivery fees Interest payable Salaries payable Mortgage payable Capital stock Retained earnings Total $193,290 CASES C7.1 Answers will vary. C7.2 1. 1 Cash Briggs, capital 2 Prepaid rent Cash 5 Office supplies Cash 8 Office furniture Accounts payable
$ 19,710 17,150 2,550 1,200 500 280 58,000 50,000 43,900 $193,290
25,000 25,000 5,400 5,400 900 900 4,800 4,800
7-15
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
10 12 15 18 20 21 25 27 31
Advertising expense Cash Accounts receivable Fees earned Cash Fees earned Insurance expense Cash Cash Unearned fees Cash Accounts receivable Accounts payable Cash Briggs, drawing Cash Salary expense Cash
250 250 850 850 350 350 300 300 5,000 5,000 200 200 1,000 1,000 2,000 2,000 1,200 1,200
2.
3.
Trial Balance Cash $19,500 Accounts receivable 650 Office supplies 900 Prepaid rent 5,400 Office furniture 4,800 Accounts payable $ 3,800 Unearned fees 5,000 Briggs, capital 25,000 Briggs, drawing 2,000 Fees earned 1,200 Advertising expense 250 Insurance expense 300 Salary expense 1,200 Total $35,000 $35,000 a. Rent expense 1,800 Prepaid rent 1,800 b. Supplies expense 650 Office supplies 650 c. Depreciation expense 40 Accumulated depreciation 40 d. Unearned revenue 400 Fees earned 400 e. Utilities expense 130 Utilities payable 130 f. Accounts receivable 350 Fees earned 350
7-16
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
7-17
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
4.
Income Statement Fees earned Less operating expenses: Advertising expense Insurance expense Salary expense Rent expense Supplies expense Depreciation expense Utilities expense Net loss Statement of Owners Equity Briggs, capital, beginning balance Add: contributions by owner Less: net loss Less: withdrawals by owner Briggs, capital, ending balance Statement of Cash Flows Operating cash: Cash received from customers Cash paid for rent Cash paid for supplies Cash paid for advertising Cash paid for insurance Cash paid for salaries Net cash flows from operations Investing cash flows: Cash paid for office furniture Financing cash flows: Cash received from owner Cash paid to owner Net cash flows from financing Net change in cash Balance Sheet Cash Accounts receivable Office supplies Prepaid rent Office furniture Accumulated depreciation Total assets
$ 1,950 $ 250 300 1,200 1,800 650 40 130
4,370 $(2,420)
-025,000 (2,420) (2,000) $20,580
$ 5,550 (5,400) (900) (250) (300) (1,200) $ (2,500) $ (1,000) $ 25,000 (2,000) $ 23,000 $ 19,500
$19,500 1,000 250 3,600 4,800 (40) $29,110
Accounts payable $ 3,800 Unearned fees 4,600 Utilities payable 130 Briggs, capital 20,580 Total liab & own eq $29,110
7-18
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
5.
Fees earned Briggs, capital Briggs, capital Advertising expense Insurance expense Salary expense Rent expense Supplies expense Depreciation expense Utilities expense Briggs, capital Briggs, drawing
1,950 1,950 4,370 250 300 1,200 1,800 650 40 130 2,000 2,000
CRITICAL THINKING CT7.1 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Heavy cream inventory Light cream inventory Sugar inventory Vanilla inventory Container inventory Ice cream inventory Equipment Accumulated depreciation Liabilities Accounts payable Income taxes payable Interest payable Salary payable Wage payable Owners Equity Capital stock Retained earnings Sales Sales discounts Sales returns and allowances Cost of goods sold Salary expense--sales Commission expense Truck rental expense Interest expense Salary expense-adm Miscellaneous exp Income tax expense Purchase discounts Manufacturing overhead
CT7.2 Answers will vary. Students should consider the importance of not only knowing how much money a person has but also the sources of that money and the uses of it. Students should also realize that the bank does not loan money just because a person has assets; the bank also needs to know that your business is profitable and that you understand the sources of that profit. ETHICAL CHALLENGES EC7.1 Answers will vary; should be an interesting class discussion. EC7.2 Answers will vary. Students must consider the ratios from Chapters 1 and 2.
7-19
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
7-20
Chapter 07 - Accounting Information Systems
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS CA7.1 Trial Balance Accounts DR CR
Cash Accounts receivable Supplies Equipment Accum Depr-Equip Accounts payable Unearned revenue Capital stock Retained earnings Service revenue Salary expense Utilities expense Insurance expense Total Supplies expense Depreciation expense Total 1,600 1,100 300 3,000 900 600 700 1,500 800 3,300 1,500 100 200 7,800
Adjustments DR CR
400 150 250 300
Adjusted Balance DR CR
1,600 1,500 150 3,000 1150 600 400 1500 800 4000 1,500 100 200
700
7,800 150 250 1100 150 250 8450
1100
8450
CA7.2
Adjusted Balance Closing Entries DR CR Post-Closing Balance DR 1,600 1,500 150 3,000 CR
Accounts
Cash Accounts receivable Supplies Equipment Accum Depr-Equip Accounts payable Unearned revenue Capital stock Retained earnings Service revenue Salary expense Utilities expense Insurance expense Supplies expense Depreciation expense Total
DR 1,600 1,500 150 3,000
CR
1,150 600 400 1,500 800 4,000 1,500 100 200 150 250 8,450
2,200 4,000
4000 1,500 100 200 150 250 6,200 0 0 0 0 0 6,250
1,150 600 400 1,500 2,600 0
8,450
6,200
6,250
7-21
You might also like
- Chapter 03 - Operating Decisions and the Income StatementDocument10 pagesChapter 03 - Operating Decisions and the Income StatementJie Bo Ti67% (3)
- Accounting for TransactionsDocument19 pagesAccounting for TransactionsRahasia RommelNo ratings yet
- Partnership and Corporation Accounting Quiz Test IDocument5 pagesPartnership and Corporation Accounting Quiz Test IDoysabas A. Scott ElizarNo ratings yet
- MGMT 501 Assi1.Document10 pagesMGMT 501 Assi1.prachi45No ratings yet
- The Effect of Profit or Loss On Capital and The Double Entry System For Expenses and RevenueDocument35 pagesThe Effect of Profit or Loss On Capital and The Double Entry System For Expenses and Revenueshabanzuhura706No ratings yet
- 1 The Accounting Equation Accounting Cycle Steps 1 4Document6 pages1 The Accounting Equation Accounting Cycle Steps 1 4Jerric CristobalNo ratings yet
- Accounting Equation (Abm)Document43 pagesAccounting Equation (Abm)EasyGaming100% (1)
- Business ModelDocument29 pagesBusiness ModelTirsolito SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Compilation of IFA QuestionsDocument67 pagesCompilation of IFA QuestionsBugoy CabasanNo ratings yet
- AKDocument9 pagesAKAnonymous cJogAxQnNo ratings yet
- Review of Ch 1 & 2 Key ConceptsDocument46 pagesReview of Ch 1 & 2 Key ConceptsBookAddict721No ratings yet
- Accounting Principle - Ujian NasionalDocument115 pagesAccounting Principle - Ujian Nasionalosusant0100% (1)
- Accounting principles assignment on chapters 1 and 2Document36 pagesAccounting principles assignment on chapters 1 and 2DrGeorge Saad AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Acctg201 - Prelim Part 1Document9 pagesAcctg201 - Prelim Part 1Rowena GayasNo ratings yet
- Asset LiabilityDocument8 pagesAsset LiabilityRohit More100% (1)
- 2.recording ProcessDocument30 pages2.recording Processwpar815No ratings yet
- Accounting Equation Service Business 6Document21 pagesAccounting Equation Service Business 6udayraj_vNo ratings yet
- Deffgh Fill inDocument5 pagesDeffgh Fill inaleah de jesusNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Basic AccountingDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 2 Basic AccountingPrincess Galicia Tres ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1Document21 pages1DrGeorge Saad AbdallaNo ratings yet
- GlobalisationDocument9 pagesGlobalisationMark Joseph TadeoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Accounting: Key Terms and Concepts To KnowDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Financial Accounting: Key Terms and Concepts To KnowAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Local Media8011400976913649007Document16 pagesLocal Media8011400976913649007Ivan dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ACCTG 1 Week 4 - Recording Business TransactionsDocument17 pagesACCTG 1 Week 4 - Recording Business TransactionsReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument6 pagesCash Flow StatementAizia Sarceda Guzman80% (5)
- Handout TopFormDocument10 pagesHandout TopFormshnappsshubhNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoicesDocument5 pagesMultiple ChoicesAdlan AfnanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Part 2Document4 pagesCH 1 Part 2Rabie HarounNo ratings yet
- ch01 Introduction Acounting & BusinessDocument37 pagesch01 Introduction Acounting & Businesskuncoroooo100% (1)
- Managerial Accounting1Document33 pagesManagerial Accounting1MM-Tansiongco, Keino R.No ratings yet
- Balance Sheet & P&LDocument66 pagesBalance Sheet & P&LAnish GhoshNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting BasicsDocument24 pagesFinancial Accounting BasicsMonirHRNo ratings yet
- Accounting Assignment PDFDocument18 pagesAccounting Assignment PDFMohammed SafwatNo ratings yet
- Ac101 ch3Document21 pagesAc101 ch3Alex ChewNo ratings yet
- Completing The Accounting CycleDocument47 pagesCompleting The Accounting CycleMeagan NelsonNo ratings yet
- Upheavals at A Single Company Pulling DowneDocument5 pagesUpheavals at A Single Company Pulling DowneShesharam ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Homework QuestionsDocument17 pagesHomework QuestionsANo ratings yet
- Fabm1 Q3 M7 WK7 9 For DigitizedDocument16 pagesFabm1 Q3 M7 WK7 9 For Digitizedquaresmarenzel715No ratings yet
- Accounting Errors and Their CorrectionDocument32 pagesAccounting Errors and Their CorrectionmillzmartoNo ratings yet
- Transactions Recording Chapter2 BDocument19 pagesTransactions Recording Chapter2 Bhassanjamil123No ratings yet
- MBA 560 Accounting Managerial NotesDocument18 pagesMBA 560 Accounting Managerial NotesDesi MarianNo ratings yet
- Wiley - Chapter 7: Cash and ReceivablesDocument33 pagesWiley - Chapter 7: Cash and ReceivablesIvan Bliminse100% (2)
- Coaching Session 2 - Basic Accounting-Accounting Equation and The Double-Entry SystemDocument7 pagesCoaching Session 2 - Basic Accounting-Accounting Equation and The Double-Entry SystemLin GulbeNo ratings yet
- Adjusting EntriesDocument4 pagesAdjusting EntriesNoj WerdnaNo ratings yet
- Wiley - Chapter 3: The Accounting Information SystemDocument36 pagesWiley - Chapter 3: The Accounting Information SystemIvan BliminseNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument59 pagesCash Flow StatementApple Crissa Mae Rejas100% (1)
- Accounting Equation For A Sole ProprietorshipDocument11 pagesAccounting Equation For A Sole Proprietorshipjobeson100% (1)
- Acct 2600 Exam 1 Study SheetDocument8 pagesAcct 2600 Exam 1 Study Sheetapi-236442317No ratings yet
- FabmDocument68 pagesFabmAllyzza Jayne Abelido100% (1)
- Accy 517 HW PB Set 1Document30 pagesAccy 517 HW PB Set 1YonghoChoNo ratings yet
- TN-4: The Accounting ProcessDocument20 pagesTN-4: The Accounting ProcessAmrutaNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument7 pagesAccountingGifford NaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SolutionsDocument100 pagesChapter 3 SolutionssevtenNo ratings yet
- A Lecture6 9 29 22Document46 pagesA Lecture6 9 29 22Kawaii SevennNo ratings yet
- Modyul 1 (Ikatlong Markahan)Document29 pagesModyul 1 (Ikatlong Markahan)delgadojudithNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?From EverandFinancial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bookkeeping for Nonprofits: A Step-by-Step Guide to Nonprofit AccountingFrom EverandBookkeeping for Nonprofits: A Step-by-Step Guide to Nonprofit AccountingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Bookkeeping 101 For Business Professionals | Increase Your Accounting Skills And Create More Financial Stability And WealthFrom EverandBookkeeping 101 For Business Professionals | Increase Your Accounting Skills And Create More Financial Stability And WealthNo ratings yet
- Management and Cost Accounting SummaryDocument82 pagesManagement and Cost Accounting SummaryflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument4 pagesDecision MakingflowerkmNo ratings yet
- PenmanDocument8 pagesPenmanvinaymathewNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument11 pagesAccountingflowerkm100% (1)
- Primary Goal of A Firm: Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument3 pagesPrimary Goal of A Firm: Chapter 1 IntroductionflowerkmNo ratings yet
- 8e ch10 Stud PDFDocument5 pages8e ch10 Stud PDFflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Chap001 LODocument12 pagesChap001 LOflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Century 21 Fundamentals Course1Document24 pagesCentury 21 Fundamentals Course1flowerkmNo ratings yet
- Student Guide For Peachtree Complete: Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts, 5eDocument41 pagesStudent Guide For Peachtree Complete: Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts, 5ehahahahabaNo ratings yet
- CH 01 ADocument68 pagesCH 01 Aflowerkm100% (1)
- Plant Assets Depreciation MethodsDocument110 pagesPlant Assets Depreciation Methodsflowerkm100% (1)
- Primary Goal of A Firm: Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument3 pagesPrimary Goal of A Firm: Chapter 1 IntroductionflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Warren SM Ch.01 FinalDocument55 pagesWarren SM Ch.01 FinalflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Horngren 9th Edition Solutions Ch2Document119 pagesHorngren 9th Edition Solutions Ch2flowerkm80% (5)
- CHAPTER 3 Adjusting The Accounts: AnswerDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 3 Adjusting The Accounts: AnswerflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Web Site AddressDocument1 pageWeb Site AddressflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Q1. Fill in The Blanks With Suitable Forms of WordsDocument4 pagesQ1. Fill in The Blanks With Suitable Forms of WordsflowerkmNo ratings yet
- IGCSE, A Level, 9th-10th Model Papers & Bcom Accounting KeyDocument1 pageIGCSE, A Level, 9th-10th Model Papers & Bcom Accounting KeyflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Fill Objective Question PaperDocument1 pageFill Objective Question PaperflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document2 pagesPaper 2flowerkmNo ratings yet
- Achieve A Grades with Our Academic HelpDocument1 pageAchieve A Grades with Our Academic HelpflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Career ObjectiveDocument1 pageCareer ObjectiveflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Paper 4Document2 pagesPaper 4flowerkmNo ratings yet
- Solution QA Ch7Document15 pagesSolution QA Ch7Erica Naranjo Rosella100% (1)
- Chapter 04 AnswersDocument6 pagesChapter 04 Answerssadfj54550% (2)
- Forecasting Models ExplainedDocument14 pagesForecasting Models ExplainedYamin Shwe Sin Kyaw100% (2)
- Chapter 03 AnswersDocument29 pagesChapter 03 AnswersJohanna Mae L. Autida92% (12)
- 2011 Sample Conceptual AnswersDocument4 pages2011 Sample Conceptual AnswersflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Accounting QuestionsDocument1 pageAccounting QuestionsflowerkmNo ratings yet
- Fill Objective Question PaperDocument1 pageFill Objective Question PaperflowerkmNo ratings yet