Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti Infective Drug Chart
Uploaded by
JessicaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anti Infective Drug Chart
Uploaded by
JessicaCopyright:
Available Formats
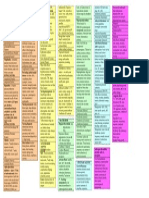
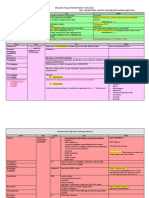
Sulfonamides- static, prevent bacterial synthesis of folic acid; broad spectrum Trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole (bactrim, septra) UTIs, otitis media,
bronchitis Silver sulfadiazine (silvadene topical cream) burn Sulfasalazine (azulfidine) ulcerative colitis, chrons disease allergic to salicylates AE- sulfa allergy, photosens, n&V, diarrhea, pancreatitis, agranulocytosis, anemia, crystalluria, convulsions, orangeyellow skin & urine, stevens-johnson syndrome- red papules on extremities, no pain or itching, treat w/ topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, emollients Implications- hydrate (crystalluria), stomatits, do not give with antacids; effects of anti-coagulants, oral glycemics, anti-seizure Tetracyclines- inhibit protein synthesis of bacteria, used in penicillinallergic pts. Tetracycline (achromycin) Demeclocycline (declomycin) oral Doxycycline (vibramycin) vein irritation Uses- clamydia,
mycoplasma, rickettsia, acne, h.pyloric, pleural effusions, PID pregnant, nursing, children<8 b/c teeth enamel AE- discoloration of teeth, retard fetal skeletal development, superinfections, bulging fontanelles in neonates, thrombocytopenia, exacerbate systems in lupus, gi upset, photosensitivity Implications- give w/food, dont give w/in 2hrs before or 3hrs after dairy or antacids Urinary tract agentsbacterialcidal, short term treatment, avoid catheterization, encourage fluids Nitrofurantoin (macrobid, macrodantin) Phenazopyridine (pyridium) not antiinfective, given for pain -lactum antibacterialsbacterialcidal, inhibit synthesis of cell walls Penicillin- from molds, staph & strep, resistance problems Uses- pharyngitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, syphilis, meningitism edocarditis, pneumococcal infections, staphyloccal, gonococcal AE- lethargy, hallucinations, depression, coma, convulsions, N&V, diarrhea, anemia,
bleeding time, bone marrow suppression, hyperkalemia/hypokale mia, taste alterations, hives, rash, most common- uticaria, pruitus, angioedema Basic penicillinspenicillin g procaine, penicillin g benthazine, penicillin g sodium, pen v potassium Penicillin- resistant penicillins- able to resist breakdown by penicillin destroying enzyme penicillinase- nafcillin, cloxzcillin, dicloxacillin, oxacillin Aminopenicillinspresence of free amino acids- amoxicillin, ampicillin, bacampicillin Extended-spectrum penicillins- ticarcillin, ampicillin, amoxicillinm, piperacillin, carbenicillin, timentin, zosyn Nursing implicationsPen v K- best absorbed on empty stomach 1hr before or 2 hr after, avoid acidic juice; Amoxicillin & carbenicillin- best absorbed if taken w/food Oral contraception reduced; false + urine glucose; very irritating to tissue and veins; blood dyscrasias; k & Na levels; probenecidslow renal excretions & serum levels Hypersensitivity reaction- do skin test 1st; epinephrine, oxygen, endotracheal intubation,
tracheostomy, hydrocortisone Cephalosporinsbroader than penicillin, less resistant, similar action, more active against gramUses- resp tract infections, bone & joint infections, septicemia, UTIs 1st generation: gram+; limited gramcefazolin cephapirin cephalexin cephradine 2nd generation: gram+, w/enhanced gramcefaclor cefuroxime cefamandole cefoxitin 3rd generation: more potent than 2&3 against gram-; less on gram + ceftazidime ceftazine ceftriaxone 4th generation: more resistant to -lactamse cefepime AE- similar to penicillin; GI upsets, bone marrow suppression Nursing implicationsasses for allergies, temp., blood count, bleeding & clotting time, renal studies, hepatic function studies, diarrhes, bloody stools, addominal pain, give with food or milk Carbapenems- cidal, broadest, preserved for most complicated infections (bone, joint, skin, pelvic), hospital
use only, not used 1st line drug therapy Imipenum-cilastatin (primaxin) Meropenem (merrem) Monobactam aztreonam (azactam)- against aerobic gram-; cidal, lysis of cell wall; e.coli, klebsiella, pseudomonas; preserves normal flora AE- drug-induced seizure activity Nursing implicationsallergies, neurologic assessment, asses hearing levels, GIdiarrhea N&V Macrolides- static, inhibit protein synthesis, treat upper and lower resp infections, skin, soft tissue, LEGIONNAIRES DIS. Erythromycin Azithromycin Clarithromycin AE- palpitaions, chest pain, HA, dizziness, vertigo, N&V, hapatoxicity, burn, diarrhea, stomatitis, flatulence, jaundice, rash, pruritis, thrombophlebitis, hearing loss, tinnitus Nursing implicationsAbsorption enhanced on an empty stomach, asses function, liver & renal function, interactions with WARFARIN (bleeding time), contraceptive failure Aminoglycosides- cidal,
potent, poor oral absorbtion, systemic infections, used w/othe antibiotics to create a synergistic effect, pseudomonas, e.coloi, proteus, klebsiella, serratia, suppress intestinal bacteria Gentamycin Kanamycin- sterile bowel Neomycin- sterile bowel decontaminate GI Tobramycin Amikacin Streptomycin CAUTION!! Cause fetal harm, deafness in children, serum drug levels monitored and adjusted, can be nephrotoxic & ototoxic, BUN & serum creatinine, hearing loss, dizziness, tinnitus, sense of fullness in ear, 8th cranial nerve Fluoroquinolonespotent, cidal, broad, alters dna of bacteria, safer than aminoglcosides, excellent oral absorption, Uses- UTIs, prostatitis, STDs, anthrax, resp. infections Ciprofloxacin Levofloxacin Gatifloxacin AE- superinfections, nausea, constipation, oral candisis, dysphagia, rash, pruritis, uticaria, photosensitiveity, fever, chills, blurred vision, tinnittus Nursing measures for
AMINO & FLUROaccurate weights, monitor BUN, serum creatinine, Peak & trough levels, hydration, photosensitivity, avoid antacids MISC. ANTIBIOTICSflagyl- HIV/aids Macrodantin- UTI ANTITUBERCULARTB effects lungs, growing ends of bones, brain, requires combination drug therapy MOA- inhibit protein & cell wall synthesis 1st line drugsINH- given prophylactic, can cause pyridoxine deficiency & liver toxicity; peripheral neuritis Ethambutol (Myambutol) Rifampin (rifadin)- red discoloration, contraceptives Streptomycinototoxicity, nephrotoxicity AE- oto & nephrotoxicity, GI disturbance, blood dyscrasias Nursing implicationsVit b6 to prevent neuropathy w/INH; hepatoxicity w/ INH & rifampin; discontinuation can reactivate TB; sputum cultures; infection control; noncompliance; give w/ food
ANTIFUNGALantimycotic- candidasis & histoplasmosis, immune system Amphotercin B- drug of choice AE- fever chills hypotension tachycardia malaise muscle pain joint pain anorexia N&V HA Give antipyretic, antihistamines, antiemetics, & pain med to AE ANTIPRASITICStropical climates, malaria, intestinal amebiasis, pneumocystosis, trichomoniasis, scabies, lice, hookworm, pinworm AE- hypotension, anemia, pruritis, anorexia, dizziness, HA, agranulocytosis, darkened urine, stomach cramps, fatigue, chills, night sweats, SOB, bronchspasms Atovaquone (mepron) Metronidazole (flagyl) Nursing implicationsmonitor urine output & liver function studies, admin w/food, avoid raw fish or under cooked meat, for STD avoid sex
You might also like
- A.1. Community-Acquired: Use Antibiotics JudiciouslyDocument33 pagesA.1. Community-Acquired: Use Antibiotics JudiciouslymaxgroovesNo ratings yet
- Antiinfectives Drug TableDocument5 pagesAntiinfectives Drug Tablecdp1587100% (3)
- Drug ChartDocument20 pagesDrug Chartstarobin100% (1)
- Basic Principles of PharmacologyDocument13 pagesBasic Principles of Pharmacologyemmanuel100% (1)
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocument3 pagesCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (2)
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001No ratings yet
- Commonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1Document9 pagesCommonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1annatw100% (10)
- Endocrine Drug ChartDocument1 pageEndocrine Drug ChartJessicaNo ratings yet
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocument5 pagesCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Pulmonary Drugs For Nursing PharmacologyDocument1 pagePulmonary Drugs For Nursing Pharmacologylhayes123475% (4)
- 100 Essential Drugs1Document8 pages100 Essential Drugs1Sudip DevadasNo ratings yet
- Family Names of DrugsDocument1 pageFamily Names of DrugsangelNo ratings yet
- MBBS Pharmacology PDFDocument20 pagesMBBS Pharmacology PDFAdeeb Aiman Rosli100% (6)
- Diabetes Mellitus Drug ChartDocument3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chartlui.stephanie1751100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Volume and Vascular Tone RegulationDocument2 pagesPharmacology of Volume and Vascular Tone RegulationgraycorypNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocument18 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Drugs XL ChartDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Drugs XL Chartcdp158767% (3)
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNo ratings yet
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 pagesNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract and Bladder DrugsDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract and Bladder Drugslhayes1234100% (2)
- Anticoagulants Drug TableDocument1 pageAnticoagulants Drug Tablecdp158767% (3)
- Respiratory Drugs XL Chart 3Document2 pagesRespiratory Drugs XL Chart 3cdp1587100% (1)
- Diuretic Drugs For Nursing PharmacologyDocument1 pageDiuretic Drugs For Nursing Pharmacologylhayes1234100% (7)
- Anticoagulants: (Parenteral)Document38 pagesAnticoagulants: (Parenteral)susan2johnson-501300No ratings yet
- Medications and assessmentsDocument225 pagesMedications and assessmentsJessica 'Baker' IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of ActionDocument3 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of Actionyanks1120No ratings yet
- Pharm Drug Outline AdrDocument1 pagePharm Drug Outline AdrCess Lagera YbanezNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs Mechanisms Effects Uses Side Effects /TITLEDocument3 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs Mechanisms Effects Uses Side Effects /TITLEdoktorcoopNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drug ChartDocument1 pageCardiovascular Drug Chartanum786110100% (1)
- Git Drugs TablesDocument3 pagesGit Drugs TablesSulochan Ssplendid Splinterr Lohani100% (1)
- Quiz With AnswersDocument8 pagesQuiz With Answersval284yNo ratings yet
- NSAIDS and SteroidsDocument2 pagesNSAIDS and Steroidsmed testNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY Anti Microbial DrugsDocument17 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Anti Microbial DrugsLeilani Sablan100% (2)
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDocument12 pagesCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxNo ratings yet
- Muscarinic and Anti-MuscarinicsDocument3 pagesMuscarinic and Anti-MuscarinicsElleJBNo ratings yet
- Common infections and recommended antibioticsDocument3 pagesCommon infections and recommended antibioticsNicole BerryNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (46)
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocument28 pagesA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Anti-Arrhythmic Agents For Pharmacy PDFDocument41 pagesAnti-Arrhythmic Agents For Pharmacy PDFKelvinTMaikanaNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolytes ImbalancesPeter John Ruiz100% (1)
- Pharmacology Test 1Document39 pagesPharmacology Test 1Niki BolinNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of ActionDocument13 pagesGeneric Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of Actionangel3424No ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- Sample - Drug Index DatabaseDocument12 pagesSample - Drug Index DatabaseEubert John VenturinaNo ratings yet
- 4 Beta-lactam antibiotics overviewDocument4 pages4 Beta-lactam antibiotics overviewVladimir GurjanovNo ratings yet
- ANTIBIOTICS CLASS MECHANISMS USES SIDE EFFECTSDocument4 pagesANTIBIOTICS CLASS MECHANISMS USES SIDE EFFECTSJoão Paulo MaresNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CaseDocument9 pagesDrug Study - CaseMay EvelynNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaAngelica Tresha RaonNo ratings yet
- Augmentin antibiotic penicillin combinationDocument3 pagesAugmentin antibiotic penicillin combinationArnulfo ArmamentoNo ratings yet
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocument19 pagesAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study... MyomaDocument12 pagesDrug Study... MyomaChristine Joy Bautista- CastroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document9 pagesDrug Study 2Justin PasaronNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OssamDocument3 pagesDrug Study OssamCharmaine IdologNo ratings yet
- Egy 1.1.2 Api Augmentin 1 GM Tabs Ipi11 1Document3 pagesEgy 1.1.2 Api Augmentin 1 GM Tabs Ipi11 1magdNo ratings yet
- Drug Tab PediaDocument9 pagesDrug Tab PediaDave Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Antineoplastic DrugsDocument5 pagesAntineoplastic DrugsharleyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Pedia)Document7 pagesDrug Study (Pedia)Caurrine Monsalud100% (1)
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsVal Ian Palmes SumampongNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia/Mood Disorders/Grief & Loss: MENTAL HEALTH NURSINGDocument19 pagesSchizophrenia/Mood Disorders/Grief & Loss: MENTAL HEALTH NURSINGJessica100% (1)
- Endocrine Drug ChartDocument1 pageEndocrine Drug ChartJessicaNo ratings yet
- Anti Viral Drug ChartDocument1 pageAnti Viral Drug ChartJessicaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular IV and VDocument6 pagesCardiovascular IV and VJessicaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal DisordersDocument11 pagesIntestinal DisordersJessica0% (1)
- Cardiovascular IV and VDocument6 pagesCardiovascular IV and VJessicaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular III Heart FailureDocument2 pagesCardiovascular III Heart FailureJessicaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular II HypertensionDocument2 pagesCardiovascular II HypertensionJessicaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsJessica100% (1)
- COVID - National Resources - DelhiDocument8 pagesCOVID - National Resources - DelhiDinesh GoelNo ratings yet
- CANCER - CLASSIFIED CANCER ANSWERS BY Marc S. Micozzi, M.D., PH.D PDFDocument16 pagesCANCER - CLASSIFIED CANCER ANSWERS BY Marc S. Micozzi, M.D., PH.D PDFPierre Le Grande100% (1)
- CrackTheNac 8 Case For The NAC OSCEDocument19 pagesCrackTheNac 8 Case For The NAC OSCEEmad Mergan100% (6)
- CIS 4 SOAP NoteDocument3 pagesCIS 4 SOAP NoteMaya LaPradeNo ratings yet
- Alexander TechniqueDocument2 pagesAlexander TechniqueathenaNo ratings yet
- Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder: Florian Daniel Zepf, Caroline Sarah Biskup, Martin Holtmann, & Kevin RunionsDocument17 pagesDisruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder: Florian Daniel Zepf, Caroline Sarah Biskup, Martin Holtmann, & Kevin RunionsPtrc Lbr LpNo ratings yet
- DNHE-1 Dec 2013Document8 pagesDNHE-1 Dec 2013Nikita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gcse Sets: Exercise 1 - Constructing Venn DiagramsDocument5 pagesGcse Sets: Exercise 1 - Constructing Venn DiagramsSwati 06No ratings yet
- Haematology MedicineDocument25 pagesHaematology MedicineSami Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Eu Yan Sang 9-29-09Document19 pagesEu Yan Sang 9-29-09putsadinNo ratings yet
- Homeo TipsDocument124 pagesHomeo TipsAditya uniyal100% (2)
- SOTAH CourseGuideDocument198 pagesSOTAH CourseGuideDee100% (1)
- Rizona Ourt of PpealsDocument6 pagesRizona Ourt of PpealsScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- How To Reverse Type 2 DiabetesDocument20 pagesHow To Reverse Type 2 Diabetesjrobinhill100% (1)
- Kailash HospitalDocument8 pagesKailash HospitalPiyush Choudhary100% (1)
- Capstone 1-3 For DefenseDocument27 pagesCapstone 1-3 For DefenseRussel AloceljaNo ratings yet
- DBT in BPD Case PresentationDocument105 pagesDBT in BPD Case PresentationPrasanta Roy100% (1)
- GMC Tomorrows DoctorsDocument22 pagesGMC Tomorrows DoctorsLuke100% (1)
- Portfolio Template for Diploma in Occupational MedicineDocument11 pagesPortfolio Template for Diploma in Occupational MedicineChengyuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- GRASP Exercise Manual Level 1Document115 pagesGRASP Exercise Manual Level 1Amit ZalaNo ratings yet
- 77items Instantly Vanish Store Shelves in Panic Prepare Crisis Not WaitDocument67 pages77items Instantly Vanish Store Shelves in Panic Prepare Crisis Not WaitTaranisaNo ratings yet
- Eric Cressey - 1 - Simplifying-Shoulder-HealthDocument17 pagesEric Cressey - 1 - Simplifying-Shoulder-HealthMarcelo Da Silva100% (3)
- ZZZZZDocument36 pagesZZZZZwuriNo ratings yet
- Topic SentencesDocument9 pagesTopic Sentencesmkanwars100% (1)
- Progressive Primary Tuberculosis in a 15-Month Old Male InfantDocument1 pageProgressive Primary Tuberculosis in a 15-Month Old Male InfantRenierose AgujetasNo ratings yet
- Source Analysis TaskDocument8 pagesSource Analysis Taskapi-299392638No ratings yet
- QBit 5 User Manual V1 0 EN 201610251522Document188 pagesQBit 5 User Manual V1 0 EN 201610251522pedropc50% (2)
- Anacyclus Pyrethrum - Scientific Review On Usage, Dosage, Side EffectsDocument9 pagesAnacyclus Pyrethrum - Scientific Review On Usage, Dosage, Side EffectsdrkameshNo ratings yet
- CD 3200 Service Manual PDFDocument334 pagesCD 3200 Service Manual PDFPhan QuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05: Selecting The Ventilator and The ModeDocument13 pagesChapter 05: Selecting The Ventilator and The Modespace100% (1)