Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hypertension NCP
Uploaded by
Christian Karl B. LlanesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypertension NCP
Uploaded by
Christian Karl B. LlanesCopyright:
Available Formats
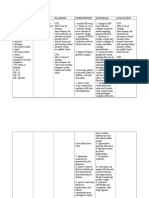
ASSESSMENT Subjective: kanayun nak maulaw, as verbalized by the patient.
Objective: >lethargic >decreased cardiac output >decreased stroke volume >increased peripheral vascular resistance >VS taken as follows: T: 37.2 PR: 83 RR: 18 BP: 180/100 NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Decreased Cardiac Output r/t hypertension as manifested by decreased stroke volume
EXPLANATION OF THE PROBLEM Cardiac output is the amount of blood per minute pumped out by each of the two ventricles of the heart. A typical value in an adult at rest is 5 litres per minute. The output of each ventricle is the product of the stroke volume (about 70 ml) and the heart rate (about 70 per minute). The output increases with muscular activity, in work or exercise perhaps to a maximum of 4-5 times the resting rate in an average healthy person, or
OBJECTIVES STO: After 6 hrs of nursing interventions, the client will have no elevation in blood pressure above normal limits and will maintain blood pressure within acceptable limits.
INTERVENTION DX>1. Monitor BP every1-2 hours, or every5 minutes during active titration of vasoactive drugs.
RATIONALE 1. Changes in BP may indicate changes in patient status requiring prompt attention.
EVALUATION STG: Goal met. If after 6 hrs of nursing interventions, the client had no elevation in blood pressure above normal limits and will maintain blood pressure within acceptable limits.
2. Monitor ECG for dysrhythmias, conduction defects and for heart rate.
2. Decrease in cardiac output may result in changes in cardiac perfusion causing dysrhythmias.
LTO:After 72 hours of nursing interventions, the client will maintain adequate cardiac output and cardiac index.
TX>3. Encourage patient to decrease intake of caffeine, cola and chocolates.
3. Caffeine is a cardiac stimulant and may adversely affect cardiac function.
4. Observe skin color, temperature, capillary refill time and diaphoresis.
4.peripheral vasoconstriction may result in pale, cool, clammy skin, with prolonged capillary refill time due to cardiac dysfunction an decreased cardiac output 5 hypertensive patients often haveS4 gallops caused by atrial hypertrophy
LTG: Goal met. If after 72 hours of nursing interventions, the client maintained an adequate cardiac output and cardiac index.
5. Auscultate heart tones.
up to 6-7 times in athletes; heart rate increases by a greater factor than stroke volume. The more blood pumped from the heart per minute (that is, the larger the cardiac output), the higher the blood pressureas long as resistance to blood flow in the arteries remains constant. The body can change the amount of blood pumped during each heartbeat by making each contraction weaker or stronger. The higher the volume of blood in the blood vessels,
6.administer medicines as prescribed by the physician
6.to promote wellness
EDX>7. instruct client &family on fluid and diet requirements and restrictions of sodium
7. Restrictions can assist with decrease in fluid retention and hypertension, thereby improving cardiac output.
8. Instruct client and family on medications, side effects, contraindications and signs to report.
8. Promotes knowledge and compliance with drug regimen.
9. Instruct for frequent position changes.
9. It may decreases peripheral venous pooling that may be potentiated by vasodilators and prolonged sitting or standing.
the higher the blood pressureas long as resistance to blood flow in the arteries remains constant. To increase or decrease blood volume, the kidneys can vary the amount of fluid excreted in urine.
SOURCE: www.wikipidea.com
CLIENT EDUCATION FOR PATIENT WITH HYPERTENSION
You might also like
- Managing Hypertension and Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesManaging Hypertension and Decreased Cardiac Outputanon_9189425950% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionFranco Razon100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionJessy MalloNo ratings yet
- Subjective:: Decreased Cardiac Output R/T HypertensionDocument3 pagesSubjective:: Decreased Cardiac Output R/T Hypertensionnurse_yramenaj100% (2)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation EffectivenessDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation EffectivenessYnah Sayoc75% (4)
- Hypertension NCPDocument1 pageHypertension NCPj4royce100% (1)
- NCP For HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP For Hypertensionrhizalyn1367% (6)
- NCP For HypertensionDocument4 pagesNCP For HypertensionCiariz Charisse83% (6)
- High Blood Pressure (HBP) or Hypertension N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesHigh Blood Pressure (HBP) or Hypertension N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP Hypertensionsinister1781% (27)
- Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesDiagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMel Christian Baldoz100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionFranco Razon100% (1)
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionFrances Mercado0% (1)
- BSNURSE: NCP - HypertensionDocument3 pagesBSNURSE: NCP - Hypertensionmickey_beeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment, Diagnosis, Intervention & EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment, Diagnosis, Intervention & Evaluationkimchi girl0% (1)
- NCP Hypertension 2Document3 pagesNCP Hypertension 2Roseben Somido50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- ANDAYA, Kristine Alexis L. BSN218 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesANDAYA, Kristine Alexis L. BSN218 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAlexis TineNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPElbert Vierneza100% (2)
- Nutrition Imbalance Care PlanDocument7 pagesNutrition Imbalance Care PlanMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care pLAN (Hypertension)Document7 pagesNursing Care pLAN (Hypertension)Rosalie Valdez Espiritu100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Hypertensionderic98% (124)
- NCP For UtiDocument3 pagesNCP For UtiAaron Sanchez100% (1)
- Nursing care plan for hypertension, renal calculi, diabetesDocument3 pagesNursing care plan for hypertension, renal calculi, diabetesGimcy Dela Fuente100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension and Knee PainDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hypertension and Knee PainEzron Kendrick Duran50% (2)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol TartrateDocument1 pageMetoprolol TartrateClifford Estilo100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Jan. 13 2011Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan Jan. 13 2011Mayls Sevilla Calizo100% (1)
- NCP For FeverDocument2 pagesNCP For FeverDominises Jade Corpuz82% (17)
- Cad NCPDocument1 pageCad NCPKrizzia Mae F. MayoresNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument3 pagesNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualNo ratings yet
- NCP For PCAPCDocument6 pagesNCP For PCAPCEnrique Lu100% (1)
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJonathan LiscanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationStefhanie DaloraNo ratings yet
- NCP CKDDocument3 pagesNCP CKDRiel TumandaNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care PlanDan Gerald Alcido SalungaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for AMI ClientDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan for AMI ClientChic Dian UsmanNo ratings yet
- Decreased Urine OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Urine OutputSj 斗力上No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputCarmela Balderas Romantco80% (5)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument9 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputChinita Sangbaan75% (4)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationKrisha Miel DomedeNo ratings yet
- CHF PBLDocument3 pagesCHF PBLqtiefyNo ratings yet
- Group6 NursinginfoDocument14 pagesGroup6 NursinginfoSlepy chngNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionRodel Yacas0% (1)
- Arizmendi G72 T10Document6 pagesArizmendi G72 T10IrvinSerranoJNo ratings yet
- Cardiology NotesDocument13 pagesCardiology NotesFreeNursingNotes78% (9)
- Cardiovascular System (Diagnostic Procedure) : Prepared By: Kriegel Paman Bihasa RM, RN, UsrnDocument17 pagesCardiovascular System (Diagnostic Procedure) : Prepared By: Kriegel Paman Bihasa RM, RN, UsrnKriegel Paman BihasaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac SurgeryDocument19 pagesCardiac SurgerySimon JosanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hypertensionmariejo89% (81)
- Decreased Cardiac Output RM 7Document9 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output RM 7api-283470660No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: SubjectiveDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: SubjectiveAlimansor M. DarpingNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease Nclex, Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument88 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Nclex, Peripheral Vascular DiseaseKrishna SapkotaNo ratings yet
- CHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYDocument12 pagesCHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYMary Cris CanonNo ratings yet
- SEC A GP 1 OsamaDocument16 pagesSEC A GP 1 OsamaAiman SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument3 pagesCardiogenic Shockmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: Medical Surgical NursingDocument7 pagesCase Analysis: Medical Surgical NursingMaria ThereseNo ratings yet
- Hyperbilirubinemia: A Risk Factor For Infection in The Surgical Intensive Care UnitDocument14 pagesHyperbilirubinemia: A Risk Factor For Infection in The Surgical Intensive Care UnitChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- PatientDocument3 pagesPatientChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- CPR Quality: Improving Cardiac Resuscitation Outcomes Both Inside and Outside The Hospital: A Consensus Statement From The American Heart AssociationDocument3 pagesCPR Quality: Improving Cardiac Resuscitation Outcomes Both Inside and Outside The Hospital: A Consensus Statement From The American Heart AssociationChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument18 pagesNCPChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Post-Appendectomy PainDocument3 pagesNursing Care for Post-Appendectomy PainChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gastroduodenal UlcersDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Gastroduodenal UlcersOrlino PeterNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Magnitudes and Intensities: What To Expect During Each Magnitude and Intensity?Document2 pagesEarthquake Magnitudes and Intensities: What To Expect During Each Magnitude and Intensity?Christian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Viii - Diagnostics Date Procedure Description Purpose/ Significance Normal Ranges Result Indication/Impr EssionDocument9 pagesViii - Diagnostics Date Procedure Description Purpose/ Significance Normal Ranges Result Indication/Impr EssionChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummaryChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesObstetric Nursing Care Planlilchristina0178% (9)
- Actual NCP IneffectiveDocument4 pagesActual NCP IneffectiveChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Post-Appendectomy PainDocument3 pagesNursing Care for Post-Appendectomy PainChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Risks of Smoking in CAR RegionDocument1 pageRisks of Smoking in CAR RegionChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- ImbalanceDocument2 pagesImbalanceChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- The Use of Domperidone Lactation For Mothers of Preterm BabiesDocument2 pagesThe Use of Domperidone Lactation For Mothers of Preterm BabiesChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Sample Psychiatric OTDocument6 pagesSample Psychiatric OTChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Journal About Fortification of Human Breast Mik For Preterm BabiesDocument2 pagesJournal About Fortification of Human Breast Mik For Preterm BabiesChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument5 pagesAspirinChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Documentation WEEK 7-Day 1 Courtesy Call and Orientation at Bokod Municipal HallDocument6 pagesDocumentation WEEK 7-Day 1 Courtesy Call and Orientation at Bokod Municipal HallChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- SurveyDocument1 pageSurveyChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- PsychDocument2 pagesPsychChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- HIV PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesHIV PathophysiologyChristian Karl B. Llanes91% (11)
- OR Write-UpDocument2 pagesOR Write-UpChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- JOURNALDocument1 pageJOURNALChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- JOURNALDocument1 pageJOURNALChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Documentation WEEK 7-Day 1 Courtesy Call and Orientation at Bokod Municipal HallDocument6 pagesDocumentation WEEK 7-Day 1 Courtesy Call and Orientation at Bokod Municipal HallChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeDocument7 pagesDrug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- HIV PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesHIV PathophysiologyChristian Karl B. Llanes91% (11)
- Drug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeDocument7 pagesDrug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- If A Particular Student Got A Score of 83, What Is Its Corresponding Z-Score?Document6 pagesIf A Particular Student Got A Score of 83, What Is Its Corresponding Z-Score?Leah Mae NolascoNo ratings yet
- Notes On Rebecca Clarke's Allegro and Pastorale For Viola and BB ClarinetDocument4 pagesNotes On Rebecca Clarke's Allegro and Pastorale For Viola and BB ClarinetK.L.No ratings yet
- Lab WorkbookDocument160 pagesLab WorkbookOye AjNo ratings yet
- Scheme Guidelines for Industry Institute Partnership CellDocument28 pagesScheme Guidelines for Industry Institute Partnership CellhariselvarajNo ratings yet
- How To Complete TSA Charts and Search The NOC Career Handbook For Potentially Suitable OccupationsDocument9 pagesHow To Complete TSA Charts and Search The NOC Career Handbook For Potentially Suitable OccupationsJohn F. Lepore100% (1)
- Vineet Kumar CV: Corporate LawyerDocument4 pagesVineet Kumar CV: Corporate LawyerSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lewiston-Porter Central School District Teacher RostersDocument12 pagesLewiston-Porter Central School District Teacher RostersJulius NNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesDifference Between Mitosis and Meiosiskumar_vikaNo ratings yet
- Theo Experienced NET - DeveloperDocument2 pagesTheo Experienced NET - DeveloperUnekwu TheophilusNo ratings yet
- Unhelpful Thinking Habits With AlternativesDocument1 pageUnhelpful Thinking Habits With AlternativesMarkDe Weekend Traveller100% (1)
- PerDev Module - With ActivityDocument63 pagesPerDev Module - With ActivityMich ResueraNo ratings yet
- English As A Foreign Language Teacher PDFDocument202 pagesEnglish As A Foreign Language Teacher PDFLidanNo ratings yet
- All Dade Swimming2Document1 pageAll Dade Swimming2Miami HeraldNo ratings yet
- Uae Hopspital and ClinicsDocument6 pagesUae Hopspital and ClinicsAhmed Scope0% (2)
- Expt1 - Specific-Heat-of-Metals - (Calorimetry)Document4 pagesExpt1 - Specific-Heat-of-Metals - (Calorimetry)Rex BayonaNo ratings yet
- Employee Attrition and Retention ChallengesDocument16 pagesEmployee Attrition and Retention ChallengesJatin GeraNo ratings yet
- Surface-Level Diversity and Decision-Making in Groups: When Does Deep-Level Similarity Help?Document17 pagesSurface-Level Diversity and Decision-Making in Groups: When Does Deep-Level Similarity Help?Noss BNo ratings yet
- Resume of Laminor27Document2 pagesResume of Laminor27api-27481876No ratings yet
- A Head Nurse Oversees Nursing Activities in A Range of Health Care SettingsDocument8 pagesA Head Nurse Oversees Nursing Activities in A Range of Health Care SettingsMitch MaLagambaNo ratings yet
- Devry University Course of StudyDocument3 pagesDevry University Course of Studyapi-291590435No ratings yet
- Healthcare Student Stereotypes: A Systematic Review With Implications For Interprofessional CollaborationDocument13 pagesHealthcare Student Stereotypes: A Systematic Review With Implications For Interprofessional CollaborationYopa YopisaNo ratings yet
- Table Setting ContestDocument6 pagesTable Setting ContestMhel Demabogte100% (1)
- The People in The SchoolDocument26 pagesThe People in The SchoolIrma CorralNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation ToolDocument3 pagesPerformance Evaluation ToolMykee Alonzo100% (1)
- Progress Test 1 - TalentedDocument2 pagesProgress Test 1 - TalentedJOSE ANDRÉS CLEMENTE MUÑOZ67% (3)
- Numerical and Experimental Studies of Sail AerodynamicsDocument282 pagesNumerical and Experimental Studies of Sail AerodynamicsMayra Karina Zezatti FloresNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Report Writing.Document29 pagesIntroduction To Report Writing.QurratUlAinRazaNo ratings yet
- The Spoken Lesson/Unspoken LessonDocument18 pagesThe Spoken Lesson/Unspoken Lessonapi-21816946100% (1)
- Own Two Hands Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesOwn Two Hands Lesson Planapi-517827694No ratings yet
- Perspectives On Psychological Science 2011 Holzel PDFDocument23 pagesPerspectives On Psychological Science 2011 Holzel PDFaranda_88No ratings yet