Professional Documents
Culture Documents
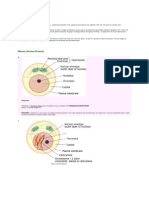
Human Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Dharmendra Singh LagoriyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Dharmendra Singh LagoriyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Endocrine System Gland Hormone Releasing and inhibiting hormones and factors Posterior pituitary hormones produced
here Functions
Hypothalamus
Control of another pituitary hormones
Posterior pituitary gland
Receives hormones from hypothalamus no hormones synthesised here Ejection of milk from mammary gland, stores and secretes the following: contraction of uterus during birth Oxytocin Reduction of urine secretion by kidney Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) (vasopressin) In male, stimulate spermatogenesis In female, growth of ovarian follicles In male testosterone secretion In female secretion of oestrogen and progesterone, ovulation and maintenance of corpus luteum Stimulates milk production and secretion Synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones growth of thyroid glands. Synthesis and secretion of adrenal cortex hormones growth of gland Protein synthesis, growth, especially of bone of limbs Increases blood calcium level Decreases blood phosphate level Regulation of basal metabolic rate, growth and development Decreases blood calcium level
Anterior pituitary gland
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinising hormone (LH) Prolactin Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH or corticotrophin) Growth hormone (GH)
Parathyroid gland Thyroid gland
Parathormone Triiodothyronine (T3)and thyroxine (T4) Calcitonin
Adrenal cortex
Protein breakdown, glucose/glycogen synthesis,adaptation to stress, antiGlucocorticoids (cortisol) inflammatory/allergy effects Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) Na+ retention in kidney, Na+ and K+ ratios in extracellular and intracellular fluids, raises blood pressure Increase rate and force of heartbeat, constriction of skin and gut capillaries Dilation of arterioles of heart and skeletal
Adrenal medulla Adrenaline (epinephrine) Noradrenaline (norepinephrine)
muscles, raising blood glucose level General constriction of small arteries, raising of blood pressure Decreases blood glucose level, increases glucose and amino acid uptake and utilisation by cells Increases blood glucose level, breakdown of glucogen to glucose in liver
Islets of Langerhans
Insulin (beta cells) Glucagon (alpha cells)
stomach Duodenum
Secretion of gastric juices Gastrin Secretion of pancreatic juice Secretin Inhibits gastric secretion Cholecystokinin (Pancreozymin) Emptying of gall bladder and release of pancreatic juice in to duodenum Renin Oestrogens(17 Beta-oestradiol) Progesterone Progesterone and oestrogen Progesterone ans oestrogen Chorionic gonadotrophin Human placental lactogen Testosterone Conversion of angiotensinogen into angiotensin Female secondary sex characteristics, oestrous cycle Gestation, inhibition of ovulation Growth and development of uterus Foetal development Maintenance of corpus luteum Stimulates mammary growth Male secondary sexual characteristics
Kidney Ovary
Corpus luteum Placenta Testis
You might also like
- DNA BarcodingDocument20 pagesDNA BarcodingDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Bsa 11 410 D.s.lagoriyaDocument21 pagesBsa 11 410 D.s.lagoriyaDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Bhendi Shoot and Fruit BorerDocument21 pagesBhendi Shoot and Fruit BorerDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- WinnowingDocument11 pagesWinnowingDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Insect Pest of CropDocument9 pagesInsect Pest of CropDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Crops - BN and FamilyDocument21 pagesCrops - BN and FamilyDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology Application in Biology and MedicenDocument31 pagesNanotechnology Application in Biology and MedicenDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Food SubstancesDocument24 pagesAromatic Food SubstancesDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Rock ......................... AssignamentDocument31 pagesRock ......................... AssignamentDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Autotrophic Plants in BriefDocument7 pagesAutotrophic Plants in BriefDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Rice MillingDocument9 pagesRice MillingDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Varieties Release From TNAU UNIVERISITYDocument18 pagesVarieties Release From TNAU UNIVERISITYDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Sea SpeciesDocument8 pagesSea SpeciesDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Sea SpeciesDocument8 pagesSea SpeciesDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- PG BulletinDocument88 pagesPG BulletinDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- NARP Zone Zonal Research Station Districts Suitable Crops Crop InformationDocument5 pagesNARP Zone Zonal Research Station Districts Suitable Crops Crop InformationDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Forest Trees With Teir Scientific NamesDocument8 pagesForest Trees With Teir Scientific NamesDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- CASTORDocument7 pagesCASTORDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Diagram of MitosisDocument5 pagesDiagram of MitosisDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- ICARDocument4 pagesICARDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Fruits Amount Minerals Contained Vitamins ContainedDocument19 pagesFruits Amount Minerals Contained Vitamins ContainedDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Food SpoilageDocument3 pagesFood SpoilageDharmendra Singh LagoriyaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Lecture No 03 Functional Foods NutraceuticalDocument15 pagesLecture No 03 Functional Foods Nutraceuticalmaryam khanNo ratings yet
- PhEn602 Spring09 Notes1Document66 pagesPhEn602 Spring09 Notes1Abd Al-Rahmman Al-qatanani100% (1)
- Kesesuaian StokDocument2 pagesKesesuaian StokResky OktavianiNo ratings yet
- CB Life Insurance Company LTDDocument18 pagesCB Life Insurance Company LTDHtet Lynn HtunNo ratings yet
- 12 MR - Norhisam Omar, Sales Manager, South East Asia of TenCate Geosynthetics Asia SDN BHDDocument4 pages12 MR - Norhisam Omar, Sales Manager, South East Asia of TenCate Geosynthetics Asia SDN BHDMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Ca LidahDocument27 pagesCa LidahArnaz AdisaputraNo ratings yet
- Brochure Men - Ingrid Auer - Angel Essences To Help MenDocument4 pagesBrochure Men - Ingrid Auer - Angel Essences To Help MenJoanne JacksonNo ratings yet
- Indian Models of Economy, Business and Management-PPT by Shlok KhandelwalDocument44 pagesIndian Models of Economy, Business and Management-PPT by Shlok KhandelwalShlok KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Alywn Cosgrove Real World Fat Loss PDFDocument75 pagesAlywn Cosgrove Real World Fat Loss PDFJM Gym Manticao100% (1)
- GINA 2021 Guidelines for Asthma Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument24 pagesGINA 2021 Guidelines for Asthma Diagnosis and TreatmentBianca Watanabe - RatillaNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Zolpidem Nasal in SituDocument12 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Zolpidem Nasal in SituGopalasatheeskumar KNo ratings yet
- Study Online,: Graduate On CampusDocument28 pagesStudy Online,: Graduate On CampusattackcairoNo ratings yet
- Lehane Histamine Scombroid ReportDocument84 pagesLehane Histamine Scombroid ReportGeraldine Pardo MariluzNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Diuretics For BPT StudentsDocument16 pagesPharmacology Diuretics For BPT StudentsDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM100% (1)
- Viii NCPDocument6 pagesViii NCPAdrian MangahasNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma and Congenital Cholesteatoma Important PointsDocument6 pagesCholesteatoma and Congenital Cholesteatoma Important PointsSuprit Sn100% (1)
- Kallman2021 (Jurnal Perundungan Atau Bullying)Document5 pagesKallman2021 (Jurnal Perundungan Atau Bullying)SAID MAULANANo ratings yet
- Final Thesis With CV (For Bookbind)Document138 pagesFinal Thesis With CV (For Bookbind)Bea Marie Eclevia100% (1)
- Individual Development FactorsDocument9 pagesIndividual Development Factorshanani_leeNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Health Status (FIHS) : Rating GuidelinesDocument3 pagesFactors Influencing Health Status (FIHS) : Rating GuidelinesAyan Kumar GhoshNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Parts PacketDocument2 pagesDigestive System Parts PacketRusherNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents:: Mariam Tariq L1F07BBAM0060 Nabeela Sattar L1F07BBAM2159 Sana Akbar L1F07BBAM2085Document9 pagesTable of Contents:: Mariam Tariq L1F07BBAM0060 Nabeela Sattar L1F07BBAM2159 Sana Akbar L1F07BBAM2085Raheem AhmedNo ratings yet
- BICOM Treatment of Chronic Fatigue and FibromyalgiaCFS ReportDocument15 pagesBICOM Treatment of Chronic Fatigue and FibromyalgiaCFS ReportAnahata Fraydon100% (1)
- Demystifying Buprenorphine Regulations For Pharmacists and CliniciansDocument10 pagesDemystifying Buprenorphine Regulations For Pharmacists and Clinicianslorien86No ratings yet
- Peace Corps Violation of Office of Victim Advocate Clearances by OVA Employee DI-16-0254 WB CommentsDocument26 pagesPeace Corps Violation of Office of Victim Advocate Clearances by OVA Employee DI-16-0254 WB CommentsAccessible Journal Media: Peace Corps DocumentsNo ratings yet
- Family Context of Mental Health Risk in Tsunami-Exposed AdolescentsDocument11 pagesFamily Context of Mental Health Risk in Tsunami-Exposed AdolescentsVirgílio BaltasarNo ratings yet
- Qila SaifullahDocument57 pagesQila SaifullahMohammad Yahya Musakhel100% (2)
- Prevent Dengue: Learn Aedes Mosquito FactsDocument30 pagesPrevent Dengue: Learn Aedes Mosquito FactstahseenhassantirmiziNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infection PicturesDocument26 pagesFungal Infection PicturesAshty RzgarNo ratings yet
- Influence of Academic Work on SHS Students' Mental HealthDocument67 pagesInfluence of Academic Work on SHS Students' Mental HealthAliekfarsey Masukat100% (1)