Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classification of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions
Uploaded by
Pauline Mariz JavierCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classification of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions
Uploaded by
Pauline Mariz JavierCopyright:
Available Formats
Classification of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions
I. Gingival Diseases A. Plaque-induced gingivitis 1. Gingivitis associated with plaque only a. Without local contributing factors b. With local contributing factors 2. Gingival diseases modified with systemic factors a. Associated with endocrine system: 1. Puberty-associated gingivitis 2. Menstrual cycle-associated gingivitis 3. Pregnancy-associated a. Gingivitis b. Pyogenic granuloma 4. Diabetes mellitus-associated gingivitis a. Associated with blood dyscrasias 1. Leukemia-associated gingivitis 2. Other 3. Gingival diseases modified by medications a. Drug-influenced gingival diseases 1. Drug-influenced gingival enlargements 2. Drug-influenced gingivitis a. Oral contraceptive-influenced gingivitis b. Other 4. Gingival diseases modified by malnutrition a. Ascorbic acid gingivitis b. Other B. Non-Plaque-Induced Gingival Lesions 1. Gingival diseases of specific bacterial origin a. Neisseria gonorrhea b. Treponema pallidum c. Streptococcal species d. Other 2. Gingival diseases of viral origin a. Herpes virus infection 1. Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis 2. Recurrent oral herpes 3. Varicella zoster
b. Other 3. Gingival diseases of fungal origin a. Candida-species infections: Generalized gingival candidosis b. Linear gingival erythema c. Histoplasmosis d. Other 4. Gingival lesions of genetic origin a. Hereditary gingival firbromatosis b. Other 5. Gingival manifestations of systemic conditions a. Mucocutaneous lesions 1. Lichen planus 2. Pemphigoid 3. Pemphigus vulgaris 4. Erythema multiforme 5. Lupus erythematous 6. Drug induced 7. Other b. Allergic reactions 1. Dental restorative materials a. Mercury b. Nickel c. Acrylic d. Other 2. Reactions attributable to: a. Toothpastes or dentrifices b. Mouthrinses or mouthwashes c. Chewing gum additives d. Foods and additives e. Other 6. Traumatic lesions (factitious, iatrogenic, or accidental) a. Chemical injury b. Physical injury c. Thermal injury 7. Foreign body reactions 8. Not otherwise specified
II. Chronic Periodontitis a. Localized b. Generalized III. Aggressive Periodontitis a. Localized b. Generalized IV. Periodontitis as a Manifestation of systemic diseases a. Hematologic disorders 1. Acquired neutropenia 2. Leukemia 3. Others b. Genetic disorders 1. Familial and cyclic neutropenia 2. Down syndrome 3. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndromes 4. Papilion-Lefvre syndrome 5. Chediak-Higashi syndrome 6. Histiocytosis syndrome 7. Glycogen storage disease 8. Infantile genetic agranulocytosis 9. Cohen syndrome 10. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (Types IV and VIII AD) 11. Hypophosphatasia 12. Other c. Not otherwise specified V. Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases a. Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis b. Necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis VI. Abscesses of the periodontium a. Gingival abscess b. Periodontal abscess VII. Periodontitis associated with endodontic lesions a. Endodontic-periodontal lesion
b. Periodontal-endodontic lesion VIII. Developmental or acquired deformities and conditions a. Localized tooth-related factors that predispose to plaque-induced gingival diseases or periodontitis b. Mucogingival deformities and conditions around teeth c. Mucogingival deformities and conditions on edentulous ridges d. Occlusal trauma
I. Gingival Disease - describes the events that begin with bacterial growth in your mouth and may end -- if not properly treated -- with tooth loss due to destruction of the tissue that surrounds your teeth.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- General PsychologyDocument7 pagesGeneral PsychologyPauline Mariz JavierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: What Is Psychology?Document7 pagesChapter 1: What Is Psychology?Pauline Mariz JavierNo ratings yet
- The Function of SleepDocument8 pagesThe Function of SleepPauline Mariz JavierNo ratings yet
- Route of Drug AdminDocument19 pagesRoute of Drug AdminPauline Mariz JavierNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- What Is Aerobic Exercise?Document27 pagesWhat Is Aerobic Exercise?Zedy GullesNo ratings yet
- High Resolution Computed Tomography of The Lungs - UpToDateDocument83 pagesHigh Resolution Computed Tomography of The Lungs - UpToDatejjjkkNo ratings yet
- ComFlor 80 Load Span Tables PDFDocument4 pagesComFlor 80 Load Span Tables PDFAkhil VNNo ratings yet
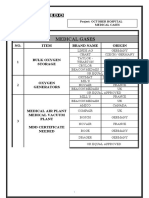
- Medical Gases: NO. Item Brand Name OriginDocument4 pagesMedical Gases: NO. Item Brand Name OriginMahmoud AnwerNo ratings yet
- LFAMS Fee Structure OCT'2013Document7 pagesLFAMS Fee Structure OCT'2013Prince SharmaNo ratings yet
- Recipe Book: Yule Logs 2020Document28 pagesRecipe Book: Yule Logs 2020Cwt Chan100% (1)
- Notice: Environmental Statements Availability, Etc.: Syngenta Crop Protection, Inc., Et Al.Document8 pagesNotice: Environmental Statements Availability, Etc.: Syngenta Crop Protection, Inc., Et Al.Justia.comNo ratings yet
- AIR Modeller 78 2018Document68 pagesAIR Modeller 78 2018StefanoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Soup ProjectDocument98 pagesComprehensive Soup ProjectSachin Soni63% (8)
- WAUZZZ8K0BA159120Document10 pagesWAUZZZ8K0BA159120Vedad VedaddNo ratings yet
- Electrical Rooms Fire FightingDocument2 pagesElectrical Rooms Fire Fightingashraf saidNo ratings yet
- Banco de Oro (Bdo) : Corporate ProfileDocument1 pageBanco de Oro (Bdo) : Corporate ProfileGwen CaldonaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Worksheet: Name PeriodDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure Worksheet: Name Periodapi-496534295100% (1)
- Helicobacter Pylori InfectionDocument18 pagesHelicobacter Pylori InfectionPMNo ratings yet
- Bandura Social Cognitive TheoryDocument93 pagesBandura Social Cognitive TheoryВикторияNo ratings yet
- Answers To Competency Assessment SectionDocument16 pagesAnswers To Competency Assessment Sectionapi-209542414100% (1)
- Cardiac AmyloidosisDocument3 pagesCardiac AmyloidosisPrasad SrbNo ratings yet
- Web Aggregator SyllabusDocument5 pagesWeb Aggregator Syllabussam franklinNo ratings yet
- Peoria County Booking Sheet 03/01/15Document8 pagesPeoria County Booking Sheet 03/01/15Journal Star police documentsNo ratings yet
- Pre-Feasibility Report: at Plot No. 15/B-3, Jigani Industrial Area Anekal Taluk, Bangalore South District Karnataka byDocument41 pagesPre-Feasibility Report: at Plot No. 15/B-3, Jigani Industrial Area Anekal Taluk, Bangalore South District Karnataka by12mchc07No ratings yet
- SM Electrical Guidelines: General Notes:: Site HereDocument1 pageSM Electrical Guidelines: General Notes:: Site HereNathaniel DreuNo ratings yet
- Ball Bearing Units Stainless SeriesDocument5 pagesBall Bearing Units Stainless SeriesRicardo KharisNo ratings yet
- Gec 014 Prelim ExaminationDocument2 pagesGec 014 Prelim ExaminationcykablyatNo ratings yet
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical Handbook: February 2022Document5 pagesSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical Handbook: February 2022Juan Gil RocaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Security Policy TemplateDocument4 pagesCorporate Security Policy TemplateCoronaNo ratings yet
- Ir33+ Range: ... Continuity, Innovation and DesignDocument4 pagesIr33+ Range: ... Continuity, Innovation and DesignbenNo ratings yet
- 1stweek Intro Quanti Vs QualiDocument18 pages1stweek Intro Quanti Vs QualiHael LeighNo ratings yet
- Polymer LedDocument14 pagesPolymer LedNaveenNo ratings yet
- School Administration and Supervision MAED 605Document24 pagesSchool Administration and Supervision MAED 605Jaynie Ann TapdasanNo ratings yet
- Heat Shrink CoatingDocument5 pagesHeat Shrink CoatingMekhmanNo ratings yet