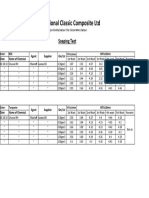
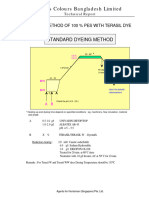
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dyeing Chemistry
Uploaded by
Khandaker Sakib FarhadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dyeing Chemistry
Uploaded by
Khandaker Sakib FarhadCopyright:
Available Formats
Textile Chemicals: Such types of organic or inorganic substances which influence the physical or chemical change of a textile material
are known as Textile chemicals. Before knowing about wet processing technology it is much essential to know about the textile chemicals and their uses. 1. Water (H2O): The material which is mostly used in a textile industry is water.
2. Wetting Agents: The textile chemical which increases the wetting property of textile material or fiber by reducing the surface tension of the liquor of the dye bath is called Wetting Agent. For example; i. Lissapol. ii. Primasol NF. iii. Rucowet VL.
3. Detergents: The chemical substances which removes various impurities such as dirt, dust, oil and other impurities present in the textile material, is called Detergent. For example; i. Lissapol. ii. Soap. iii. Kerolin Jet-B. iv. Washing Detergents.
4. Emulsifiers: The chemical substances which help to mix water and oily chemicals are called Emulsifiers. For example; i. Emulsion. ii. Glycosin.
5. Sizing components: The chemical substances which remove the protruding fibers from the textile materials and increases the strength of the textile material is called sizing chemicals. For example; i. Enzyme.
6. Leveling Agents: The chemical substances which ensures the even dyeing of the fabric throughout the fabric, is called Leveling Agents. For example; i. Lyo-col.
7. Dye Fixing Agents: The chemical substances which help the fixation of dyes on the textile material or the fabric are called Dye Fixing Agents. For example; i. Fixanal. ii. Tartarematic.
8. Carriers: Carriers are one kind of organic compounds or substantive swelling agents which help the 0 swelling of hydrophobic polyester fibers at relatively low temperature such as; 90 C and increases the dye uptake from the dye bath or print paste. After completion of the dyeing the carriers eventually evaporates completely. The carriers are mostly used for disperse dyes. For example; i. Diphenyl. ii. Carrier DCT.
9. Oxidizing Agents: The chemical substances which add oxygen or free hydrogen particles from the textile material are called Oxidizing Agents. For example; i. O3. ii. H2O2.
10. Sodium Alginate: The chemical substance which thickens the dye solution of reactive dyes but does not react with the dyes or use up the dyes is called Alginate or Algin. It comes in a number of variations that have different properties. Such as; i. Low Viscosity Types: Appropriate for reducing migration of wet dye solution. Mainly used for making dye solution for woven continuous dyeing. High Viscosity Types: Appropriate for making printing paste.
ii.
11. Acid: The chemical substance which has the ability to reduce the pH to less than 7 of a solution and ionize in a solution is called Acid. All the acids are represented by HA groups where + H ions combine water molecules to make an ion called Hydronium. There are many types of acid which may vary from stronger to weaker acids. It is necessary to add water while making an acid solution as some acids are extremely volatile. For example; i. Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) is a strong Acid. ii. iii. Acetic Acid (CH3COOH) is a weak Acid. Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) is a strong Acid.
12. Oxidizing Agent: The chemical substance which contain certain atoms that has the ability to extract electron ion from the molecules of other substances is called oxidizing agent. For example; i. Sodium Hypo Chlorate (NaClO). ii. Bromic Acid (HBrO2). iii. Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2).
13. Reducing Agent: The chemical substances which contain certain atoms that has the ability to provide electron ion to the molecules of other substances is called reducing agent. It has the ability to reduce other substances chemically and in the process reducing agent itself is oxidized. For example; i. Sodium Hydro Sulfite or Hydroz (Na2S2O4). ii. Rongolite C (Sodium Formaldehyde Sulfoxylate). iii. Thiourea Dioxide. iv. Sodium Bisulfite. Properties of Reducing Agent: a. Reducing Agents are often used in discharge and stripping processes. b. Reducing Agents are used for converting insoluble vat and sulfur dyes into soluble form by reduction process. c. Reducing Agent is also used for removing disperse dyes from the surface of cotton fiber of a CVC (Chief Value Cotton) fabric or PC (Polyester-Cotton) fabric. d. Disperse dyes attached to the surface of the cotton fiber may cause wash fastness problems and yet are very difficult to remove by only washing, so reducing agent is used. e. Reduction cleaning process does no harm to the dyes remaining inside the Polyester fiber.
14. Anti-Migrating Agent: The chemical substance which is used in dyes or pigments to prevent the undesired movement or spreading of the wet dye on the fabric surface is called Anti-Migrating Agent. These Anti-Migrating Agents are mostly used in continuous dyeing processes or in printing processes to thicken the dye solution and ensure uniform dyeing throughout the fabric. For example; i. Primasol V. ii. Siligen FA. iii. Sodium Alginate. iv. Thermocol MP. Properties of Anti-Migrating Agents: a. Anti-Migrating Agents are used in continuous dyeing processes or in printing processes as both dye thickener and undesired dye migration preventer. b. Anti-Migrating Agents are mostly used for preventing undesired migration of wet dyes on the surface of the fabric. c. Anti-Migrating Agents are used for preventing uneven shading of dyes across the width of the fabric. d. Anti-Migrating Agents are used in dye pastes of printing pastes so that the printed pattern will retain its sharply defined edges. 15. Binder: The chemical substance which is used for attaching the pigment colour on both side of the fabric surface is called Pigment Binder. For Example; i. Helizarin Binder CFF. ii. ECO Size A. iii. EVO Top U-50. Properties of Binders: a. Binders are normally colourless. b. Binders are mostly in glue form which holds the pigment colour in place. c. Most of the binders used in textile paints are acrylic polymers.
You might also like
- Reactive Dyes EditedDocument6 pagesReactive Dyes EditedusmanazeemNo ratings yet
- Hs Code of Clariant ProductsDocument2 pagesHs Code of Clariant ProductsSaif Rahman0% (1)
- Product SurveyDocument26 pagesProduct SurveyAdnan PervaizNo ratings yet
- Migration Inhibitors Effect On Fabric PropertiesDocument61 pagesMigration Inhibitors Effect On Fabric PropertiesAsad Jamil Rana100% (6)
- Reports On Soaping Agent& Fixing AgentDocument59 pagesReports On Soaping Agent& Fixing AgentRashed Hasan100% (4)
- Dekol Disperse SNS MSDSDocument11 pagesDekol Disperse SNS MSDSMuhammad Aasim HassanNo ratings yet
- Resil GarmentsbrochureDocument16 pagesResil GarmentsbrochureSupriya NandaNo ratings yet
- D.K.T.E.S Textile & Engineering Institute, Ichalkaranji-416115 (M.H), India, February 1, 2014Document10 pagesD.K.T.E.S Textile & Engineering Institute, Ichalkaranji-416115 (M.H), India, February 1, 2014shreeket3953No ratings yet
- Isostearic Acid EstersDocument21 pagesIsostearic Acid EstersMilena BaljakNo ratings yet
- Intro, Classification & Functions of Auxiliaries .PPTX Lecture 123Document16 pagesIntro, Classification & Functions of Auxiliaries .PPTX Lecture 123nida0% (1)
- Precaution Manual For Colour Blooming Auxiliaries Applications On Textiles.Document12 pagesPrecaution Manual For Colour Blooming Auxiliaries Applications On Textiles.L.N.CHEMICAL INDUSTRY100% (1)
- Antistain RDL 2 - SDSDocument10 pagesAntistain RDL 2 - SDSchoton_iii0% (1)
- Dyeing CalculationDocument4 pagesDyeing CalculationIftakharul IslamNo ratings yet
- 1 Huntsman Textile Effects Product Innovation by MR V MuthuswamyDocument36 pages1 Huntsman Textile Effects Product Innovation by MR V Muthuswamy郭哲宏100% (1)
- Albafix ECO MsdsDocument5 pagesAlbafix ECO MsdsRafiqul AlamNo ratings yet
- Textile Auxiliaries: Zschimmer & SchwarzDocument54 pagesTextile Auxiliaries: Zschimmer & SchwarzRezoanul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Archroma - Passion For Hometextiles DigitalDocument8 pagesArchroma - Passion For Hometextiles DigitalNguyễn Huy CườngNo ratings yet
- Optavon Mex: Highly Effective Complexing Agent of Versatile Application During All Pretreatment ProcessesDocument2 pagesOptavon Mex: Highly Effective Complexing Agent of Versatile Application During All Pretreatment ProcessesRezoanul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Aeea TDS PDFDocument2 pagesAeea TDS PDFMannar1No ratings yet
- New Dimensions of SoftnessDocument9 pagesNew Dimensions of SoftnessEugene PaiNo ratings yet
- Garment Product CatalogueDocument24 pagesGarment Product CatalogueM.MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Used in TextileDocument24 pagesChemical Used in TextileFeroz Alam0% (1)
- CHT Textile Auxiliaries Core RangeDocument72 pagesCHT Textile Auxiliaries Core RangeDidar YazhanovNo ratings yet
- RAN Chemicals - Textile - Finishing - Ready To Use - Silicone - Hydrophilic (For Terry Towel) - Finishing Softener For Textile - RSF-AT-40-SDocument3 pagesRAN Chemicals - Textile - Finishing - Ready To Use - Silicone - Hydrophilic (For Terry Towel) - Finishing Softener For Textile - RSF-AT-40-ScrplzNo ratings yet
- Brochure ZytexDocument12 pagesBrochure ZytexKinjal PatelNo ratings yet
- DyStar Product Selection - CA RSL - Version Apr 2013 - 3sep13 - Final PDFDocument39 pagesDyStar Product Selection - CA RSL - Version Apr 2013 - 3sep13 - Final PDFAzizNo ratings yet
- DyStar Product Selection Guidance HM Chemical Restrictions May 082014Document57 pagesDyStar Product Selection Guidance HM Chemical Restrictions May 082014rajasajjad100% (1)
- Sapamine SPL New TDSDocument5 pagesSapamine SPL New TDSraju_hosssenNo ratings yet
- Leatex-Shunsol RHDocument1 pageLeatex-Shunsol RHDyeing DyeingNo ratings yet
- Improve Textile Dye Fastness with Non-Formaldehyde Fixing AgentsDocument3 pagesImprove Textile Dye Fastness with Non-Formaldehyde Fixing AgentsMaggieWoodsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Softeners for TextilesDocument30 pagesChemical Softeners for Textileshammadfarrukh644100% (2)
- Sandoclean LFDI LiqDocument2 pagesSandoclean LFDI Liqriqpwri1120% (1)
- Lnci Technical Information: Altranol-NoviDocument4 pagesLnci Technical Information: Altranol-Novithe griffendorsNo ratings yet
- Project Final File 000Document102 pagesProject Final File 000usmanazeemNo ratings yet
- Albatex DBC Protective Colloid: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesAlbatex DBC Protective Colloid: Technical Data SheetsaskoNo ratings yet
- GG Organics Company ProfileDocument7 pagesGG Organics Company ProfileSeenivasan Kannan MbaNo ratings yet
- Pigment Printing of CottonDocument14 pagesPigment Printing of Cottonrbchavan100% (1)
- Everzol Dyes StructuresDocument9 pagesEverzol Dyes StructuresNestor Mauricio Florian RamirezNo ratings yet
- Arc RomaDocument31 pagesArc RomaMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Zyperse DLS: Dispersing, Leveling and Soaping AgentDocument4 pagesZyperse DLS: Dispersing, Leveling and Soaping AgentVinod ShelkeNo ratings yet
- Albaflow: UNI Penetration AccelerantDocument5 pagesAlbaflow: UNI Penetration AccelerantsaskoNo ratings yet
- Reactive SoftenerDocument5 pagesReactive Softenerbosontomax100% (1)
- Pad BatchDocument6 pagesPad BatchBabaNo ratings yet
- Softner Compatibility TestDocument8 pagesSoftner Compatibility TestDyeing DyeingNo ratings yet
- Test For The Suitability of Thickener in The Print Paste Formulation and Other ConcepttestDocument21 pagesTest For The Suitability of Thickener in The Print Paste Formulation and Other ConcepttestGaurav DhawanNo ratings yet
- Colour and Textile Chemistry-A Lucky Career Choice: Aatcc Review April 2009Document32 pagesColour and Textile Chemistry-A Lucky Career Choice: Aatcc Review April 2009Neva BernadetteNo ratings yet
- Clariant NewDyestuffWorldDocument12 pagesClariant NewDyestuffWorldNaeem Shehzad50% (2)
- Albaflow: JET Penetration AccelerantDocument5 pagesAlbaflow: JET Penetration AccelerantGokhan RamiNo ratings yet
- Silicone Compatibility TestDocument2 pagesSilicone Compatibility TestDyeing DyeingNo ratings yet
- f3c7a08543f11dc50c88dc7a76212879Document3 pagesf3c7a08543f11dc50c88dc7a76212879孙兴峰No ratings yet
- Z&s PADocument8 pagesZ&s PAguven44No ratings yet
- Lyoprint DT-CS PDFDocument5 pagesLyoprint DT-CS PDFLambo SunNo ratings yet
- Dispersol PL - TDSDocument1 pageDispersol PL - TDSAshis PalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Used in TextileDocument31 pagesChemical Used in TextileMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledbklove49No ratings yet
- Auxalaries Chemicals in Wet ProcessDocument31 pagesAuxalaries Chemicals in Wet ProcessAyman SebaeiNo ratings yet
- Detergent 1Document4 pagesDetergent 1Muhammad Zubair SharifNo ratings yet
- Surfactant:: History of DetergentDocument9 pagesSurfactant:: History of DetergentSharaf NourNo ratings yet
- True Timeline of World History-_compressedDocument7 pagesTrue Timeline of World History-_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- The Hidden One or the Antichrist_compressedDocument3 pagesThe Hidden One or the Antichrist_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- The Gameplay Called War_compressedDocument1 pageThe Gameplay Called War_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- The Gameplay of Targeted Human Beings_compressedDocument2 pagesThe Gameplay of Targeted Human Beings_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Is Albert Einstein a Genius or a Fake_compressedDocument2 pagesIs Albert Einstein a Genius or a Fake_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- What We Sell in the Name of Women Power_compressedDocument1 pageWhat We Sell in the Name of Women Power_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- The Image of AI Based Interrogation in the Name of Avoiding Self Abuse_compressedDocument2 pagesThe Image of AI Based Interrogation in the Name of Avoiding Self Abuse_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- COVID Kitchens of Hell_compressedDocument2 pagesCOVID Kitchens of Hell_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- The Gameplay Called Moon Voyage_compressedDocument2 pagesThe Gameplay Called Moon Voyage_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- The Divide and Conquer Policy_compressedDocument1 pageThe Divide and Conquer Policy_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Economical Take Over by the International Organizations_compressedDocument2 pagesEconomical Take Over by the International Organizations_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Proof of Allah Being the Almighty_compressedDocument1 pageProof of Allah Being the Almighty_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- PVC Coating Uses and PropertiesDocument18 pagesPVC Coating Uses and PropertiesAhmed SaidNo ratings yet
- Corruption Done by New Industrialists to Turn Their Carrier of Servitude to Entrepreneurship_compressedDocument2 pagesCorruption Done by New Industrialists to Turn Their Carrier of Servitude to Entrepreneurship_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- List of Unfortunate Countries of the World and the Conspiracy Surrounding Those_compressedDocument8 pagesList of Unfortunate Countries of the World and the Conspiracy Surrounding Those_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Tender Documents For Freight Forwarding, Clearing & Transportation Agent Dated 23.01.14.Document27 pagesTender Documents For Freight Forwarding, Clearing & Transportation Agent Dated 23.01.14.Khandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Christians an Entire Religion Turned Into a Joke_compressedDocument2 pagesChristians an Entire Religion Turned Into a Joke_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Approach Towards Developing Education Program_compressedDocument2 pagesApproach Towards Developing Education Program_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Consumption For FabricDocument5 pagesConsumption For Fabrickimtienthao_26289No ratings yet
- Knitting CalculationsDocument10 pagesKnitting CalculationsWaqas Ashraf100% (3)
- Effect of Tannic Acid and Metallic Mordants On The DyeingDocument5 pagesEffect of Tannic Acid and Metallic Mordants On The DyeingHëss EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Battle Strategy of Israel and the Possible Outcome_compressedDocument2 pagesBattle Strategy of Israel and the Possible Outcome_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Terasil STD MethodDocument1 pageTerasil STD MethodKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Calculation in Weft KnittingDocument13 pagesCalculation in Weft KnittingFazley BD80% (10)
- Terasil STD MethodDocument1 pageTerasil STD MethodKhandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- NH Desn 1Document96 pagesNH Desn 1Khandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- Research & Development in TextileDocument40 pagesResearch & Development in Textileapi-19978170100% (2)
- Market Structures ExplainedDocument18 pagesMarket Structures ExplainedAmii RahNo ratings yet
- Tender Documents For Freight Forwarding, Clearing & Transportation Agent Dated 23.01.14.Document27 pagesTender Documents For Freight Forwarding, Clearing & Transportation Agent Dated 23.01.14.Khandaker Sakib FarhadNo ratings yet
- I M Com QT Final On16march2016Document166 pagesI M Com QT Final On16march2016Khandaker Sakib Farhad0% (1)
- Retracted: Electrochemical Degradation of Levafix CA Reactive Dyes in Textile Dyeing Wastewater Using Iron ElectrodesDocument9 pagesRetracted: Electrochemical Degradation of Levafix CA Reactive Dyes in Textile Dyeing Wastewater Using Iron Electrodesapi-3828788No ratings yet
- Saree - A PoemDocument4 pagesSaree - A PoemShipra AlamNo ratings yet
- Textile Internship Insights: Alok IndustriesDocument37 pagesTextile Internship Insights: Alok IndustriesHitesh Kumar100% (1)
- Rifacophor Byb Conc. 400%: Special PropertiesDocument4 pagesRifacophor Byb Conc. 400%: Special Propertieshamidrahmany3657No ratings yet
- Digital Online Fabric Costing Book: Chapter # 1 Fabric Width (Greige & Finished)Document11 pagesDigital Online Fabric Costing Book: Chapter # 1 Fabric Width (Greige & Finished)Shabbir Muhammad50% (2)
- Document-Is Any Material Which Contains Marks, Symbols or Signs, Either Visible, PartiallyDocument16 pagesDocument-Is Any Material Which Contains Marks, Symbols or Signs, Either Visible, PartiallyBimboy CuenoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Scheme and Syllabus of II Year BFAD (Effective From 2017-18) PDFDocument42 pagesEvaluation Scheme and Syllabus of II Year BFAD (Effective From 2017-18) PDFAvnishNo ratings yet
- Natural Dyes & Colorants GuideDocument2 pagesNatural Dyes & Colorants GuideHomer RendonNo ratings yet
- Production of Indigo Dye from PlantsDocument47 pagesProduction of Indigo Dye from PlantsDewan Ajuad Hossain RifatNo ratings yet
- Clariant Brochure Sales Range Printing Ink Paints Plastics Industries 201503 EN - Abcdpdf - PDF - para - ExcelDocument202 pagesClariant Brochure Sales Range Printing Ink Paints Plastics Industries 201503 EN - Abcdpdf - PDF - para - ExcelJari Rene BrazNo ratings yet
- Hair and Fiber AnalysisDocument11 pagesHair and Fiber AnalysisJames Van Arquero NaronNo ratings yet
- COC Level VDocument12 pagesCOC Level VeyasuNo ratings yet
- Wet Processing I Water PDFDocument7 pagesWet Processing I Water PDFkabir_ce06038No ratings yet
- Dyes Classified by IntermediatesDocument629 pagesDyes Classified by IntermediatesUlises Saviñón50% (2)
- Proficiency TestDocument9 pagesProficiency TestbuntheounphokNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Degradation of Textile Dye Bath Effluent Using Halomonas SPDocument5 pagesAnaerobic Degradation of Textile Dye Bath Effluent Using Halomonas SPFlor GonzalezNo ratings yet
- JBES Vol7No1 p501 525Document26 pagesJBES Vol7No1 p501 525Kirti KachhapNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Inkjet Inks For Digital Textile Printing - ReviewDocument19 pagesThe Chemistry of Inkjet Inks For Digital Textile Printing - ReviewCarlos HormigoniNo ratings yet
- Green Synthesis of Zerovalent Copper Nanoparticles For Efficient Reduction of Toxic Azo Dyes Congo Red and Methyl OrangeDocument9 pagesGreen Synthesis of Zerovalent Copper Nanoparticles For Efficient Reduction of Toxic Azo Dyes Congo Red and Methyl OrangeMar ClassicNo ratings yet
- TEGEWA Nomenclature of Textile AuxiliariesDocument3 pagesTEGEWA Nomenclature of Textile AuxiliariesKushagradhi DebnathNo ratings yet
- Dye Removal ProposalDocument15 pagesDye Removal ProposalnorsiahNo ratings yet
- Dyeing Fabric DissertationDocument33 pagesDyeing Fabric DissertationBathrinath 007No ratings yet
- Synthetic Dyeing of Indigenous FibersDocument22 pagesSynthetic Dyeing of Indigenous FiberskleomarloNo ratings yet
- Kayacion Cf-Comw Dyestuffs: Reactive Dyestuffs With Very Remarkable ReproducibilityDocument8 pagesKayacion Cf-Comw Dyestuffs: Reactive Dyestuffs With Very Remarkable ReproducibilityNguyễn Huy CườngNo ratings yet
- Curious & Mischievous: State of Mind IIDocument12 pagesCurious & Mischievous: State of Mind IIRahul TiwariNo ratings yet
- Environmental Challenges DONE Compressed PDFDocument205 pagesEnvironmental Challenges DONE Compressed PDFowais khanNo ratings yet
- Winch Dyeing MachineDocument8 pagesWinch Dyeing MachineUsama KhanNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain MGT ReportDocument49 pagesSupply Chain MGT ReportsitaraNo ratings yet
- Fibres, Yarns and FabricsDocument121 pagesFibres, Yarns and FabricsTedra BulginNo ratings yet
- COLOUR FASTNESS TESTING STANDARDSDocument4 pagesCOLOUR FASTNESS TESTING STANDARDSkasun148100% (1)