Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plantation, Crops, Spices
Uploaded by
Mahendar VanamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plantation, Crops, Spices
Uploaded by
Mahendar VanamCopyright:
Available Formats
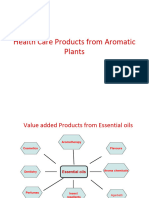
Plantations Crops, Spices &Condiment Technology Unit 1 1. What are plantation crops?
Describe the steps involved in the processing of coffee and cocoa. Mention the flavouring principles present in them. 2. Describe the steps involved in Processing of Coconut and Areca nut. Explain in detail preparation of any two values added products from each. 3. Describe the steps involved in processing of Coffee, tea & Cocoa. Mention the flavoring principles present in them? How instant tea is prepared? 4. What are Plantation Crops? Describe the steps involved in the processing of Areca nut & Coconut. Explain in detail the preparation of any two values added products from Coconut and Arecanut Unit 2 1 Explain nutritional and health aspects of any four leafy spices along with their botanical names. 2 Explain the processing, uses and health benefits of curry leaves and coriander leaves. Mention their flavouring constituents. 3 Mention the chemical constituents present in curry leaves and coriander leaves and mention their botanical names. How they are dehydrated and mention the packaging materials suitable for preservation. Unit 3 1 What are the parameters studied in the proximate composition of spices. Write the laboratory method with a sketch for volatile oil estimation in pepper? 2 Write short notes on: a) Spices as nutraceuticals b) Proximate composition of any two spices c) Flavouring constituents of any two spices Unit 4 10 How Tamarind and Garlic pastes are prepared and what are the critical steps involved in popularizing these products for the consumer? 11 How ginger and chilli pastes are prepared and what are the steps involved in storage and preservation of these pastes? Unit 5 1 Two g of pepper powder was extracted with extracting solvent (ethanol+methanol). The extract made up to 500 ml. Two ml of this extract was diluted to 100 ml, absorbance measured at 343 nm, gave an absorbance (O.D.) of 0.38. Calculate the percentage of piperine in pepper powder. The absorbance of pure piperine at a concentration of 400g/100ml is 0.46 at 343nm. 2 What is the principle in cryogenic grinding and advantage of cryogenic grinding in preparation of spice powders? 3 Sixty g of ginger powder with a moisture content of 8 percent, on hydrodistillation gave 2 ml of volatile oil. What is the percentage of volatile oil in ginger on dry weight basis.
5 6
Two g of turmeric powder was refluxed with ethanol and the extract volume was made up to 500 ml. One ml of this extract was diluted to 100 ml with ethanol. This solution gave an absorbance of 0.3 at 425 nm. Calculate the percentage of curcumin in turmeric powder. The standard absorbance value for pure curcumin of is 0.42 at a dilution of 0.0025 g per 1000 ml is 0.42. How curry powder is produced commercially and explain their importance in culinary preparations. Mention the health benefits of Garlic and Turmeric. How curry powder from spices is produced commercially and marketed? Mention advantages and disadvantages of different types of mills employed for grinding spices? Unit 6 Differentiate between spice oil & oleoresin. Explain different methods for obtaining spice oils. What are the parameters studied to evaluate the quality of spice oil.
Differentiate between Spice Oil and Oleoresin. What are the criterias for selecting a suitable solvent for oleoresin extraction. 3 How ginger oil is produced commercially? How spice oils are incorporated into food products Unit 7 1 Explain the counter current extraction method for oleoresin extraction. What are the sources of natural pigments and indicate class of pigments in any four plant materials. Mention the class of pigment present in Beetroot and how the colour is extracted and estimated? 2 What are the sources of natural colors and indicate the class of pigments present in them. Explain how color is extracted from blue grapes. 3 What are the advantages of spice oleoresins compared to spices? Explain how pepper- oleoresin is produced by counter-current extraction. Unit 8 1 Write short notes on Rosemary, Sage and Mint 2 2 write short notes on processing and packaging of (ii) Sage (iii) Mint
a) Rosemary
You might also like
- Curry PowderDocument8 pagesCurry PowderMahendar Vanam100% (1)
- Extraction and Purification of Terpenes From NutmegDocument3 pagesExtraction and Purification of Terpenes From NutmegrafenNo ratings yet
- Roasters DictionaryDocument10 pagesRoasters Dictionarydiegocardona88No ratings yet
- Herbs Spices and Essential OilsDocument70 pagesHerbs Spices and Essential OilsGulzar Ahmad RawnNo ratings yet
- Fish Vegetable Siomai Doooooneeeee Version EditedDocument35 pagesFish Vegetable Siomai Doooooneeeee Version EditedLoyd Dyrus100% (4)
- Niir Modern Technology Perfumes Flavours Essential Oils 2nd EditionDocument15 pagesNiir Modern Technology Perfumes Flavours Essential Oils 2nd EditionRabi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Essential Oil From Cinnamon (Cinnamomum Zeylanicum)Document11 pagesExtraction of Essential Oil From Cinnamon (Cinnamomum Zeylanicum)xiuhtlaltzinNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils From Steam Distillation: Pre-LabDocument9 pagesEssential Oils From Steam Distillation: Pre-LabMuhammad Nur ShidiqNo ratings yet
- Turmeric ProjectDocument21 pagesTurmeric ProjectNARESH WALIANo ratings yet
- Modern Technology of PerfumesDocument65 pagesModern Technology of Perfumesmghaffarzadeh100% (3)
- Lemongrass2006 PDFDocument36 pagesLemongrass2006 PDFMary Bethelgeuse LadaranNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Essential Oil From Orange PeelsDocument10 pagesExtraction of Essential Oil From Orange Peelsاحمد الدلال100% (1)
- 132 KV Substation EquipmentsDocument48 pages132 KV Substation EquipmentsMamatha Marri77% (31)
- Chapter 3Document8 pagesChapter 3larra100% (2)
- Glossary of Wine-Tasting Terminology, Matei Alina Mihaela, MTI Anul 1Document30 pagesGlossary of Wine-Tasting Terminology, Matei Alina Mihaela, MTI Anul 1Alina-Mihaela Matei100% (2)
- Modern Technology of Perfumes, Flavours and Essential Oils (2nd Edition)Document14 pagesModern Technology of Perfumes, Flavours and Essential Oils (2nd Edition)Bala Ratnakar Koneru50% (2)
- 10 Cookery Q2M1Document70 pages10 Cookery Q2M1Rodel Camposo100% (1)
- Extraction and Production of Essential Oils: WWW - Entrepreneurindia.coDocument56 pagesExtraction and Production of Essential Oils: WWW - Entrepreneurindia.coshubham yaduwansiNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils For Beginners: Aromatherapy and Essential Oils for Weight Loss, Natural Remedy, Stress Relief, Body Massage and BeautyFrom EverandEssential Oils For Beginners: Aromatherapy and Essential Oils for Weight Loss, Natural Remedy, Stress Relief, Body Massage and BeautyNo ratings yet
- Mindful Eating:: Enjoying Your Food With All Your SensesDocument27 pagesMindful Eating:: Enjoying Your Food With All Your SensesFirDaus100% (2)
- Essential Oils in Food Processing: Chemistry, Safety and ApplicationsFrom EverandEssential Oils in Food Processing: Chemistry, Safety and ApplicationsSeyed Mohammed Bagher HashemiNo ratings yet
- Extraction of EssentialDocument49 pagesExtraction of EssentialPrasanth VngNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Oleoresin Extraction Plant From ChillisDocument10 pagesProject Report On Oleoresin Extraction Plant From ChillisEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils in Nepal - A Practical Guide To Essential Oils and AromatherapyDocument6 pagesEssential Oils in Nepal - A Practical Guide To Essential Oils and Aromatherapykhilendragurung4859No ratings yet
- Feasibility StudyDocument37 pagesFeasibility StudyPraveen PuthuparambilNo ratings yet
- Extracting Essential Oil From OrangeDocument2 pagesExtracting Essential Oil From OrangeHerbert Espinel MaqueNo ratings yet
- A. Experiment TitleDocument23 pagesA. Experiment TitleLailatul BadriyahNo ratings yet
- Materials and Methods: Using Arjun (Terminalia Arjuna) Bark and Drumstick (Moringa Oleifera) Leaves" WasDocument26 pagesMaterials and Methods: Using Arjun (Terminalia Arjuna) Bark and Drumstick (Moringa Oleifera) Leaves" WasAnonymous IPmHmtQNkKNo ratings yet
- 3711 9421 1 SPDocument11 pages3711 9421 1 SPrahtiajamilaNo ratings yet
- CHE140.1 - UM1 - Extraction of Essential Oil From Citronella Leaves and Orange Peel - LLuspe-AMutiaDocument6 pagesCHE140.1 - UM1 - Extraction of Essential Oil From Citronella Leaves and Orange Peel - LLuspe-AMutiaMahieda MutiaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument13 pagesProjectNoorpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- (180 185) V13N3PTDocument7 pages(180 185) V13N3PTSukmana Laksana SaputraNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Essential Oil Extraction From Ging - RhizomesDocument49 pagesThesis On Essential Oil Extraction From Ging - RhizomesKaarruu TufaaNo ratings yet
- Minyak Angin Aromaterapi ShintawatiDocument10 pagesMinyak Angin Aromaterapi ShintawatiFatim FatimahNo ratings yet
- Module No 7: Technology of Manufacturing Spice Oil & OleoresinsDocument3 pagesModule No 7: Technology of Manufacturing Spice Oil & OleoresinsmadeshNo ratings yet
- Niir Modern Technology Perfumes Flavours Essential Oils 2nd Edition PDFDocument8 pagesNiir Modern Technology Perfumes Flavours Essential Oils 2nd Edition PDFDamayanti MohantyNo ratings yet
- Basil Oil (Ocimum Basilicum L.) As An Antibacterial Substance in Aromatherapy Bath SoapDocument8 pagesBasil Oil (Ocimum Basilicum L.) As An Antibacterial Substance in Aromatherapy Bath Soapadelina fiaNo ratings yet
- Emulsion OleoresinDocument4 pagesEmulsion OleoresinGuneet kaurNo ratings yet
- PetiteGuideBrochure 100712 BRTPGA V3 WebDocument13 pagesPetiteGuideBrochure 100712 BRTPGA V3 WebirinanistorNo ratings yet
- SocoDocument4 pagesSocoJerwilyn LicuasenNo ratings yet
- KTI MinyakDocument16 pagesKTI MinyakSandi PutraNo ratings yet
- AMADI CHEMICAL PROJECT CoreectedDocument29 pagesAMADI CHEMICAL PROJECT CoreectedErhueh Kester AghoghoNo ratings yet
- 5 Thottlaganahalli 4 22Document5 pages5 Thottlaganahalli 4 22Ali RizieqNo ratings yet
- The Study On Extraction Process and Analysis of Components in Essential Oils of Black Pepper (Piper VietnamDocument16 pagesThe Study On Extraction Process and Analysis of Components in Essential Oils of Black Pepper (Piper VietnamMachaiah M.DNo ratings yet
- (NIIR) The Complete Book On Spices & Condiments (With Cultivation, Processing & Uses)Document26 pages(NIIR) The Complete Book On Spices & Condiments (With Cultivation, Processing & Uses)hemachalNo ratings yet
- Final DocumentDocument10 pagesFinal DocumentTherese AnneNo ratings yet
- Rochelle Final IIIDocument17 pagesRochelle Final IIIJohn Enrick ManuelNo ratings yet
- Technical Presentation Report On FFDCDocument24 pagesTechnical Presentation Report On FFDCApurv RajNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Plant ProductsDocument100 pagesAromatic Plant ProductsAlbert AinstineNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Oil From Wild Walnut and Some Nutritional Characteristics of Nut and Oil of Wild Walnut (JuglansDocument4 pagesExtraction of Oil From Wild Walnut and Some Nutritional Characteristics of Nut and Oil of Wild Walnut (JuglansCtNo ratings yet
- Seed Oil ExpDocument13 pagesSeed Oil Expdasunnayan4No ratings yet
- Research Plan 2Document7 pagesResearch Plan 2kepe.czayNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Extraction and Identification of Essential Oil Using Gas Chromatography and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry AnalysisDocument3 pagesExperiment 4 Extraction and Identification of Essential Oil Using Gas Chromatography and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry AnalysisMUHAMMAD FARIS FIKRI BIN MOHD FAKRINo ratings yet
- Handbook On Spices and Condiments - Cultivation Processing and ExtractionDocument62 pagesHandbook On Spices and Condiments - Cultivation Processing and ExtractionSvsSridharNo ratings yet
- Uvspectrophotometric Method Development For Estimation of Piperine in Chitrakadi VatiDocument5 pagesUvspectrophotometric Method Development For Estimation of Piperine in Chitrakadi VatiAliya Nur HasanahNo ratings yet
- Proceeding of Mulawarman Pharmaceuticals Conferences: Journal HomepageDocument6 pagesProceeding of Mulawarman Pharmaceuticals Conferences: Journal HomepageNuur AtmodjoNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Essential Oils: Eucalyptus Oil Extraction Techniques and MethodsDocument6 pagesExtraction of Essential Oils: Eucalyptus Oil Extraction Techniques and MethodsSushank SaneNo ratings yet
- CHE140.1 - LabAct1 - Expt2 - Extraction of Essential Oils - AMutiaDocument4 pagesCHE140.1 - LabAct1 - Expt2 - Extraction of Essential Oils - AMutiaMahieda MutiaNo ratings yet
- CitralDocument11 pagesCitralLithin LekkalaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Oleoresin Using Solvent Extraction MethodDocument8 pagesProject Report On Oleoresin Using Solvent Extraction MethodEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument17 pagesProject Proposalabebe belahNo ratings yet
- Essential OilsDocument37 pagesEssential OilsbabithyNo ratings yet
- IJERD (WWW - Ijerd.com) International Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesIJERD (WWW - Ijerd.com) International Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentIJERDNo ratings yet
- Design and Evaluation of Allium Sativum GelDocument3 pagesDesign and Evaluation of Allium Sativum GelInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- PC 4. Emulsiones Tipo MayonesasDocument10 pagesPC 4. Emulsiones Tipo MayonesasmadarahuchihaNo ratings yet
- Journal Research - Leni Nurlinayanti - Pancasila UniversityDocument17 pagesJournal Research - Leni Nurlinayanti - Pancasila UniversityCAHYO HADINo ratings yet
- BjkolllllDocument10 pagesBjkolllllmobileveejay3No ratings yet
- The Art of Aromatherapy and Essential Oils: A Practical HandbookFrom EverandThe Art of Aromatherapy and Essential Oils: A Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- A5 Chem Herbs SpicesDocument53 pagesA5 Chem Herbs SpicesMahendar VanamNo ratings yet
- CorriaderDocument6 pagesCorriaderMahendar VanamNo ratings yet
- VanillinDocument10 pagesVanillinshishirchemNo ratings yet
- Organic Joint Support Turmeric ShotDocument4 pagesOrganic Joint Support Turmeric ShotmelissaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Techniques For Flavor Recovery in LiquidDocument15 pagesRecent Advances in Techniques For Flavor Recovery in LiquidBianca LeyvaNo ratings yet
- Spex670 07 Cba Report NelsonDocument12 pagesSpex670 07 Cba Report Nelsonapi-521363790No ratings yet
- Applications of Solid-Phase Microextraction in Food AnalysisDocument28 pagesApplications of Solid-Phase Microextraction in Food AnalysisAnonymous xGc8MRRysNo ratings yet
- Addictive FoodDocument4 pagesAddictive FoodZahariuc Andreea0% (1)
- Group 3 SPDocument7 pagesGroup 3 SPLawrence CezarNo ratings yet
- Flavor of Meat, Meat Products and Seafoods 018Document13 pagesFlavor of Meat, Meat Products and Seafoods 018lovesilentNo ratings yet
- Powerful Reasons To Choose Over Hot Coffee: Cold BrewDocument11 pagesPowerful Reasons To Choose Over Hot Coffee: Cold BrewAlex Gallardo MontesNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 Quarter 2 LAS No. 2Document5 pagesCOOKERY 10 Quarter 2 LAS No. 2Chema Paciones100% (1)
- Unit 7 Food Additives: StructureDocument23 pagesUnit 7 Food Additives: StructurePragya SourabhNo ratings yet
- Simulated Assignment - Deliverable 3 - CLA - Group-3Document81 pagesSimulated Assignment - Deliverable 3 - CLA - Group-3Bhavya GautamNo ratings yet
- The Technology of Sugar ProductionDocument7 pagesThe Technology of Sugar ProductionPopa Anne MarieNo ratings yet
- Meat Quality IndicatorsDocument8 pagesMeat Quality IndicatorsmujiNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 Quarter 2 LAS No. 10Document9 pagesCOOKERY 10 Quarter 2 LAS No. 10Pauleen Alexa GarciaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus New PDFDocument5 pagesSyllabus New PDFShishir Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Honey Its Characteristics Sensory Aspects and Applications-2Document18 pagesHoney Its Characteristics Sensory Aspects and Applications-2Zeina ZwayhedNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 Food Additives Lesson M-VII.18. Aroma Compounds in Food & Flavour Enhancers - Monosodium Glutamate, NucleotidesDocument5 pagesMODULE 7 Food Additives Lesson M-VII.18. Aroma Compounds in Food & Flavour Enhancers - Monosodium Glutamate, NucleotidesAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Article 1Document33 pagesArticle 1Deepak Kumar Verma100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - 5 December 17, 2019 PDFDocument180 pagesChapter 4 - 5 December 17, 2019 PDFMeredith VillareteNo ratings yet
- Saqeeb PPT LiqueurDocument21 pagesSaqeeb PPT LiqueurSæqéëb Æl HæssåñNo ratings yet
- Earlmerwin Flavor History-1Document150 pagesEarlmerwin Flavor History-1born2dive 9702No ratings yet
- Defects in Milk Products, Their Preventions and Remedies.Document5 pagesDefects in Milk Products, Their Preventions and Remedies.kanti priya KondalaNo ratings yet
- Informe Milka Case StudyDocument5 pagesInforme Milka Case StudyCesar D. VillanuevaNo ratings yet